Professional Documents
Culture Documents
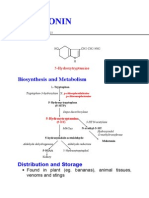
Autocoids - Serotonin
Uploaded by
Triras ManandharOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Autocoids - Serotonin
Uploaded by
Triras ManandharCopyright:
Available Formats
AUTOCOIDS –
Serotonin and Anti-serotonins
1
DR. SABYATA GAUTAM
(M. PHARM, PH.D)
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Outline
2
Introduction
Serotonin Receptors
Pharmacological actions
Serotonin receptor agonist
Migraine & use of serotonin agonists in migraine
Serotonin antagonist drugs
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
SEROTONIN
3
Serotonin or 5-HT (5-hydroxytryptamine) is the
vasoconstrictor substance which appeared in serum
when blood clotted.
In 1950’s “Enteramine” or serotonin was found in the
smooth muscle contracting substance present in entero-
chromaffin cells of gut mucosa.
About 90% of body’s content of 5-HT is localized in the
intestines; most of the rest is in platelets and brain.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Dr. Sabyata Gautam 4
Serotonin receptors
5
Serotonergic (5-HT) receptors:
Four families of 5-HT receptors (5-HT1, 5-HT2, 5-HT3, 5-HT4)
comprising of 14 receptor subtypes have been recognized.
Play role in several diseases
Depression – changes in serotonin concentration in the brain
Migraine – potent constrictor of cerebral blood vessels
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Five subtypes (HT1A, B, D, E, and F) have been identified. It is present in
5-HT1 raphe nuclei of brain stem and hippocampus.
Three sub-types (5-HT 2 A, B, C, D-type) are present and located in
5-HT2 vascular and visceral smooth muscle, platelets and cerebral neurons.
It rapidly depolarizes nerve endings by opening the cation channel located
within it. It mediates the reflex effect at nerve endings in myenteric plexus
5-HT3 and also in area postrema and nucleus tractus solitarious (NTS) in brain stem
causing nausea and vomiting.
Present in mucosa, plexus and smooth muscle of gut causing intestinal
secretion and peristalsis. It causes hyperpolarization by decreasing K+
5-HT4
conductance in brain.
Cisapride and renzapride are selective 5-HT 4 agonists.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam 6
7
The recently cloned 5-HT5, 5-HT6 and 5-HT7
receptors are closely related to the 5-HT4 receptor.
These are mainly located in specific brain areas, but
their functional role is not known.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Pharmacological actions
8
1. CVS: The net action is complex. Larger arteries and veins are
characteristically constricted. It dilates small arterioles and
constricts venules: capillary pressure rises and fluid escapes
(prolonged fall in BP).
2. Smooth muscles: It is potent stimulator of g.i.t, increasing
peristalsis. It constricts bronchi, but is less potent than
histamine. Action on other smooth muscles is inconsistent.
3. Glands: It inhibits gastric secretion (both acid and pepsin), but
increases mucus production. So, it has ulcer protective property.
Effect on other glandular secretions is not significant.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Pharmacological actions…
9
4. Nerve endings and adrenal medulla: Afferent nerve endings are activated
tingling & pricking sensation, pain. Depolarization of visceral afferents causes
nausea & vomiting. It is less potent than histamine in releasing CAs from
adrenal medulla.
5. Respiration: A brief stimulation of respiration and hyperventilation occurs; but
large doses can cause transient apnea.
6. Platelets: It causes change in shape of platelets and is a weak aggregator through
5-HT2A receptors.
7. CNS: Injected i.v, 5-HT does not produce central effects because it poorly crosses
BBB. However, it serves as a inhibitory transmitter. Direct injection in the brain
produces sleep, change in body temperature, hunger and variety of behavioral
effects.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Depolarization
10
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
11
Serotonin agonists Serotonin
antagonists
Cisapride 5HT4
Sumitriptan 5HT1 Cyproheptadine (anti
Buspirone 5HT1 histamine) 5HT1
Odansetron 5HT3
Metaclopramine 5HT3
Ketanserin 5HT1+2
Ritanserin 5HT2
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Serotonin Receptor Agonists
12
Direct-acting 5-HT-receptor agonists have widely different
chemical structures, as well as diverse pharmacological properties.
