Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid and Electrolyte Management
Uploaded by
Rintho0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagespanduan cairan dan elektrolit
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentpanduan cairan dan elektrolit
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Management
Uploaded by
Rinthopanduan cairan dan elektrolit
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
GEJALA DARI KELAINAN ELEKTROLIT
Signs and Symptoms of Volume Disturbances
System Volume Deficit Volume Excess
Generalized Weight loss Weight gain
Decreased skin turgor Peripheral edema
Cardiac Tachycardia Increased cardiac output
Orthostasis/hypotension Increased central venous pressure
Collapsed neck veins Distended neck veins
Murmur
Renal Oliguria —
Azotemia
GI Ileus Bowel edema
Pulmonary — Pulmonary edema
Clinical Manifestations of Abnormalities in Serum Sodium Level
Body System Hyponatremia
Central nervous Headache, confusion, hyperactive or hypoactive deep tendon reflexes,
system seizures, coma, increased intracranial pressure
Musculoskeletal Weakness, fatigue, muscle cramps/twitching
GI Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, watery diarrhea
Cardiovascular Hypertension and bradycardia if significant increases in intracranial
pressure
Tissue Lacrimation, salivation
Renal Oliguria
Body System Hypernatremia
Central nervous Restlessness, lethargy, ataxia, irritability, tonic spasms, delirium,
system seizures, coma
Musculoskeletal Weakness
Cardiovascular Tachycardia, hypotension, syncope
Tissue Dry sticky mucous membranes, red swollen tongue, decreased saliva and
tears
Renal Oliguria
Metabolic Fever
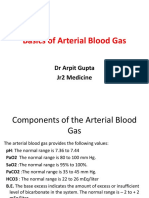
Predicted Changes in Acid-Base Disorders
Disorder Predicted Change
Metabolic
Metabolic acidosis Pco2 = 1.5 x HCO3– + 8
Metabolic alkalosis Pco2 = 0.7 x HCO3– + 21
Respiratory
Acute respiratory acidosis
pH = (Pco2 – 40) x
0.008
Chronic respiratory acidosis
pH = (Pco2 – 40) x
0.003
Acute respiratory alkalosis
pH = (40 – Pco2) x
0.008
Chronic respiratory alkalosis
pH = (40 – Pco2) x
0.017
The normal AG is <12 mmol/L and is due primarily to the albumin effect, so that the estimated
AG must be adjusted for albumin (hypoalbuminemia reduces the AG).19
Corrected AG = Actual AG – (2.5 (4.5-albumin))
Treatment of Symptomatic Hyperkalemia
Potassium removal
Kayexalate
Oral administration is 15–30 g in 50–100 mL of 20% sorbitol
Rectal administration is 50 g in 200 mL of 20% sorbitol
Dialysis
Shift potassium
Glucose 1 ampule of D50 and regular insulin 5–10 units IV
Bicarbonate 1 ampule IV
Counteract cardiac effects
Calcium gluconate 5–10 mL of 10% solution
Electrolyte Replacement Therapy Protocol
Potassium
Serum potassium level <4.0 mEq/L:
Asymptomatic, tolerating enteral nutrition: KCl 40 mEq per enteral access x 1 dose
Asymptomatic, not tolerating enteral nutrition: KCl 20 mEq IV q2h x 2 doses
Symptomatic: KCl 20 mEq IV q1h x 4 doses
Recheck potassium level 2 h after end of infusion; if <3.5 mEq/L and asymptomatic, replace as per
above protocol
Magnesium
Magnesium level 1.0–1.8 mEq/L:
Magnesium sulfate 0.5 mEq/kg in normal saline 250 mL infused IV over 24 h x 3 d
Recheck magnesium level in 3 d
Magnesium level <1.0 mEq/L:
Magnesium sulfate 1 mEq/kg in normal saline 250 mL infused IV over 24 h x 1 d, then 0.5 mEq/kg in
normal saline 250 mL infused IV over 24 h x 2 d
Recheck magnesium level in 3 d
If patient has gastric access and needs a bowel regimen:
Milk of magnesia 15 mL (approximately 49 mEq magnesium) q24h per gastric tube; hold for diarrhea
Calcium
Normalized calcium level <4.0 mg/dL:
With gastric access and tolerating enteral nutrition: Calcium carbonate suspension 1250 mg/5 mL q6h
per gastric access; recheck ionized calcium level in 3 d
Without gastric access or not tolerating enteral nutrition: Calcium gluconate 2 g IV over 1 h x 1 dose;
recheck ionized calcium level in 3 d
Phosphate
Phosphate level 1.0–2.5 mg/dL:
Tolerating enteral nutrition: Neutra-Phos 2 packets q6h per gastric tube or feeding tube
No enteral nutrition: KPHO4 or NaPO4 0.15 mmol/kg IV over 6 h x 1 dose
Recheck phosphate level in 3 d
Phosphate level <1.0 mg/dL:
Tolerating enteral nutrition: KPHO4 or NaPO4 0.25 mmol/kg over 6 h x 1 dose
Recheck phosphate level 4 h after end of infusion; if <2.5 mg/dL, begin Neutra-Phos 2 packets q6h
Not tolerating enteral nutrition: KPHO4 or NaPO4 0.25 mmol/kg (LBW) over 6 h x 1 dose; recheck
phosphate level 4 h after end of infusion; if <2.5 mg/dL, then KPHO 4 or NaPO4 0.15 mmol/kg (LBW) IV
over 6 h x 1 dose
Preoperative Fluid Therapy
For the first 0 to 10 kg Give 100 mL/kg per day
For the next 10 to 20 kg Give an additional 50 mL/kg per day
For weight >20 kg Give an additional 20 mL/kg per day
For example, a 60-kg female would receive a total of 2100 mL of fluid daily: 1000 mL for the
first 10 kg of body weight (10 kg x 100 mL/kg per day), 500 mL for the next 20 kg (10 kg x 50
mL/kg per day), and 80 mL for the last 40 kg (40 kg x 20 mL/kg per day).
