Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Simple Present and Continuous Tenses Guide
Uploaded by
Katherine JuleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Present and Continuous Tenses Guide
Uploaded by
Katherine JuleCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Present Tense
The simple present tense in English is used to describe an action that
is regular, true or normal.
We use the present tense:
1. For repeated or regular actions in the present time period.
I take the train to the office.
The train to Berlin leaves every hour.
John sleeps eight hours every night during the week.
2. For facts.
The President of The USA lives in The White House.
A dog has four legs.
We come from Switzerland.
3. For habits.
I get up early every day.
Carol brushes her teeth twice a day.
They travel to their country house every weekend.
4. For things that are always / generally true.
It rains a lot in winter.
The Queen of England lives in Buckingham Palace.
They speak English at work.
Present Continuous
1. For actions happening now.
They’re talking on the phone.
They are reading their books.
They are not watching television.
2. For actions occurring during a time period in the
present.
This year I’m studying English.
I am reading the book Tom Sawyer.
I am not reading any books right now.
Are you working on any special projects at work?
3. For some Future actions, especially those already
planned.
Thrursday I’m going to the theater
I am meeting some friends after work.
I am not going to the party tonight.
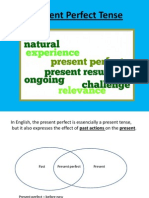
Present Perfect
1. Unspecified point in the past
I have been to Spain three times.
(At some unspecified time in the past, I went to Spain).
Compare with the simple past:
I went to Spain three times in 2005.
(specified time in the past - the year 2005)
2. An action that occurred in the past, but has a result in the present (now)
We can't find our luggage. Have you seen it?
(The luggage was lost in the past, do you know where it is now?)
3. Talking about general experiences (ever, never)
It usually refers to an event happening at some moment in your life.
Has she ever tried Chilean wine before? (in her life)
I've never eaten monkey brains before. (in my life)
4. Events that recently occurred (just)
Do you want to go to a restaurant with me?
No, thanks. I've just eaten lunch. (I recently ate lunch.)
5. Events that have occurred up to now (yet)
Are Carlos and Rodrigo here? No, they haven't arrived yet. (they're still not here now)
6. Events that occurred before you expected (already)
I've already graduated from University. (I expected to graduate at a later date.)
7. Events that began in the past and haven't changed (for, since)
Mike has worked at Woodward for 3 years.
(Mike started working at Woodward 3 years ago and he still works there now.)
Julie has worked at Woodward since September last year.
(Julie began working at Woodward in September of last year, and that hasn't changed -
she still works here now.)
Present Perfect Continuous
FORM
[has/have + been + present participle]
1. For unfinished or continuous actions.
I have been living here since 2007.
I have been living here for five years.
You have been waiting here for two hours.
They have been talking for the last hour.
She has been working at that company for three years.
We use the Present Perfect Continuous to show that
something started in the past and has continued up until now.
"For five minutes," "for two weeks," and "since Tuesday" are
all durations which can be used with the Present Perfect
Continuous.
Past Continuous
FORM
[was/were + present participle]
1. For one or more actions in progress at a time in the
past.
At 7:00, we were eating dinner.
They were swimming and we were sitting on the
beach.
I Wasn’t listening.
2. For an action that interrupted a continuing action in the
past.
You phoned while I was having a bath.
It started to rain just as we were getting ready to
have our picnic.
The boy was standing on the table when the
principal came into the room.
Many people were shopping in the market when the
bomb exploded.
While I was writing the email, the computer
suddenly went off.
A: What were you doing when you broke your leg?
B: I was snowboarding.
3. Atmosphere
In English, we often use a series of parallel actions to describe the atmosphere at a
particular time in the past.
Example:
When I walked into the office, several people were busily typing,
some were talking on the phones, the boss was yelling directions, and
customers were waiting to be helped. One customer was yelling at a
secretary and waving his hands. Others were complaining to each other
about the bad service.
