0% found this document useful (0 votes)
359 views6 pagesSingle Effect Reciprocating Pump
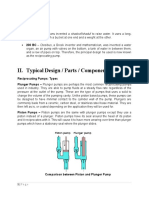
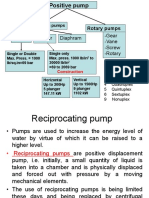
This document discusses a single effect reciprocating pump. It provides 5 objectives for understanding how the pump works and calculating its performance parameters. The document then provides theory on how reciprocating pumps function, defines types of reciprocating pumps, and shows the calculations and equations for actual discharge flow rate, theoretical discharge flow rate, volumetric efficiency, slip, and slip percentage. Graphs and tables of test data and results are also included.
Uploaded by
Fawwaz ZayedCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
359 views6 pagesSingle Effect Reciprocating Pump
This document discusses a single effect reciprocating pump. It provides 5 objectives for understanding how the pump works and calculating its performance parameters. The document then provides theory on how reciprocating pumps function, defines types of reciprocating pumps, and shows the calculations and equations for actual discharge flow rate, theoretical discharge flow rate, volumetric efficiency, slip, and slip percentage. Graphs and tables of test data and results are also included.
Uploaded by
Fawwaz ZayedCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd