Professional Documents
Culture Documents
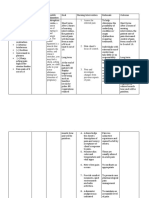
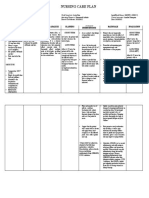
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Outcome Intervention Implementation Evaluation
Uploaded by
Nur Fatima SanaaniOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Outcome Intervention Implementation Evaluation
Uploaded by
Nur Fatima SanaaniCopyright:
Available Formats
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
(NURSING CARE PLAN) NCP
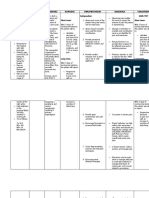
Assessment Nursing Nursing Intervention Implementation Evaluation
diagnosis outcome
Subjective Acute pain related After 8 hours of Consider reports of After 8 hours of
“Hindi ako pwede to distension of nursing care, pain, noting location Considered nursing care,
tumayo o umupo ng tissues by the patient will and intensity. Note reports of pain, patient will
matagal dahil sasakit accumulation of incorporate nonverbal pain cues. noting location incorporate
ang tuhod ko,” as fluid/inflammatory relaxation skills and intensity. relaxation skills
verbalized by patient. process, Reports and diversional Assess and manage and diversional
of activities into chronic and acute pain. activities into
Objective pain/discomfort, the pain control Favorable in Assessed and the pain control
vital signs: fatigue program: determining pain managed chronic program:
BP: 110/90 mmHg -reduced pain management needs and acute pain. -reduced pain
PR: 94 cpm sensation in and effectiveness of the sensation in
RR: 18 bpm joints program. Assessed home joints
Temperature: 37.5 C -Able to Have environment for -Able to Have
O2 Sat: 97% minimal motility Assess home factors that adequate
Pale during motion environment for factors create barriers to motility during
Active and of movement that create barriers to physical mobility. motion of
responsive -Reduce the physical mobility. To movement
Unable to bend pain scale from know if client needs Maintained bed -Reduce the pain
knee 7 out of 10, to 4 referral. rest or chair rest scale from 7 out
completely out of 10 when indicated. of 10, to 4 out of
Swelling on left Maintain bed rest or 10
and right chair rest when Recommend or
patella indicated. Schedule provided a firm
Limited ROM frequent rest periods mattress or
Rheumatoid and uninterrupted bedboard, small
nodules on nighttime sleep. pillow. Elevate
small joints of Systemic rest is linens with bed
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
fingers, wrist mandatory during cradle as
and toes. acute exacerbations needed.
Gait changes and important
Pain scale of 7 out of 10 throughout all phases Established
of disease to reduce frequent changes
fatigue, improve of position. Assist
strength. the patient to
move in bed,
Recommend or provide supported
a firm mattress or affected joints
bedboard, small pillow. above and below,
Elevate linens with bed avoiding jerky
cradle as needed. movements.
Soft and sagging
mattress, large pillows Established
prevent maintenance patient to
of proper body perform ADLs
alignment, placing such as
stress on affected practicing good
joints. Elevation of bed hygiene,
linens reduces pressure dressing, and
on inflamed or painful feeding himself
joints.
Provided patient
Encourage frequent to take a warm
changes of position. bath or shower
Assist the patient to upon arising or at
move in bed, bedtime. Applied
supporting affected warm, moist
joints above and below, compresses to
avoiding jerky affected joints
movements. Prevents several times a
general fatigue and day. Monitored
joint stiffness. Stabilizes water
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
joint, decreasing joint temperature of
movement and compress, baths,
associated pain. and so on.
Urge patient to perform
ADLs such as practicing Encouraged
good hygiene, dressing, activity/exercise
and feeding himself to as tolerated.
promote self-care ADLs Patients feel
that can be done fatigue easily, but
should be encouraged daily exercise can
to maximize and help loosen
function. joints.
