Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Life Cycle of Babesia SPP.: Salivary Glands, Developing
Uploaded by
Irina AtudoreiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Life Cycle of Babesia SPP.: Salivary Glands, Developing
Uploaded by
Irina AtudoreiCopyright:
Available Formats
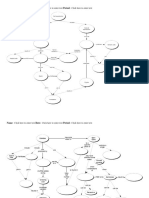
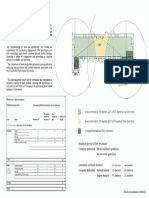
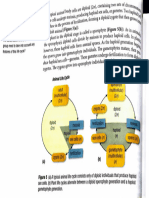
Life cycle of Babesia spp.
I.H.
Vertebrate
Kinete migrates to the
salivary glands, developing
into infective sporozoites
Infe
ctio
Transstadial transmission:
nd
larvae, nymphs, adults
urin
g tic
k fe
edin
g
transmission
Transovarial
Sporozoite
penetrates
the host’s red
blood cells
ays
4d
7–1
Kinete
Tick
Gamont Zygote
inges
Multiply, rupture
and infect other red
ts inf
Reproduction in tick gut cells blood cells
ected
blood
Tick species varies depending
upon Babesia species
D.H. D.H. = definitive host
Hard tick
I.H. = intermediate host
Extracted from the Textbook of Clinical Parasitology in dogs and cats, Beugnet F., Halos L., Guillot J., Ed Servet, 2018.
Life cycles adapted from Pet Owner Educational Atlas. Parasites, Carithers D. and Miro G., Ed Servet, 2012.
You might also like
- Parasitology Babesia SPP CatDocument1 pageParasitology Babesia SPP CatIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of RHDDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of RHDshmily_0810No ratings yet
- Repro On AninimalDocument32 pagesRepro On AninimalAnush GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Cell ReproductionConceptMapfillableDocument2 pagesCell ReproductionConceptMapfillableJanet NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A-E VirusesDocument7 pagesHepatitis A-E VirusesmandrakesMDNo ratings yet
- PSM Routine Vaccines VaccineDocument4 pagesPSM Routine Vaccines VaccinePramila MahaleNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Ms Sara KhanDocument37 pagesForm 4 Biology Ms Sara KhanSyahirahNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument70 pagesUntitledAhmad QuraanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument30 pagesMitosis and MeiosisAmalina Ismail100% (4)
- 64b2bc7c3de5b60018322afb - ## - Human Health and Diseases Handwritten Notes (Of Lecture 07)Document6 pages64b2bc7c3de5b60018322afb - ## - Human Health and Diseases Handwritten Notes (Of Lecture 07)sourajeetsahoo2610No ratings yet
- Pro To ZoologyDocument9 pagesPro To Zoologytxhj82xcnmNo ratings yet
- Benigno: T.locoliaoeat - EsDocument8 pagesBenigno: T.locoliaoeat - EsTeonaNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument35 pagesConnective Tissues vNo ratings yet
- Guide Gi CancerDocument1 pageGuide Gi Cancerapi-446887131No ratings yet
- WA10004-Directed Differentiation Pluripotent Stem CellsDocument1 pageWA10004-Directed Differentiation Pluripotent Stem CellsJorge Mario “Jorge” Gamboa CarvajalNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument168 pagesUntitledIcaro KashamuraNo ratings yet
- Animalia File 2023-1Document12 pagesAnimalia File 2023-1Syed Zee Waqar GillaniNo ratings yet
- Paci Ent I I Croni Ci Caract Eri ST I CiDocument1 pagePaci Ent I I Croni Ci Caract Eri ST I CiAlexandru StancuNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseaseDocument24 pagesHuman Health and DiseaseD SamyNo ratings yet
- Virus Chart For Med MicroDocument2 pagesVirus Chart For Med MicroAndie RaczNo ratings yet
- Hematology - Red Blood CellsDocument1 pageHematology - Red Blood CellsChewyNo ratings yet
- Embal Mi NG PL Ate Book of The DeadDocument2 pagesEmbal Mi NG PL Ate Book of The Deadanna_bogomolovaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology - 24. Male Reproductive System - Spermatogenesis - KeyDocument1 pageEndocrine Physiology - 24. Male Reproductive System - Spermatogenesis - Keyranag59100No ratings yet
- Biol 23Document820 pagesBiol 23defnedemircayNo ratings yet
- Cestodes and Trematodes: A Comparison of Tapeworms and FlukesDocument4 pagesCestodes and Trematodes: A Comparison of Tapeworms and FlukesNatalie EnriquezNo ratings yet
