Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chronic Transfusion Therapy For Sickle Cell Disease
Uploaded by
Phương Ly Lê0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesChronic transfusion therapy involves patients receiving blood transfusions once a month for many years. It allows normal red blood cells to circulate freely and decreases complications for patients with sickle cell disease by lowering the amount of sickle hemoglobin. Chronic transfusions are primarily used to prevent stroke in children with sickle cell disease who have already had a stroke or are at high risk for one based on screening results. They reduce the risk of recurrent strokes by more than 80%. While transfusions provide benefits, they also carry risks like iron overload, infections, and developing antibodies against foreign blood antigens that can make finding compatible blood difficult.
Original Description:
Original Title
Chronic Transfusion Therapy for Sickle Cell Disease
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChronic transfusion therapy involves patients receiving blood transfusions once a month for many years. It allows normal red blood cells to circulate freely and decreases complications for patients with sickle cell disease by lowering the amount of sickle hemoglobin. Chronic transfusions are primarily used to prevent stroke in children with sickle cell disease who have already had a stroke or are at high risk for one based on screening results. They reduce the risk of recurrent strokes by more than 80%. While transfusions provide benefits, they also carry risks like iron overload, infections, and developing antibodies against foreign blood antigens that can make finding compatible blood difficult.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesChronic Transfusion Therapy For Sickle Cell Disease
Uploaded by
Phương Ly LêChronic transfusion therapy involves patients receiving blood transfusions once a month for many years. It allows normal red blood cells to circulate freely and decreases complications for patients with sickle cell disease by lowering the amount of sickle hemoglobin. Chronic transfusions are primarily used to prevent stroke in children with sickle cell disease who have already had a stroke or are at high risk for one based on screening results. They reduce the risk of recurrent strokes by more than 80%. While transfusions provide benefits, they also carry risks like iron overload, infections, and developing antibodies against foreign blood antigens that can make finding compatible blood difficult.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
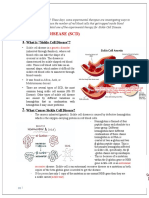
Chronic Transfusions
Chronic transfusion therapy occurs when
a patient receives a blood transfusion
once a month for many years. Chronic 111 Michigan Ave NW
transfusions allow normal red blood cells Washington, DC 20010-2970
(RBCs) to live longer in the body and Phone: 202-476-5000
flow freely in blood vessels. Fax: 202-476-2976
ChildrensNational.org
The most common reason why children
with sickle cell disease (SCD) are placed Sickle Cell Disease Program
on chronic transfusion therapy is to Chronic Transfusion
prevent stroke (or repeat stroke) from
occurring. Chronic transfusions may also Therapy
be used for a period of six months to two
years to prevent further episodes of
other severe sickle-related complications
(i.e. acute chest syndrome, splenic Other Options
sequestration). Hydroxyurea and stem cell
(bone marrow) transplants are
Children with SCD have sickle additional treatment options.
hemoglobin S (HbS) in their red blood Hydroxyurea has been proven
cells. Chronic transfusions decrease to control many symptoms of
sickle cell related complications by sickle cell disease. Stem cell
decreasing the amount of HbS. This is transplants can cure sickle cell
done by giving a blood transfusion to disease, but require a suitable
maintain the HbS at 30 to 50 percent. In donor. Severe side effects can
order to maintain the HbS level within occur.
this range, transfusions are usually For information about the
repeated every three to four weeks. Transfusion Buddy Program at
Children with SCD who have had a Children's National, call
stroke or are determined to be at high (202)476-KIDS (5437)
risk of having a stroke by Transcranial
Doppler screening tests often receive For questions regarding the
chronic transfusions for many years. chronic transfusion program,
contact:
Jennifer Webb, M.D.
jwebb@ChildrensNational.org
Primary Stroke Prevention Types of Transfusions Risks of Transfusion, Continued
Simple Transfusion. Blood is given to the Alloimmunization:
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is the most patient through an IV (most common).