Recommend that
patient take a warm Administered
bath or shower upon medication
arising or at bedtime. appropriately
Apply warm, moist
compresses to affected
joints several times a Established
day. Monitor water positive self-
temperature of image.
compress, baths, and
so on. Heat
promotes muscle relax Discussed and
ation and mobility, provided safety
decreases pain, and needs such as
relieves morning raised chairs
stiffness. Sensitivity to and toilet seat,
heat may be use of handrails
in shower and
diminished and dermal
toilet, proper
injury may occur.
use of mobility
Encourage aids.
activity/exercise as
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
tolerated. Patients feel
fatigue easily, but daily
exercise can help Nutrition and
loosen joints. Promotes lifestyle
joint stability to reduce education.
risk of injury, maintain Educated
proper body position. patients make
healthy diet
choices by
Administer medication
following an
appropriately To reduce anti-
inflammation and slow inflammatory
joint damage. diet..
Promote positive self-
image. Patients with
joint deformities may
experience a negative
body image
Discuss and provide
safety needs such as
raised chairs and toilet
seat, use of handrails in
shower and toilet,
proper use of mobility
aids. Relieves pressure
on tissues and
promotes circulation.
Facilitates self-care and
patient’s
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
independence.
Nutrition and lifestyle
education. Educate
patients make healthy
diet choices by
following an anti-
inflammatory diet.
Encourage hydration.
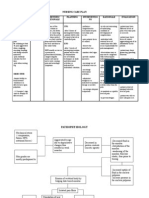
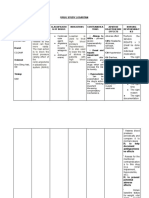
Learning objectives Content outline Method(s) of Time allotted Resources Method of
teaching(teaching (instruction evaluation
strategies) materials)
After 15-45mins of Interactive
health teaching on food 1. (definition) lecture with visual
poisoning, client will be Rheumatoid arthritis images and
able to: (RA), is a type of demonstration
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
arthritis that results in 3mins Flyers infographic
1. Defined what is joint pain, swelling,
rheumatoid stiffness, and loss of 1. By
arthritis is function (mediline, sharing
2. Differentiate 2012). An autoimmune facts and
rheumatoid disease that causes the informati
arthritis body to attack its own on about
3. Enumerate the soft tissue and joints on how
available a systemic level. rheumato
treatment and Rheumatoid arthritis id
management in affects the hands and arthritis
bouts related to feet the most, although because a
pain due to it can also affect the burdens
rheumatoid elbows, shoulders, and to one’s
arthritis neck. life Standardized test,
4. State the 2. Rheumatoid arthritis 10mins Inforgraphic and Q and A
importance of versus other types of
compliance to arthritis 2. By citing
treatment and -osteoarthritis(While it example
management to is commonly referred that
lessen to as "wear-and-tear" trigger
complication arthritis, this ailment is the
5. Display a caused by more than occurrenc
positive just the surface of the e of the Demonstration of
behaviour in the joints wearing away. disease video, and live
course of health The most prevalent and its
teaching type of arthritis is complica Active recall of
osteoarthritis. It is most tion if it the educatiosn
commonly caused by worsen
pain and limited
motion in the knee and 3. By
hip joints.) showing
-gouty arthritis (is a picture
condition that is caused what it
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
by the accumulation of looks like
crystals made of urate to be a
within the joints. The person
urate crystals are with
formed by an unusual rheumato
breakdown of normal id
body surface. arthritis
Accumulation of urate
within joints causes 4. By briefly
gouty arthritis, thse explain
most commonly affced the topic
joints are the big toe, by using
and the knee. ) images
-juvenile rheumatoid and
arthritis, or JRA(is portraits
another auto-immune
condition, but it tends 5. By
to affects children and encouragi
adolescent, there is a ) ng
cooperati
3. Etiology and clinical on and
manifestation active
-Although the specific participati
etiology of RA is on during
unknown, it appears the
that the disease is discussion
caused by a
combination of genetic
predisposition,
environmental triggers,
and chance. 9 The
genetic contribution to
the variance in RA
liability, which is
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
equivalent to RA
heritability, was
investigated in a study
of monozygotic and
dizygotic twins.
-Clinical manifestations
of RA vary, usually Lecture discussion
reflecting the stage and
severity of tge disease:
*Joint pain. One of the
classic signs, joints that
are painful are not
easily moved.
*Swelling. Limitation in
function occurs as a Demonstration
result of swollen joints.
*Warmth. There is Inquiry-based
warmth in the affected instruction
joint and upon
palpation, the joints are
spongy or boggy.
*Erythema. Redness of
the affected area is a
sign of inflammation.
*Lack of function.
Because of the pain,
mobilizing the affected
area has limitations.
