Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phlebothrombosis: Azole, I. (2021) - PHLEBOTHROMBOSIS. - PPT Download. Retrieved 25 October 2021, From
Uploaded by
Sureen RegularOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Phlebothrombosis: Azole, I. (2021) - PHLEBOTHROMBOSIS. - PPT Download. Retrieved 25 October 2021, From
Uploaded by
Sureen RegularCopyright:
Available Formats
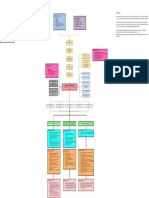
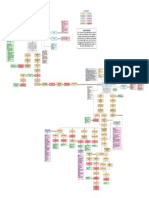
Phlebothrombosis Concept map
Legend:
Disease Process
Predisposing Factors
Precipitating Factors
Disease and Definition
Complications
Nursing Diagnosis
Nursing Assessment
References
Nursing Interventions
Predisposing Factors
Sign & Symptoms Precipitating Factors Azole, I. (2021). PHLEBOTHROMBOSIS. - ppt download. Retrieved 25 October 2021, from
Sex
Patient Outcomes
Age Surgery https://slideplayer.com/slide/12104675/
Pregnant and postpartum women Medication
Laboratory tests Personal history of Hospital stay
Phlebothrombosis Smoking Frisk, C. (2012). Bacterial and Fungal Diseases. The Laboratory Rabbit, Guinea Pig, Hamster,
Pharmacologic Therapy Immobility i.e. prolonged bed Virchow's triad (venous stasis,
rest, sitting, inactivity hypercoagulation, and damage)
And Other Rodents, 797-820. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-380920-9.00030-4
Medical Management Clotting disorders
Pathogenesis line Wells scor, H. (2021). By: abdulkrim al-kharashi naif alsikan - ppt video online download.
Connecting line
Retrieved 25 October 2021, from https://slideplayer.com/slide/6037102/
Kong, L. (2014). Thrombophlebitis. Retrieved 25 October 2021, from
https://www.slideserve.com/lixue/thrombophlebitis
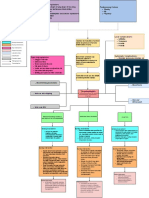
Signs and Symptoms
Vessel trauma
stimulates the clotting Pieces of thrombus may
Inflammation is triggered,
Pain cascade break loose and travel
causing tenderness,
Edema through circulation -->
swelling
Positive palpation maneuvers Embolus
- Homan's sign (+)
- Lowenber's sign (+)
Platelets aggregate at the site
particularly when venous stasis is
Enlarged superficial collaterals present Repeated small
Change of skin color and embolisation
temperature (cyanosis)
Platelets and fibrin Post-phlebitic syndrome
form the initial clot
Chronic venous
insufficiency
Anticoagulation Therapy. Initial treatment is RBC are trapped in
with low molecular weight heparin or the fibrin meshwork
unfractioned heparin for at least 5 days,
followed by warfarin for at least 3 months
The thrombus propagates in the
Thrombolytics. To dissolve an existing clot direction of the blood flow
Nonsurgical Management
such as IV streptokinase
Duplex venous ultrasound
Analgesics. Pain medications
Venography
Phlebothrombosis Blood Tests (CMP, CBC, D-
A condition of venous thrombosis without Dimer Test)
inflammation; occurs much more immediately, and
pain is not a prominent feature
Inferior vena cava filter. Only when anticoagulant is Magnetic Resonance
contraindicated; this prevents clots that can break loose Imaging (MRI)
in the legs and travel to the lungs
Computed tomography
(CT) scan
Surgical ligation and stripping. High ligation of the long
saphenous vein at the saphenofemoral junction together Surgical Management
with ligation of all tributaries
Venous thrombectomy. The surgical removal of a vein
clot; only in very serious cases
Impaired gas exchange Impaired skin integrity
Risk for Bleeding
Nursing Assessment Nursing Assessment
Nursing Assessment
Assess the characteristics of ulcers:
Assess level of consciousness
Assess signs and
and changes in mentation
Location
symptoms of bleeding.
Auscultate lungs for areas of Tissue bed
decreased and absent breath Monitor Heparin-
induced platelet Surrounding tissue
sounds and the presence of
aggregation (HIPA)
adventitious sounds (crackles).
status.
Nursing Intervention Nursing Intervention
Nursing Intervention Elevate the leg as per the
Provide oxygen therapy with an
appropriate method as ordered. physician’s advice.
