Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revenue Recognition: Understanding the Key Concepts and Steps
Uploaded by
kathlene keith navarroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Revenue Recognition: Understanding the Key Concepts and Steps
Uploaded by
kathlene keith navarroCopyright:
Available Formats
Revenue Recognition
First, lets define What is Revenue?
Revenue is the income generated from normal business operations. It is the top line or
gross income figure from which costs are subtracted to determine net income. It is the
money brought into a company by its business activities. And it is considered as the heart
of all business performance.
Next, What is Revenue Recognition?
Revenue recognition is an accounting principle that outlines the specific conditions under
which revenue is recognized.
Conditions for Revenue Recognition
For a revenue to be recognized, the following conditions must be satisfied:
1.Risks and rewards of ownership have been transferred from the seller to the buyer.
2.The seller does not have control any longer over the goods sold.
3.The collection of payment from goods or services is reasonably assured.
4.The amount of revenue can be reasonably measured.
5.Costs of revenue can be reasonably measured.
Conditions (1) and (2) are referred to as Performance. Regarding performance, it occurs
when the seller has done what is to be expected to be entitled to payment.
Condition (3) is referred to as Collectability. The seller must have a reasonable
expectation that he or she will be paid for the performance.
Conditions (4) and (5) are referred to as Measurability. the seller must be able to match
the revenues to the expenses. Hence, both revenues and expenses should be able to be
reasonably measured.
Steps in Revenue Recognition from Contracts
The five steps for revenue recognition in contracts are as follows:
1. Identifying the Contract
•Both parties must have approved the contract (whether it be written, verbal, or implied).
•The point of transfer of goods and services can be identified.
•Payment terms are identified.
•Collection of payment is probable.
2. Identifying the Performance Obligations
Performance obligations must be distinct from each other. The following conditions must
be satisfied for a good or service to be distinct:
•The buyer (customer) can benefit from the goods or services on its own.
•The good or service is separately identified in the contract.
3. Determining the Transaction Price
The transaction price is usually readily determined; most contracts involve a fixed amount.
4. Allocating the Transaction Price to Performance Obligations
The allocation of the transaction price to more than one performance obligation should be
based on the standalone selling prices of the performance obligations.
5. Recognizing Revenue in Accordance with Performance
Recall the conditions for revenue recognition. Conditions (1) and (2) state that revenue
would be recognized when the seller has done what is expected to be entitled to payment.
Therefore, revenue is recognized either:
•At a point in time; or
•Over time
accrual accounting/accruals. It is the accounting principle that recognizes revenue when
earned and associated expenses when incurred, not when money is received/paid.
cash accounting. It is the accounting principle that recognizes revenue when cash is
received and recognizes expense when cash is paid.
2 Methods of Revenue Recognition
1. Completed Contract Method- under this method, all revenues, costs, and
income are recognized only at completion of the construction project, ordinarily
at the end of the construction contract.
2. Next is what our company has been currently using-the % of Completion
Method – wherein recognizes revenue over the life of the construction contract
based on the degree of completion. revenue is recognized proportionately to
"the extent of work accomplished" by the contractor and is usually documented
or attested to by an engineer
% complete = Total costs incurred to date/ Estimated total cost
The percentage of completion is then derived from a simple formula, "actual
costs incurred to date" divided by "estimated total costs to complete the
contract". In this formula, the total cost to complete a project is equal to actual
costs incurred to date for a project plus the estimated costs to complete the
project.
