Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rev. Elharam
Uploaded by
Hossam Gomaa Ali0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views10 pagesRev. Elharam
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRev. Elharam
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views10 pagesRev. Elharam
Uploaded by
Hossam Gomaa AliRev. Elharam
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
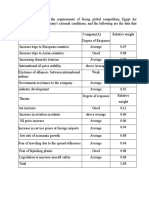
Economics 2023
Economics: is the study of how societies use scarce resources to produce valuable commodities and distribute them
among different peaple to fulfill peoples needs and wants,
Behind this definition there are key ideas in economics.
Searce resources Producing ——-Fullfilling needs & wants, -Efficlency
“Not rare “Poor or Rich can have them for free
“Rare “you have to pay to get them “not for free ”
Needs: A good or service which is necessary for living, (Limited somehow)
Wants: A good or service whieh one would like to have, but not essential for living: (Unlimited)
Microeconomics: The branch of economics which is concemed with the behavior of individual entities such as
markets, firms, and households
‘Macroeconomics: The branch of econamics which is concerned with the overall performange of the economy
Factors of production:-
A-Land: All natural resources as land, water 24abor: Man power; the human ti
3-capital: Goods praduced in order to produce other goods; as machines, buildy
4-Enterprise: Management skis and ability to take a risk
Economic problem: All resources are relatively scarce.
We have to choose from alternatives. All people and societies s
Opportunity cost: In a world af scarcity, choosing one thing means gi
The oppartunity cast of a decision: is” the value of the good of Bry
Types of economic system:
‘-market economy: 's one in which individuals and private:
consumption. Free Market Capitals
2-command econamy: is one in whi
distribution . Communism Socialism
3-mixed economy: They
mixed economies,
Inverse Relation: |t ocour when
in the value of the other number
increase in the value of one variable
‘order to satisty people's wants and needs,
Inot make anyone better, economically wise, without
e maximurn amounts of production of a pair af goods or services that can be
produced (one of them economy of a factory, given resources, assuming that all resources are fully
employed,
1¢ quantity of gaod (x) praduced is measured along theharizontal axis,
‘* The quantity of good (¥) is measured along the vertical axis,
‘*Any point on the diagram indicates some amount of each kind of good produced.
‘The production-possibility Frontier (boundary) separates the attainable combinations, such as “a”, "b", and."c",
from unattainable combinations, such as “a”.
*Paints “a” and “b" represent efficient uses of society's resources.
*Point “c” represents either an inefficient use of resources or a failure to use all the resources that are available.
‘The boundary is negatively sloped because in 3 fully employed economy more of one good can be produced only if
resourees are freed by producing (allow to produce) less of other goods.
‘*Maving from point (with coordinates cO and gO )to paint b (with coordinates c1 and ga) implies producing
additional amount of good (x), indicated by an.AG in the figure
-Etonamie growth shifts the boundary outwards. ( to the Right side) (upward)
-Some combinations of goods that were previously unattainable become attainable.
-Economic deterioration shifts the boundary inwards. ( to the Left side) (downward),
-Some combinations of goods that were previously attainable become unattainabl
Productive efficiency occurs when an economy cannot produce more of one g
Bood.
Demand
1-Qd: the number of units of a goods that consumers are willin
2.8 demand schedule: is a table showing how Qd of som
changes as price of that product changes, holding all o
Nate: when the price increase, the quantity demanded
3-A demand curve: is a graphic r
‘Acchange in the price of a goods
and curve from paint B ta G
But: EX: consumers decide tl ore th demand curve shifts outword
from DoDp to D:D)
lifts to left from DeDoto D:D;
ices rise,the demand curve shifts to right fram Deo to OD;
4-prices and availability of related goods: increases In the prices of goods that are substitutes for the
goods move to demand curve to the right.And increase in the prices of goods that are complementary
With the goods shifts the demand curve to the left.
Supply
1-Qsithe number of units of a goods thatsellers want to sell over a specified period of time.
2-A supply schedule:is a table showing how Qs of some produict during a specified period of thme changes
as the price of that product changes, holding all other determinants constant.
Note: as the price of any product inereases, The Qs increase.
3- A supply eurve: is a graphic representation of relationship between Qs and price of goods.
‘Achange in the price of goods produces a movement along a fixed supply curve.
But, a change in any other variable that influences Qs produces a new supply curve .
