Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MSU Newborn Practices Guide
Uploaded by
Mimie Cali0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views3 pagesThis document outlines recommended newborn practices and assessments including:
1) Essential newborn care such as thermoregulation, dry cord care, early breastfeeding, and eye care.
2) APGAR scoring which assesses appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration of the newborn. Low APGAR scores can indicate risks for cerebral palsy.
3) Gestational age assessments including the Ballard Score which evaluates physical parameters to determine preterm vs. term status.
Original Description:
Original Title
Newborn Assessment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines recommended newborn practices and assessments including:
1) Essential newborn care such as thermoregulation, dry cord care, early breastfeeding, and eye care.
2) APGAR scoring which assesses appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration of the newborn. Low APGAR scores can indicate risks for cerebral palsy.
3) Gestational age assessments including the Ballard Score which evaluates physical parameters to determine preterm vs. term status.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views3 pagesMSU Newborn Practices Guide
Uploaded by
Mimie CaliThis document outlines recommended newborn practices and assessments including:
1) Essential newborn care such as thermoregulation, dry cord care, early breastfeeding, and eye care.
2) APGAR scoring which assesses appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration of the newborn. Low APGAR scores can indicate risks for cerebral palsy.
3) Gestational age assessments including the Ballard Score which evaluates physical parameters to determine preterm vs. term status.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
MSU - COL L E GE OF ME D ICINE
LEVEL 1 | Growth and Development Module
Physical Diagnosis - NEWBORN
RECOMMENDED NEWBORN PRACTICES:
NEWBORN • Antenatal steroids
- For preterm babies ( <37 weeks)
Oct. 15, 2020 – Dr. Apipa Domato
• Thermoregulation (25 – 28 C)
OUTLINE • Dry cord care
• Early breastfeeding
THE NORMAL NEWBORN……………. 1 • Eye care, weighing, PE, injection last
ESSENTIAL INTRAPARTUM
• Bathing
AND NEWBORN CARE (EINC)…...………….…1
- 6 – 24 hours after birth
APGAR SCORE…………………………………...1
NEWBORN CLASSIFICATION…………………..1
ASSESSMENT OF GESTATIONAL AGE………2 APGAR SCORE (AS)
NEW BALLARD SCORE……………………….…2 • Appearance (color)
EXTREMITIES AND SKELETAL SYSTEM.…….2 • Pulse (heart rate)
NEUROLOGICAL EXAM…………………...…….3 • Grimace (reflex irritability)
KANGAROO MOTHER CARE…………………...3 • Activity (muscle tone)
• Respirations
THE NORMAL NEWBORN
- Cursory assessment of cardiopulmonary/
COMPONENTS OF NEONATAL HISTORY:
neurologic systems
• Complete Maternal History: - Done at 1, 5 minutes; every 5 minutes until 20
- Age, parity, prenatal history minutes or 2 successive scores of 7
- Blood type, occupation - Subjective; may not be accurate
- Illnesses, STDs, maintenance - Low score not diagnostic of asphyxia
medications
- Previous pregnancy SCORE:
- Prohibited drug intake, alcohol
• 10: Perfect score
- Current pregnancy- AOG, fetal
• 7 – 10: Normal
testing, infection
• 0 – 3: at 5 minute, increase risk for cerebral
• Natal History:
palsy from 0.3% to 1%.
- Labor; duration, presentation,
- at 10, 15, 20 minutes, have higher
distress, fever
correlation with future neurological
- Delivery; caesarean vs. normal,
handicaps but still not specific in
sedation, assisted, APGAR score,
absence of other clinical evidence
resuscitation
like encephalopathy.
