Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Diagnosis 2
Uploaded by
anon_1684108160 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pages
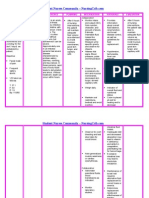
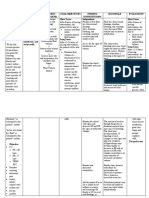
Monitor and record: These parameters
- PR, RR, T, BP, help assess the
weight, I&O effectiveness of
interventions and
the client's fluid
status.
Provide comfort Comfort measures
measures as needed help reduce stress
and promote
relaxation.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document
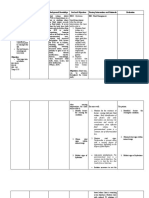
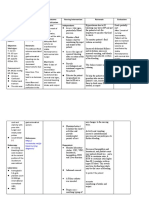
Monitor and record: These parameters
- PR, RR, T, BP, help assess the
weight, I&O effectiveness of
interventions and
the client's fluid
status.
Provide comfort Comfort measures
measures as needed help reduce stress
and promote
relaxation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesNursing Diagnosis 2
Uploaded by
anon_168410816
Monitor and record: These parameters
- PR, RR, T, BP, help assess the
weight, I&O effectiveness of
interventions and
the client's fluid
status.
Provide comfort Comfort measures
measures as needed help reduce stress
and promote
relaxation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Nursing
Assessment Inference Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis
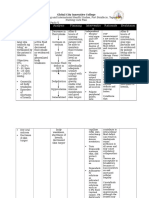
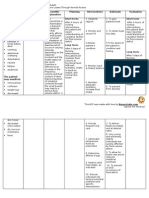
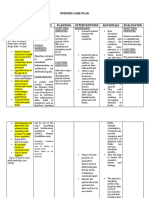
Subjective Data: Risk for Deficient Fluid Volume (also Date: October 18, 2021 Independent: Date: October 19, 2021
- vomited 10 times deficient fluid known as Fluid Volume Deficit Time: 12:30 pm Time 12:30 pm
- undocumented fever volume related (FVD), hypovolemia) is a state Shift 7am - 3pm Assess the client’s A loss of interstitial Shift: 7am - 3pm
- abdominal pain to excessive or condition where the fluid skin turgor and fluid causes the
- loose bowel losses through output exceeds the fluid intake. Short Term Goal: mucous loss of skin turgor. Actual Evaluation:
movement diarrhea and Risk factors for deficient fluid After 24 hours of membranes for After 24 hours of
vomiting. volume are as follows: nursing intervention, signs rendering nursing
Objective Data: vomiting, diarrhea, GI patient will report of dehydration. intervention, the patient
- sunken eyeballs suctioning, sweating, decreased adequate fluid volume reported adequate fluid
- weak and pale intake, nausea, inability to gain as evidenced by good Assess the volume Vomiting is volume as evidenced by
appearance access to fluids, adrenal skin turgor, stable vital and frequency of associated with good skin turgor, stable
- soft abdomen insufficiency, osmotic diuresis, signs,and absence of vomiting. fluid loss. vital signs,and absence
- poor skin turgor hemorrhage, coma, third-space orthostasis. of orthostasis.
- nausea fluid shifts, burns, ascites, and Assess the Gastroenteritis is
PR: 139 bpm liver dysfunction. Fluid volume consistency and associated with an
RR: 28 cpm deficit may be an acute or number of bowel increased
T: 38 C/axilla chronic condition managed in movements. frequency of very
Wt: 11kg the hospital, outpatient center, loose or watery
or home setting. bowel movements.
The inflammation
in the large
intestine limits the
colon’s ability to
absorb water,
leading to fluid
volume deficit.
Monitor and assess Usually, the pulse
client’s PR and is weak and may be
temperature. irregular
if electrolyte
imbalance also
occurs. Also, fever
that occurs with
gastroenteritis
increases fluid loss
through
perspiration and
increased
respiration.
Dependent:
Give: These drugs will
- Ranitidine 25mg IV reduce vomiting
every 8hrs and the risk for
- Metroclopromide fluid volume
15mg SIV now, then deficit.
every 8hrs for vomiting
Give: It helps replenish
- Bacillus clausii and support the
nebule, 1 nebule BID normal flora of the
- Zinc Syrup 2.5 mL gut. Additionally, it
OD is considered a
probiotic which are
indications for
chronic diarrhea
and certain vitamin
malabsoption
disorders. Zinc also
treat diarrheal
episodes.
Administer: Controls fever,
- Paracetamol reducing insensible
125mg/5 mL (5mL loss. Fever that
every 4hrs RTC) occurs with
- Paracetamol gastroenteritis
100mg IV every 4hrs increases fluid loss
through
perspiration and
increased
respiration.
D5IMB; 500mL x For maintenanace
14 hrs of fluid and
electrolytes
especially to
patients who need
calories and
hydration..
Collaborative:
Facilitate fecalysis. A culture is a test
Submit for client’s to detect which
stool for culture. causative
organisms cause an
infection.
