Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pre-Reading: I. Brainstorm The Cloud Words Related To The Word Muscle'. How Do They Interact With Each Other?
Uploaded by
Victoria VintuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pre-Reading: I. Brainstorm The Cloud Words Related To The Word Muscle'. How Do They Interact With Each Other?
Uploaded by
Victoria VintuCopyright:
Available Formats
Pre-reading:
I. Brainstorm the cloud words related to the word ‘muscle’. How do they interact with each other?
Muscle [ˈmʌsl]- fibers tissue aimed to produce bodily movement
Bundle [ˈbʌn.dl̩ ]- groups of fibers
Fibre [ˈfaɪ.bər]- extracellular filamentous structures
Tendon [ten´don]- inelastic collagenous tissue that attaches a muscle to a bone
Wrap [ ræp ]- cover, envelop, or encase
Fascia [ ˈfeɪ.ʃə ] sheet or band of fibrous connective tissue enveloping smooth muscle
Myoneural- neuromuscular
Myocardium [ˌmaɪ.əˈkɑː.di.əm ]- muscular tissue of the heart, pl.myocardia
Squeeze [ skwiːz ]- exert pressure on, as by way of extracting liquid
Subconscious [ˌsʌbˈkɒn.ʃəs ] - acting or existing without one's awareness
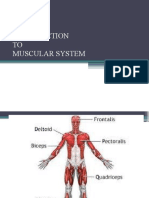
MUSCLES
Muscles are bundles of parallel muscle tissue fibers. As these fibers contract (shorten in
length) they produce movement of or within the body. The movement may take the form of
bringing two bones closer together, pushing food through the digestive system, or pumping
blood through blood vessels. In addition to producing movement, muscles also hold the body
erect and generate heat. The special characteristics of the muscular tissue are irritability
(excitability), contractility, extensibility, and elasticity. Irritability is the ability to respond to a
stimulus, which may be delivered from a motor neuron or a hormone. Contractility is the
property which enables muscles to change their shape and become shorter and thicker.
Extensibility means that the muscles can be stretched or extended. Elasticity is the ability to
recoil or bounce back to the muscle's original length after being stretched.
The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.
Muscle tissue may be either voluntary or involuntary. Voluntary muscles are those muscles for
which a person consciously chooses to contract and for how long and how hard to contract them.
The skeletal muscles of the arm and leg are examples of this type of muscle. Involuntary muscles
are the muscles under the control of the subconscious regions of the brain. The smooth muscles
found in internal organs and cardiac muscles are examples of involuntary muscle tissue.
Skeletal Muscle are fascia motor neurons myoneural junction striated muscles tendon.
A skeletal muscle is directly or indirectly attached to a bone and produces voluntary
movement of the skeleton. It is also referred to as a striated muscle because of its striped
appearance under the microscope. Each muscle is wrapped in layers of fibrous connective tissue
called fascia. The fascia tapers at each end of a skeletal muscle to form a very strong tendon. The
tendon then inserts into the periosteum covering a bone to anchor the muscle to the bone.
Skeletal muscles are stimulated by motor neurons of the nervous system. The point at which the
motor nerve contacts a muscle fiber is called the myoneural junction.
Smooth muscle, or visceral muscle. Smooth muscle tissue is found in association with
internal organs. For this reason, it is also referred to as visceral muscle. The name smooth muscle
refers to the muscle’s microscopic appearance; it lacks the striations of skeletal muscle. Smooth
muscle is found in the walls of the hollow organs, such as the stomach, tube-shaped organs, such
as the respiratory airways, and blood vessels. It is responsible for the involuntary muscle action
associated with movement of the internal organs, such as churning food, constricting a blood
vessel, and uterine contractions.
Cardiac muscle, or myocardium, makes up the wall of the heart. With each involuntary
contraction the heart squeezes to pump blood out of its chambers and through the blood vessels.
Comprehension check:
II. Answer the following questions:
1.What is the muscle?
2.What are the functions of the muscle?
3. What is the striated muscular tissue?
4. What is the smooth muscle tissue?
5.What is the cardiac muscle tissue?
III. Derivatives:
Visceral, or 1.(smoothly, smoother, smooth)__________ muscles 2.(to be) __________ found
inside organs such as the stomach and intestines, as well as in blood vessels. It is called so,
because, unlike skeletal muscle, it 3.(not have)__________ the 4.(band, banded, banding)
__________ appearance of skeletal or cardiac muscle. The 5.(weak)__________ of all muscle
tissues, visceral muscles contract to 6.(moving, moved ,move)__________ substances through the
organ. Because visceral muscle is controlled 7.(of, by, upon)__________ the 8.(unconscious,
un-conscious, unconsciouss)__________ part of the brain, it is 9.(knew, known)__________ as
involuntary muscle, as it cannot 10.(be, being, been) __________ controlled by the conscious
mind.
