Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Regeneration (Vital Pulp Theraby 2)
Uploaded by
Nasser Hashim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views8 pagesOriginal Title
Regeneration_(_vital_pulp_theraby_2)[1]
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views8 pagesRegeneration (Vital Pulp Theraby 2)
Uploaded by
Nasser HashimCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
er
>
e
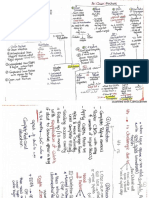
. Stem cells
Regeneration
Definition: Biologically based Procedures designed to replace damaged
structures such as dentin structure and cells of the pulp-dentin complex. Srst Shidie
Regenerative strategies:
Regenerative Endodontics are dependent upon those elements associated with
normal tissue development and tissue engineering: (the triad of tissue
engineering): Deal t
Signaling molecules (Growth factors).
. extracellular matrix/cellular scaffold (Hydrogel is the scaffold of choice)
Targeting these elements has been approached in a variety of ways (approaches)
. Cell-based Approaches
or Gafclels
Cell-based regenerative strategies include the transplantation of cells to the site
of injury in the tissue to promote regeneration.
. Cell-free Approaches
Cellular synthesis and secretion of tissue components are imperative to the
formation of any tissue. However, its regeneration can also be achieved from
populations already present in the patient’s body that can be recruited to the site
of injury to stimulate self-healing mechanisms and unlock the innate powers of
regeneration, where localized areas of cellular necrosis exist within a tissue,
without the need to directly transplant cells to the injury site.
fox Apiad papilla SC - Safeated Decides teth $C
Stem Cells
Cells that are able to Proliferate, differentiate into Odontoblasts like cells to form
Pulp Tissue.
= The plasticity of the stem cell defines its ability to produce cells of different
tissues
™ Stem cells are also commonly subdivided into
1. Pluripotent
2. Multipotent cells
16
‘Scanned with CamScanner
v
aeNG
Pluripotentstem cells have the capacity of becoming specialized cells and belong
to all three germ layers. Embryonic stem cells are the best example of pluripotent
cells. BUT: | :
ethical, legal, and medical (tissue-rejection) issues can render these cell types
unsuitable for clinical applications. -Neds
True pluripotent stem cells can only be found in the developing embryo, and the
harvesting of these cells requires destruction of the embryo, hence the legal and
ethical concerns with such practice
. Multipotent stem cells: These cells can be found compartmentalized within
tissues in “stem cell niches.” The mesenchymal tissues - Mathipdesk cals ar prac
Location: Fost-rutal
These cells were first found in bone marrow decades ago and were characterized
as self-renewing but later received the now widely accepted name mesenchymal
stem cells (MSCs), (ted thon flutist
Most stem cells found in the orofacial region are MSCs.
SCAP (stem cells from apical papilla) {st wed
SHED (stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth)
DPSC (dental pulp stem cells) from adult pulp -+ Fixx Siedly Chealed -¥ OF Ferma cue
PLSC (periodontal ligament stem cells)
‘Scanned with CamScanner
shy S$ Culhtie
a hon)
ep ae dakchel yj ster» undegan A Spe t
~ Food Washiy hale te ope of desepy
Re & optal ou th Ye lyfe etoven Aptal Pape
\ = due 5 clay Ku tebe! by
[TONS Swe tas neces iNfon
he -sy an . he eationment™ 0 x Ney Hobe: ac it
FANT Mectebes ol ah ed ace meek
age Sa wall utken ob x
we Ciecaledidn wth ercbln
ors pene stb
Reis 4 Sem Gl Sue
Bh Set OME $ cfealeiin Ye cblelals Conveetah pr Treat
© Mabsrecsr 5 au a
ee tehEchy Rl
PON or Fibreduclinng, 4 fee
Oh cites meted wad sy tales
Wok perodls cet is
creak AS le offal win oT vat at Sphe OPEC. Cf athovtn
FT peti
= Sk ety ute Ped ow) a) te Genalsbastever oly he Gils clise to He opal
Bat "Wuben cen 8
2 aed Oud + Wyss > Bene endotoxin,
4
So, QW Free Agprarch ula tehhoducedl
(GN Aowetng)
‘Scanned with CamScanner
pas we eee
a Sep gC eb Gb Hreeton oy
Pedi uel Seyse APR WEA Gan ple
Heck pwchansnes a othe seal Zhe
Dental stem cells:
a. SCAP stem cells:
* They are derived from the apical part of a developing tooth and have high
proliferation, migration and regeneration capabilities.
* They contain fibroblast-like and odontoblast like cells.
* The apical papilla is a dense reservoir of undifferentiated MSCs with great
proliferative and odontogenic differentiation capacity. ; ;
* the close proximity of the apical papilla to the apices of teeth in continuum with
the root canal space makes this rich source of stem cells readily available for
regenerative endodontic therapeutics through autologous cell transfer without
the necessity to harvest and manipulate these cells exogenously.
b. Dental pulp derived stem cells (DPSC):
* These are the most common source of dental tissue derived stem cells and are
obtained from the pulp of permanent teeth. Vettel Wiicorns
DPSCs can be found throughout the dental pulp but are known to accumulate in
the perivascular region and the cell-rich zone adjacent to the odontoblastic
layer, Ney Gn dNrechile Yo Gudheead Gl, (utet Rode |
* can produce pulp dentin complex.