You might also like
- Acid-Base and Electrolyte DisordersDocument41 pagesAcid-Base and Electrolyte Disordersaantoxx84No ratings yet
- Acid Base Disorders: Mr. Ahmed Alnaji Mbchb. Mrcs 1+2 Palestinian Board G. Surgery European Gaza HospitalDocument60 pagesAcid Base Disorders: Mr. Ahmed Alnaji Mbchb. Mrcs 1+2 Palestinian Board G. Surgery European Gaza Hospitalpt.mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Acid Base DisordersDocument51 pagesAcid Base Disordersmmkavitha98No ratings yet
- Arterial Blood GasDocument66 pagesArterial Blood GasThea DinoNo ratings yet
- Moderator: Dr. R. K. Yadav (MD) Presented By: Ashish JaisawalDocument47 pagesModerator: Dr. R. K. Yadav (MD) Presented By: Ashish Jaisawalimranqazi11No ratings yet
- DkaDocument38 pagesDkaHam SotheaNo ratings yet
- Body FluidsDocument6 pagesBody FluidsMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine TNDocument3 pagesInternal Medicine TNZeeshan Ahmed100% (2)
- MetabolicDocument23 pagesMetabolicbtidipNo ratings yet
- Renal, Fluid & ElectrolyeDocument21 pagesRenal, Fluid & ElectrolyeremeroseNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument61 pagesAcid Base BalanceAshwin ChandNo ratings yet
- ABG - Manuel Antonio Ko, MD 2008Document58 pagesABG - Manuel Antonio Ko, MD 2008Nguyen Minh DucNo ratings yet
- Acid/Base Am Didactic Teaching Guide: Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pagesAcid/Base Am Didactic Teaching Guide: Learning ObjectivesAdrian CamposNo ratings yet
- ABIDocument27 pagesABIekramNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Acidosis: Dr. Ann Valerie F. Habana Critical Care MedicineDocument21 pagesRespiratory Acidosis: Dr. Ann Valerie F. Habana Critical Care Medicineannv748687No ratings yet
- Angela Heithaus, MD, PS Internal Medicine Seattle Healing Arts CenterDocument32 pagesAngela Heithaus, MD, PS Internal Medicine Seattle Healing Arts CenterMarwan M.No ratings yet
- Fluid Therapy and ElectroliteDocument36 pagesFluid Therapy and ElectroliteAriefBudimanHidayatNo ratings yet
- Basics in Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocument41 pagesBasics in Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationyasinNo ratings yet
- ArpitDocument73 pagesArpitDurgesh PushkarNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument89 pagesAcid BaseEdouinaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument20 pagesAcid Base BalanceAyat AdilNo ratings yet
- ABGAnalysis Resident LectureDocument71 pagesABGAnalysis Resident LecturePutu AdhekNo ratings yet
- LRP CriticalCare Sample2Document46 pagesLRP CriticalCare Sample2Aniket ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Acid Base DisordersDocument28 pagesAcid Base DisordersSaif AliNo ratings yet
- Acid - Base Balance & Abg AnalysisDocument71 pagesAcid - Base Balance & Abg AnalysisMohan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas InterpretationDocument67 pagesBlood Gas Interpretationmajdy2006No ratings yet
- Abg PPT NewDocument69 pagesAbg PPT NewMalaka Atapattu100% (2)
- Arterial Blood GasDocument48 pagesArterial Blood GaslovianettesherryNo ratings yet
- 1 Fluid and ElectrolyteDocument51 pages1 Fluid and ElectrolyteSanjiv SharmaNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas AnalysisDocument39 pagesBlood Gas Analysisjtalan9No ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas: IM 2013 (AVM)Document66 pagesArterial Blood Gas: IM 2013 (AVM)Wilsonne ChuaNo ratings yet
- 1 Fluid and ElectrolyteDocument51 pages1 Fluid and ElectrolyteSanjiv SharmaNo ratings yet
- Management of Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument19 pagesManagement of Diabetic KetoacidosisSharafuddin SalimiNo ratings yet
- ABG ElectrolytesDocument48 pagesABG ElectrolytesDRwaqas Gulzar100% (1)
- ABG MMHG InterpretationDocument92 pagesABG MMHG InterpretationManmeet SNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base BalanceDocument28 pagesAcid-Base Balanceps4only100% (1)
