Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Central Tendencies
Uploaded by
Syaifa KarizaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Central Tendencies
Uploaded by
Syaifa KarizaCopyright:
Available Formats
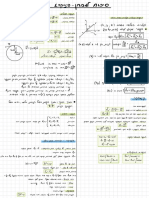
ex :
74/8 , ¢ ,
10 ,
11/12/17
Central Tendencies
Data with even N
'
measurement to determine a
single score to describe → the average of the two scores in the middle of the
the center
of a distribution distribution
→ to
find a that are the 7, 8 9 10
11,112 , 13, 14
single score ex : , ,
,
most representative of the entire group lot "
= to ,
s
2 I
identify
"
> to the "
scores
average
Purposes : 3) Mode
1) Describe the population 1
Sample
→
score that has the highest frequency
" "
Compare called the
customary fashion
2) I
groups
( correlation
further statistical attributes )
→
Continue be to scales
3) t test etc can
applied any
-
, ,
.
→ but car, only be use at measurement from nominal data
Types of central tendency values
1) Mean types of mode i
arithmetic normal 1 mode
→
average -
→
Notation :
-
Bimodal → 2 modes
" "
I
" "
sample mean :
M or
-
Multimodal → 72 modes
"
Population
"
mean
Rectangular no modes due similar frequency
-
:
µ → to
> also called parameter
bcuz normal bimodal multimodal
belongs to population rectangular
-
/
> there no modes
(
are
be /
•
>
in interval data
!,.h
only used ratio tremens
!µµ
can
bseggy.ge
.
all the
> ex :
J = Zfx =
Z X
'
, I
h = 8 f n
I = lot 18 t 32 to t 6
66
=
8
8 to use the
IX.Deciding central tendencies
,
8,251
=
weighted mean
-
Mean
class A class B combined → the most reliable central tendency
n = 50 n =
52 n = 102 → Suitable the most in interval / ratio data
3750+4056
2x = 50×75--3750 2X = 52×78=4056 Ex = →
necessary for further stastitical Measurement
7806
for
=
M = 75 M =
78 → suitable symmetrical ,
not skewed and no
a =
76,5 Outliers score
→ sensitive towards extreme score
weighted mean -
Median
>
2X , t 2×2 191 .
hi t Mz -
Nz → the most suitable for ordinal data ,
but can also be
- or
n ,
t ha Ni t na used in interval 4 ratio
ni nz → suitable for outliers and extreme scores
or o M, t . M2
hi the hitnz
→
when the distribution is skewed
→ when there is undetermined value
Median the class has
open ended
→
2) when one of intervals -
→ scores that divides a freq . distribution into two
equal distribution
parts
-
Mode
) Median P 50 or 50-1 I can be used for nominal data
only
= .
the data should be ordered from smallest to → can be used data for discreet variable
→
only
largest →
for quick measurement of central tendencies
describe
ordinal data
of distribution
→ suitable
most to
shape
→
for want the
Data with Odd N
the located in the middle distribution
exactly
→ score of
-
central Tendencies and shape of distribution
1) Symmetrical distribution → where the left and right
side are
mirroring each
other
-
normal
aint mean
,
median
,
modes score
> normal bell shapes
-
bimodal -
rectangular
> no modes
µ
modes mode I
mean
mean median
median
Stewed 1 distribution
2)
Asymmetrical
→
when the central tendencies are located in different
positions
types
:
positively skewed → Mode L Median L Mean
Y the skewed distribution
→ name of
×
followed the side of tail
g¥€
I positively
nigh side tail =
skewed
j left side till =
negatively skewed
= E E
>
X
score
negatively skewed s Mode 7 Median 7 Mean
-
y
A
¥
¥
£
S
. .