Administer anticoagulant therapy Keep the skin clean and well
Provide supplemental
as per physician’s advice
humidification, such as lubricated
(continuous IV heparin/low
ultrasonic nebulizers. Avoid possible injury even in
molecular weight heparin).
Keep the head of bed elevated. ambulation
If bleeding occurs when the Clean the wound with non-
Encourage coughing, deep
patient is on heparin therapy:
breathing exercises, and toxic cleaner or normal saline
Stop infusion.
suctioning as indicated.
Assist with frequent changes of
position, and encourage
ambulation as tolerated.
Patient Outcomes
The patient will have intact skin
Patient Outcomes without signs of infection.
Patient Outcomes The patient maintains a
Client will demonstrate therapeutic level of blood
adequate ventilation and coagulation bleeding.
oxygenation by ABGs within The patient does not
client’s normal range.
experience bleeding.
Client will report or display
resolution or absence of
symptoms of respiratory
distress
You might also like
- Venous Thrombosis: Complications of Deep Vein Thrombosis. Saint Luke's Health System. (N.D.) - Retrieved OctoberDocument1 pageVenous Thrombosis: Complications of Deep Vein Thrombosis. Saint Luke's Health System. (N.D.) - Retrieved OctoberSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Research Clinicopathologic Profile of Patients Who Underwent ThyroidectomyDocument8 pagesResearch Clinicopathologic Profile of Patients Who Underwent ThyroidectomyElvin Louie LisondraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0001299810000152 MainDocument22 pages1 s2.0 S0001299810000152 MainANDERSON DE LA CRUZ HERNANDEZ HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceuticals 15 00762 v2Document20 pagesPharmaceuticals 15 00762 v2Aiman SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Complications of Injectable Fillers, Part 2: Vascular ComplicationsDocument17 pagesComplications of Injectable Fillers, Part 2: Vascular ComplicationsIvan CardenasNo ratings yet
- Articulo de Feocromocitoma para InglesDocument16 pagesArticulo de Feocromocitoma para Inglesjmichel2No ratings yet
- Derrame Pleural 2015Document16 pagesDerrame Pleural 2015MARIA NEGRETE MOSCOTENo ratings yet
- Terlecki 2015Document5 pagesTerlecki 2015andreea1465No ratings yet
- Vesicovaginal FistulaDocument54 pagesVesicovaginal FistuladanielNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Hyaluronic Acid Filler-Induced Impending Necrosis With Hyaluronidase: Consensus RecommendationsDocument7 pagesTreatment of Hyaluronic Acid Filler-Induced Impending Necrosis With Hyaluronidase: Consensus RecommendationsAna GNo ratings yet
- Effects of Virtual Reality On Pain During Venous Port Access in Pediatric Oncology Patients: A Randomized Controlled StudyDocument10 pagesEffects of Virtual Reality On Pain During Venous Port Access in Pediatric Oncology Patients: A Randomized Controlled StudyZafitri AsrulNo ratings yet
- Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy: Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 63, Number 1, 134-151Document19 pagesIntrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy: Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 63, Number 1, 134-151Von BernalNo ratings yet
- Pterygium - EyeWikiDocument1 pagePterygium - EyeWikiPaudel SujanNo ratings yet
- Oral LPDocument5 pagesOral LPkahkashanahmed065No ratings yet
- Vascular Complication of Injectable FillerDocument17 pagesVascular Complication of Injectable Fillerahmed100% (1)
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)Document2 pagesDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)JoyyNo ratings yet
- Main PDFDocument8 pagesMain PDFrubramNo ratings yet
- 9800 9800 WJCC-2-866Document8 pages9800 9800 WJCC-2-866An Nisaa DejandNo ratings yet
- Stein 2009Document14 pagesStein 2009Med ZinNo ratings yet
- Risk Prediction of Developing Venous Thrombosis in Combined Oral Contraceptive UsersDocument12 pagesRisk Prediction of Developing Venous Thrombosis in Combined Oral Contraceptive Usersjuananzaldo266No ratings yet
- Therapeutic Plasma Exchange Protects Patients With Sepsis Associated Disseminated IntravascularDocument10 pagesTherapeutic Plasma Exchange Protects Patients With Sepsis Associated Disseminated IntravascularBhanu KumarNo ratings yet