- GROUP STUDY KIDNEY FUNCTIONSDocument3 pagesGROUP STUDY KIDNEY FUNCTIONShayat yimerNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument6 pagesHepatitis BCarmen MargoNo ratings yet
- Vi Orr A Ant I Sept I C Wi Pes Product Appl I Cat I OnDocument1 pageVi Orr A Ant I Sept I C Wi Pes Product Appl I Cat I Onadiosadios14No ratings yet
- Analysis of Disease: ElephantiasisDocument1 pageAnalysis of Disease: ElephantiasisAkash YadavNo ratings yet
- Fire Strategies For 7039Document1 pageFire Strategies For 7039Gabe BestyNo ratings yet
- Cooperation LifeDocument2 pagesCooperation LifeBasie NuñezNo ratings yet
- Hours: PlanceDocument1 pageHours: PlanceSayandeep DuttaNo ratings yet
- Sporozoa TableDocument2 pagesSporozoa TableJoshua TrinidadNo ratings yet
- ACECashDirectDeposit PDFDocument1 pageACECashDirectDeposit PDFMelchizedek33No ratings yet
- LocalScriptMan Character Map Vers 1 With ExamplesDocument1 pageLocalScriptMan Character Map Vers 1 With ExamplesthanhdzhNo ratings yet
- Ani Mal Assi Sted Therapy Center: Ji Yan Heal I NG GardenDocument1 pageAni Mal Assi Sted Therapy Center: Ji Yan Heal I NG GardenDeemaNo ratings yet
- A - Called A Sporophyte (Figure 5 (B) ) - As in An P: Es. ZygoDocument1 pageA - Called A Sporophyte (Figure 5 (B) ) - As in An P: Es. Zygo973132No ratings yet
- Interpreting PDX Dot BlotsDocument2 pagesInterpreting PDX Dot BlotsSpy CameraNo ratings yet
- FAB Quickstart - 2 - FrontDocument1 pageFAB Quickstart - 2 - FrontnakanoakanefstNo ratings yet
- SASE LIFE Science REVIEWER PDFDocument4 pagesSASE LIFE Science REVIEWER PDFanne abadiezNo ratings yet
- Catalog MarketingDocument1 pageCatalog MarketingAlexandru StancuNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland (Anterior Pituitary)Document7 pagesPituitary Gland (Anterior Pituitary)MID IMRANNo ratings yet
- Form inductive embryonic-like DP precursors from patient-derived iPS cells via redifferentiation or direct reprogrammingDocument4 pagesForm inductive embryonic-like DP precursors from patient-derived iPS cells via redifferentiation or direct reprogrammingSaifuddin HaswareNo ratings yet
- Zoonosis (Plu - ZoonosessDocument8 pagesZoonosis (Plu - Zoonosess6wcdwfcfydNo ratings yet
- Negative Feedback Loop Controls Blood Oxygen LevelsDocument1 pageNegative Feedback Loop Controls Blood Oxygen LevelsJack DavisNo ratings yet
- Playing TogetherDocument85 pagesPlaying TogetherPatrícia ValérioNo ratings yet
- Chron Skin Allergy Oct 2010Document32 pagesChron Skin Allergy Oct 2010shannon3458No ratings yet
- The Basic Process of Gene Therapy Erica GDocument2 pagesThe Basic Process of Gene Therapy Erica GDianne LabisNo ratings yet
- Haematology Part 1Document152 pagesHaematology Part 1Sai praveen DasariNo ratings yet
- Taenia Solium Taenia Saginata Diphyllobotrium Latum Dipylidium Caninum Hymenolepis Nana Hymenolepis Diminuta Echinococcus SPPDocument1 pageTaenia Solium Taenia Saginata Diphyllobotrium Latum Dipylidium Caninum Hymenolepis Nana Hymenolepis Diminuta Echinococcus SPPKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- 10 6 21 Asm Assig2Document3 pages10 6 21 Asm Assig2elsayedahmed01234No ratings yet
- Pericardium - HeartDocument9 pagesPericardium - HeartAmrinder MaanNo ratings yet
- Cycles within Ecosystems QPDocument10 pagesCycles within Ecosystems QPemilysacre123No ratings yet
- Blood SmearsDocument4 pagesBlood SmearsAmor KourdouliNo ratings yet
- 12 Laboratory Diagnosis of HIV 2Document11 pages12 Laboratory Diagnosis of HIV 2Melody Jane PardilloNo ratings yet
- Clocks An Rulers in Life... and Synthetic BiologyDocument133 pagesClocks An Rulers in Life... and Synthetic BiologySaúlNo ratings yet
- Coniferous BrochureDocument16 pagesConiferous BrochureVedansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Kardex LolDocument3 pagesKardex LolChristian Edward MacabaliNo ratings yet
- Menu - Bar - Opti Ons - Bands - : Pur Chase Ti CketsDocument1 pageMenu - Bar - Opti Ons - Bands - : Pur Chase Ti CketsNoah HaynesNo ratings yet