You might also like
- Revenue Recognition Principles ExplainedDocument8 pagesRevenue Recognition Principles ExplainedshekarNo ratings yet
- Revenue RecognitionDocument6 pagesRevenue RecognitionBOBBY212No ratings yet
- Revenue recognition key conceptsDocument5 pagesRevenue recognition key conceptsadela_iunieNo ratings yet
- BAB 6 Analyzing Operating ActivitiesDocument56 pagesBAB 6 Analyzing Operating ActivitiesMaun GovillianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document29 pagesChapter 3Minh Khanh LeNo ratings yet
- Revenue Recognition MethodsDocument14 pagesRevenue Recognition MethodsPiyushE63No ratings yet
- AS9 Revenue RecognitionDocument2 pagesAS9 Revenue RecognitionrajNo ratings yet
- Revenue From Contracts With Customers: Pfrs 15Document23 pagesRevenue From Contracts With Customers: Pfrs 15Marimel TizonNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument32 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisMuhammad KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Revenue:: Presenting Revenue: Gross vs. Net RevenueDocument3 pagesRevenue:: Presenting Revenue: Gross vs. Net RevenueNaureen AyubNo ratings yet
- Understanding Income StatementsDocument62 pagesUnderstanding Income StatementsJhoni LimNo ratings yet
- Revenue Recognition EssentialsDocument13 pagesRevenue Recognition EssentialsAnastasha GreyNo ratings yet
- AFARevenue RecognitionDocument34 pagesAFARevenue RecognitionRameen ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Revenue Recognition Issues GuideDocument13 pagesRevenue Recognition Issues Guideraghavendra_20835414No ratings yet
- 07FAR1 IM Ch7 1LPDocument4 pages07FAR1 IM Ch7 1LPargxn22No ratings yet
- 2019 CIA P3 SIV 1D 1 Revenue CycleDocument15 pages2019 CIA P3 SIV 1D 1 Revenue CycleMarieJoiaNo ratings yet
- Timing of Revenue RecognitionDocument22 pagesTiming of Revenue Recognitionmc2hin9No ratings yet
- REVENUE RECOGNITION and MeasurementDocument16 pagesREVENUE RECOGNITION and MeasurementMukesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- $RJABQCODocument28 pages$RJABQCONgọc Tâm Anh đang học bài T.TNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3Nguyễn Quỳnh AnhNo ratings yet
- Cfas Revenue Recognition - StudentsDocument41 pagesCfas Revenue Recognition - StudentsMiel Viason CañeteNo ratings yet
- What is Revenue and How is it RecognizedDocument9 pagesWhat is Revenue and How is it RecognizedonsongoalexmunaviNo ratings yet
- Engage - Revenue Recognition-1Document129 pagesEngage - Revenue Recognition-1Johhahawie jajwiNo ratings yet
- Revenue Recognition Semester 1Document19 pagesRevenue Recognition Semester 1AbhayNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting 1 UnIt 5Document29 pagesFinancial Accounting 1 UnIt 5chuchuNo ratings yet
- IAS 18 Revenue: Technical SummaryDocument2 pagesIAS 18 Revenue: Technical SummaryKyleRodSimpsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Revenue RecognitionDocument7 pagesChapter 6 - Revenue RecognitionGebeyaw BayeNo ratings yet
- Revenue Recognition PPPDocument69 pagesRevenue Recognition PPPmyschoolwork100% (1)
- A Simple Definition of Income Measurement Is The Calculation of Profit or LossDocument7 pagesA Simple Definition of Income Measurement Is The Calculation of Profit or LossKirosTeklehaimanotNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PFRS 15 Revenue From Contracts With CustomersDocument4 pagesReviewer PFRS 15 Revenue From Contracts With CustomersJezela CastilloNo ratings yet
- Booklet 6 PFRS LTCC Service Concession & FranchiseDocument57 pagesBooklet 6 PFRS LTCC Service Concession & FranchisejustoahrajoyceNo ratings yet
- Ipsas - 9 - Revenue From Exchange TransactionDocument24 pagesIpsas - 9 - Revenue From Exchange TransactionduncanNo ratings yet
- IAS18Document2 pagesIAS18Farah DibaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 Long Term ConstructionDocument13 pagesLesson 9 Long Term ConstructionheyheyNo ratings yet
- 4 Recognition PrinciplesDocument7 pages4 Recognition PrinciplesShamae Duma-anNo ratings yet