This diversity is not surprising in light of the number of 5-HT-
receptor subtypes. 5-HT1A receptor-selective agonists have helped
elucidate the functions of this receptor in the brain & have resulted
in a new class of anti-anxiety drugs including buspirone, gepirone,
and ipsapirone.
5-HT1D receptor-selective agonists, such as sumatriptan, have
unique properties that result in constriction of intracranial blood
vessels. Sumatriptan was first in a series of new serotonin-receptor
agonists available for treatment of acute migraine attacks.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Clinical actions of SEROTONIN AGONISTS
13
Neurotransmission: Cells containing 5-HT are present in the raphe
nuclei of brainstem and few other sites. Compounds such as
fluoxetine and other SSRIs, modulate serotonergic transmission by
blocking reuptake of the transmitter, and so prescribed for the
management of depression.
Intestinal motility: It regulates peristalsis and local reflexes in the
gut. Cisapride, a 5-HT4 agonist, was used in the treatment of gastro-
esophageal reflux and motility disorders.
Sleep regulation: 5-HT is probably involved in sleep, temperature
regulation, thought and mood (imbalance may result in affective
disorders and schizophrenia). It is precursor of melatonin in pineal
gland.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
14
Side-effects: tingling and warmth sensation, dizziness, muscle
weakness, neck pain, chest discomfort (1-5%) probably due to
ability of these drugs to cause coronary vasospasm.
Contraindication: Coronary artery disease and in patients with
angina. Naratriptan and eletriptan are contraindicated in patients
with severe hepatic or renal impairment; frovatriptan in patients
with peripheral vascular diseases; and zolmitriptan in patients with
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
15
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Migraine
16
Migraine headache afflicts 10% - 20% of the population, producing a
morbidity estimated at 64 million missed workdays per year in the
US. Although migraine is a specific neurological syndrome, the
manifestations vary widely.
Aura may begin as long as 24 hrs before the onset of pain. A migraine
attack may last for hours or days and be followed by prolonged pain-
free intervals. The frequency of migraine attacks is extremely
variable, but usually ranges from 1-2 a year to 1-4 per month.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
USE OF 5-HT-RECEPTOR AGONISTS IN MIGRAINE
17
In migraine, there is vasodilatation of cranial blood vessels with
release of substance P, accompanied by nausea, vomiting,
photophobia, phonopobia, and aura.
The efficacy of anti-migraine drugs varies with the absence or
presence of aura, duration of the headache, its severity and
intensity, and as yet undefined environmental and genetic factors
(Deleu et al., 1998).
A rather vague and inconsistent pathophysiological characteristic
of migraine is vasoconstriction followed by vasodilation.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Triptans…
18
MOA: Hypothesis implicates the capacity of 5-HT1B/1D receptors
to cause constriction of intracranial blood vessels including arterio-
venous anastomoses.
According to a prominent pathophysiological model, unknown
events lead to the abnormal dilation of carotid arteriovenous
anastomoses in the head (mainly cranial skin & ears). Around 80%
of carotid arterial blood flow has been reported to be “shunted” due
to anastomoses diverting blood from the capillaries cerebral
ischemia and hypoxia headache
So, an effective anti-migraine agent would close the shunts and restore blood
flow as well as block the release of pro-inflammatory neuropeptides.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Triptans…
19
5-HT1-Receptor Agonists: the Triptans, Sumatriptan,
zolmitriptan, rizatriptan have led to significant progress in
preclinical and clinical research on migraine. 5-HT is said to
initiate the vasoconstrictor phase ↓ neurogenic inflammation
of the affected blood vessels.