- Bread Consumption and Waste of Households in UrbanDocument15 pagesBread Consumption and Waste of Households in UrbanIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Safety and Health Perceptions in Work-Related TranDocument20 pagesSafety and Health Perceptions in Work-Related TranIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Wcms 400598Document76 pagesWcms 400598Irina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Workplace Transport Safety An Employers GuideDocument144 pagesWorkplace Transport Safety An Employers GuideIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Composition Physical and Sensory PropertiDocument13 pagesChemical Composition Physical and Sensory PropertiIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Bread MetDocument32 pagesBread MetIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- 101-112 18946 UchrońskiDocument12 pages101-112 18946 UchrońskiIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Belts For The Airport Industry: Helping AchieveDocument6 pagesBelts For The Airport Industry: Helping AchieveIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Legea 307 DIN 2006Document18 pagesLegea 307 DIN 2006BogdanNo ratings yet
- AdvanceDocument11 pagesAdvanceIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Extended Abstract Joao CoutoDocument10 pagesExtended Abstract Joao CoutoIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Best Bread Production Handbook ENDocument55 pagesBest Bread Production Handbook ENma hNo ratings yet
- Customer S Information Security ManagemeDocument5 pagesCustomer S Information Security ManagemeIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- ACRP DesignCompetition 2ndplace ManagementDocument54 pagesACRP DesignCompetition 2ndplace ManagementIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Ijser: Cyber Security in E-CommerceDocument7 pagesIjser: Cyber Security in E-CommerceIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Policies For Information Security & PrivacyDocument166 pagesPolicies For Information Security & PrivacyIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Best Environmental Management Practice in The Tourism Sector PDFDocument721 pagesBest Environmental Management Practice in The Tourism Sector PDFKlinik Jurnal KJ FH UBNo ratings yet
- Bag Tracking enDocument4 pagesBag Tracking enIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Commerce in China Information Security Management System Strategy ResearchDocument3 pagesElectronic Commerce in China Information Security Management System Strategy ResearchIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Research Article Management Model On Electronic Commerce Data Based On Cloud ComputingDocument10 pagesResearch Article Management Model On Electronic Commerce Data Based On Cloud ComputingIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 PDFDocument9 pagesChapter5 PDFSambit Kumar BiswalNo ratings yet
- The Main Characteristics of Travel Agencies in Montenegro: SSRN Electronic Journal January 2012Document8 pagesThe Main Characteristics of Travel Agencies in Montenegro: SSRN Electronic Journal January 2012Irina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Tourism: Concept and Types of TourismDocument22 pagesTourism: Concept and Types of TourismMuhammad DaniNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies of Travel Agencies: A Quantitative ApproachDocument20 pagesMarketing Strategies of Travel Agencies: A Quantitative ApproachSai Kumar RaoNo ratings yet
- Improving The Management of Tourist Destinations: A New Approach To Strategic Management at The DMO Level by Integrating Lean TechniquesDocument22 pagesImproving The Management of Tourist Destinations: A New Approach To Strategic Management at The DMO Level by Integrating Lean TechniquesRHEZA OCTAMA 201721778No ratings yet
- A Typology of Tourism Related Web Sites: Its Theoretical Background and ImplicationsDocument37 pagesA Typology of Tourism Related Web Sites: Its Theoretical Background and ImplicationsIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Security - A Life Cycle ApproachDocument22 pagesE-Commerce Security - A Life Cycle ApproachchagantisasikiranNo ratings yet