±
> X
score
You might also like
- Bury My Heart SATBDocument4 pagesBury My Heart SATBAnn Mullet VanzuelaNo ratings yet
- Understandable Statistics Solutions Manual Sosany2Document238 pagesUnderstandable Statistics Solutions Manual Sosany2hotboanga100% (12)
- פיזיקה 1 - סיכום למבחןDocument4 pagesפיזיקה 1 - סיכום למבחןEvellina YurkovskiyNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods Midterm - FInal Quiz 2Document90 pagesQuantitative Methods Midterm - FInal Quiz 2Jeff Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Math 7 LM-Statistics v2.0Document23 pagesMath 7 LM-Statistics v2.0Claudette Tolentino50% (2)
- Bogra Sub-Station Dimension MapDocument1 pageBogra Sub-Station Dimension Mapأون جهادNo ratings yet
- Бах- МенуэтDocument1 pageБах- МенуэтАлексей БуральовNo ratings yet
- (1846) Henry W. Haynes (HWH) Athenaeum 1846Document1 page(1846) Henry W. Haynes (HWH) Athenaeum 1846Spencer S. DilleyNo ratings yet
- Astro Chart1Document1 pageAstro Chart1bal1976No ratings yet
- It's So Easy Going Green: An Interactive, Scientific Look at Protecting Our EnvironmentFrom EverandIt's So Easy Going Green: An Interactive, Scientific Look at Protecting Our EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- Delhi Police Constable 29nov Shift 1 Hindi Paper PDFDocument22 pagesDelhi Police Constable 29nov Shift 1 Hindi Paper PDFVinay VermaNo ratings yet
- 19 - Everythinh About YouDocument2 pages19 - Everythinh About YouAndre LucknerNo ratings yet
- Hidroneumatica - Plano - A101 - Sin Nombre-Layout1Document1 pageHidroneumatica - Plano - A101 - Sin Nombre-Layout1Nueva CuentaNo ratings yet
- Map VSBDocument1 pageMap VSBrhinoricoNo ratings yet
- Vermont School Districts: Leas Eligible For The 2014 Small Rural School Achievement Program (Srsa)Document8 pagesVermont School Districts: Leas Eligible For The 2014 Small Rural School Achievement Program (Srsa)Lori MendezNo ratings yet
- Fadil 2013 Fix-A3 (Plot)Document1 pageFadil 2013 Fix-A3 (Plot)Dimas WiryaNo ratings yet
- How News WorksDocument1 pageHow News WorksTiffany Amber F. CagampangNo ratings yet
- New Mexico School Districts: Leas Eligible For The 2016 Small Rural School Achievement Program (Srsa)Document4 pagesNew Mexico School Districts: Leas Eligible For The 2016 Small Rural School Achievement Program (Srsa)Gerson Tampolino AcostaNo ratings yet
- DHQC Cecb MB Ti Ar DW ML 02 80529Document1 pageDHQC Cecb MB Ti Ar DW ML 02 80529Kumudu PereraNo ratings yet
- Detail - B3: Typical Door Detail (SHEET 11 OF 12)Document1 pageDetail - B3: Typical Door Detail (SHEET 11 OF 12)Kumudu PereraNo ratings yet
- Tema 6 - Derivación DiscretaDocument5 pagesTema 6 - Derivación DiscretaLuyi WangNo ratings yet
- Gulumoerrgin SeasonsDocument1 pageGulumoerrgin Seasonshmcdonald28No ratings yet
- PDS Tahal Water and SanitationDocument2 pagesPDS Tahal Water and SanitationVivek GuptaNo ratings yet
- 0445 s12 QP 21Document4 pages0445 s12 QP 21Chilekezi DanielNo ratings yet
- CS-20 15 Ms Byekwaso CDocument5 pagesCS-20 15 Ms Byekwaso CkitstonNo ratings yet
- Terminal Head and Direct Mounting Terminal Head and Direct MountingDocument1 pageTerminal Head and Direct Mounting Terminal Head and Direct MountingRavenShieldXNo ratings yet
- Theme 1Document11 pagesTheme 1lavishbailsNo ratings yet
- M3M CornerWalkDocument40 pagesM3M CornerWalkNidhi YadavNo ratings yet
- Route 296 08-01-07Document2 pagesRoute 296 08-01-07Jason BentleyNo ratings yet
- Braces & Wires Protocols: Als - EvidenceDocument21 pagesBraces & Wires Protocols: Als - EvidenceMirza GlusacNo ratings yet
- Amigos Traigan Cerveza - SaxoDocument2 pagesAmigos Traigan Cerveza - SaxoDavid MeloNo ratings yet
