Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Radioactivity
Radioactivity
Uploaded by
Waleed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views19 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views19 pagesRadioactivity
Radioactivity
Uploaded by
WaleedCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
remem of Radanhion
fa oaeer cae hace 4 TWO rotons ond 2 notre
ecm 4 +4 — Helm the
“
a ‘aes ‘Sete a ov f
‘ype ofraition
“hte diferent sons ada tat rus cnet hen ays
‘fae ton There arate mas of Tye non nd
Shara gage ote Tay anbevwiten 303i. ———
The crore tat beta orice cone ran he nace
00
wna gedicepe hgciewanerere Bo
con ra “ Tis nomterrepreenes erp es .
Positrons re h-ene gh seed particles wth he same massas B
‘erat achat ey cn be ritn sorte
2 owwatsitossaaie
Sechager and
rate moses ofthe lens ate real mate parties
fredeen ypesot | sdgontons ae antinnt artes
fadatenenitedtom | fy portamento the
Stomic ul, ‘wo parce wl snitch ete
2 catonizuasute | eninge Terry ee
‘ral ceil flan RASA rE
Canbeseda pore gucecatt .
Eplanwhch ofthese
G lowest
Y= least perratrb9 ( yorge
~ highly ionaring
a me generating
(gamma) ~ least vounng
d-Fartiele
A \
yas Kr on
= z
6 — vod oh
Any hy L of vob chia
5 a
a-farticele
teen eet (ret
Ae eu ht er hig a a E
bee al
TWD Dsborstesyninswediorpreenttevtus pare, The seston |p| e
atomic (proton) number for anucleus oan alpha partici also represents [neu |
{theamount af posite charge, We ive beta particles and positions
+1 indiate hee charge.
Radium-226 emis an alpha parle What she oter product?
pa e+?
(On the right of thearow the nucleus has anatomic number of 88-2 6
“hisisraon in Che atomic numbers also represent the paste charges)
‘Maus numbers must als balance. The radon nucleus has amass number
of 226-4222,
Bre Hen
lode anderoes decay Mat the oer ed?
ayo fee? [checkpoint
Hew confident can you answer
‘The mass umber stay the same. The atomic number goes up by 11054. the Progression questions?
‘Thisis xenon (fe. The atomic numbers represent postive charges ard
‘the-1 onthe beta particle represents a negative charge ————
aaa 1 Draw up table tosummare
ope 0
pe theaierent ypesof
‘noc dey ond what
Oo ‘Write balanced nuclear equations to show the following decays. ae eee eae
Youll ned tus a pode tabi. ssa ease wa
cs umber cf thence
$B + Poi 208 7 nderoes a decay
fe 52 Carbon-16 (30 undergoes
I> exrnatism 9 ee undergoes ecay B decoy We bleed
EI reason 7 (0 undergoes decay, ‘cleo equation to show this
O! meteor ns
‘reaction i the way new aubtanens ae formed coer z ie a
tndegas lp decy ond
oc iisoncee
BF dcay re two nclar
Deere what happens when ances undergoes deco andthe cuanto show tis
eet shes onthe noes mors) | Sequence of deny.
i
‘+ How does the activity ofa substance change overtime?
+ What does the half fe of radioactive substance describe?
‘+ How can the hafife be used to work out how much ofa substance decays?
Mare Curie (1867-1934) made many important
scorers connected with radioactivity, before ts
‘angers were known Her laboratory notebooks ae still
radioactive and willbe dangerous frat lebst another
1500 years.
When an unstable nucleus undergoes radioactive deca
Torucleus changes to ney = 2 decay pe second
Tsone nuclear decay exch second
4A sample of uranium 235 has a decay rate of
@unataleraions @ decayed mucus you get a sic and sometimes you dort. The probability of
petting asics)
{na simitar way. at any given moment there is a certain
probability that a particular unstable nucleus wll decay.