4. Repetition and Irritation with "Always"
The Past Continuous with words such as "always" or "constantly" expresses the
idea that something irritating or shocking often happened in the past. The concept
is very similar to the expression "used to" but with negative emotion. Remember to
put the words "always" or "constantly" between "be" and "verb+ing."
She was always coming to class late.
He was constantly talking. He annoyed everyone.
I didn't like them because they were always complaining.
5. ACTIVE / PASSIVE
The salesman was helping the customer when the thief came into the
store. ACTIVE
The customer was being helped by the salesman when the thief came into the
store. PASSIVE
You might also like
- Past Tense HandoutDocument7 pagesPast Tense HandoutAnaNițuNo ratings yet
- Active / Passive Verb FormsDocument37 pagesActive / Passive Verb FormshusnaNo ratings yet
- Student List and Simple Past TenseDocument31 pagesStudent List and Simple Past Tensegalih febriandryNo ratings yet
- Exercise Your Past Tense With KeyDocument8 pagesExercise Your Past Tense With KeyAnaNițuNo ratings yet
- Tenses: PresentDocument11 pagesTenses: PresentGhulam MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple and ContinuousDocument7 pagesPresent Perfect Simple and ContinuousCristinaNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Does He Play Tennis?Document7 pagesPresent Simple: Does He Play Tennis?Marija MarkovićNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Past ContinuousDocument13 pagesPast Simple Past ContinuousbiffinNo ratings yet
- TENSESDocument17 pagesTENSESJonathan AmadeusNo ratings yet
- Progressive TensesDocument7 pagesProgressive TensesAinin SofiaNo ratings yet
- Present Tenses GuideDocument12 pagesPresent Tenses GuideLuis Enrique Ramirez PadillaNo ratings yet
- English Present TensesDocument8 pagesEnglish Present TensesAreFrayNo ratings yet
- Review of TensesDocument17 pagesReview of TensesStefany Serret Trejo100% (1)
- PRESENT CONTINUOUS ENGLISHDocument5 pagesPRESENT CONTINUOUS ENGLISHLidiaNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument9 pagesPresent Perfectsherry0% (1)
- Verb TensesDocument33 pagesVerb TensesThiago Teixeira100% (1)
- Clasa A VIII A B 4.05.2020 Present TensesDocument7 pagesClasa A VIII A B 4.05.2020 Present TensesLiliana GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Verb Tenses: Present SimpleDocument6 pagesUnit 1. Verb Tenses: Present SimpleAurelio PulidoNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument29 pagesGrammarEsma Nur AktaşNo ratings yet
- How Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Document8 pagesHow Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Syazwan ZentNo ratings yet
- tensesDocument22 pagestensesZinebNo ratings yet
- 12 Tenses and ExplanationDocument20 pages12 Tenses and Explanationkiransdb100% (1)
- LIMBA ENGLEZA 2 Id Anul 1 L. Andrei-CocartaDocument43 pagesLIMBA ENGLEZA 2 Id Anul 1 L. Andrei-CocartaEvelina AnileveNo ratings yet
- Portafolio Ingles AlexisDocument11 pagesPortafolio Ingles AlexisHugo Alexis Dena GallegosNo ratings yet
- ENG-101 Assignment on Verb TensesDocument6 pagesENG-101 Assignment on Verb TensesShamsul Islam RaisyNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument7 pagesPresent PerfectLuis Rosique MartinezNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous (I Am Doing)Document12 pagesPresent Continuous (I Am Doing)Luvsanjamiyan GanzorigNo ratings yet
- RepasoDocument11 pagesRepasoMatias NicolasNo ratings yet