- Therockmap 2007Document1 pageTherockmap 2007kindredNo ratings yet
- 00192-Response LetterDocument3 pages00192-Response LetterlegalmattersNo ratings yet
- Bouchiers Road To Jumping Creek Reserve: WarrandyteDocument1 pageBouchiers Road To Jumping Creek Reserve: WarrandyteSunnyNo ratings yet
- Standard Tube MapDocument2 pagesStandard Tube Mapsumit_sahni3944No ratings yet
- Pick N Pay InlandDocument3 pagesPick N Pay InlandBusinessTech0% (1)
- Line Graph The Official Guide To IELTSDocument1 pageLine Graph The Official Guide To IELTSKues MinsNo ratings yet
- Singer 478 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocument74 pagesSinger 478 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet
- College List For Stock Mock CompetitionDocument143 pagesCollege List For Stock Mock CompetitionRajatNo ratings yet
- BBC Sky at Night - Stargazing LiveDocument100 pagesBBC Sky at Night - Stargazing LivegeorgetacaprarescuNo ratings yet
- Texas School DistrictsDocument8 pagesTexas School DistrictsDeepak GoraiNo ratings yet
- Theft From Motor Vehicle Maps For Aug. 19 To 25, 2019Document3 pagesTheft From Motor Vehicle Maps For Aug. 19 To 25, 2019Teresa VerencaNo ratings yet
- สาธุ99Document2 pagesสาธุ99Chaiwat Anunt-areechoteNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument1 pageEthics鈴木結月No ratings yet
- Week 2 VectorDocument1 pageWeek 2 VectorPhruek NatthaphatNo ratings yet
- If Everyone Cared NickelbackDocument7 pagesIf Everyone Cared NickelbackПавелNo ratings yet
- Poem 1 - The City Planners - AtwoodDocument1 pagePoem 1 - The City Planners - AtwoodAlyssa Wong Yi ReiNo ratings yet
- Construction of Cjia - New Office - Building - 2021 - Updated (1) Hvac K.s-Foundation PlanDocument1 pageConstruction of Cjia - New Office - Building - 2021 - Updated (1) Hvac K.s-Foundation PlanEnrique HeviaNo ratings yet
- Route 34 - Location MapDocument1 pageRoute 34 - Location MapHelen BennettNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Morning Civ-Com CompleteDocument269 pagesDay 2 Morning Civ-Com CompletegbenjielizonNo ratings yet
- Struja Synergy 2.0Document6 pagesStruja Synergy 2.0Milan RadisicNo ratings yet
- Math 2ge19 2trim3Document2 pagesMath 2ge19 2trim3Ghiles OularbieNo ratings yet
- Pronostico PeriodontalDocument25 pagesPronostico PeriodontalRodrigo RojasNo ratings yet
- Mikafu Mawu by RaphaelDocument2 pagesMikafu Mawu by RaphaelsimondegboNo ratings yet
- Sheridan Hollow Board - FINAL - ReducedDocument1 pageSheridan Hollow Board - FINAL - ReducedScott TownsendNo ratings yet
- Soul With A Capital S TranscripciónDocument4 pagesSoul With A Capital S TranscripciónDaniel GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Question On Hardware - Software-Storage 4it01 PDFDocument28 pagesQuestion On Hardware - Software-Storage 4it01 PDFAsif Zubayer PalakNo ratings yet
- Kalamazoo County MapDocument1 pageKalamazoo County MapGabrielle DawsonNo ratings yet
- Nas Equipment List 1 - 1Document1 pageNas Equipment List 1 - 1Hatem Al-KhleweeNo ratings yet
- Arizona School Districts: Leas Eligible For The 2016 Small Rural School Achievement Program (Srsa)Document13 pagesArizona School Districts: Leas Eligible For The 2016 Small Rural School Achievement Program (Srsa)Gerson Tampolino AcostaNo ratings yet
- 창모 (ChangMo) -메테오 (Meteor)Document4 pages창모 (ChangMo) -메테오 (Meteor)오성균No ratings yet
- 8 Breaths of DesignDocument1 page8 Breaths of DesignTarek AminNo ratings yet
- Relationship of Sample and Population in ResearchDocument9 pagesRelationship of Sample and Population in ResearchIbironke OsunbawoNo ratings yet