IV. Complete the table:
Functions of the muscular tissues
Skeletal muscular tissue Smooth muscular tissue Cardiac muscular tissue
You might also like
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular SystemZoological science classesNo ratings yet
- MYOLOGYDocument20 pagesMYOLOGYNatty ChikumbaNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System-251606Document8 pagesThe Muscular System-251606sselt gayNo ratings yet
- Reading 4 The Muscular SystemDocument16 pagesReading 4 The Muscular Systemlephuongvy1406No ratings yet
- The Muscular System NotesDocument32 pagesThe Muscular System NotesVivien Talavera0% (1)
- Unit Four: Muscular System: Cilia Flagellum AmoeboidDocument7 pagesUnit Four: Muscular System: Cilia Flagellum AmoeboidKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Sistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)Document38 pagesSistem Otot Muskular 2 (Muscular System)PaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaNo ratings yet
- Musclular SystemDocument69 pagesMusclular SystemYahya JuneydiNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy - Lec. 2 - GR1Document9 pagesHuman Anatomy - Lec. 2 - GR1bmydwoybx482No ratings yet
- The Muscular SystemDocument14 pagesThe Muscular SystemOana Maria FrancNo ratings yet
- Muscles EngDocument3 pagesMuscles Engkaneki.ghoul1710No ratings yet
- Activity 9 Group 3 Muscle Physiology - OdtDocument9 pagesActivity 9 Group 3 Muscle Physiology - OdtAMEER MUHMIEN JALMAANI. LERIOSNo ratings yet
- Muscular System AnatomyDocument12 pagesMuscular System AnatomyTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document6 pagesUnit 4CLAUDIU---ALIN BOARTANo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesMuscular Systemchristianoliver.aceroNo ratings yet
- 4 MyologyDocument57 pages4 MyologyAbhijith S. PNo ratings yet
- MedmuscleDocument38 pagesMedmuscleTesfanew SeteNo ratings yet
- UNIT-6 Muscular SystemDocument48 pagesUNIT-6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument13 pagesMusclessoulpatch_85100% (1)
- Muscular System Anatomy Muscle TypesDocument5 pagesMuscular System Anatomy Muscle TypesĘđı AzøıcăNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 6 Muscle TissueDocument10 pagesExercise No. 6 Muscle TissueRyan Aaron Cruz ParNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of MuscleDocument3 pagesStructure and Functions of MuscleJames PascoNo ratings yet
- Functions of MusclesDocument5 pagesFunctions of MusclesJoseph RefuerzoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On The Muscular SystemDocument46 pagesLecture Notes On The Muscular SystemDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RM100% (1)
- Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesMuscular Systemtheodore_estradaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument29 pagesMuscular SystemJoanna Alecxa PagunsanNo ratings yet
- Neuron Motor PeriferDocument15 pagesNeuron Motor PerifernunualoneNo ratings yet
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 011 Chapter 7Document4 pagesZoology Notes: 011 Chapter 7humanupgradeNo ratings yet
- READING MATERIAL - Muscular TissuesDocument2 pagesREADING MATERIAL - Muscular TissuescharuislostNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular SystemDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Unit 6 - The Muscular Systemnur100% (1)
- Muscular TissueDocument5 pagesMuscular Tissuenitesh.th15005No ratings yet
- Unit - 6 Muscular SystemDocument17 pagesUnit - 6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy 1Document55 pagesBasic Human Anatomy 1ZzzNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissuDocument3 pagesMuscular Tissunikifarnaz8No ratings yet
- Muscular Tissues: Skeletal MusclesDocument3 pagesMuscular Tissues: Skeletal Musclesalimsaadun alimsaadunNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument23 pagesMuscular SystemAland BakrNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Muscular SystemDocument2 pagesIntroduction To The Muscular SystemJehannahBaratNo ratings yet
- Muscular-System-Handouts - BiologyDocument7 pagesMuscular-System-Handouts - BiologyApril Joy T. GrijaldoNo ratings yet
- Muscular System AnatomyDocument23 pagesMuscular System Anatomymichaelryann madayagNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesMuscular SystemadequateNo ratings yet
- Histology Muscle and Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesHistology Muscle and Nervous Tissuejosh100% (1)
- Anatomy Group 5 PRESENTATIONDocument21 pagesAnatomy Group 5 PRESENTATIONambaig661No ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise - MuscleDocument3 pagesLaboratory Exercise - MuscleJohn Henry G. Gabriel IVNo ratings yet