- 12 English TensesDocument113 pages12 English Tensescharles izquierdoNo ratings yet
- Active voiceDocument125 pagesActive voiceAyesha AfzalNo ratings yet
- T IS NOT Important That This Fact IS UntrueDocument20 pagesT IS NOT Important That This Fact IS UntrueURS_ANDRIANNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect: Dragana FilipovicDocument31 pagesPresent Perfect: Dragana FilipovicToda0210No ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument12 pagesPresent Perfect TenseBiel FreitasNo ratings yet
- Eng Gram Mod 5 TensesDocument5 pagesEng Gram Mod 5 Tensesvikas1onlyNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Tense GuideDocument27 pagesPast Continuous Tense Guidewendy nguNo ratings yet
- Present Tense Revision Guide Under 40 CharactersDocument24 pagesPresent Tense Revision Guide Under 40 CharactersBalonash Q SclipiciNo ratings yet
- Anglais CdsDocument55 pagesAnglais CdsHassan AboullaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present USE 1 Repeated ActionsDocument16 pagesSimple Present USE 1 Repeated ActionsGaram Esther GohNo ratings yet
- Apuntes Ingles b2Document25 pagesApuntes Ingles b2Arancha ManeiroNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple ContinuousDocument17 pagesPresent Perfect Simple ContinuousLiliana RaduNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous Tense ExplainedDocument25 pagesPresent Continuous Tense ExplainedAisyah AminyMarwanNo ratings yet
- Simple Past and Past Continuous Verb TensesDocument4 pagesSimple Past and Past Continuous Verb TensesPaula DiazNo ratings yet
- 3rd Year-Complete Grammar LessonDocument47 pages3rd Year-Complete Grammar LessonJojo AlipioNo ratings yet
- USE 1 Completed Action in The Past: Did You Have Dinner Last Night?Document25 pagesUSE 1 Completed Action in The Past: Did You Have Dinner Last Night?Dashrathsinh RathodNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument9 pagesTensesTaTaNo ratings yet
- Do You Speak English?Document6 pagesDo You Speak English?Vale SierraNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Vs Present ContinuousDocument2 pagesPresent Simple Vs Present ContinuousSerpin AlpiniNo ratings yet
- 2 - TenseDocument24 pages2 - TenseHaibat Sultan StationeryNo ratings yet
- Engleski Gramatika Sva VremenaDocument13 pagesEngleski Gramatika Sva VremenaMirjana BrčićNo ratings yet
- Tenses Oft He Verb QWDocument9 pagesTenses Oft He Verb QWvincentc84No ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument19 pagesEnglish Grammarsashi.ucscNo ratings yet
- Review Units 1 To 4Document5 pagesReview Units 1 To 4ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Session 1 A JUST IN TIME Set B1Document24 pagesSession 1 A JUST IN TIME Set B1Jorge MadridNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Tense Guide for Relating Past Events to Present ResultsDocument5 pagesPresent Perfect Tense Guide for Relating Past Events to Present Resultsdyssey60300% (1)
- Present Perfect and Past SimpleDocument22 pagesPresent Perfect and Past Simplephalla oudomNo ratings yet
- Verb Perfect and ProgressiveDocument12 pagesVerb Perfect and ProgressiveJoanne JoanneNo ratings yet
- 12 (All) English Tenses with ExamplesDocument14 pages12 (All) English Tenses with ExamplesMurat AlpaslanNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Vs Present PerfectDocument4 pagesPast Simple Vs Present PerfectLolaMilickovicNo ratings yet