*Deformities.
Deformities of the
hands and feet may be
caused by
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
misalignment resulting
in swelling.
*Rheumatoid nodules.
Rheumatoid nodules
may be noted in
patients with more
advanced RA, and they
are nontender and
movable in the
subcutaneous tissue.
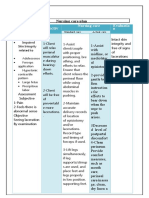
4. Complication
-Rheumatoid arthritis
medications can have
dangerous and perhaps
fatal side effects.
Suppression of the
bone marrow.
Immunosuppressants
used incorrectly can
cause bone marrow
suppression.
Anemia.
Immunosuppressive
drugs like
methotrexate and
cyclophosphamide are
extremely dangerous
and can cause anemia.
Disturbances in the
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
gastrointestinal tract.
Gastric inflammation
and ulceration are
possible side effects of
several NSAIDs.
5. Available treatment
-The drugs used in
each phase of
rheumatoid arthritis
include:
Early Rheumatoid
Arthritis
*NSAIDs. COX-2
medications block the
enzyme involved in
inflammation while
leaving intact the
enzyme involved in
protecting the stomach
lining.
*Methotrexate.
Methotrexate is
currently the standard
treatment of RA
because of its success
in preventing both joint
destruction and long-
term disability.
*Analgesics. Additional
analgesia may be
prescribed for periods
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
of extreme pain.
Moderate, Erosive
Rheumatoid Arthritis
*Cyclosporine. Neoral,
an immunosuppressant
is added to enhance
the disease modifying
effect of methotrexate.
Persistent, Erosive
Rheumatoid Arthritis
*Corticosteroids.
Systemic
corticosteroids are
used when the patient
has unremitting
inflammation and pain
or needs a “bridging”
medication while
waiting for slower
DMARDs to begin
taking effect.
Advanced, Unremitting
Rheumatoid Arthritis
*Immunosuppressants
. Immunosuppressive
agents are prescribed
because of their ability
to affect the production
of antibodies at the
cellular level.
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
*Antidepressants. For
most patients with RA,
depression and sleep
deprivation may
require the short-term
use of low-dose
antidepressants such as
amitriptyline,
paroxetine, or
sertraline, to
reestablish an
adequate sleep pattern
and to manage chronic
pain.
6. Therapy
For persistent, erosive RA,
reconstructive surgery is
often used.
*Reconstructive surgery.
Reconstructive surgery is
indicated when pain cannot
be relieved by conservative
measures and the threat of
loss of independence is
eminent.
*Synovectomy.
Synovectomy is the
excision of the synovial
membrane.
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
*Tenorrhaphy.
Tenorrhaphy is the suturing
of a tendon.
*Arthrodesis. Arthrodesis
is the surgical fusion of the
joint.
*Arthroplasty. Arthroplasty
is the surgical repair and
replacement of the joint.
7. Mom-pharmacological
management
*Rest enough to avoid
fatigue
*Exercises for
conditioning and
maintaining strength
and flexibility
*Local therapy
including moist hot
packs or cold following
trauma
*Physical supports for
wrists for pain control,
although does not
prevent deformity
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA,M
NCM-114J
*Patient education and
psychosocial support
*Orthopedic surgery to
repair structural
damage that may lead
to disability over the
long term
NCM 114 Geriatric Assessment
You might also like
- Pain Free 1-2-3: A Proven Program for Eliminating Chronic Pain NowFrom EverandPain Free 1-2-3: A Proven Program for Eliminating Chronic Pain NowRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Desired Outcomes Subjective: "Napakasakit NG Mga Kasukasuhan Ko" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument5 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Desired Outcomes Subjective: "Napakasakit NG Mga Kasukasuhan Ko" As Verbalized by The PatientAngelou Mortos100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan of Breech PresentationDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan of Breech PresentationDr-Sanjay Singhania100% (3)
- Kinesiology Taping for Rehab and Injury Prevention: An Easy, At-Home Guide for Overcoming Common Strains, Pains and ConditionsFrom EverandKinesiology Taping for Rehab and Injury Prevention: An Easy, At-Home Guide for Overcoming Common Strains, Pains and ConditionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Nursing Care Plan2Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan2gaeLtorvzNo ratings yet