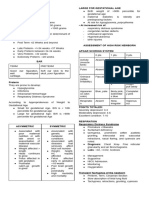
ESSENTIAL INTRAPARTUM AND NEWBORN BIRTH WEIGHT
CARE (EINC) Classification Weight
- Prevention and management of premature Micropreemie < 800g or 1.8lb
birth and low birth weight Extremely LBW < 1000g or 2.2lb
- The 4 Core Steps of immediate newborn care
Very LBW < 1500g or 3.3lb
- Postnatal care of mother and newborn
- Basic Newborn Resuscitation Low BW < 2500g or 5.5lb
- Evidence-based practices Normal BW 2500g (5.5lb) – 4000g (8.8lb)
- Time-bound, chronologically ordered High BW 4000g (8.8lb) – 4500g (9.9lb)
standard procedures Very HBW > 4500g (9.9lb)
- Baby receives at birth • 3kg for Filipino baby
4 CORE STEPS OF EINC: NEWBORN CLASSIFICATION
1. Immediate and thorough drying
2. Skin-to-skin contact Category Abbr. Percentile
3. Properly-timed cord clamping Small for gestational age SGA <10th
- 1-3 minutes or when pulsations stops Appropriate for gestational age AGA 10-90th
4. Nonseparation of mother and baby Large for gestational age LGA >90th
NORONSALIH JRA. ALI 1
MSU - COL L E GE OF ME D ICINE
LEVEL 1 | Growth and Development Module
Physical Diagnosis - NEWBORN
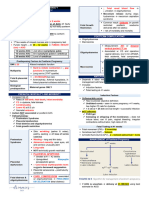
SMALL FOR GESTATIONAL AGE (SGA) RAGING FOLLOWING DELIVERY:
• SYMMETRIC: 33% of SGA FIVE PHYSICAL PARAMETERS:
(Head circumference = Weight = Length, all <10%) 1. Creases in the sole of the feet
- Genetic 2. Breast nodule
Small maternal size 3. Scalp hair
Chromosomal abnormalities 4. Earlobe
(Trisomy 13, 18, 21 and 5. Testes and scrotum
Turner’s syndrome)
Congenital abnormalities ASSESSMENT OF GESTATIONAL AGE
- Intrauterine infections
• Old Ballard Score:
Viruses (rubella, CMV, HIV)
- Overestimated age of PT,
Bacteria (tuberculosis)
underestimated age of postterm,
Spirochete (syphilis)
inaccurate in VLBW
Protozoan (toxoplasmosis,
• New Ballard Score:
malaria)
- Extended range and accuracy within
• ASSYMETRIC: 55% of SGA
2 weeks; useful among < 28 weeks if
(Head circumference = Length <10%, Weight <10%)
done after stabilization or by 12h.
- Uteroplacental insuffieciency
Chronic hypertension
Preeclampsia NEW BALLARD SCORE
Renal disease SCORE WEEKS
Cyanotic heart disease -10 20
Hemoglobinopathies
-5 22
Placental infarcts or chronic
abruption, velamentous 0 24
insertion, circumvallate 5 26
PRETERM
placenta, multiple gestation 10 28
Altitude 15 30
• COMBINED: 12% of SGA
- Environmental 20 32
Drugs (including ethanol) 28 34
Smoking 30 36
- Placental unit insufficiency 38 38
Placental infarcts or chronic
40 40 TERM
abruption, velamentous
insertion, circumvallate 48 42
placenta, multiple gestation 50 44 POSTTERM
LARGE FOR GESTATIONAL AGE (LGA)
EXTREMITIES AND SKELETAL SYSTEM
• Large mother (familial)
• Infants of diabetic mothers ORTOLANI MANUEVER
- To check for developmental
• Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
dysplasia of the hip
• Hydrops fetalis
- Gently abduct infant’s leg with thumb
while placing anterior pressure on
GESTATIONAL AGE
the greater trochanter using
Classification Gestational age
examiner’s index and forefinger.