- Jamafacial Rayess 2017 Oi 170051Document8 pagesJamafacial Rayess 2017 Oi 170051陳沂仿No ratings yet
- Surgery For Glaucoma in Patients With Facial Port Wine MarkDocument6 pagesSurgery For Glaucoma in Patients With Facial Port Wine MarkPutri kartiniNo ratings yet
- Penile Traction Therapy and Peyronie's Disease: A State of Art Review of The Current LiteratureDocument7 pagesPenile Traction Therapy and Peyronie's Disease: A State of Art Review of The Current LiteraturePablo AmadorNo ratings yet
- ARDS Concept Map - BunayogDocument2 pagesARDS Concept Map - BunayogJacela Annsyle BunayogNo ratings yet
- Endophthalmitis Viterectomy Study WJORV 2012Document7 pagesEndophthalmitis Viterectomy Study WJORV 2012Rasha Mounir Abdel-Kader El-TanamlyNo ratings yet
- Complicaciones de Cirugía DentoalveolarDocument26 pagesComplicaciones de Cirugía DentoalveolarElvia Maria Rios BeltranNo ratings yet
- Fbioe 10 968482Document12 pagesFbioe 10 968482DR RISKA WAHYUNo ratings yet
- Current and Emerging Biomarkers of Frailty in The Elderly: Clinical Interventions in Aging DoveDocument10 pagesCurrent and Emerging Biomarkers of Frailty in The Elderly: Clinical Interventions in Aging DoveSanrio NeuroNo ratings yet
- Use of Chlorhexidine Mouthwash in Children Receiving Chemotherapy: A Review of LiteratureDocument6 pagesUse of Chlorhexidine Mouthwash in Children Receiving Chemotherapy: A Review of LiteraturebanyubiruNo ratings yet
- VMRR 53266 Diagnosis Prevention and Management of Canine Hip Dysplasia - 051915Document12 pagesVMRR 53266 Diagnosis Prevention and Management of Canine Hip Dysplasia - 051915Lauura Cristina BarriosNo ratings yet
- Clinical and CT COVID19 in PediatricDocument2 pagesClinical and CT COVID19 in PediatricDannth YudhizNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Adhesion DevelopmentDocument20 pagesPostoperative Adhesion Developmentkenny StefNo ratings yet
- Medicina 57 00895 v2Document15 pagesMedicina 57 00895 v2Fatimah AssagafNo ratings yet
- 23 - Azzotti - Complications and Treatment Errors in Root Coverage ProceduresDocument28 pages23 - Azzotti - Complications and Treatment Errors in Root Coverage ProceduresGuadalupe GasparNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention Of.20Document13 pagesDiagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention Of.20fernando.suarez.mtzNo ratings yet
- Grand Rounds FinalDocument31 pagesGrand Rounds Finalapi-549451092No ratings yet
- Aneurysmal Bone Cysts of The JawsDocument12 pagesAneurysmal Bone Cysts of The JawsThành Luân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Articulo Pos 3Document7 pagesArticulo Pos 3JuanitaEnriquezOrtizNo ratings yet
- Predicting Neck Abscess With Contrast-Enhanced Computed TomographyDocument10 pagesPredicting Neck Abscess With Contrast-Enhanced Computed TomographyMuhammad Dody HermawanNo ratings yet
- Complications of Injectable Fillers, Part 2: Vascular ComplicationsDocument17 pagesComplications of Injectable Fillers, Part 2: Vascular ComplicationsIsabel JiménezNo ratings yet
- Merga-2022 SurgicalsiteinfectionDocument11 pagesMerga-2022 SurgicalsiteinfectionAddisNo ratings yet
- Association Between Pre-Delivery Coagulation Indicators and Invasive Placenta Accreta SpectrumDocument8 pagesAssociation Between Pre-Delivery Coagulation Indicators and Invasive Placenta Accreta SpectrumRahmayantiYuliaNo ratings yet
- JCM 12 00453Document15 pagesJCM 12 00453AndreiMunteanuNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Its Prevalence, Causes and Management in ChitwanDocument3 pagesAbnormal Uterine Bleeding Its Prevalence, Causes and Management in ChitwanShierly KencanaNo ratings yet
- Fpubh 10 823680Document7 pagesFpubh 10 823680Alessandra Gobbi Matta SNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Chitosan On The Healing Process ofDocument16 pagesThe Effects of Chitosan On The Healing Process ofRebeca FloresNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Therapy For Prostate Tuberculosis: Ekaterina Kulchavenya, Elena Brizhatyuk and Victor KhomyakovDocument6 pagesDiagnosis and Therapy For Prostate Tuberculosis: Ekaterina Kulchavenya, Elena Brizhatyuk and Victor KhomyakovYoza DelvinaNo ratings yet
- DIC in PregnancyDocument24 pagesDIC in PregnancySergio Alberto Sulub NavarreteNo ratings yet