- OA NCPDocument5 pagesOA NCPsnow.parconNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluatio NFc CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- NCP OsteosarcomaDocument1 pageNCP OsteosarcomaDarylle Hannah De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Mrs. Patao Ob Ward, GSGH Assessment SubjectiveDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Mrs. Patao Ob Ward, GSGH Assessment Subjectiveraizelc100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Pott's DiseaseDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Pott's Diseasederic95% (21)
- Nursing Care Plan2Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan2Fc CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainAngel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain OsteosarcomaDocument8 pagesAcute Pain OsteosarcomaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan-Well Pregnant ClientDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan-Well Pregnant ClientWallen Jey Velasco100% (3)
- Assessment Cues Nursing Outcome Planning Nursing Interventions Evaluation Diagnosis Identification Interventions RationaleDocument6 pagesAssessment Cues Nursing Outcome Planning Nursing Interventions Evaluation Diagnosis Identification Interventions RationaleAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Problem List 1. Acute Pain 2. Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements 3. Impaired Physical Mobility 4. Impaired Skin Integrity 5. Disturbed Body ImageDocument12 pagesProblem List 1. Acute Pain 2. Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements 3. Impaired Physical Mobility 4. Impaired Skin Integrity 5. Disturbed Body Imagebernadette babaranNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Labor Pain FinaloutputDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Labor Pain FinaloutputVic Intia Paa100% (5)
- NCP NewDocument16 pagesNCP Newmsfts.No ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationGj PaguidianNo ratings yet
- Norbe COMFORT MEASURESDocument10 pagesNorbe COMFORT MEASURESMarlo Dañez NorbeNo ratings yet
- NCP Cholecystectomy RevisedDocument7 pagesNCP Cholecystectomy RevisedMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan-Herniated Nucleus PulposusDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan-Herniated Nucleus PulposusJasmin Jacob67% (3)
- Case Scenario 5 NCPDocument10 pagesCase Scenario 5 NCPkdfhjfhfNo ratings yet
- Planning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byDocument10 pagesPlanning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byNicole Anne TungolNo ratings yet
- NCP - Fluids & ElectrolytesDocument12 pagesNCP - Fluids & ElectrolytesAnabelle RicoNo ratings yet
- Assessmen T Nursing Diagnosi S Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Cues: Independent IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessmen T Nursing Diagnosi S Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Cues: Independent IndependentKim Glaidyl BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Wabinga, Shyn Margareth B. Sas 23 Case Study BDocument3 pagesWabinga, Shyn Margareth B. Sas 23 Case Study BShyn MargarethNo ratings yet
- TablesDocument10 pagesTablesCAMILLE GAIL HADJIRANINo ratings yet
- NCP 2020Document5 pagesNCP 2020Gwen Stefanie Lagrimas ValloyasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Basis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationAgnes GeolinaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlansAngelie Sanchez86% (14)
- La Salle University Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesLa Salle University Nursing Care PlanKristine NacuaNo ratings yet
- Subjective Data: Objective Data: - Well Appearing But Independent Nursing Interventions: - Review Intraoperative Desired Outcome. Goal Met. Patient Was Able ToDocument3 pagesSubjective Data: Objective Data: - Well Appearing But Independent Nursing Interventions: - Review Intraoperative Desired Outcome. Goal Met. Patient Was Able ToMariel GamaloNo ratings yet
- Final Zollinger-Ellison SyndromeDocument9 pagesFinal Zollinger-Ellison SyndromeGLYDEL CORDERONo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid NCPDocument2 pagesRheumatoid NCPMARK OLVIER E. MELCHORNo ratings yet
- نسخة vaginal delieveryDocument4 pagesنسخة vaginal delieveryرهف الرفاعيNo ratings yet
- NCP ReviseDocument7 pagesNCP ReviseRhobic ManansalaNo ratings yet
- NCP Case StudyDocument21 pagesNCP Case StudyMontero, Ma. Cecilia - BSN 3-BNo ratings yet
- Manguiat, Ncma 111 RomeoDocument4 pagesManguiat, Ncma 111 RomeoCiara ManguiatNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 Impaired Physical MobilityDocument3 pagesNCP 1 Impaired Physical Mobilityaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- NSG Process JohnsonDocument11 pagesNSG Process JohnsonvishnukulakkadaNo ratings yet
- NCP Breast CADocument3 pagesNCP Breast CAreeyahjonna100% (8)
- NCP ImmobilityDocument1 pageNCP ImmobilityBcoi QuilacioNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJanice SolamilloNo ratings yet