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocument46 pagesArterial Blood Gas AnalysisMedi - LecturesNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood GasDocument55 pagesArterial Blood GasRathis Dasan100% (1)
- Acid Base BalanceDocument44 pagesAcid Base BalanceKenny JapNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: 4 Signs of DKA: Acidosis (Metabolic, Raised Anion Gap), Ketosis, Dehydration and HyperglycaemiaDocument3 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis: 4 Signs of DKA: Acidosis (Metabolic, Raised Anion Gap), Ketosis, Dehydration and HyperglycaemiajsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas Analysis: Review By: DR - JeansenDocument35 pagesBlood Gas Analysis: Review By: DR - JeansenJeansen GantengNo ratings yet
- Lab Values WorksheetDocument57 pagesLab Values WorksheetpcbthyNo ratings yet
- Abg by DR Manna, Department of Emergency Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sceinces, Kochi, KeralaDocument50 pagesAbg by DR Manna, Department of Emergency Medicine, Amrita Institute of Medical Sceinces, Kochi, KeralaAETCM Emergency medicine100% (1)
- Adult Health Nursing I: Joseph Mariano, RN, MDDocument89 pagesAdult Health Nursing I: Joseph Mariano, RN, MDairon0000No ratings yet
- ABG Algorithm PDFDocument2 pagesABG Algorithm PDFamin2014No ratings yet
- Roumilla Mendoza, M.D. Roumilla Mendoza, M.D. Pediatric Gastroenterologist Pediatric GastroenterologistDocument59 pagesRoumilla Mendoza, M.D. Roumilla Mendoza, M.D. Pediatric Gastroenterologist Pediatric GastroenterologistYenyen DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Fluid ElectrolytesDocument31 pagesDisorders of Fluid ElectrolytesjabirNo ratings yet
- Interpreting ABG - An Interative Session: Dr. Manjunath Patil Professor, Dept. of Anaesthesiology J.N.Medical CollegeDocument31 pagesInterpreting ABG - An Interative Session: Dr. Manjunath Patil Professor, Dept. of Anaesthesiology J.N.Medical CollegeMadhan Mohan Reddy KatikareddyNo ratings yet
- AbgDocument52 pagesAbgm07wwpNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Fall 2008Document34 pagesAcid Base Fall 2008anon-252165No ratings yet
- American Thoracic Society - Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs)Document8 pagesAmerican Thoracic Society - Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases (ABGs)muhammadridhwanNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument42 pagesBody Fluids and ElectrolytesQusaiBadr100% (1)
- S.gaus-Management of Life-Threatening (Kuliah Sistem) 2Document46 pagesS.gaus-Management of Life-Threatening (Kuliah Sistem) 2Ta RaNo ratings yet
- Acid - Base Basics: Dr. Fawzeya Aboul Fetouh Prof of Anesthesia Cairo UnversityDocument54 pagesAcid - Base Basics: Dr. Fawzeya Aboul Fetouh Prof of Anesthesia Cairo UnversityPaolo Uccello100% (1)
- Acid Base TutorialDocument74 pagesAcid Base TutorialuedmarineNo ratings yet
- Acid Base: Prep by Clement UWASE PGY2Document48 pagesAcid Base: Prep by Clement UWASE PGY2TWISUNGANE PROTOGENENo ratings yet
- Acid Base ImbalanceDocument32 pagesAcid Base ImbalanceIftikhar AliNo ratings yet
- Acid - Base BalanceDocument37 pagesAcid - Base BalanceSittie RamosNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Dr. Taufin SpOT - Operating RoomDocument29 pages3.2 Dr. Taufin SpOT - Operating RoomTaqwatin Ma'rifahNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Dr. Taufin SpOT - Operating RoomDocument29 pages3.2 Dr. Taufin SpOT - Operating RoomTaqwatin Ma'rifahNo ratings yet
- Appendectomy in BPJSDocument29 pagesAppendectomy in BPJSRinthoNo ratings yet
- AWM - BURN Series 3 - Infection Management in Burns - 24072020Document2 pagesAWM - BURN Series 3 - Infection Management in Burns - 24072020RinthoNo ratings yet
- Mengambil Tindakan Yang Tepat Untuk Mengendalikan COVID-19Document2 pagesMengambil Tindakan Yang Tepat Untuk Mengendalikan COVID-19PERDHAKINo ratings yet