Preterm <34 weeks - (+) sign: distinctive ‘clunk’ which can
Late preterm 34-36 weeks be heard and felt as the femoral head
Term 37- 42 weeks relocates anteriorly into the
Postterm >42 weeks acetabulum
- This tests for posterior hip dislocation
NORONSALIH JRA. ALI 2
MSU - COL L E GE OF ME D ICINE
LEVEL 1 | Growth and Development Module
Physical Diagnosis - NEWBORN
NEUROLOGICAL EXAM
REFLEXES APPEARS DISAPPERS
Moro Newborn 3 months
Grasp Newborn 3 months
LE crossed Birth 1 month
extensors
Extensor plantar Newborn 8 – 12 months
Placing/Stepping Birth 1 – 2 months
ATNR Newborn 3 months
KANGAROO MOTHER CARE
- 1978, Instituto Materno Infantil in Bogota,
Columbia
- Dr. Edgar Rey and Dr. Hector Martinez
- Humane, low cost method of care for LBW
infants
- Concept/method of care for the baby/mother
dyad and the family
1. Skin to skin contact
- Intermittent (8 hrs/day)
- Continuous (20 cumulative hrs/day)
2. Breastfeeding the premature infant
3. Empowerment of the mother and the family
(KMC rooms)
4. Home discharge in kangaroo position
5. Appropriate growth and development in a
healthy enviroment
• Show the mother how to hold her baby
- She should hold the baby’s head and
body straight
- Make the baby face her breast, the
baby’s nose opposite her nipple
- Hold the baby’s body close to her
body
- Support the baby’s whole body, not
just the neck and shoulders.
• Show the mother how to help her baby. She
should:
- Touch her baby’s lips with her nipple
- Wait until her baby’s mouth is
opening wide
- Move her baby onto her breast,
aiming the infant’s lower lip more of
areola below nipple in mouth.
• Look for the signs of good attachment and
effective sucking (that is slow, deep sucks,
sometimes pausing)
• If breast engorgement, express a small
amount of breast milk before starting
breastfeeding to soften nipple area so that it
is easier for the baby to attach.
NORONSALIH JRA. ALI 3
You might also like
- Care of The NewbornDocument5 pagesCare of The Newbornbuzz Q100% (2)
- Pediatric PDFDocument5 pagesPediatric PDFCzarah Mechelle Sia PalmaNo ratings yet
- ? - PEDIA PRELIMS Lessons 1 and 2Document8 pages? - PEDIA PRELIMS Lessons 1 and 2ysabel.mendozaNo ratings yet
- 209 Handouts High RiskDocument26 pages209 Handouts High RiskxiumethemoneyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Newborn 1 PDFDocument15 pagesNursing Care of Newborn 1 PDFLaeli Nur HanifahNo ratings yet
- QR Management of Neonatal Jaundice (Second Edition) PDFDocument8 pagesQR Management of Neonatal Jaundice (Second Edition) PDFOlayinka AwofoduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24Document19 pagesChapter 24Sabrina Porquiado Magañan SNNo ratings yet
- SCORING NEWBORNS TO DETECT HEALTH RISKSDocument45 pagesSCORING NEWBORNS TO DETECT HEALTH RISKSrahermd1971No ratings yet
- Ncma219 Lec MidtermDocument51 pagesNcma219 Lec MidtermMacababbad Joshua MiguelNo ratings yet
- MCN Day 2Document7 pagesMCN Day 2Jekka Ann Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PediatricsDocument321 pagesPediatricsJulian GalindoNo ratings yet
- Study ThisDocument30 pagesStudy ThisKamva DukadaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Natal Care: Jennifer F. Aficial Man. RNDocument21 pagesPre-Natal Care: Jennifer F. Aficial Man. RNshana ferrerNo ratings yet
- Newborn assessment within first dayDocument1 pageNewborn assessment within first dayCristina AdolfoNo ratings yet