etait (80)
cera ete gam
aan ndhidunl nutes bea TETRIS
owever the hate does allow us to predic the activity
cf a large number of nucle. The half-ifeis the same
for any mass ofa particular isotope. Some half.ives are
shown in table C
er each haf he murber of unstable nuclei aes,
uranum 235 700 millon yeas
© z whordoesthehattteofanisotope ———eaboncta | 50 yeu
descrber
. coos 137 Soyer
42} > 410g sample of caesium-137 has ahalfife
hayentnatetatiecteste Bae aa
Sample Chote fone ators
102
4 Strontium-90 has a half
life of 29 years. How many
therefore also a measure oF how Tong it takes for the activity to halve. It can strontium-90 half-lives is:
be found by recording the activity of a sample over a period of time.
a 29 years b 58 years
i
In figure D, the activity at 3 minutes is 800 counts per second. After one 5
half-life the count rate will have decreased to 400 counts per second,
‘There are 10 million atoms
in a sample of radon-222.
This occurs at 9.5 minutes, o the half-life is 9.5 -3 = 65 minutes. How many undecayed
_ nuclei are left after:
1200.
1 WP a 5.8 daysb 7.6days
WF Lddays d 1.9 days?
‘When the Earth was formed
around 45 billion years ago, most.
of it was molten. The Earth has
o 6% 1 2 2 00 3 been cooling down ever since but
ime (minutes) part of the core is still molten,
partly because of the energy
released by radioactive isotopes
in the Earth
How confidently can you answer
the Progression questions?
$1 A sample of caesium-137 has
ity of 100.8q, What will
its activity be in 90 years time?
1 Explain what the half-life of a
D graph of activity against time for a radioactive substance
Activity (Ba)
E graph showing the decay of two different radioactive substances eacecheeareceetetl
about how its activity and the
SEF © Work out the half-lives of the two sources shown in Figure E. PR eee EERO aia
change over time.
2 Asample containing
carbon-14 has an activity of
Describe how you could find the halflife of a newly discovered 115Bq, How long ago would it
radioactive substance (2 marks) have had an activity of 24 Bq?
103
‘+ How can radioactivity be used to preserve food?
+ How is radioactivity used in industry?
+ How is radioactivity used in smoke alarms?
Killing microorganisms
All foods contain microorganisms that eventually cause them to decompose.
Some bacteria also cause food poisoniny with
gamma rays to kill bacteria. This makes itsafer ans that
it can be stored for longer before going off. it does not make the food more
radioactive, although some foods are naturally radioactive.
fhe usual
AAll these strawberries are several days metho rem, i cannot
old, The ones on the left were irradiated _be sterilised using heat, so they are sealed into bags and irradiated with
with gamma rays. gamma rays, which can penetrate the bags and the equipment.
{33 1 What happens when food is irradiated?
2 2 Suggest why surgical equipment is sealed into bags before
irradiation.
Radioactive detecting
Radioactive isotopes can be wscastcesr example, a gamma source
added to water is used to detect Teaks in Water pipes buried underground,
Where there is a leak, water flows into the surrounding earth. A Geiger-
Miller tube following the path of the pipe will detect higher levels of
radiation where there is a leak.
_-Geiger-Maller tube Cancer
jelp
he
can also be
fou will learn more about
this in SP6j Radioactivity in medicine.
S23 3 Explzin why gamma
sources are used as tracers
Busing a gamma source to detect a leak rather than beta sources.
Checking thickness
Paper can be made
the wood pulp
The detector in
articles get through the paper
from a source on
104
When the paper ito thin, more
beta particles penetrate the paper
and the detector ecords higher
count rate A computer senses that
the count rate has risen and reduces
the force applied to the oles to
‘make the pape thicker When the
paper is too thick, the opposite
happens.
processor unt
yrmecen Way wot 0
=
radiaton source
{chbetapaice eter ived oconathe tines of paper dueng manufacture
+ Leokatcagram plan what happens when the paper tooth
D5 wrywulé yourctusan apa sure tmnt paper thickness?
‘Smoke alarms ‘The detector senses the amount
‘Asmoke alarm contains a source of An americaum-241 source gives, of current. f the current falls the
Aiphaparicis usualy araciacive OF 8caeant eam ofepte sreeords |
isotope called americium-241. The 5
detector has once ath
anairganbetrcen wo sevialy
Charged plates The meu 24)
source release alpha particles,
\whichionise molecules inthe ai,
These ions are attracted to pltes
with an oppesitecharge ands allow
small electrical curentto flow
Aslongas tis caret
treslrm ntsc When
tote peut te gp te
Soke pres sow do helons
‘homes tha te coe Now
ton the pp dese Thea a
‘Scns whenticen dope —=
Geet laee the Progression questions?