- 3M Publication DecontaminationDocument4 pages3M Publication DecontaminationAgus Gede Made ArthaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Disinfektan UpdateDocument2 pagesDaftar Disinfektan UpdateSRINo ratings yet
- Ventilation Cleaning DesinfectingDocument5 pagesVentilation Cleaning DesinfectingRinthoNo ratings yet
- 631 1571 1 PB PDFDocument5 pages631 1571 1 PB PDFRinthoNo ratings yet
- Above Knee AmputationDocument8 pagesAbove Knee AmputationAbdul Ghafoor SajjadNo ratings yet
- Why Your Muscles Get SoreDocument11 pagesWhy Your Muscles Get SoreanaluieNo ratings yet
- Assesment Preop - Rohemi 28.09.21Document27 pagesAssesment Preop - Rohemi 28.09.21Reza Devianto HambaliNo ratings yet
- Pharma NotesDocument69 pagesPharma NotesJawad Ahmad100% (1)
- 2016 Opioid Presribing Rate Part DDocument104 pages2016 Opioid Presribing Rate Part DJennifer EmertNo ratings yet
- Proforma For PH CertificateDocument2 pagesProforma For PH CertificateDivakar MauryaNo ratings yet
- Blood CancerDocument22 pagesBlood CanceranjanaNo ratings yet
- Sleep Consult TemplateDocument5 pagesSleep Consult Templatesbonvallet3912100% (1)
- OT Relevance RMTDocument12 pagesOT Relevance RMTFredy RamoneNo ratings yet
- HSN CodesDocument50 pagesHSN CodesManoj T PNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal DetailsDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Personal DetailskadekNo ratings yet
- Ethical Dilemma PaperDocument6 pagesEthical Dilemma PaperMary KenuiNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Central Nervous System 2A2016Document63 pagesPathology of The Central Nervous System 2A2016Rose AnnNo ratings yet
- Arabic Clerking Etc-3Document26 pagesArabic Clerking Etc-3walefamousNo ratings yet
- Prevalence of Rifampicin Resistance Tuberculosis and Associated Factors Among Presumptive TB or MDRDocument3 pagesPrevalence of Rifampicin Resistance Tuberculosis and Associated Factors Among Presumptive TB or MDRTigray OutlookNo ratings yet
- Pricelist 13 Juli 2020Document21 pagesPricelist 13 Juli 2020Achmad Sya'idNo ratings yet
- Activity Instructions FdarDocument10 pagesActivity Instructions FdarJae HeeNo ratings yet
- Difficulty in SwallowingDocument1 pageDifficulty in SwallowingmawelNo ratings yet
- Drug Information of SilodosinDocument8 pagesDrug Information of SilodosinSomanath BagalakotNo ratings yet
- COPARDocument7 pagesCOPARMar VinNo ratings yet
- Dengue Fever: Centre For Health Protection, Department of Health October 2019Document18 pagesDengue Fever: Centre For Health Protection, Department of Health October 2019Rajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Types: There Is A Range Of, IncludingDocument15 pagesTypes: There Is A Range Of, IncludingBhossneil Betonio LacadenNo ratings yet
- 3.trauma Vaskular Richard SDocument79 pages3.trauma Vaskular Richard SAdang SunandarNo ratings yet
- PTSD - Diagnostic CriteriaDocument5 pagesPTSD - Diagnostic Criteriagreg sNo ratings yet
- Lidocaine Infusion A Promising Therapeutic Approach For Chronic PainDocument14 pagesLidocaine Infusion A Promising Therapeutic Approach For Chronic PaingabhekNo ratings yet
- Screening For Psychological Burden of Vitiligo Using Vitiligo Impact ScaleDocument6 pagesScreening For Psychological Burden of Vitiligo Using Vitiligo Impact ScaleNadaaFahmiShofiNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument70 pagesCancerapi-3735995100% (1)
- nsg-320cc Care Plan 1Document14 pagesnsg-320cc Care Plan 1api-509452165No ratings yet
- Mat Presentation ProvidersDocument13 pagesMat Presentation Providersapi-649066372No ratings yet
- Acute Necrotizing Sinusitis Caused by Staphylococcus Lugdunensis 2011Document3 pagesAcute Necrotizing Sinusitis Caused by Staphylococcus Lugdunensis 2011J Sebastian PeinadoNo ratings yet
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (24)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (80)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyFrom EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)