- 1.02 Einc Part 2 - Physical Examination of The Newborn and Ballard ScoringDocument15 pages1.02 Einc Part 2 - Physical Examination of The Newborn and Ballard ScoringJoher Bolante Mendez Jr.No ratings yet
- 4.classification of NewbornDocument33 pages4.classification of NewbornSaeda AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fetal Biophysical Profile: Decreased Fetal BreathingDocument5 pagesFetal Biophysical Profile: Decreased Fetal BreathingYuly Andrea Marquez CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Pedia (Abnormal) - LectureDocument2 pagesPedia (Abnormal) - LectureD A M N E R ANo ratings yet
- CARE OF THE MOTHER, CHILD AND ADOLESCENT: WELL CLIENT ASSESSMENTDocument4 pagesCARE OF THE MOTHER, CHILD AND ADOLESCENT: WELL CLIENT ASSESSMENTAlec AnonNo ratings yet
- CARE OF THE MOTHER, CHILD AND ADOLESCENT: WELL CLIENT ASSESSMENTDocument4 pagesCARE OF THE MOTHER, CHILD AND ADOLESCENT: WELL CLIENT ASSESSMENTAlec AnonNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Fetal Surveillance: Chandani PandeyDocument98 pagesAntepartum Fetal Surveillance: Chandani Pandeychandani pandeyNo ratings yet
- Postterm PregnancyDocument2 pagesPostterm PregnancyicNo ratings yet
- Newborn Care LectureDocument65 pagesNewborn Care LectureNichole daFonsecaNo ratings yet
- PediatricsDocument10 pagesPediatricssachinsaaho123No ratings yet
- Kejang Demam Sederhana Ec - FaringitisDocument30 pagesKejang Demam Sederhana Ec - FaringitisPramita RukmanaNo ratings yet
- Well Baby 2020 With NotesDocument119 pagesWell Baby 2020 With NotesSamsam Almarez BacaltosNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Specialty AreaDocument7 pagesPediatric Specialty Areadg34625No ratings yet
- High Risk Newborn and FamilyDocument93 pagesHigh Risk Newborn and FamilyJen IlaganNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Growth Restriction: Moderator: DR S Choudhuri Speaker: DR Mrinmoy RoyDocument49 pagesIntrauterine Growth Restriction: Moderator: DR S Choudhuri Speaker: DR Mrinmoy RoySaurabh SahaNo ratings yet
- PediaDocument52 pagesPediakayperez100% (1)
- CH 040 Evaluation and Management of Status Epilepticus in ChildrenDocument7 pagesCH 040 Evaluation and Management of Status Epilepticus in Childrensuheena.CNo ratings yet
- Labor Delivery NewbornDocument4 pagesLabor Delivery NewbornMello D. ConsulNo ratings yet
- NEURODEVELOPMENTAL ASSESSMENTS FOR PREDICTION OF CEREBRAL PALSYDocument39 pagesNEURODEVELOPMENTAL ASSESSMENTS FOR PREDICTION OF CEREBRAL PALSYkawaljit000No ratings yet
- Neonatal Care: Dr. Bhuwan Sharma Asst. ProfessorDocument28 pagesNeonatal Care: Dr. Bhuwan Sharma Asst. Professorrevathidadam55555No ratings yet
- 4-Lifespan-Ch 4 - Birth & Physical Dev 1st 3 YearsDocument15 pages4-Lifespan-Ch 4 - Birth & Physical Dev 1st 3 YearsJoseph Barnes100% (1)
- Obgyn Revalida Review 2022 RcsDocument248 pagesObgyn Revalida Review 2022 RcsSophia SaquilayanNo ratings yet
- (RLE) Assessment of High-Risk Infants: Sumalinog, Tiffany Marie L. BSN 2BDocument19 pages(RLE) Assessment of High-Risk Infants: Sumalinog, Tiffany Marie L. BSN 2Blala byuNo ratings yet
- Newborn Assessment PDFDocument51 pagesNewborn Assessment PDFMilca DavidNo ratings yet
- Third Trimester Workup and Dr. Pratima Mittal's AlgorithmsDocument37 pagesThird Trimester Workup and Dr. Pratima Mittal's AlgorithmsAparna MohanNo ratings yet