‘Soe nthe deuce
‘he ons and so wake the cent al
3) 6 what ype faavon peace by ameriur 217
7 Twehatte ofr 243142 years Vy does thsmaket st peste fe ses for
‘table source ofp partes ina snake aa? fadoocty
EX Explain the characterises
needed inradioacve sources
ies sctcsionen,
Sertangsrgeaeqipe
Desde how youu ue eatin fo menitrthe tenes of feces contin pe
aliminum oles tisbong mae ‘emats) thet and
sesamin cnt a
ere ‘i Tntoraity |,
Napee sh gy
© Shue
sistance from Ke souve -
+ Mininaae Hae devotion
Ceqpose sme)
Nuclear accidents
Occasionally there is an accident in a nuclear power station, allowing
radioactive materials to escape into the environment. Accidents such as this,
cause a hazard, as they may lead to people bélfig)ifadiated or eohtaminated:
‘Someone is irradiated when they are\BRB6SeaO|slpha, beta or gamma
radiation from nearby radioactive materials. Once the person moves away
the irradiation stops.
‘Someone becomes|eehitaminated if they get particles of radioactive
material on their skin oF side their body{THeY.Will]BSlexposed to radiation
as the unstable isotopes in the material decay,and this wilt Continue uot.
tine material has all decayed or until the source of contamination is removed
{which is not always possible), Water and soils can also be contaminated
50 contamination can spread into the food chain. Contaminationwith
radioactive materials with long half-lives poses a greater hazard as the
effects will last longer than for materials with shorter half-lives.
D These workers are cleaning up after an accident at a nuclear reactot. The overalls
stop their clothing becoming contaminated,
itis important to understand that the dangers of radiation from medicine,
industry and power generation are small compared with many other aspects
‘OF our modem Tives, However, many people are concerned that accidents
may happemmmiuclear power stations.
42} 3 Look at photo D. Suggest why the workers are wearing masks.
4 Explain whether an alpha or beta source is the most harmful if
both sources are:
$2} a outside the body
$EP inside the body (e.g, if breathed in or swallowed).
9} 5 Explain how the half-life ofa radioactive source affects the potential
hazard it poses.
Describe the difference between contamination and irradiation. (2 marks)
107
behind a radiation shield ina hospital
Did you know?
When radioactivity was first
discovered, people did not
know of the harm it could cause.
Radioactive substances such
as thorium and radium were
pout into face creams and other
products because people thought
they might have health benefits
Checkpoint
How confidently can you answer
the Progression questions?
Strengthen
$1 What are the hazards posed
by radiation?
S2 Describe three ways of
minimising the risk from
radiation.
Extend
E1 Explain two precautions that
should be taken by people:
a working with radioactive
sources in industry
busing radioactive sources in
hospitals
€ cleaning up after a nuclear
accident.
gt) Ls
+ What are some of the uses of radioactive substances in diagnosis?
+ Why do isotopes used in PET scanners have to be produced nearby?
+ How is radiation used to treat tumours?
Diagnosing with gamma
technetium-99m s attached to ——_
a drug that collects inthe brain rays
Radioactive materials are used to
radioactive fono-125 absorbed ——} Glognose medical conditions without
krypton-81m gas can be inhaled
to investigate lung function
isotope attached to molecules that
wil be taken up by particular organs
inthe body. Te tracers usualy
injected int the bloodstream, but
lodine-125 is made into a compound
excreted by the kidneys.
Indium-111 can be attached to white ale
blood cells to locate infections @ {
detected using one or more gamma
[A Different tracers are absorbed by different parts of the body. cameras
‘Tracers can be injected into the blood to find sources of inter
radioactive glucose molecules because very active cells, such as cancer cells
takeup glucose morequhty thon ora
3) 1 Name wo medial condition that canbe investigated using
gamma ray traces,
B This gamma camera sean shows a 3} 2 Look at photo Whereis the main cancer in this person?
bone tumour The brighter the colour,
themoreradation has been detected, 3) 3. Whyare alpha and beta sources not used in medical radioactive
tracers?