Facilitate typhidot. The only way to
know for sure if an
illness is typhoid
fever or
paratyphoid fever
is to have a sample
of blood or stool
(poop) tested for
Salmonella Typhi
or Salmonella
Paratyphi.
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to Blood in Stools, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Blood in Stools, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Amnesia With Focus On Post Traumatic AmnesiaDocument27 pagesAmnesia With Focus On Post Traumatic AmnesiaWilliam ClemmonsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For DM PatientDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan For DM PatientRainier Rhett Concha100% (5)
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocument7 pagesCirrhosis of LivermOHAN.S100% (3)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocument3 pagesNCP Excess Fluid VolumeJ.G RNo ratings yet
- NCP Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesNCP Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceVitha100% (1)
- NCP - AgeDocument5 pagesNCP - Ageunsp3akabl386% (7)
- Chapter 22Document6 pagesChapter 22Danielle ShullNo ratings yet
- Deficient Fluid Volume (AGEDocument2 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (AGENursesLabs.com83% (6)
- Deficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)Document7 pagesDeficient Fluid Volume (Vanene)jajalerNo ratings yet
- NCP - DM - FatigueDocument12 pagesNCP - DM - FatigueJisel-Apple BulanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan AmoebiasisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Amoebiasisderic97% (35)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - CholeraDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Choleraderic87% (30)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Excess NCPDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Excess NCPAfia TawiahNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument7 pagesResearch Paperapi-242499715No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan Diarrhea Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationKrahNo ratings yet
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP Excess Fluid VolumeIngrid Nicolas100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Histolytica, ADocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Histolytica, AkristennemarieNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialDocument4 pagesNCP Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume PotentialArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Kode BPJSDocument40 pagesKode BPJSDwi FortunaNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesNCP Liver Cirrhosismarlx5100% (3)
- Module 2 1Document3 pagesModule 2 1Lacangan, Thea YvonneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planmust dietNo ratings yet
- NCPs Durano Aireen E.Document6 pagesNCPs Durano Aireen E.Doneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background and Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationKristiene Kyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Nursing Care PlanTipey SegismundoNo ratings yet
- Salva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Document7 pagesSalva, R.D NCP & Drug Study (Isph - Gs Pediaward)Rae Dominick Aquino SalvaNo ratings yet
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationKRISTINE BULACANNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - FormatDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan - FormatKyle VargasNo ratings yet
- Volume 1Document2 pagesVolume 1roxybiscanteNo ratings yet
- Actual and Potencial NCP Peptic Ulcer. Adepoju Iyinoluwa EDocument3 pagesActual and Potencial NCP Peptic Ulcer. Adepoju Iyinoluwa EAdepoju IyinoluwaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan TemplateTricia LiporadaNo ratings yet
- MS Soapie #1Document2 pagesMS Soapie #1Fatima KateNo ratings yet
- Prado NCPDocument4 pagesPrado NCPalleah pradoNo ratings yet
- NCP 3rd ROTATIONDocument17 pagesNCP 3rd ROTATIONMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentOPssslNo ratings yet
- NCP GI EditedDocument4 pagesNCP GI EditednicoleNo ratings yet
- NPR Deficient FluidDocument4 pagesNPR Deficient FluidDj KurtNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario: Dependent/ Independent/ Collaborative RationaleDocument3 pagesCase Scenario: Dependent/ Independent/ Collaborative RationaleRhos Antonette GuimbanNo ratings yet
- Ncp.-Fluid Volume DeficitDocument1 pageNcp.-Fluid Volume DeficitAdia Cavrinni De JesusNo ratings yet
- Choler A: Prepared By: Angelou Mortos John Radley SantosDocument11 pagesCholer A: Prepared By: Angelou Mortos John Radley SantosAdhaNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea, Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument6 pagesDiarrhea, Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitEfzell Dean BangilanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: STO: (Goal Met)Document3 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Outcomes Interventions Rationale Evaluation Sto: STO: (Goal Met)Arian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Duty RequirementsDocument13 pagesDuty RequirementsRey Jean GarciaNo ratings yet
- NCP 3rd YearDocument6 pagesNCP 3rd YearTotoro AblogNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Document4 pagesNCP and Drug Study (Isph-Gs Nursery)Cristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocument6 pagesROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- JVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesJVJV NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitvicenteturasNo ratings yet