Methysergide and pizotifen (5-HT antagonist) are effective
prophylactics and sumatriptan (5-HT1D agonist) can control an
attack. However, the role of 5-HT in this condition is not precisely
known.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Sumatriptan
20
Sumatriptan and the other triptans are selective agonists for 5-HT1D and 5-
HT1B receptors. They probably function as pre-synaptic receptors and mediate
vasoconstriction prevent migraine attacks. MOA: a. Block release of
vasodilator neuropeptides (Substance P, Calcitonin gene-related peptide) b.
Selective constriction of intracranial blood vessels.
The efficacy of triptan 5-HT1 agonists in migraine is equal to or greater than
that of other acute drug treatments, e.g., parenteral, oral, or rectal ergot
alkaloids.
Oral Bioavailability: Around 14%. T1/2 : 2hrs. Metabolism: Liver
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Other triptans…
21
Zolmitriptan reaches its peak plasma concentration 1.5-2 hrs
after oral administration. Oral Bioavailability: 40%. It is
metabolized to an active N-desmethyl metabolite, which has
several fold higher affinity for 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors than
does the parent drug.
Rizatriptan: Bioavailability = 45% and reaches peak plasma levels
within 1-1.5 hours. Metabolism: oxidative deamination.
Plasma protein-binding of the triptans ranges from about 14%
(sumatriptan and rizatriptan) to 30% (naratriptan).
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Drug Routes Time to Single Dose Max. Half-
(mg) Dose/d Life
Onset (h)
(mg) (h)
Almotriptan Oral 2.6 6.25–12.5 25 3.3
Eletriptan Oral 2 20–40 80 4
Frovatriptan Oral 3 2.5 7.5 27
Naratriptan Oral 2 1–2.5 5 5.5
Rizatriptan Oral 1–2.5 5–10 30 2
Sumatriptan Oral, nasal, 1.5 (0.2 for 25–100 (PO) 200 2
subcutaneous subcutaneous)
Zolmitriptan Oral, nasal 1.5–3 1.25–2.5 10 2.8
Dr. Sabyata Gautam 22
ERGOT ALKALOIDS
23
The active principles of ergot were isolated and identified in the
early 20th century. It is the product of a fungus (Claviceps
purpurea) that grows on rye and other grains.
These alkaloids affect adrenoceptors, dopamine receptors, 5-HT
receptors, and perhaps other receptor. Ergotamine is drug of choice/
highly specific for migraine which can be given by oral, rectal,
nasal, sublingual route.
It is partial agonists at serotonin receptors (esp. 5-HT1A and 5-
HT1D); & agonist/ partial agonist at dopamine receptors. Its
vasoconstriction effect is long-lasting and cumulative.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
ERGOT ALKALOIDS…
24
Pkt’s: Low oral bioavailability due to extensive first-pass
metabolism. Bioavailability (sublingual) = less than 1%.
Bioavailability of rectal suppositories is greater. Metabolism:
liver (various pathways). Excretion: 90% of the metabolites are
excreted in the bile.
t1/2: 2hrs, but vasoconstriction that lasts for 24hrs or longer. Di-
hydroergotamine is eliminated more rapidly than ergotamine,
presumably due to its rapid hepatic clearance.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
ERGOT ALKALOIDS…
25
Dose for ergotamine tartrate = 2mg sublingually, which can be
repeated at 30 mins intervals if necessary, total dose = 6mg in a
24 hrs or 10mg a week.
Dihydroergotamine mesylate inj. can be given i.v, s.c, or i.m.
The recommended dose is 1 mg, which can be repeated after 1
hour if necessary. Total dose: 2mg (i.v) or 3mg (s.c or i.m) in
24hrs or 6mg in a wk. Nasal spray i.e 0.5 mg (one spray) in each
nostril, repeated after 15 mins for a total dose of 2 mg (4 sprays).
Side-effects: Nausea and vomiting, Leg weakness and muscle
pains, numbness and tingling of fingers and toes.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
SEROTONIN ANTAGONISTS
26
The actions of serotonin, like those of histamine, can be
antagonized in several ways. A wide variety of drugs with actions at
other receptors (adrenoceptors, H1-histamine receptors, etc.) are
also serotonin receptor-blocking agents.