- The Main Characteristics of Travel Agencies in Montenegro: SSRN Electronic Journal January 2012Document8 pagesThe Main Characteristics of Travel Agencies in Montenegro: SSRN Electronic Journal January 2012Irina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies of Travel Agencies: A Quantitative ApproachDocument20 pagesMarketing Strategies of Travel Agencies: A Quantitative ApproachSai Kumar RaoNo ratings yet
- Romanian Tour Operators A Qualitative ApDocument7 pagesRomanian Tour Operators A Qualitative ApIrina AtudoreiNo ratings yet
- ApexDocument18 pagesApexbaronggamingNo ratings yet
- Dental BooklistDocument14 pagesDental Booklistالمكتبة المليونيةNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium Vivax - Habitat, Characteristics, Structure, Life CycleDocument7 pagesPlasmodium Vivax - Habitat, Characteristics, Structure, Life CycleАнна КатраженкоNo ratings yet
- Identificación PolygonumDocument8 pagesIdentificación PolygonumvalentinaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lab Experiments 1-8Document23 pagesBiochemistry Lab Experiments 1-8Claudette LopezNo ratings yet
- Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics and Postbiotics in Inhibition of PathogensDocument16 pagesRole of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics and Postbiotics in Inhibition of PathogensJulianoAlvesNo ratings yet
- Approach To Skin Adnexal TumorsDocument20 pagesApproach To Skin Adnexal TumorsNirmalya Chakrabarti100% (1)
- L. Poorter, F. Bongers, F.N. Kouamý, W.D. Hawthorne Biodiversity of West African Forests 2004Document528 pagesL. Poorter, F. Bongers, F.N. Kouamý, W.D. Hawthorne Biodiversity of West African Forests 2004colosseum_emNo ratings yet
- Hematologic EffectsDocument8 pagesHematologic EffectsGiralph NikkoNo ratings yet
- The Biomedical Engineering Handbook: Second EditionDocument13 pagesThe Biomedical Engineering Handbook: Second EditionEng-Mugahed AlmansorNo ratings yet
- Classification of NF by DR MKBDocument33 pagesClassification of NF by DR MKBiloveusonNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids & ElectrolytesDocument26 pagesBody Fluids & ElectrolytesMohamad Zekry Zuhairy100% (1)
- RFLP & RapdDocument25 pagesRFLP & RapdBalaji Prasanna KumarNo ratings yet
- Marine Biology-LecNote-Unit-2 PDFDocument9 pagesMarine Biology-LecNote-Unit-2 PDFYashNo ratings yet
- Early Farmers From Europe Directly Descended From Neolithic Aegeans PDFDocument128 pagesEarly Farmers From Europe Directly Descended From Neolithic Aegeans PDFbilldekNo ratings yet
- Review Work 2019, CHM145020Document14 pagesReview Work 2019, CHM145020mahfooz zin noorineNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of Fruitbodies and SclerotiaDocument4 pagesCultivation of Fruitbodies and SclerotiaEsporas De MexicoNo ratings yet
- KEY - Experimetnal ScenariosDocument2 pagesKEY - Experimetnal ScenariosArabellaNo ratings yet
- Cell Size Comparison LabDocument3 pagesCell Size Comparison Labs.paulhuff1No ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Document2 pagesCell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Kirsten Troupe100% (1)
- RuelliaDocument21 pagesRuelliabioandreyNo ratings yet
- AIIMS May 2019 - PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAIIMS May 2019 - Physiologyshibira surendran vkNo ratings yet
- Breathe Strong, Perform Better by Alison McConnellDocument288 pagesBreathe Strong, Perform Better by Alison McConnellabacaterct100% (1)
- Placental PhysiologyDocument6 pagesPlacental Physiologylindsay_weiss_6No ratings yet
- Gonadotropin Releasing HormoneDocument9 pagesGonadotropin Releasing HormoneNTA UGC-NETNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument168 pagesScienceadi22-22No ratings yet
- ESE200 Online TextbookDocument594 pagesESE200 Online TextbookSuren UlaganathanNo ratings yet
- Plant TransportDocument32 pagesPlant Transport송준혁No ratings yet
- HAPL 3 & 4 - The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesHAPL 3 & 4 - The Nervous SystemwelpNo ratings yet
- Paper 6 Marking Scheme June 2009Document3 pagesPaper 6 Marking Scheme June 2009MSHNo ratings yet