- Simple Present: USE 1 Repeated ActionsDocument11 pagesSimple Present: USE 1 Repeated ActionsNicolás De los riosNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Emission InspectionDocument7 pagesAcoustic Emission InspectionAntonio PerezNo ratings yet
- X-Plane Installer LogDocument3 pagesX-Plane Installer LogMarsala NistoNo ratings yet
- Studies of Land Restoration On Spoil Heaps From Brown Coal MiningDocument11 pagesStudies of Land Restoration On Spoil Heaps From Brown Coal MiningeftychidisNo ratings yet
- Lifeboat Equipment ListDocument1 pageLifeboat Equipment Listjosua albertNo ratings yet
- Gujrat Newspaper IndustryDocument14 pagesGujrat Newspaper IndustryAlok MahajanNo ratings yet
- Uconnect User GuideDocument113 pagesUconnect User GuidetamilarasansrtNo ratings yet
- BITS ZG628T Dissertation (For Students of M. Tech. Software Systems)Document21 pagesBITS ZG628T Dissertation (For Students of M. Tech. Software Systems)Shiva Beduduri100% (1)
- The 9 Building Blocks of Business ModelsDocument3 pagesThe 9 Building Blocks of Business ModelsTobeFrankNo ratings yet
- Tugas 3vDocument4 pagesTugas 3vRomie SyafitraNo ratings yet
- WEG Low Voltage Motor Control Center ccm03 50044030 Brochure English PDFDocument12 pagesWEG Low Voltage Motor Control Center ccm03 50044030 Brochure English PDFRitaban222No ratings yet
- Linkstar RCST Installation Guide: Version DDocument56 pagesLinkstar RCST Installation Guide: Version Djorge_chavez01No ratings yet
- Serv Manual SM 100 FREEDocument75 pagesServ Manual SM 100 FREEGustavo Vargas Ruiz100% (1)
- Bizagi Licensing Explained ENGDocument7 pagesBizagi Licensing Explained ENGGuidoNo ratings yet
- Airport Design GuidelinesDocument408 pagesAirport Design Guidelinesnickolololo67% (9)
- Duane Grant, A099 743 627 (BIA Sept. 9, 2016)Document12 pagesDuane Grant, A099 743 627 (BIA Sept. 9, 2016)Immigrant & Refugee Appellate Center, LLCNo ratings yet
- About WELDA Anchor PlateDocument1 pageAbout WELDA Anchor PlateFircijevi KurajberiNo ratings yet
- Measure Science AccuratelyDocument41 pagesMeasure Science AccuratelyAnthony QuanNo ratings yet
- Saura, Jasmin E. - DVM - 2B Biochemistry (Activity 2)Document2 pagesSaura, Jasmin E. - DVM - 2B Biochemistry (Activity 2)Jasmin SauraNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA) Software MarketDocument3 pagesFinite Element Analysis (FEA) Software Marketsurendra choudharyNo ratings yet
- Student quiz answer sheetsDocument26 pagesStudent quiz answer sheetsSeverus S PotterNo ratings yet
- 02+sebring+2.7+timing+chainDocument10 pages02+sebring+2.7+timing+chainMaushil Salman MarkNo ratings yet
- WEEK 7 ICPS - and - ICSSDocument31 pagesWEEK 7 ICPS - and - ICSScikguhafidzuddinNo ratings yet
- BISE Sukkur HSC Part 2 Results 2015Document12 pagesBISE Sukkur HSC Part 2 Results 2015ajayNo ratings yet
- Kristine Jane T. Zipagan Assignment: 1. Parts of InfographicsDocument2 pagesKristine Jane T. Zipagan Assignment: 1. Parts of InfographicsChristyNo ratings yet
- Mercedes Vario 1996 2003 PDF Service ManualDocument22 pagesMercedes Vario 1996 2003 PDF Service Manualveronicamurphy070288aqwNo ratings yet
- CAPS LESSON PLAN, KAHOOT QUIZ, PPT VIDEODocument3 pagesCAPS LESSON PLAN, KAHOOT QUIZ, PPT VIDEOMandisa MselekuNo ratings yet
- Sajid Bhuiya CVDocument3 pagesSajid Bhuiya CVapi-612088476No ratings yet
- Urbanclap 160731135642Document20 pagesUrbanclap 160731135642Kaustav Dey100% (1)
- At-15 Series III 3B6 Operator ManualDocument39 pagesAt-15 Series III 3B6 Operator ManualFausto Herrera B100% (4)