Such antagonism is clearly desirable in those rare patients who have
carcinoid tumor and may also be valuable in certain other
conditions.
Serotonin synthesis can be inhibited by p-chlorophenylalanine and
p-chloroamphetamine. However, these agents are too toxic for
general use.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
Drugs Action/ Uses Dose Side-effects
Phenoxybenzamine It has a long-lasting blocking action 10mg initial, Nasal congestion,
at 5-HT2 & α-blockers. 20-40mg in dizziness,
Uses: high b.p and divided doses stomach upset,
pheochromocytoma. sexual
dysfunction
Cyproheptadine It has potent H1, 5-HT2A-blocking & 12–16 mg/d tid drowsiness, dry
anti-muscarinic effects. Causes or qid mouth,
sedation. confusion, ataxia
Uses: carcinoid tumor, urticaria. and weight gain
Ketanserin It blocks 5-HT1c, 5-HT2 & α1 1-2mg/kg/day. Mild dizziness,
receptors. It blocks vasoconstriction, Bioavailability tiredness, nausea
platelet aggregation and contraction : 50% due to and dry mouth
of guinea pig ileum. first pass
metabolism.
Ondansetron It is the selective 5-HT3 antagonist. 8mg i.v. Blurred vision,
Uses: Nausea and vomiting infusion, decrease heart
associated with chemotherapy. 15min-30mins rate, anxiety
Oral bioavailability: 60-70%. t½: 3hr. before chemo-
therapy.
Dr. Sabyata Gautam 27
Dr. Sabyata Gautam 28
thanks
29
Dr. Sabyata Gautam
You might also like
- Neurotransmitters and Psychiatry PDFDocument22 pagesNeurotransmitters and Psychiatry PDFcapriciousbelal93% (14)
- Love Birds SpeciesDocument6 pagesLove Birds SpeciesAravind Kumar0% (1)
- SerotoninDocument6 pagesSerotoninghinsavitNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Slides - Introduction To Clinical DermatologyDocument34 pagesDermatology Slides - Introduction To Clinical DermatologyAzry Mustapa100% (1)
- INTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHARMACOLOGYyyDocument27 pagesINTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHARMACOLOGYyyEbad RazviNo ratings yet
- Serotonin ReceptorsDocument23 pagesSerotonin ReceptorsAnonymous cCMY2pNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionEllenare Racion100% (1)
- Serotonin & MigraineDocument10 pagesSerotonin & Migrainepetri_jvNo ratings yet
- AutacoidsDocument103 pagesAutacoidsKamran Ali100% (1)
- AutacoidsDocument38 pagesAutacoidsdrmayangNo ratings yet
- Pedia Normal Abnormal Long Bond PDFDocument17 pagesPedia Normal Abnormal Long Bond PDFMary Claire MasoNo ratings yet
- Cyber AddictionDocument50 pagesCyber AddictionFlorin TudoseNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Nursing: Understanding Suicidal IdeationDocument5 pagesMental Health Nursing: Understanding Suicidal IdeationCeline Cabading90% (29)
- Pharmacology of SerotoninDocument52 pagesPharmacology of SerotoninSunilNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER ONE: NUTRITION SCREENING TOOLSDocument4 pagesCHAPTER ONE: NUTRITION SCREENING TOOLSMeyar Y. Abu AsadNo ratings yet
- Procedure On Abdominal ParacentsisDocument22 pagesProcedure On Abdominal ParacentsisBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE (5-HT, Serotonin)Document6 pages5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE (5-HT, Serotonin)Ranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Autacoids Serotonin MigraineDocument43 pagesAutacoids Serotonin MigraineMohamad MostafaNo ratings yet