Partial Manual Exchange Transfusion. Blood When a child receives blood that has
common cause of childhood stroke. The different proteins (antigens) from their
is first removed through an IV, then
majority of strokes in this population own, they may develop antibodies against
replaced with a blood and saline
occur between the ages of three and 15 combination to ensure safe blood counts these foreign antigens. This condition is
years old. The annual risk of stroke in and volume (for high hemoglobin levels). called alloimmunization. People who are
children with SCD is 0.6 to one percent Automated Exchange Transfusion - Blood is transfused frequently, such as patients
per year. This rate is approximately 300 removed and replaced with blood from with sickle cell disease, can form one or
times higher than in children without healthy donors (done through IVs or special more antibodies against RBCs. This can
SCD. Transcranial Doppler (TCD) central lines) using an apheresis machine
make it very difficult to find blood for
screening should be done every year in the patient. Rarely, reactions can occur
children with SCD starting at age two. Risks of Transfusions in patients with antibodies bringing on
If the results of the TCD are abnormal, Iron overload fevers, muscle aches, joint pain, anemia,
your child has a risk of stroke as high Excess iron from transfused red blood cells or dark urine.
as 40 percent within three years of can build up and remain in the body. If left
the abnormal TCD without treatment. untreated, this iron can harm the liver, heart,
Chronic transfusions given every three and other organs. Your child’s hematologist At Children’s National the focus is
to four weeks reduce the stroke risk in will monitor for iron overload through on preventing the development of
children with SCD and abnormal TCDs by monthly labs and yearly MRIs of the liver. antibodies in several ways. Prior to
more than 90 percent. After about one to two years of chronic each transfusion (within three days)
transfusions, patients often need to be the blood bank screens your child’s
Prevention of Recurrent Stroke treated with medicines to help remove iron blood for any new antibodies that the
from the body (iron chelators). child may have developed. We try to
Children with SCD who have had one decrease the amount of antibodies SCD
stroke are at extremely high risk of patients develop by closely matching
Infectious disease transmission
having another stroke. Research has the blood donor type to the patient’s
Every effort is made to ensure that
shown that chronic transfusion therapy type. The Blood Donor Center at
the blood your child receives is safe of
reduces the risk of additional strokes. Children’s National has established the
Without chronic transfusion therapy, infectious agents. Donors are interviewed to
Transfusion Buddy Program to provide
approximately 67 percent of children make sure they are healthy, and every unit
our chronically transfused SCD patients
with SCD who have had a stroke will of blood is tested for known transfusion-
with antigen matched blood products,
suffer from another stroke. However, trasnsmittable infections. All blood is
which dramatically decreases the rate of
with chronic transfusion therapy, the risk screened for viruses and other infections,
of recurrent stroke rate falls to less than alloimmunization.
including those that cause hepatits, human
20 percent. The highest risk of having immunodeficiency virus (HIV), human T-cell
another stroke is in the first five years. Despite the risks, transfusions can provide
lymphotropic virus (HTLV), and syphilis. As a
Your child’s hematologist will determine substantial benefits to children with SCD.
result, the chance of becoming infected
what the target level of HbS they want to
keep your child at, which is usually 30 with one of these viruses is extremely small.
percent.
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- CriticalThinking ProjectReport GroupcriDocument19 pagesCriticalThinking ProjectReport GroupcriPhương Ly LêNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Project Report Group777Document14 pagesCritical Thinking Project Report Group777Phương Ly LêNo ratings yet
- THỰC HÀNH NHÓM 1 - TRIỆU PHONGDocument5 pagesTHỰC HÀNH NHÓM 1 - TRIỆU PHONGPhương Ly LêNo ratings yet