* These cells are recruited to the site of injury following a gradient of chemotactic
agents released by resident immune cell
ls and from the damaged dentin.
* The reparative dentin formed by these cells is distinct from the primary,
secondary, and reactionary dentin that has been lost. It is often called
“osteodentin”.
¢- Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHED):
* They are derived from exfoliated teeth and ai
* They have high regenerative and renewal power, so they have high effect in
Wound healing, ~ t Pepreulte. pobkil Specific Yon DYSC
* With proteins on the dental pulp, they can differentiate into bone, PDL, nerve
cells, pulp and adipocytes
© They differentiate into odontoblast-like cell
* The SHED are able of forming microvascul
blood supply to the generated pulp.
+ They can differentiate into fibroblasts, .
* They induce formation of osteoblasts, thus forming bone.
* (SHED, unlike DPSCs, cannot be differentiated into osteoblasts or osteocytes
but are able to induce the host cells to undergo osteogenic Sirulske CAF lease
3. Induction of bleeding in the canal + MTA + Coronal seal — (y \uigdliaa, at
4, Periodical follow-ups will take place to observe any continued maturation of the t
Toot. — evey 3 Morthes
Pengpical ree
‘Bicod ot seats
SMTA in Gnital,
Ms dy booth
renraion
Revascularization protocol
20
‘Scanned with CamScanner
Clinical considerations for regenerative endodontic procedures
Primary goal (essential): The elimination of symptoms and the evidence of
bony healing
= Secondary goal (desirable): Increased
length
root wall thickness and/or increased root
= Tertiary goal:
positive response to vitality testing
‘Scanned with CamScanner
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- 4 5908732095613635466Document5 pages4 5908732095613635466Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Regeneration (Vital Pulp Theraby 2)Document8 pagesRegeneration (Vital Pulp Theraby 2)Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Vital Pulp Therapy and Regeneration: Prof. Abeer ElgendyDocument22 pagesVital Pulp Therapy and Regeneration: Prof. Abeer ElgendyNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Operative 2017Document180 pagesOperative 2017Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- TraumaDocument5 pagesTraumaNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Case Selection EndoDocument21 pagesCase Selection EndoNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Vital Pulp Therapy and Regeneration: Prof. Abeer ElgendyDocument22 pagesVital Pulp Therapy and Regeneration: Prof. Abeer ElgendyNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Regeneration (Vital Pulp Theraby 2)Document8 pagesRegeneration (Vital Pulp Theraby 2)Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Vital Pulp Therapy and Regeneration: Prof. Abeer ElgendyDocument22 pagesVital Pulp Therapy and Regeneration: Prof. Abeer ElgendyNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Vital Pulp Therapy and Regeneration: Prof. Abeer ElgendyDocument22 pagesVital Pulp Therapy and Regeneration: Prof. Abeer ElgendyNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Case File For Comprhensive InternsDocument19 pagesCase File For Comprhensive InternsNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Pain ControlDocument13 pagesPain ControlNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- 4 5908732095613635466Document5 pages4 5908732095613635466Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Fatal Complications (Presentation) 2020-2021Document51 pagesFatal Complications (Presentation) 2020-2021Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Vital Pulp Therapy and Regeneration: Prof. Abeer ElgendyDocument22 pagesVital Pulp Therapy and Regeneration: Prof. Abeer ElgendyNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Regeneration (Vital Pulp Theraby 2)Document8 pagesRegeneration (Vital Pulp Theraby 2)Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Regeneration (Vital Pulp Theraby 2)Document8 pagesRegeneration (Vital Pulp Theraby 2)Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Fatal Complications (Presentation) 2020-2021Document51 pagesFatal Complications (Presentation) 2020-2021Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Operative Chapter 12 Intermediary Liners and BasesDocument14 pagesOperative Chapter 12 Intermediary Liners and BasesNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- OpertiveDocument12 pagesOpertiveNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- OpertiveDocument12 pagesOpertiveNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Oper TiveDocument10 pagesOper TiveNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Complications of Extraction 2Document6 pagesComplications of Extraction 2Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Vital Pulp Therapy and Regeneration: Prof. Abeer ElgendyDocument22 pagesVital Pulp Therapy and Regeneration: Prof. Abeer ElgendyNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Fatal Complications (Presentation) 2020-2021Document51 pagesFatal Complications (Presentation) 2020-2021Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- 4 5908732095613635466Document5 pages4 5908732095613635466Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- Operative Chapter 12 Intermediary Liners and BasesDocument14 pagesOperative Chapter 12 Intermediary Liners and BasesNasser HashimNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2017-05-03Document17 pagesNew Doc 2017-05-03Nasser HashimNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2017-05-03Document17 pagesNew Doc 2017-05-03Nasser HashimNo ratings yet