- Katzung & Trevor's Pharmacology - Examination & Board Review, 11e-Serotonin 5-Hydroxytryptamine 5-Ht and Related AgonistsDocument3 pagesKatzung & Trevor's Pharmacology - Examination & Board Review, 11e-Serotonin 5-Hydroxytryptamine 5-Ht and Related Agonistsfreemind323No ratings yet
- 5-Ht, 5-Ht Antagonists Drug Therapy of Migraine: Dr. Anil Kumar SaxenaDocument26 pages5-Ht, 5-Ht Antagonists Drug Therapy of Migraine: Dr. Anil Kumar SaxenaLuqman Al-Bashir FauziNo ratings yet
- Autocoids - 5 Hydroxy Tryptamine and AntagonistsDocument27 pagesAutocoids - 5 Hydroxy Tryptamine and Antagonistsalay_brahmbhattNo ratings yet
- SerotoninDocument16 pagesSerotoninBaidawu Weso-amo IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Serotonin & Anti-Serotonin DrugsDocument23 pagesSerotonin & Anti-Serotonin DrugsTurky TurkyNo ratings yet
- Guide to Serotonin: Sources, Receptors, EffectsDocument34 pagesGuide to Serotonin: Sources, Receptors, EffectsGarry LasagaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Serotonin in Depression EssayDocument4 pagesThe Role of Serotonin in Depression EssayscholifyNo ratings yet
- Reseptor SerotoninDocument11 pagesReseptor SerotoninJuliana FeronNo ratings yet
- Serotonin and the Heart: Effects and TherapiesDocument16 pagesSerotonin and the Heart: Effects and TherapiesIffat RiktaNo ratings yet
- Document 2Document4 pagesDocument 2Zainab alkhalifahNo ratings yet
- Serotonin (5-Hydroxytryptamine)Document74 pagesSerotonin (5-Hydroxytryptamine)matchees-gone rogueNo ratings yet
- Serotonin 2Document34 pagesSerotonin 2Ismail Hossain SirageeNo ratings yet
- SerotoninDocument11 pagesSerotoninidjacobsNo ratings yet
- 2011 - Hutchenson, Et Al - Serotonin Receptors and Valve Heart Disease - It Was Meant 2BDocument29 pages2011 - Hutchenson, Et Al - Serotonin Receptors and Valve Heart Disease - It Was Meant 2Bcolompar80No ratings yet
- نسخة Pharma 2 New 2 3Document4 pagesنسخة Pharma 2 New 2 3rwanmohameed7No ratings yet
- Endogenous Lipid Mediators and Their Complex Physiologic RolesDocument34 pagesEndogenous Lipid Mediators and Their Complex Physiologic RolesIndira NoormaliyaNo ratings yet
- Serotonin and NoradrenalineDocument35 pagesSerotonin and Noradrenalineeileen_ding_2No ratings yet
- AUTACOIDSDocument7 pagesAUTACOIDSElijah ChiumyaNo ratings yet
- Autacoid - SerotoninDocument4 pagesAutacoid - SerotoninJohn Ellard M. SaturnoNo ratings yet
- Structure-Activity Relationships of Phenylalkylamines As Agonist Ligands For 5-HT2A ReceptorsDocument11 pagesStructure-Activity Relationships of Phenylalkylamines As Agonist Ligands For 5-HT2A ReceptorsAlex FulkroadNo ratings yet
- Autacoids and Their AntagonistsDocument9 pagesAutacoids and Their AntagonistsSwapnilPagareNo ratings yet
- Master of Pharmacy (Pharmacology) Advanced Pharmacology-I (22PHT-622) AutacoidsDocument28 pagesMaster of Pharmacy (Pharmacology) Advanced Pharmacology-I (22PHT-622) AutacoidsPKay RecordsNo ratings yet
- AutacoidsDocument34 pagesAutacoidsBrîndușa PetruțescuNo ratings yet
- Serotonin and Molecular Neuroimaging in Humans Using PET PDFDocument19 pagesSerotonin and Molecular Neuroimaging in Humans Using PET PDFWynn TheinNo ratings yet
- Amine Autacoids: Histamine & 5-HydroxytryptamineDocument25 pagesAmine Autacoids: Histamine & 5-HydroxytryptamineJames PerianayagamNo ratings yet