- Pain - Post Partum MotherDocument2 pagesPain - Post Partum Motherulrikov91% (11)
- NCPDocument18 pagesNCPStephanie Villanueva AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Romero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Gouty Arthritis)Document15 pagesRomero, Deinielle Ingrid M. (Gouty Arthritis)Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- Pain Related To Perineal Suture NCPDocument3 pagesPain Related To Perineal Suture NCPDharylle CariñoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Operative (Incision & Drainage of Abscess)Document6 pagesPre-Operative (Incision & Drainage of Abscess)Eunice MañalacNo ratings yet
- NCP Proper Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNCP Proper Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMarc Jordan EstebanNo ratings yet
- NCP FormatDocument1 pageNCP FormatNathaniel NograNo ratings yet
- Sabalo NCP 1Document2 pagesSabalo NCP 1baby_doll05062003No ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Post Operation and Impaired MobilityDocument9 pagesAcute Pain Related To Post Operation and Impaired MobilityChryst Louise SaavedraNo ratings yet
- NCP Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument2 pagesNCP Rheumatoid ArthritisPatty RomeroNo ratings yet
- NCP Breast CADocument3 pagesNCP Breast CAHannah Lacambra100% (1)
- Nurco-2 (Deliverables) Group 4-2Document3 pagesNurco-2 (Deliverables) Group 4-2Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- 7 Bates Assessment ToolDocument10 pages7 Bates Assessment ToolNur Fatima Sanaani0% (1)
- (Case Week 5-6) With DaranginaDocument3 pages(Case Week 5-6) With DaranginaNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Kardex VS Monitoring Sheet SanaaniDocument2 pagesKardex VS Monitoring Sheet SanaaniNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin Sulfate Drug Study 1 2Document3 pagesGentamicin Sulfate Drug Study 1 2Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 3Document3 pagesFelixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 3Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Basic Guides To Conduct Effective MeetingDocument3 pagesBasic Guides To Conduct Effective MeetingNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- NCM119QUIZDocument3 pagesNCM119QUIZNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Individual Work 15Document5 pagesIndividual Work 15Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Continuing Professional Development Handout 2Document19 pagesContinuing Professional Development Handout 2Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study (SANAANI, NUR) LOSARTANDocument11 pagesDrugs Study (SANAANI, NUR) LOSARTANNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- (SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA, M.) Plan-Of-ActivitiesDocument3 pages(SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA, M.) Plan-Of-ActivitiesNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 1Document2 pagesFelixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 1Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Manifestations of Altered F e Balance Part 2Document2 pagesFelixcharlie Manifestations of Altered F e Balance Part 2Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Aina ArrhytmiaDocument2 pagesAina ArrhytmiaNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Manifestations of Altered F e BalanceDocument2 pagesFelixcharlie Manifestations of Altered F e BalanceNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 4Document2 pagesFelixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 4Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 2Document1 pageFelixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 2Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- NCP (Sanaani, Nur)Document5 pagesNCP (Sanaani, Nur)Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Filipino Management StylesDocument18 pagesFilipino Management StylesNur Fatima Sanaani100% (1)