- Peadiatrics Case 2 and Journal AppraisalDocument15 pagesPeadiatrics Case 2 and Journal AppraisalAvneelNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics:: History and Physical Examination of Newborns and InfantsDocument20 pagesPediatrics:: History and Physical Examination of Newborns and InfantsJüdith Marie Reyes BauntoNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics SamplesDocument50 pagesPediatrics SamplesErik Judika2No ratings yet
- Pediatric Physical Therapy Theories and DevelopmentDocument15 pagesPediatric Physical Therapy Theories and Developmentsilentchaos11No ratings yet
- CASE-STUDY-ON-PLACENTA-PREVIADocument19 pagesCASE-STUDY-ON-PLACENTA-PREVIAgherlethrNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of G2 P1 (2023) of 35 2/7 Weeks Aog by Normal Spontaneously Vaginal Delivery To A Live Baby GirlDocument19 pagesA Case Study of G2 P1 (2023) of 35 2/7 Weeks Aog by Normal Spontaneously Vaginal Delivery To A Live Baby GirlMikes CastroNo ratings yet
- Fetal DistressDocument10 pagesFetal DistressLady Jane CaguladaNo ratings yet
- SE 502-Week 3: Etiology Part 2Document4 pagesSE 502-Week 3: Etiology Part 2Elyssa DaggettNo ratings yet
- Nutrition assessment guideDocument4 pagesNutrition assessment guideAubrey MitraNo ratings yet
- 4th Lesson Assesing Newborns and InfantsDocument5 pages4th Lesson Assesing Newborns and InfantsdaningdubouzetNo ratings yet
- Transient Tachypneu of The Newborn: Supervisor: Dr. Nazardi Oyong Sp. ADocument57 pagesTransient Tachypneu of The Newborn: Supervisor: Dr. Nazardi Oyong Sp. AWella FadillahNo ratings yet
- Maternal Rle ReviewerDocument4 pagesMaternal Rle ReviewerPrincess Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Newborn Care 1Document6 pagesNewborn Care 1Francine LaxaNo ratings yet
- Genetics in IVF, Prenatal DiagnosisDocument33 pagesGenetics in IVF, Prenatal DiagnosisavanthikagettyNo ratings yet
- Cornell's Note 4Document5 pagesCornell's Note 4Angel BriboneriaNo ratings yet
- Kardiotokografi YBSDocument62 pagesKardiotokografi YBSUmmi RosmalasariNo ratings yet
- PGT and Prenatal GeneticsDocument50 pagesPGT and Prenatal GeneticsavanthikagettyNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing L E C T U R EDocument12 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing L E C T U R EAngelica Dalit MendozaNo ratings yet
- Modul PBL 1 Kelompok 9aDocument34 pagesModul PBL 1 Kelompok 9aWahyuni NurdinNo ratings yet
- Reversing Cerebral Palsy in Early Infancy: A Protocol for Using Normalization Through Neuroplastic Manipulation (NTNM)From EverandReversing Cerebral Palsy in Early Infancy: A Protocol for Using Normalization Through Neuroplastic Manipulation (NTNM)No ratings yet
- Using Non-Fiction BooklistDocument6 pagesUsing Non-Fiction BooklistTracyNo ratings yet
- QSP Qad 08Document2 pagesQSP Qad 08prabha_1No ratings yet
- Ferriols, Roque J. - A Memoir of Six YearsDocument4 pagesFerriols, Roque J. - A Memoir of Six YearsCharlene TanNo ratings yet
- Workforce Plan 20xx-20xxDocument22 pagesWorkforce Plan 20xx-20xxRani EndarweniNo ratings yet
- Slevin 1986Document9 pagesSlevin 1986YuliaNo ratings yet
- Game On! - Gamification, Gameful Design, and The Rise of The Gamer Educator PDFDocument216 pagesGame On! - Gamification, Gameful Design, and The Rise of The Gamer Educator PDFNelson LopezNo ratings yet