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentDocument2 pagesCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Data: IndependentArabelle GONo ratings yet
- NCP Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument5 pagesNCP Deficient Fluid VolumeCHRISTINE GRACE ELLONo ratings yet
- 1 NCP and 2 Drug StudyDocument3 pages1 NCP and 2 Drug StudyCristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- Assessment SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Subjectivejeziel_16No ratings yet
- NCP Electrolyte and Fluid BalanceDocument2 pagesNCP Electrolyte and Fluid BalanceJoyce BalasuelaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 5Document6 pagesCase Study 5Anthony jesusNo ratings yet
- NCP ProperDocument9 pagesNCP Properstephanie eduarteNo ratings yet
- Assessment Inference Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Inference Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationSteffi Blair OngNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPyamie sulongNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisFrom EverandIntestinal Ills: Chronic Constipation, Indigestion, Autogenetic Poisons, Diarrhea, Piles, Etc. Also Auto-Infection, Auto-Intoxication, Anemia, Emaciation, Etc. Due to Proctitis and ColitisNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Irrigation: Why, How and When to Flush the ColonFrom EverandIntestinal Irrigation: Why, How and When to Flush the ColonNo ratings yet
- Rules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesFrom EverandRules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesNo ratings yet
- REPORT (Traits of An Entrepreneur)Document14 pagesREPORT (Traits of An Entrepreneur)anon_168410816No ratings yet
- The Contemporary World-ACT 5Document4 pagesThe Contemporary World-ACT 5anon_168410816No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyanon_168410816No ratings yet
- University of Northern Philippines Ivf Computations Mdh-Ob/GyneDocument1 pageUniversity of Northern Philippines Ivf Computations Mdh-Ob/Gyneanon_168410816No ratings yet
- NURSING DIAGNOSIS (2) On Pregnant Woman Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNURSING DIAGNOSIS (2) On Pregnant Woman Knowledge Deficitanon_168410816No ratings yet
- NURSING DIAGNOSIS On Pregnant WomanDocument2 pagesNURSING DIAGNOSIS On Pregnant Womananon_168410816No ratings yet
- 46 135 1 PB PDFDocument6 pages46 135 1 PB PDFpriscilla harmanyNo ratings yet
- 1 - Fiafinalize Na Prema, LBW, & SepsisDocument132 pages1 - Fiafinalize Na Prema, LBW, & SepsisJeizel IgnacioNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Chapter 36 Skin Integrity and Wound Care (Canvas)Document121 pagesNCM 103 Chapter 36 Skin Integrity and Wound Care (Canvas)AinaB ManaloNo ratings yet
- Villar PRC Cases (DONE)Document5 pagesVillar PRC Cases (DONE)Meijie Vino ManiegoNo ratings yet
- NU 120 Skin Integrity - Care - PlanDocument4 pagesNU 120 Skin Integrity - Care - Planmrsfelic08100% (3)
- Conectys Clinic ProceduresDocument13 pagesConectys Clinic Proceduresjmmos207064No ratings yet
- Assisting in BedpanDocument32 pagesAssisting in BedpanAbby Trisha MadularaNo ratings yet
- Ashwagandha Leaves Medicinal UsesDocument3 pagesAshwagandha Leaves Medicinal UsesSanjay PatilNo ratings yet
- World Psychiatry - 2022 - Reynolds - Mental Health Care For Older Adults Recent Advances and New Directions in ClinicalDocument28 pagesWorld Psychiatry - 2022 - Reynolds - Mental Health Care For Older Adults Recent Advances and New Directions in ClinicalpujakpathakNo ratings yet
- Physic An Checklist SampleDocument1 pagePhysic An Checklist SampleNida AtmimNo ratings yet
- BicitraDocument1 pageBicitraKerra AnasatasiaNo ratings yet
- Final ProgrammeDocument204 pagesFinal ProgrammeimagigatoNo ratings yet
- Truviv Trumed M1 Shiatsu Massage BeltDocument2 pagesTruviv Trumed M1 Shiatsu Massage BeltTruvivukNo ratings yet
- Framingham PaperDocument6 pagesFramingham PaperLikhna PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ahmed Shafik CVDocument4 pagesDr. Ahmed Shafik CVAhmed ShafikNo ratings yet
- Beta Thalassemia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument16 pagesBeta Thalassemia: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchFrancis GathiraNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides and SulfonamidesDocument35 pagesAminoglycosides and SulfonamidesPhoenixNo ratings yet
- Create PDFDocument92 pagesCreate PDFSri muyaroahNo ratings yet
- At The Doctor - Multiple ChoiceDocument10 pagesAt The Doctor - Multiple ChoiceGinaNo ratings yet
- National Clinical Guidelines For Safe Conception and Infertility - 2021Document64 pagesNational Clinical Guidelines For Safe Conception and Infertility - 2021shobhitbhargava39No ratings yet
- Addiction Treatment Center Near Houston, TXDocument2 pagesAddiction Treatment Center Near Houston, TXSharon DikirrNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions: EpilatorDocument7 pagesOperating Instructions: EpilatorMohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- So Ok Windi Nov 20Document16 pagesSo Ok Windi Nov 20Ruby BriandaNo ratings yet
- Etiology of Stroke PDFDocument2 pagesEtiology of Stroke PDFMichelle0% (1)
- 1976 - Johansson, Berglund, Kjellman - Comparison of IgE Values As Determined by Different Solid Phase Radioimmunoassay MethodsDocument9 pages1976 - Johansson, Berglund, Kjellman - Comparison of IgE Values As Determined by Different Solid Phase Radioimmunoassay Methodspond_1993No ratings yet