- Sem 5/unit-3 Autocoids & Related DrugsDocument28 pagesSem 5/unit-3 Autocoids & Related DrugsDARSHAN BhirudNo ratings yet
- Serotonin (5-HT)Document35 pagesSerotonin (5-HT)adeesasaadNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Role of 5HT1A Receptors in Treating Extrapyramidal Motor DisordersDocument13 pagesTherapeutic Role of 5HT1A Receptors in Treating Extrapyramidal Motor Disordershellen pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Autacoids (Local Hormones) and Their Pharmacolo-Gical ModulationDocument75 pagesAutacoids (Local Hormones) and Their Pharmacolo-Gical ModulationAgung PutraNo ratings yet
- Serotonin or 5-Hydroxytryptamine and Its AntagonistsDocument42 pagesSerotonin or 5-Hydroxytryptamine and Its AntagonistsNikhil BhangaleNo ratings yet
- Altered Glucocorticoid Rhythm Attenuates The Ability of A Chronic SSRI To Elevate Forebrain 5-HT: Implications For The Treatment of DepressionDocument7 pagesAltered Glucocorticoid Rhythm Attenuates The Ability of A Chronic SSRI To Elevate Forebrain 5-HT: Implications For The Treatment of DepressionCony GSNo ratings yet
- 5HTP As PrecursorDocument8 pages5HTP As PrecursorjenkinscorneliusNo ratings yet
- Understanding Serotonin: Its Discovery, Receptors, Actions and Role in HealthDocument28 pagesUnderstanding Serotonin: Its Discovery, Receptors, Actions and Role in HealthMuhammad TahirNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Pharmacotherapies for OCDDocument12 pagesMechanisms of Pharmacotherapies for OCDjosephbaroneNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of AutacoidsDocument13 pagesPharmacology of AutacoidsInocenteNo ratings yet
- Polyclona/lMonoclonal AB To Serotonin Receptors As Therapeutic Agents.Document26 pagesPolyclona/lMonoclonal AB To Serotonin Receptors As Therapeutic Agents.Dmitri PopovNo ratings yet
- Ondansetron A Selective 5-HT3 Receptor AntagonistDocument16 pagesOndansetron A Selective 5-HT3 Receptor AntagonistRonald WiradirnataNo ratings yet
- Serotonin PPT Notes 2023Document20 pagesSerotonin PPT Notes 2023adhi85099No ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Serotonergic and Central Adrenergic Neurotransmission-Week 6Document46 pagesPharmacology of Serotonergic and Central Adrenergic Neurotransmission-Week 6boboNo ratings yet
- Serotonin and Beyond: Therapeutics For Major Depression: ReviewDocument7 pagesSerotonin and Beyond: Therapeutics For Major Depression: ReviewmarielaNo ratings yet
- AutocoidsDocument13 pagesAutocoidsKarveer AghadeNo ratings yet
- Autocoids & Related DrugsDocument25 pagesAutocoids & Related DrugsKarveer AghadeNo ratings yet
- 2001 Gray and Roth Brain Research BulletinDocument11 pages2001 Gray and Roth Brain Research BulletinBrener Santos Da SilvaNo ratings yet
- AutacoidsDocument62 pagesAutacoidsMohan RajNo ratings yet
- Histamine How It Effects Our Brain and Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesHistamine How It Effects Our Brain and Nervous SystemHerbie KawaihauNo ratings yet
- Update On Management of The Oral and Maxillofac - 2022 - Oral and MaxillofacialDocument8 pagesUpdate On Management of The Oral and Maxillofac - 2022 - Oral and MaxillofacialFadi Al HajjiNo ratings yet
- Neurophysiology of Depression and Bipolar Affective DisorderDocument17 pagesNeurophysiology of Depression and Bipolar Affective DisorderShivan A.C.No ratings yet