- Kinds of JointsDocument1 pageKinds of JointsCarla EmbayNo ratings yet
- Systems In. The BodyDocument18 pagesSystems In. The BodyMG GeminoNo ratings yet
- MUSCULAR SYSTEM (Systema Musculare) General Structure of MuscleDocument36 pagesMUSCULAR SYSTEM (Systema Musculare) General Structure of MuscleJuliaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Muscular SystemDocument54 pagesAnaphy Muscular SystemZosia SageNo ratings yet
- Muscle SystemDocument7 pagesMuscle System910907No ratings yet
- Cell Modifications and TissuesDocument4 pagesCell Modifications and TissuesElla PascuaNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesMuscular SystemTyrone LeeNo ratings yet
- MyologyDocument7 pagesMyologyheaveɴNo ratings yet
- Muscle PhysiologyDocument6 pagesMuscle Physiologytewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Report Summary and QuestionsDocument7 pagesReport Summary and QuestionsSkyNayvieNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument14 pagesBiologyNur Maisarah AnuarNo ratings yet
- What Do You Call The Arrowed Part?Document13 pagesWhat Do You Call The Arrowed Part?Earl GenodipaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocument20 pagesModule 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNo ratings yet
- MusclesDocument5 pagesMusclesHannah Mae Supeña CatedrillaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyFrom EverandAnatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Gout Fact SheetDocument4 pagesGout Fact SheetVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Joint Stiffness - : The Feeling That The Motion of A Joint Is Limited or Difficult. of Synovial Joints. Smaller, EtcDocument4 pagesJoint Stiffness - : The Feeling That The Motion of A Joint Is Limited or Difficult. of Synovial Joints. Smaller, EtcVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Gout Fact SheetDocument4 pagesGout Fact SheetVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Fact SheetDocument4 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis Fact SheetVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Bacteria: - Archaebacteria - EubacteriaDocument15 pagesBacteria: - Archaebacteria - EubacteriaVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- What Is Psoriatic Arthritis?Document2 pagesWhat Is Psoriatic Arthritis?Victoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Gr5 Wk15 Fungi Are Alive PDFDocument2 pagesGr5 Wk15 Fungi Are Alive PDFHappy AyichNo ratings yet
- Bacteria: - Archaebacteria - EubacteriaDocument15 pagesBacteria: - Archaebacteria - EubacteriaVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Medical Sciences Vocabulary 1 2019 PDFDocument2 pagesMedical Sciences Vocabulary 1 2019 PDFDindi Ria SNo ratings yet
- Protozoa Are Usually Found A. Decomposition of Organic MatterDocument9 pagesProtozoa Are Usually Found A. Decomposition of Organic MatterVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument8 pagesThe Endocrine SystemVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- The Human Nervous: SystemDocument3 pagesThe Human Nervous: SystemVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Sensory OrgansDocument11 pagesSensory OrgansVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- History of Medicine Quiz 1Document3 pagesHistory of Medicine Quiz 1Victoria VintuNo ratings yet
- VitaminDocument11 pagesVitaminVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- The Muscular and Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesThe Muscular and Nervous SystemVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- The Tongue (Text)Document2 pagesThe Tongue (Text)Victoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Thanks To Penicillin Lesson PDFDocument11 pagesThanks To Penicillin Lesson PDFVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Penicillin: Culture PlatesDocument5 pagesPenicillin: Culture PlatesVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Healthy FoodDocument12 pagesHealthy FoodVictoria Vintu100% (1)
- Protozoa Are Usually Found A. Decomposition of Organic MatterDocument9 pagesProtozoa Are Usually Found A. Decomposition of Organic MatterVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Thanks To Penicillin Lesson PDFDocument11 pagesThanks To Penicillin Lesson PDFVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Healthy FoodDocument12 pagesHealthy FoodVictoria Vintu100% (1)