- Accounting Notes ALL at MBADocument43 pagesAccounting Notes ALL at MBABabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- BAB 6 Analyzing Operating Activities 081016Document56 pagesBAB 6 Analyzing Operating Activities 081016Haniedar NadifaNo ratings yet
- Residual Equity TheoryDocument3 pagesResidual Equity Theorybrix simeonNo ratings yet
- In Accounting For ContractsDocument7 pagesIn Accounting For Contractsone formanyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 - Income Measurement and Profitability AnalysisDocument38 pagesChapter 05 - Income Measurement and Profitability Analysismad2kNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 2 Revenue From ContractsDocument13 pagesStudy Unit 2 Revenue From ContractsKarabo MofokengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 Revenue RecognitionDocument15 pagesChapter 18 Revenue RecognitionjingyanNo ratings yet
- Accounting Period Shareholders DividendsDocument3 pagesAccounting Period Shareholders DividendsAmaranathreddy YgNo ratings yet
- Accounting Seminar - Assignment CH 10 (Doni Rahmad & Fachriza Mizafin)Document5 pagesAccounting Seminar - Assignment CH 10 (Doni Rahmad & Fachriza Mizafin)Kazuyano DoniNo ratings yet
- Recenue Recognition PDFDocument33 pagesRecenue Recognition PDFVinay GoyalNo ratings yet
- Construction ContractsDocument33 pagesConstruction ContractsJaira Mae AustriaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal MartinDocument6 pagesJurnal MartinastridNo ratings yet
- BS Is RatioAnalysisDocument84 pagesBS Is RatioAnalysisSujit ParabNo ratings yet
- Income Statement: Alexei Alvarez, CFA, FRM Fabricio Chala, CFA, FRMDocument53 pagesIncome Statement: Alexei Alvarez, CFA, FRM Fabricio Chala, CFA, FRMJhonatan Perez VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Fa Chapter 3Document24 pagesFa Chapter 3Abdii DhufeeraNo ratings yet
- Understanding Revenue RecognitionDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Revenue RecognitionMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- PSAK 72 - Revenue From Contracts With Customers: Alya Khaira Nazhifa (1710531009) Amelia Rahmadani P.A (1710531019)Document31 pagesPSAK 72 - Revenue From Contracts With Customers: Alya Khaira Nazhifa (1710531009) Amelia Rahmadani P.A (1710531019)ameNo ratings yet
- Construction Contract - EDITED Reporting-ASTDocument70 pagesConstruction Contract - EDITED Reporting-ASTVatchdemonNo ratings yet
- MODULE 8 (Part 2)Document6 pagesMODULE 8 (Part 2)trixie maeNo ratings yet
- IFRS 15 - Revenue From Contracts With CustomersDocument7 pagesIFRS 15 - Revenue From Contracts With CustomersamananandxNo ratings yet
- GAAP: Generally Accepted Accounting PrinciplesDocument7 pagesGAAP: Generally Accepted Accounting PrinciplesTAI LONGNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Franchise Operations2Document21 pagesAccounting For Franchise Operations2Jaira Mae AustriaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandIntermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- 1040 Exam Prep Module III: Items Excluded from Gross IncomeFrom Everand1040 Exam Prep Module III: Items Excluded from Gross IncomeRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Financial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?From EverandFinancial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Build Simple CSHP for Residential ConstructionDocument2 pagesBuild Simple CSHP for Residential Constructioneliabeth dagunoNo ratings yet
- Plumbing PowerPoint Template 4 3Document4 pagesPlumbing PowerPoint Template 4 3kathlene keith navarroNo ratings yet
- Sanitizing Stored Water Supplies: Guide W-101Document2 pagesSanitizing Stored Water Supplies: Guide W-101kathlene keith navarroNo ratings yet
- PD 1586 The Philippine EIS SystemDocument101 pagesPD 1586 The Philippine EIS Systemkathlene keith navarroNo ratings yet
- DMC 2002-03 PDFDocument5 pagesDMC 2002-03 PDFRyan BosngonNo ratings yet
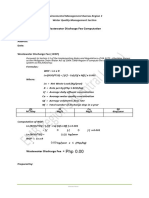
- Wastewater Discharge Fee Computation SecuredDocument1 pageWastewater Discharge Fee Computation Securedkathlene keith navarroNo ratings yet
- DMC 2002-03 PDFDocument5 pagesDMC 2002-03 PDFRyan BosngonNo ratings yet