- AKI vs. CKD FinalDocument1 pageAKI vs. CKD FinalMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion - ClinicalKeyDocument13 pagesPleural Effusion - ClinicalKeyWialda Dwi rodyahNo ratings yet
- Tumor Staging of Endocervical Adenocarcinoma .8Document10 pagesTumor Staging of Endocervical Adenocarcinoma .8elisasitohangNo ratings yet
- Sugawara J Cath 2012Document7 pagesSugawara J Cath 2012nurfitriaNo ratings yet
- Lithotripsy Salivary Stones OhpDocument5 pagesLithotripsy Salivary Stones Ohpaysha mksNo ratings yet
- Bhat AK, Acharya AM. Current Concepts in The Management Radial Longitudinal Deficiency. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020Document9 pagesBhat AK, Acharya AM. Current Concepts in The Management Radial Longitudinal Deficiency. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020AsdfNo ratings yet
- Vats Fewer ComplicationsDocument1 pageVats Fewer ComplicationsAlin Ionut BurlacuNo ratings yet
- Bacteremia After Supragingival Scaling and Dental Extraction - Rosa - Domingues - Etal - INI - Lapclin - 2017Document7 pagesBacteremia After Supragingival Scaling and Dental Extraction - Rosa - Domingues - Etal - INI - Lapclin - 2017Carolina Rodríguez RamírezNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 NB - Care of Clients With Problem in Nutrition and Gi, Metabolism and Endocrine, PerceptionDocument4 pagesNCM 116 NB - Care of Clients With Problem in Nutrition and Gi, Metabolism and Endocrine, PerceptionSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- C. at Pi, Amino Acids Are Protonated So They Have Zero ChargeDocument1 pageC. at Pi, Amino Acids Are Protonated So They Have Zero ChargeSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Echocardiogram,: Supine Semi-Fowler'sDocument3 pagesEchocardiogram,: Supine Semi-Fowler'sSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Dpa For Surgical AreaDocument1 pageDpa For Surgical AreaSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Dpa For or (Holding Area)Document1 pageDpa For or (Holding Area)Sureen RegularNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 RLE Virtual Duty Operating Room Rotation (Week 2) : Ma'am Jesseca P. Monsanto, RN, MANDocument8 pagesNCM 112 RLE Virtual Duty Operating Room Rotation (Week 2) : Ma'am Jesseca P. Monsanto, RN, MANSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PosttestDocument1 pageModule 3 PosttestSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Endotracheal Tracheal SuctioningDocument3 pagesEndotracheal Tracheal SuctioningSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Biochem Proteins AssigmentDocument1 pageBiochem Proteins AssigmentSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Note Proteins BiochemistryDocument1 pageNote Proteins BiochemistrySureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Katz Index of Independence (ADL)Document2 pagesKatz Index of Independence (ADL)Ana Dominique EspiaNo ratings yet
- Regular Quiz HydrocarbonsDocument2 pagesRegular Quiz HydrocarbonsSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Indwelling Urinary Catheter FemaleDocument9 pagesIndwelling Urinary Catheter FemaleVinz Khyl G. CastillonNo ratings yet
- Neurological Exam Lecture NotesDocument26 pagesNeurological Exam Lecture NotesNaveen KovalNo ratings yet
- Neurological Exam Lecture NotesDocument26 pagesNeurological Exam Lecture NotesNaveen KovalNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesNCM 112 Lecture NotesSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors: Sitting Down or Lying Down For Too Long ObesityDocument1 pagePrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors: Sitting Down or Lying Down For Too Long ObesitySureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Dpa For or (Holding Area)Document1 pageDpa For or (Holding Area)Sureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Dpa For Surgical AreaDocument1 pageDpa For Surgical AreaSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Note Proteins BiochemistryDocument1 pageNote Proteins BiochemistrySureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Biochem Proteins AssigmentDocument1 pageBiochem Proteins AssigmentSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Chem AssignmentDocument1 pageChem AssignmentSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Biochem Proteins AssigmentDocument1 pageBiochem Proteins AssigmentSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Bone Tissue EngineeringDocument352 pagesBone Tissue EngineeringKeri Gobin SamarooNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic SurgeryDocument4 pagesLaparoscopic SurgerycaioaccorsiNo ratings yet