Diagnosing with positrons
ow fh “Tracers that emit postons can also be used to detect medical problems. The
The electron-positron annihilation _detector in a PET scanner moves around the patient, building up a set of
causes wo ganmavaysto beemitted images showing wheré diferent amounts of gamma radiation are coming from.
in opposite directions.
108
“5 Tracer
joactive isotopes used in slrmedatuacei et tohave a short
iso that other parts of the body are affected as little as possible.
pans that they lose their radioactivity quickly and so must be made
close to the hospital. They are often used within hours or even minutes of
production,
D PET scans showing the activity in a healthy brain (left) and one with Alzheimer's,
disease (right). The radioactive isotope is attached to a substance that is used by
active brain ce
Treating cancer
Cancer cells divide mi
more susceptible to being killed by radiation.
Internal radiotherapy uses a beta emitter such agjodine-13} placed inside
the body, within of 2 This does not always require
surgery —the patient stays in a room alone while the source is in place
wand so are
2 5 Suggest why patients are kept away from other people while
being treated with internal radiotherapy.
Most radiotherapy is external radiotherapy, which uses beams of gamma
2s rays proto dusted ema am gus the Dd
Several Tower strength beams may be directed at the tumour from different
directions so that only the tumour absorbs a lot of the energy and the
surrounding tissues are harmed as little as possible.
6 Explain why beta emitters are usually used for internal but not for
external radiotherapy.
Explain why both the half-life and the type of radiation produced are
taken into account when choosing tracers for use in medical diagnosis.
(6 marks)
109
Radioactive isotopes are
produced in cyclotrons.
Suggest why cyclotrons
are located around the
UK, sometimes within
hospitals,
How confidently can you answer
the Progression questions?
S1 Describe two ways in which
radiation is used to diagnose
medical conditions.
S2 Write down one similarity
and one difference between
internal and external
radiotherapy.
E1 Explain how radioactive
tracers are used to diagnose
medical conditions.
E2 Compare and contrast,
the treatment of tumours
using internal and external
radiotherapy.
eng:
clea Fiwion
TY
Oo
sy Nurlew Power stobror 3
Nuclear Fecion
does rot qroduce ms 3 Ptomiéc Bomlo
J tadipache fo
was a 2
5 non-renewrole Nuclear fusen
3 2 OF wore ehemenit
cormdarng F452)
ro +emy (S)
oe se
Convertons powers that buon fae
dma change Cavetonal paws sates cn
aught 3 =
guid sate mas vey epee
re ssf» paver sation at the
her seins nce ace cree Rene
@ > Eoinore avrg andoredosbortage yim scone eae nein
cfnaa pm asconpacsa tt Ges xn sg at
Nes pow statins are dese Fea Mower acceso
‘onetime ocr incngamal este aac es near
a aaa
ft fe semtegetn| | feyorntety anyon aoner
= tonnonnconneneaoaeneneenene
De ch aay sen caine iy
St escbe tee ferent pes
Dantes on sarap
sf sing race 10
4 panty ppl ing nea cer power ston wey ey
© * rer steetenebeininetatee =
@ + Lookataagam sugges ty may people tok tht mae ey
O» metgeatncngeeti ESSE
cedeotge ng
Sleciaty mtr the
Caps races ana fol eld per satan interme fn arent sly ane
peltin ey cae, ‘Bmats) | ubleaprien
235 i val ae
Ut n — bat kr
o 36 Bb
apy
Funan
veachion
Uncontvolied _. Momic Bow
Chau Reaction
Contoll) 3 Power Stastons
Chron RAC
Faery M 5. dow dom werctvons
odo ator’ so Bok Yay con be
albspvbad by UvaRiuw mpclows
+o comse ” Reser
con ve lowshd ¢ Conhol Rads + olbcot neutrons +o caibol
oY ice A a ne bake of eatin Ont
1 oveidh uncpnivdied chasm venutry
conholing
Rede af Fission
Reaction
+ hyve alfonso doe ya?