- SMR Blank FormDocument18 pagesSMR Blank FormVinz SelabeNo ratings yet
- Seismic AnalysisDocument17 pagesSeismic Analysiskathlene keith navarroNo ratings yet
- Advanced Taxation: Page 1 of 8Document8 pagesAdvanced Taxation: Page 1 of 8Muhammad Usama SheikhNo ratings yet
- R17 - Understanding Income Statements - 2022Document57 pagesR17 - Understanding Income Statements - 2022Ihuomacumeh100% (1)
- Important Formats For o Level Accounting 2Document23 pagesImportant Formats For o Level Accounting 2abdulmuqsit055No ratings yet
- Taxability of The Gifts During The (1) : (2) MarchDocument3 pagesTaxability of The Gifts During The (1) : (2) MarchKetan BhoiNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis - Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesCVP Analysis - Lecture NotesOtenyo MeshackNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 (New)Document3 pagesActivity 3 (New)Sharina Mhyca SamonteNo ratings yet
- Income Tax For Corporation PDFDocument7 pagesIncome Tax For Corporation PDFKristine Lirose BordeosNo ratings yet
- What Is A Business Partnership?Document3 pagesWhat Is A Business Partnership?Skylar FunnelNo ratings yet
- Taxation Sec A May 2024 1703224575Document10 pagesTaxation Sec A May 2024 1703224575Umang NagarNo ratings yet
- Basic Framework of Direct TaxationDocument41 pagesBasic Framework of Direct TaxationKirankumarkvNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Mcgraw Hills Taxation of Individuals 2020 Edition 11th by SpilkerDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Mcgraw Hills Taxation of Individuals 2020 Edition 11th by Spilkergenevieveprattgllhe100% (23)
- How State Funding Models Can Cause Educational InequalityDocument5 pagesHow State Funding Models Can Cause Educational InequalityIjahss JournalNo ratings yet
- Girum Tsega PerfectDocument13 pagesGirum Tsega PerfectMesi YE GINo ratings yet
- Payslip For The Month of Mar 2021Document1 pagePayslip For The Month of Mar 2021Loan LoanNo ratings yet
- Accounting Fundamentals 1 Learning Activity SheetsDocument95 pagesAccounting Fundamentals 1 Learning Activity SheetsCHRISTINE JOY BONDOC100% (1)
- MAXIMIZES RETIREMENT INCOME THROUGH TAX EFFICIENCYDocument12 pagesMAXIMIZES RETIREMENT INCOME THROUGH TAX EFFICIENCYPalak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Acc407 Test 2 Feb 2022 QQ (1) EpjjDocument6 pagesAcc407 Test 2 Feb 2022 QQ (1) EpjjShahrillNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of WALMART INCDocument5 pagesRatio Analysis of WALMART INCBrian Ng'enoNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting - Group ReportingDocument18 pagesFinancial Accounting - Group ReportingPravallika RavikumarNo ratings yet
- Section 194J - TDS On Fees For Professional or Technical ServicesDocument24 pagesSection 194J - TDS On Fees For Professional or Technical ServicesShaik MastanvaliNo ratings yet
- Exercise 7-7. Multiple Choice Problem: Items 1 and 2 Are Based On The Following InformationDocument14 pagesExercise 7-7. Multiple Choice Problem: Items 1 and 2 Are Based On The Following InformationSheie WiseNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Midterm ExamDocument2 pagesIncome Tax Midterm ExamWycliffe Luther RosalesNo ratings yet
- BE National AccountsDocument3 pagesBE National AccountsfarwaNo ratings yet
- ACW1120-Practice Questions: Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesACW1120-Practice Questions: Page 1 of 5Gan ZhengweiNo ratings yet
- Sivanesan Project ReportDocument6 pagesSivanesan Project ReportSivanesan RamamoorthyNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Basic ConceptsDocument6 pagesCH 1 Basic Conceptscaps videosNo ratings yet
- ACCTG1 PrefinalsDocument23 pagesACCTG1 PrefinalsJAN RAY CUISON VISPERAS100% (1)
- Lecture Notes Dealings in PropertyDocument9 pagesLecture Notes Dealings in PropertyweewoouwuNo ratings yet
- Special Tansaction Quiz 1 and 2Document4 pagesSpecial Tansaction Quiz 1 and 2Helen Fiedalan Falcutila MondiaNo ratings yet
- INTAX 01 - General PrinciplesDocument5 pagesINTAX 01 - General PrinciplesDjustize GaboniNo ratings yet