- Medium Term Plan On Teaching Scratch in Year 4Document5 pagesMedium Term Plan On Teaching Scratch in Year 4api-272550320No ratings yet
- (13a) Active and Passive VoiceDocument2 pages(13a) Active and Passive VoiceVedhNo ratings yet
- ElectrodynamicsDocument4 pagesElectrodynamicsHarold Favian Diaz LeonisNo ratings yet
- Qualiry Technical Rrequirement User S Handbook VW MexicoDocument23 pagesQualiry Technical Rrequirement User S Handbook VW MexicoOscar Javier Olivares Tronco0% (1)
- Mental Health and Self-Care ReflectionDocument2 pagesMental Health and Self-Care Reflectionapi-472652222No ratings yet
- Jumping SpidersDocument3 pagesJumping SpidersMostakim IeltsNo ratings yet
- Henry Derozio and Toru Dutt - Pioneers of Indian English PoetryDocument14 pagesHenry Derozio and Toru Dutt - Pioneers of Indian English PoetrySwatarup KapporNo ratings yet
- 10 Steps For Avoiding Teacher BurnoutDocument3 pages10 Steps For Avoiding Teacher BurnoutSarah DeNo ratings yet
- "Under The Aegis of Man" - The Right To Development and The Origins of The New International Economic Order Daniel J. WhelanDocument17 pages"Under The Aegis of Man" - The Right To Development and The Origins of The New International Economic Order Daniel J. WhelanDavid Enrique ValenciaNo ratings yet
- WQS Ac400 0XXCDocument8 pagesWQS Ac400 0XXCTony ChenNo ratings yet
- 10th MICROCURRICULAR - PLANNING PROJECT 1Document7 pages10th MICROCURRICULAR - PLANNING PROJECT 1Vinicio Marcelo ChicaizaNo ratings yet
- Michael Irving Jensen - The Political Ideology of Hamas - A Grassroots Perspective (Library of Modern Middle East Studies) - I. B. Tauris (2009)Document217 pagesMichael Irving Jensen - The Political Ideology of Hamas - A Grassroots Perspective (Library of Modern Middle East Studies) - I. B. Tauris (2009)Andreea Toma100% (1)
- 0607 s14 Ms 43Document6 pages0607 s14 Ms 43wizard guyNo ratings yet
- Is Umeme Worth 300 BillionsDocument5 pagesIs Umeme Worth 300 Billionsisaac setabiNo ratings yet
- Managing Sleep Apnea Risks During Anesthesia and SurgeryDocument1 pageManaging Sleep Apnea Risks During Anesthesia and SurgeryMuhammad SyammNo ratings yet
- Public Assessment Report Mutual Recognition ProcedureDocument29 pagesPublic Assessment Report Mutual Recognition ProcedureamcolacoNo ratings yet
- Lal Bahadur ShastriDocument17 pagesLal Bahadur Shastribhaskar124970No ratings yet
- NP Performance Appraisal Sample PDFDocument2 pagesNP Performance Appraisal Sample PDFHamss Ahmed80% (5)
- The Kugelmass EpisodeDocument6 pagesThe Kugelmass EpisodeJohn WilkinsNo ratings yet
- NCC - Binding The Nation Together - National Integration - NDocument4 pagesNCC - Binding The Nation Together - National Integration - Nselva_raj215414No ratings yet
- Procurement-Lecture 3 Customer Service and Logistics: Abdikarim Mohaidin AhmedDocument33 pagesProcurement-Lecture 3 Customer Service and Logistics: Abdikarim Mohaidin AhmedMA. CHRISTINE BODUANNo ratings yet
- Points in Community Health NursingDocument9 pagesPoints in Community Health NursingkuyarahimNo ratings yet
- Building Rapport 2Document13 pagesBuilding Rapport 2Kuldeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Ankit - KP Horary Software - Prashna Kundali Software - Free KP Astrology SoftwareDocument3 pagesAnkit - KP Horary Software - Prashna Kundali Software - Free KP Astrology SoftwareANKIT SINGHNo ratings yet