- Valentine's Day: in MoldovaDocument5 pagesValentine's Day: in MoldovaVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Test AnatomieDocument1 pageTest AnatomieVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- English For Medicine Part 2 PDFDocument161 pagesEnglish For Medicine Part 2 PDFVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Check Your English Vocabulary For MedicineDocument65 pagesCheck Your English Vocabulary For MedicineOlga Poleszak100% (1)
- B2 Health and Medicine TOP004: WWW - English-Practice - atDocument2 pagesB2 Health and Medicine TOP004: WWW - English-Practice - atVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Names of Raw Material and of Primary Products Medicinal Remedies of The First Type-GroupDocument2 pagesNames of Raw Material and of Primary Products Medicinal Remedies of The First Type-GroupVictoria VintuNo ratings yet
- Rewriting Medical History: Charles Best and The Banting and Best MythDocument22 pagesRewriting Medical History: Charles Best and The Banting and Best Mythjnbp1No ratings yet
- Embryology Notes - emDocument18 pagesEmbryology Notes - emrigario80% (5)
- Renal Ultrasound in CKD OmicsDocument24 pagesRenal Ultrasound in CKD Omicskrishnadoctor1No ratings yet
- STEMSDocument13 pagesSTEMSYasmin MiroNo ratings yet
- Ns-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNs-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 9700/42 May/June 2018Document20 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 9700/42 May/June 2018shabanaNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Final Requirements in Advanced Health Assessment MSN 205Document13 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of The Final Requirements in Advanced Health Assessment MSN 205Gummie Akalal SugalaNo ratings yet
- 8.1 - AVL Blank Medical Fitness ReportDocument2 pages8.1 - AVL Blank Medical Fitness ReportEdo-Abasi EkereNo ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Review MaterialDocument11 pagesINTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Review MaterialSALGIE SERNALNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System of CockroachDocument18 pagesCirculatory System of Cockroachyayeg rajaNo ratings yet
- O o o O: Paso de Blas National High School Senior High School DepartmentDocument3 pagesO o o O: Paso de Blas National High School Senior High School Departmentana jean gamoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Bone Structure and Directional Terminology - ShilandDocument20 pagesChapter 2 - Bone Structure and Directional Terminology - ShilandAdityaNo ratings yet
- VectorsDocument73 pagesVectorsZohra SafdariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14:: Skin Barrier:: Akiharu Kubo & Masayuki AmagaiDocument21 pagesChapter 14:: Skin Barrier:: Akiharu Kubo & Masayuki Amagaililis nur faridaNo ratings yet
- Skin Touch Receptors Prac. Names ..: Two Point Discrimination Test Results Part 1 and Part 2Document2 pagesSkin Touch Receptors Prac. Names ..: Two Point Discrimination Test Results Part 1 and Part 2Chippy RabeNo ratings yet
- Desribe Facial ExpressionDocument3 pagesDesribe Facial ExpressionAsmidar HashimNo ratings yet
- VVK112200090Document2 pagesVVK112200090Kalyan.adavi100% (1)
- Be at Ease ChecklistDocument2 pagesBe at Ease ChecklistDaniel Henderson100% (1)
- Expt. 5 BIOCHEMLABDocument9 pagesExpt. 5 BIOCHEMLABEloisah Vin Santiago Ragodon100% (1)
- HyperthyroidismDocument54 pagesHyperthyroidismAsiah JelitaNo ratings yet
- Ujian Bio Tingkatan 4Document4 pagesUjian Bio Tingkatan 4amanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Class 9 Bio Cell Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 Class 9 Bio Cell Unit of LifeL Sri MadhiNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Pathophysiologyjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Positions GuideDocument3 pagesNursing Positions Guidepianoman95No ratings yet
- Pages From 1894 Carey The Biochemic System of Medicine-Part 1of 9Document51 pagesPages From 1894 Carey The Biochemic System of Medicine-Part 1of 9Shiva Maru100% (3)
- Hematology (Ferrokinetics HemoglobinometryDocument3 pagesHematology (Ferrokinetics HemoglobinometryAbby TorresNo ratings yet
- Post-Herpetic Neuralgia: A Review: Current Pain and Headache Reports March 2016Document6 pagesPost-Herpetic Neuralgia: A Review: Current Pain and Headache Reports March 2016headseNo ratings yet
- IARI PHD Entrance Question Paper 2011 - Molecular Biology and BiotechnologyDocument14 pagesIARI PHD Entrance Question Paper 2011 - Molecular Biology and BiotechnologyAbhay Kumar100% (8)
- Should CO2 Be A Critical Process Parameter WhiteDocument4 pagesShould CO2 Be A Critical Process Parameter WhitesalemNo ratings yet
- PATHFIT 1 Module 2 FinalDocument14 pagesPATHFIT 1 Module 2 FinalScarlet VillamorNo ratings yet