- 5-HTP - The Complete Guide - Exploring Its Therapeutic Potential In Depression, Anxiety, Insomnia, And Much More - Benefits, Side Effects, And Scientific Evidence For Human HealthFrom Everand5-HTP - The Complete Guide - Exploring Its Therapeutic Potential In Depression, Anxiety, Insomnia, And Much More - Benefits, Side Effects, And Scientific Evidence For Human HealthNo ratings yet
- Global Water Research Review 2018-20Document19 pagesGlobal Water Research Review 2018-20Triras ManandharNo ratings yet
- BK How Change Happens 211016 en PDFDocument287 pagesBK How Change Happens 211016 en PDFdon_h_manzanoNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy 2IN1Document35 pagesChemotherapy 2IN1Triras ManandharNo ratings yet
- Global Water Research Review 2018-20Document19 pagesGlobal Water Research Review 2018-20Triras ManandharNo ratings yet
- RESUS 8904 Special CircsDocument68 pagesRESUS 8904 Special CircsCroBranNo ratings yet
- Cpap - A Gentle VentilationDocument24 pagesCpap - A Gentle VentilationrobystwnNo ratings yet
- Functions of PlacentaDocument18 pagesFunctions of PlacentaMohammad NabeelNo ratings yet
- Rett Syndrome1Document4 pagesRett Syndrome1api-544862486No ratings yet
- Biology Marking SchemeDocument6 pagesBiology Marking SchemeMohd AqeelNo ratings yet
- Test 18 2Document30 pagesTest 18 2Temesgen M. MandersoNo ratings yet
- Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Cocci: Unit 3: Neisseriaceae and Moraxella CatarrhalisDocument18 pagesGram-Positive & Gram-Negative Cocci: Unit 3: Neisseriaceae and Moraxella CatarrhalisKathleen RodasNo ratings yet
- Uji Efektivitas Salep Ekstrak Etanol Daun Bunga Kertas Terhadap Luka EksisiDocument7 pagesUji Efektivitas Salep Ekstrak Etanol Daun Bunga Kertas Terhadap Luka EksisiAugia Hernita pasaribuNo ratings yet
- PhcogCommn 13 1 9Document6 pagesPhcogCommn 13 1 9Priyanka SujithNo ratings yet
- NCMB ReviewerDocument9 pagesNCMB Reviewer5S CASTILLEJO Danica M.No ratings yet
- Ligasure Retractable Hook Information SheetDocument2 pagesLigasure Retractable Hook Information SheetCristina PerjuNo ratings yet
- What Are The 3 Types of MeningitisDocument7 pagesWhat Are The 3 Types of MeningitisdrchandrilchughNo ratings yet
- Best Thing Joey Lott PreviewDocument23 pagesBest Thing Joey Lott Previewhanako1192No ratings yet
- OPTHA 2.3 OPTIC NERVE - Dr. FerminDocument4 pagesOPTHA 2.3 OPTIC NERVE - Dr. FerminPatricia ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Supplements Who Needs Them?: A Behind The Headlines Report June 2011Document34 pagesSupplements Who Needs Them?: A Behind The Headlines Report June 2011Sa AsNo ratings yet
- PTLS BrochureDocument2 pagesPTLS BrochuremomhoppNo ratings yet
- Role of Gis Application in Controlling Spread of (Covid-19)Document28 pagesRole of Gis Application in Controlling Spread of (Covid-19)kiswah computersNo ratings yet
- Research Article TMJ and Hearing LossDocument8 pagesResearch Article TMJ and Hearing LossMusthafa Afif WardhanaNo ratings yet
- BrachytherapyDocument96 pagesBrachytherapymahmoud el attar0% (1)
- Understanding The Black Death Lesson Plan - 0Document8 pagesUnderstanding The Black Death Lesson Plan - 0Anonymous 5P2aJj0oyNo ratings yet
- Presention SdaDocument13 pagesPresention SdaBikhu MatreNo ratings yet
- MATERIAL SAFETY Ava - X-PrimaDocument5 pagesMATERIAL SAFETY Ava - X-Primafs1640No ratings yet