- EINC Essential Intrapartim NC ChecklistDocument7 pagesEINC Essential Intrapartim NC ChecklistNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bondinggg 1Document2 pagesChemical Bondinggg 1Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - MCH Course 2019 FINAL 1 1Document8 pagesSyllabus - MCH Course 2019 FINAL 1 1Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- BL NurChem Activity 5 Physical Chemical ChangesDocument4 pagesBL NurChem Activity 5 Physical Chemical ChangesNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- POST TEST FUNDA - StudentDocument4 pagesPOST TEST FUNDA - StudentNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- BL NurChem Activity 3 Measurement - REVISED 081920Document8 pagesBL NurChem Activity 3 Measurement - REVISED 081920Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- COURSE OUTLINE For STUDENT 1Document5 pagesCOURSE OUTLINE For STUDENT 1Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- BL NurChem Activity 4 Physical Properties - Density FINALDocument6 pagesBL NurChem Activity 4 Physical Properties - Density FINALNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Attachment B SAMPLE Laboratory Report EDITABLE WORD VERSIONDocument3 pagesAttachment B SAMPLE Laboratory Report EDITABLE WORD VERSIONNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- NCM 120J Handout # 1: 2.decent Work Is Employment That "Document10 pagesNCM 120J Handout # 1: 2.decent Work Is Employment That "Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Done By: Team Leader:: Heba Allsharif Khulood AlraddadiDocument4 pagesDone By: Team Leader:: Heba Allsharif Khulood AlraddadiMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Arthritis PDFDocument4 pagesArthritis PDFArchana MoreyNo ratings yet
- Lec 20 GoniometryDocument165 pagesLec 20 GoniometryBhargavNo ratings yet
- Smith 2018Document10 pagesSmith 2018Emre DöngelNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology Cases For The Internist: Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPHDocument40 pagesRheumatology Cases For The Internist: Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPHNaziBrola TsivadzeNo ratings yet
- Cuñas MetalicasDocument8 pagesCuñas MetalicasOciel AcostaNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Spine Ortho TestsDocument3 pagesLumbar Spine Ortho Testsmasso23684100% (3)
- Signs of Nursemaid'S ElbowDocument2 pagesSigns of Nursemaid'S ElbowsuperkshiluppyNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafy (2020-2021)Document101 pagesRheumatology - Internal Medicine, Dr. A. Mowafy (2020-2021)Mohammed RisqNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System-Key AnswersDocument8 pagesMusculoskeletal System-Key AnswersF6imNo ratings yet
- Injuri & Trauma Saat Olahraga & Penatalaksanaannya (DR - Arief Faisal, SP - OT)Document53 pagesInjuri & Trauma Saat Olahraga & Penatalaksanaannya (DR - Arief Faisal, SP - OT)Wulan Nindira WarasudiNo ratings yet
- Acetabular FracturesDocument8 pagesAcetabular FracturesJayNo ratings yet
- Dequervain MWMDocument12 pagesDequervain MWMirongrafNo ratings yet
- Information MSQ KROK 2 Medicine 2007 2020 TraumatologyDocument7 pagesInformation MSQ KROK 2 Medicine 2007 2020 TraumatologyJeet JainNo ratings yet
- Wet Cupping TherapyDocument2 pagesWet Cupping TherapyBoris VidakovicNo ratings yet
- Examen FisicoDocument26 pagesExamen FisicoAmada Angel VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Role of Panchakarma in Management of Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument5 pagesRole of Panchakarma in Management of Rheumatoid ArthritisIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Arthritis in Cats-Diagnosis, Relevance and TratmentDocument3 pagesArthritis in Cats-Diagnosis, Relevance and TratmentLaura Carolina Moreno RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Bone and Joint Disorders of The Foot and Ankle - A Rheumatological Approach PDFDocument366 pagesBone and Joint Disorders of The Foot and Ankle - A Rheumatological Approach PDFDaniela Stefan100% (2)
- Differential Diagnosis IIDocument32 pagesDifferential Diagnosis IIRaymondNo ratings yet
- List of 206 Bones and Their LocationDocument3 pagesList of 206 Bones and Their LocationJemaicah ArañoNo ratings yet
- Ankle Foot and Knee OrthosesDocument53 pagesAnkle Foot and Knee Orthosesnicole bejasaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Approach To Polyarticular Joint Pain - American Family PhysicianDocument12 pagesDiagnostic Approach To Polyarticular Joint Pain - American Family PhysicianKalin TsenovNo ratings yet
- A Fracture of The Distal Radius or UlnaDocument3 pagesA Fracture of The Distal Radius or UlnaSweetie StarNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Applications of Chondroitin Sulphate, Collagen and Rosehip Extract in The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument13 pagesTherapeutic Applications of Chondroitin Sulphate, Collagen and Rosehip Extract in The Musculoskeletal SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Esr Range - Google Search PDFDocument1 pageEsr Range - Google Search PDFAwais FarooqNo ratings yet
- Lec Activity6 Skeletal SystemDocument11 pagesLec Activity6 Skeletal SystemYda Maxine Palma50% (2)
- Kalten BornDocument34 pagesKalten BornjayadevanNo ratings yet
- 3rd Coxa Vara ValgaDocument30 pages3rd Coxa Vara ValgaMandar printNo ratings yet
- PFODocument15 pagesPFOB N Chaturvedi100% (1)