> a cn
kame ge sot al acti i
9:
Qe
ny ca el.
aaa
Nuveay IO"
oe’ onary
a Sun
3 No CDy
ay No vadiaactve waste
> Lot of energy 20 overcome
vepulsion between nucle of tv0 alam)
2000 m/s 2000 m/s > 1000000 m/s > 1000000 mis
Sa eee
ey, Samet
‘At normal temperatures the ‘At very high temperatures the
particles are repelled if they speed of the particles overcomes
get close to one another. the repulsion and fusion can ocour.
Electrosta
ic repulsion can be overcome if the nucle! are moving very fast.
Fusion reactors couldjiigoretically produce a lot more energy than fission
reactors. The helium produced in nuclear fusion is not radioactive but any
materials used to contain fusion reactions do become radioactivestowever,
there are far fewer problems with safely disposing of radioactive waste
materials from fusion reactors than from fission reactors.
Itis very difficult tdlBUistainjthelextteme temperatures and pressures
Fequiredifonfusion. So far none of the experimental reactors have produced
Tore energy than has been put in, so fusion power is a long way off
D The inside of the Joint European Torus fusion reactor. Magnetic fields are used
to-contain the very hot gases, as they would melt any materials they came into
contact with.
GE} 5 Describe the difficulties of building a commercial fusion power
station
Explain how electrostatic repulsion is overcome in fusion reactors.
(4 marks)
15
3 3 Why does fusion
not happen at room
temperature?
© 4 Why does fusion happen
at a lower temperature in
the Sun than ina fusion
reactor on Earth?
Did you know?
The temperature in the centre
of the Sun, where most of the
fusion reactions take place, is
nearly 16 million degrees Celsius
(1.6 « 107°C), Temperatures up
to 100 million degrees Celsius
(1 « 108°C) can be produced
inside fusion reactors.
Checkpoint
How confidently can you answer
the Progression questions?
Strengthen
S11 Describe the differences
between nuclear fusion and
nuclear fission. You may need
to look back at SP6! Nuclear
fission.
Extend
E1 Explain the differences
between nuclear fusion and
nuclear fission, including their
use as energy resources for
generating electricity
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- CH 6 Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow Part IIDocument78 pagesCH 6 Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow Part IIWaleedNo ratings yet
- W4 Intake Runner DesignDocument43 pagesW4 Intake Runner DesignWaleedNo ratings yet
- Automotive - Motorsport Powertrain Lecture 3 Turbo - Characteristics&TheoryDocument36 pagesAutomotive - Motorsport Powertrain Lecture 3 Turbo - Characteristics&TheoryWaleedNo ratings yet
- W3 Pressure WAVEDocument31 pagesW3 Pressure WAVEWaleedNo ratings yet
- Q81 Q82Document1 pageQ81 Q82WaleedNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument143 pagesDifferential EquationsWaleedNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem 3.4Document13 pagesSample Problem 3.4WaleedNo ratings yet
- Homework No 7Document2 pagesHomework No 7WaleedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids: Pure BendingDocument11 pagesMechanics of Solids: Pure BendingWaleedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids: TorsionDocument17 pagesMechanics of Solids: TorsionWaleedNo ratings yet
- Homework No 6Document2 pagesHomework No 6WaleedNo ratings yet
- Homework No 8Document1 pageHomework No 8WaleedNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Compressible FlowDocument68 pagesCH 11 Compressible FlowWaleedNo ratings yet
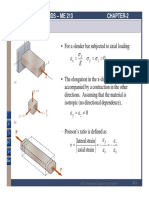
- Poisson's Ratio: Mechanics of Solids - Me 213 Chapter-2Document22 pagesPoisson's Ratio: Mechanics of Solids - Me 213 Chapter-2WaleedNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow Part III Viscous FlowDocument46 pagesCH 6 Differential Analysis of Fluid Flow Part III Viscous FlowWaleedNo ratings yet
- Flow Over Immersed Bodies: General CharacteristicsDocument120 pagesFlow Over Immersed Bodies: General CharacteristicsMahesh LohanoNo ratings yet