- Dvt. BPTDocument25 pagesDvt. BPTAanchal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Organ DR - Siti Rafiah HusainDocument73 pagesAnatomi Organ DR - Siti Rafiah HusainfitrahfajrianihamingNo ratings yet
- A Study To Evaluate Effectiveness of Cold Application and Magnesium Sulphate Application On Superficial Thrombophlebitis Among Patients Receiving Intravenous Therapy in Selected Hospitals Amritsar.Document25 pagesA Study To Evaluate Effectiveness of Cold Application and Magnesium Sulphate Application On Superficial Thrombophlebitis Among Patients Receiving Intravenous Therapy in Selected Hospitals Amritsar.Navjot Brar71% (14)
- Medical Terminology Systems A Body Systems Approach 8Th Edition Gylys Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument46 pagesMedical Terminology Systems A Body Systems Approach 8Th Edition Gylys Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkhuyentryphenakj1100% (9)
- AR Benjie Manila 2017Document76 pagesAR Benjie Manila 2017Benjie Modelo ManilaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Mixed Venous Oxygen SaturationDocument3 pagesChapter 4 - Mixed Venous Oxygen SaturationJamesNo ratings yet
- Inguinal HerniaDocument19 pagesInguinal HerniaArdham ChesukoruNo ratings yet
- GemmotherapyDocument5 pagesGemmotherapySatyendra Rawat100% (2)
- Ulcers of The Lower Extremity: Ajay K. Khanna Satyendra K. TiwaryDocument483 pagesUlcers of The Lower Extremity: Ajay K. Khanna Satyendra K. TiwaryMirtel MongiNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Cardiovascular System#Document36 pagesHistology of The Cardiovascular System#DonaldNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument23 pagesPulmonary EmbolismBianca Dizon0% (1)
- VARICOCELEDocument65 pagesVARICOCELEParamartha KesumaNo ratings yet
- LEsson-Guide-G9-Biology Module 1 On TemplateDocument29 pagesLEsson-Guide-G9-Biology Module 1 On Templateconstancia G, caraan0% (1)
- Anatomic Exposure in Vascular Surgery, 3E (2013) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Document605 pagesAnatomic Exposure in Vascular Surgery, 3E (2013) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Rafael Castillo85% (13)
- Diosmin + Hisperidin: DaflonDocument10 pagesDiosmin + Hisperidin: DaflonMark Anthony Mabini LlanosNo ratings yet
- Bab 20 PDFDocument43 pagesBab 20 PDFFuad AssodiqiNo ratings yet
- Simple Meniscus Repair - 2023Document16 pagesSimple Meniscus Repair - 2023MmaNo ratings yet
- CUSADocument28 pagesCUSAhoangducnamNo ratings yet
- GIT & Urinary SystemDocument50 pagesGIT & Urinary SystemRenishya ManiarasuNo ratings yet
- Admixture Lesions in Congenital Cyanotic Heart Disease: Hemodynamic RoundsDocument8 pagesAdmixture Lesions in Congenital Cyanotic Heart Disease: Hemodynamic RoundsTejeshwar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Summative Test (Respiratory & Circulatory System)Document3 pagesSummative Test (Respiratory & Circulatory System)jimbo09100% (3)
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemYusuf AzeezNo ratings yet
- Background + RefDocument40 pagesBackground + Refبشير حيدرNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels Lecture Slides PDFDocument32 pagesBlood Vessels Lecture Slides PDFRaluca AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 - Blood Vessels I - Histology of Artery and Vein ArteriesDocument28 pagesLaboratory 3 - Blood Vessels I - Histology of Artery and Vein ArteriesSofia NNo ratings yet
- Causes of Death in TraumasDocument51 pagesCauses of Death in Traumasjeevan ghimireNo ratings yet
- Dialysis Arteriovenous Fistulas The Critical RoleDocument12 pagesDialysis Arteriovenous Fistulas The Critical Rolehermalina sabruNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 6th Edition by AehlertDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Ecgs Made Easy 6th Edition by AehlertWoodrow Fleming100% (31)