- Quality Management : TotalDocument123 pagesQuality Management : Totaltubai25No ratings yet
- The Standard Deviation and VarianceDocument14 pagesThe Standard Deviation and VarianceCharlie BautistaNo ratings yet
- Community Dental Health Flashcards - QuizletDocument20 pagesCommunity Dental Health Flashcards - QuizletRMNo ratings yet
- BTS Quality Improvement Methodology OverviewDocument19 pagesBTS Quality Improvement Methodology OverviewOmdah DhNo ratings yet
- Ciexercises Extract PDFDocument21 pagesCiexercises Extract PDFRoshan SinghNo ratings yet
- The Principal Components of Response StrengthDocument24 pagesThe Principal Components of Response StrengthjsaccuzzoNo ratings yet
- The Role of Hierarchy in International PoliticsDocument11 pagesThe Role of Hierarchy in International PoliticsLauraPimentelNo ratings yet
- Deviatia Standard Si Eroarea StandardDocument17 pagesDeviatia Standard Si Eroarea Standardalina1194No ratings yet
- Instructions To CandidatesDocument7 pagesInstructions To CandidatesPeng Peng KekNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17 Control ChartsDocument26 pagesLecture 17 Control Chartstanveer_buitemsNo ratings yet
- Statistica DescriptivaDocument10 pagesStatistica DescriptivaCristian FarcasNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics Assignment 5 Manish Chauhan (09-1128)Document14 pagesBusiness Statistics Assignment 5 Manish Chauhan (09-1128)manishNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Case Study Analysis: ECON1193B: Business Statistics 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1 - Case Study Analysis: ECON1193B: Business Statistics 1Phong LữNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing Z-Test Z-Test: State The HypothesesDocument9 pagesHypothesis Testing Z-Test Z-Test: State The HypothesesJhaydiel JacutanNo ratings yet
- Research Final Chapter 4Document32 pagesResearch Final Chapter 4Arnel Baldrias Lopez100% (1)
- Pham Khoa Vien GBS190915 GBS0903 Truong Ngoc ThinhDocument58 pagesPham Khoa Vien GBS190915 GBS0903 Truong Ngoc ThinhKhoa ViênNo ratings yet
- PortaCom Risk AnalysisDocument36 pagesPortaCom Risk AnalysisJayaKhemaniNo ratings yet
- Practice Quiz (Chapter 10)Document24 pagesPractice Quiz (Chapter 10)Sainz MNo ratings yet
- R Software Presentation SyllabusDocument114 pagesR Software Presentation SyllabusAyushi PatelNo ratings yet
- IPPTCh 008Document30 pagesIPPTCh 008Jacquelynne SjostromNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication: Ass - prof.Ph.D. Cornelia TOMESCU-DUMITRESCUDocument13 pagesEffective Communication: Ass - prof.Ph.D. Cornelia TOMESCU-DUMITRESCUtigubarcelos2427No ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics: Dr.-Ing. Erwin Sitompul President UniversityDocument22 pagesProbability and Statistics: Dr.-Ing. Erwin Sitompul President UniversityKezia RachelNo ratings yet
- Basic Business Statistics For: 12 EditionDocument34 pagesBasic Business Statistics For: 12 EditionMustakim Mehmud TohaNo ratings yet
- 4 Normal and Binomial Distribution 2021Document45 pages4 Normal and Binomial Distribution 2021Haikal DinieNo ratings yet
- The Answer For Each Item Is Already Provided. Make A Written Explanation or Justification About The Answer. Briefly Explain The Reason and Show The Complete Solution If NeededDocument3 pagesThe Answer For Each Item Is Already Provided. Make A Written Explanation or Justification About The Answer. Briefly Explain The Reason and Show The Complete Solution If Neededmariegold mortola fabela87% (23)
- Descriptive Statistics DeCastroRoseshel UntalanLezyl 1Document15 pagesDescriptive Statistics DeCastroRoseshel UntalanLezyl 1Cecille UntalanNo ratings yet