Ex: if P increases from 7.00$ to 7.30S: Qs inereasesand we mave a long supply curve SoSofrom point G to C
But: Ex: if one determinants of supply have changed, resulting in an entirely new supply curve SiS;
1 suppl J"
L-size of industry: increase in size of industry (enter new firm) shifts supply curve to rightfram SpSp to $35:
2-Teehnological process: will shifts the supply curve to the right.
}-Prices of inputs: increases in the prices of inputs the supply curve shifts to the lift from SoSp to S52
Supply and Demand Equilibrium
L-shortage: ExcessQd over Qs 2-surplus: Excess QsoverQd —_3- Equilibrium;
Ql: what happen to price if Demand and supply increase?
Note: price will change according to the percentage of demand and supply,
a+ Increase in demand by 10% and increase in supply by 20% (price
2+ Increase in demand by 10% and increase in supply by 10% (price
‘Afirm is an organization that transforms resources (inputs) int Fy producing
nits in'a market economy.
‘An entrepreneur is a persan who orgapii anew idea oranew
sseholds in input and output
services are exchanged,
and fand—used to produce products, are
governments use to
lssues Addressed by -What determines a nation’s long-run economic growth?
What causes unemploymer hat causes a nation’s economic activity to fluctuate?
What causes prices to rise? does being a part of a global economic system affect nations’ economies?
-Can government policies be used to improve economic performance?
Long-Run Economic Growth Rich nations have expetienced extended periods of rapid economic growth
-Paor nations either have never experienced them or economic growth was offset by economic decline.
Total output is increasing because of increasing population, ie. the number of available workers.
Increasing average labour productivity: the amount of output produced per unit of labour input.
Rates of growth of output (or output per worker) are determined by:
= rates of savingand investment; -ratesof technological change; -rates of change In other
factors.
Business cycles: are short-run contractions and expansions of economic activity.
Recession is the downward phase of a business cycle when national output is falling or growing slowly.
-Hard times for many people -A major political concern
Recessions are usually accompanied by high unemployment: the number of people who are available
for work and are actively seeking it but cannot find jobs.
Unemployed
Unemployme at Rate = SPOS
Labour Force
-When prices of most goods and services are rising over time it is inflation. When they are falling itis deflation,
-The inflation rate is the percentage increase in the average level of prices,
-When the inflation rate reaches an extremely high level the economy tends to function poorly, The purchasing
power of money erades quickly, which forces people to spend thelr money as soon as they receive it.
“Trade surplus: exports exceed imports, “Trade deficit: imports exceed exports
‘exchange rate: the amount of Canadian dollars that can be purchased with a unit of fore
Fiscal policy: government spending and taxation at different government levels.
Monetary policy: the central bank's control of short-term interest rates and th
‘budget deficits: the excess of government spending over tax collection.
Borrowing from the public might divert funds from more productive uses.
Federal budget deficits might be linked to the decline in productivity g
Elasticity is a ratio of percentages, so a change the units of me:
But it is the magnitude, or absolute
Demand can be inelastic, unit elastic:
You might also like
- Seasion 5Document2 pagesSeasion 5Hossam Gomaa AliNo ratings yet
- اهم الاسئلة في التأمين مهم جداًDocument5 pagesاهم الاسئلة في التأمين مهم جداًHossam Gomaa AliNo ratings yet
- test bank مجمعDocument20 pagestest bank مجمعHossam Gomaa AliNo ratings yet
- True or FalseDocument8 pagesTrue or FalseHossam Gomaa AliNo ratings yet
- المراجعة النهائية في الكمبيوترDocument15 pagesالمراجعة النهائية في الكمبيوترHossam Gomaa AliNo ratings yet
- Principles of Managerial Finance, 16e (Zutter/Smart)Document23 pagesPrinciples of Managerial Finance, 16e (Zutter/Smart)Hossam Gomaa AliNo ratings yet
- تست بنك ش 1 تأمينDocument4 pagesتست بنك ش 1 تأمينHossam Gomaa AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 CFA Questions: B Is Correct. Primary Markets Are The Markets in Which Issuers Sell TheirDocument18 pagesChapter 15 CFA Questions: B Is Correct. Primary Markets Are The Markets in Which Issuers Sell TheirHossam Gomaa AliNo ratings yet
- شابتر 6 قانون جزء 1Document8 pagesشابتر 6 قانون جزء 1Hossam Gomaa AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 CFA Questions: C Is Correct. Investment Needs Are Directly Affected by Personal Situations, SuchDocument13 pagesChapter 16 CFA Questions: C Is Correct. Investment Needs Are Directly Affected by Personal Situations, SuchHossam Gomaa AliNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)