- What Is Sickle Cell Disease?Document16 pagesWhat Is Sickle Cell Disease?Phương Ly LêNo ratings yet
- L-Glutamine Is A NaturallyDocument3 pagesL-Glutamine Is A NaturallyPhương Ly LêNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobin Called Hemoglobin S or Hbs or Sickle Hemoglobin, in The Red Blood CellsDocument13 pagesHemoglobin Called Hemoglobin S or Hbs or Sickle Hemoglobin, in The Red Blood CellsPhương Ly LêNo ratings yet
- What Is Sickle Cell DiseaseDocument6 pagesWhat Is Sickle Cell DiseasePhương Ly LêNo ratings yet
- What Is Sickle Cell DiseaseDocument11 pagesWhat Is Sickle Cell DiseasePhương Ly LêNo ratings yet
- Treatment: SwimmingDocument3 pagesTreatment: SwimmingPhương Ly LêNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 2 2 1 1 5b Equipmend Data Sheets CommDocument40 pages2 2 1 1 5b Equipmend Data Sheets CommMilic MilicevicNo ratings yet
- Physics Assessment 1 - Lab Report: Jessica Yam Year 10 Peace MR - SlosbergDocument19 pagesPhysics Assessment 1 - Lab Report: Jessica Yam Year 10 Peace MR - Slosbergapi-36149866550% (2)
- GalvInfoNote 1 4Document4 pagesGalvInfoNote 1 4rplata63No ratings yet
- Broadway CafeDocument13 pagesBroadway CafeIoana Taon100% (1)
- HP Compaq 6531s Inventec Zzi MV Rev A03 (6820s)Document54 pagesHP Compaq 6531s Inventec Zzi MV Rev A03 (6820s)y2k_yah7758No ratings yet
- Test Intensiv Engleza 5Document30 pagesTest Intensiv Engleza 5Simona Singiorzan90% (30)
- Comsol ProfileDocument4 pagesComsol ProfilePrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- 2021 Lifting Points Main Catalogue V1 - V - RUDDocument120 pages2021 Lifting Points Main Catalogue V1 - V - RUDmengyu hanNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis Textile IndustryDocument23 pagesSWOT Analysis Textile Industrydumitrescu viorelNo ratings yet
- Coffee Vibes: Here Is Where Your Presentation BeginsDocument86 pagesCoffee Vibes: Here Is Where Your Presentation Beginssyeda salmaNo ratings yet
- Exam of Refinery PDF 2Document20 pagesExam of Refinery PDF 2ئارام ناصح محمد حسێن0% (1)
- Svabodhodaya-Mañjarī by VāmanadattaDocument15 pagesSvabodhodaya-Mañjarī by Vāmanadattajuan pablo mejia100% (1)
- Raw Material Chemical AnalysisDocument41 pagesRaw Material Chemical AnalysisVinod Kumar VermaNo ratings yet
- 09.3090 USTR2433b T Series Cassettes Omega IFU enDocument51 pages09.3090 USTR2433b T Series Cassettes Omega IFU enAdi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Amenzade Yu.a. - Theory of Elasticity-Mir (1979)Document284 pagesAmenzade Yu.a. - Theory of Elasticity-Mir (1979)Javier100% (1)
- Transes - Male & Female GenitaliaDocument10 pagesTranses - Male & Female GenitaliacamatoviancaNo ratings yet
- Lover Album LyricsDocument34 pagesLover Album LyricsMichael PlanasNo ratings yet
- Truss Design GuidDocument3 pagesTruss Design GuidRafi HasanNo ratings yet
- Designing New Vanillin Schiff Bases and Their Antibacterial StudiesDocument4 pagesDesigning New Vanillin Schiff Bases and Their Antibacterial StudiesAvinash PurohitNo ratings yet
- Exam Materials ScienceDocument10 pagesExam Materials ScienceChimzoe CatalanNo ratings yet
- Our School Broke Up For The Winter VacationsDocument7 pagesOur School Broke Up For The Winter VacationsprinceNo ratings yet
- Anna Kingsford, Edward Maitland - The Perfect Way, or The Finding of Christ (1909)Document484 pagesAnna Kingsford, Edward Maitland - The Perfect Way, or The Finding of Christ (1909)Momir Miric100% (1)
- Baykon Bx3 Filling Controller CatalogueDocument2 pagesBaykon Bx3 Filling Controller CatalogueAhmed alkadhlly100% (1)
- Table of Content and PrefaceDocument5 pagesTable of Content and PrefaceHaiderEbrahimNo ratings yet
- Features and Highlights - : CapableDocument2 pagesFeatures and Highlights - : CapableaarianNo ratings yet
- Speaking With Confidence: Chapter Objectives: Chapter OutlineDocument12 pagesSpeaking With Confidence: Chapter Objectives: Chapter OutlinehassanNo ratings yet
- Post Graduate Diploma in Psychological CounselingDocument1 pagePost Graduate Diploma in Psychological CounselingAvalokiteswari KurupNo ratings yet
- Heavy Earth Moving MachinaryDocument34 pagesHeavy Earth Moving MachinaryMAZHAR ALAMNo ratings yet
- Dark Elves WarbandDocument9 pagesDark Elves Warbanddueydueck100% (1)
- Namma Kalvi 12th English Slow Learners Study MaterialDocument28 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th English Slow Learners Study MaterialSTANLEY RAYEN100% (1)