Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 4
Uploaded by
Nur Fatima SanaaniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 4
Uploaded by
Nur Fatima SanaaniCopyright:
Available Formats
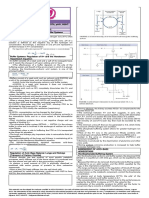
Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 4 Cheat Sheet
by felixcharlie (felixcharlie) via cheatography.com/142439/cs/31032/
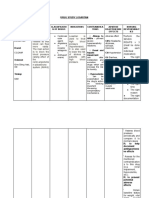
Blood pH levels Renal
Dependent on H+ concentration Secretes free hydrogen ions into renal tubules
Normal pH: 7.35-7.45 Excretes weak acid
Alkalosis: 7.45-7.8 Excretes HCO3 (if there is metabolic acidosis)
Acidosis: 7-7.35
Reading arterial blood gases (ABG)
Anything >7.8 or <7 is deadly
Respiratory
Buffers Acidosis
Buffering is the primary regulator of acid-base balance. Respiratory
Alkalosis
Buffers act chemically to change strong acids into weaker ones, or
bind them to neutralise them Metabolic Acidosis
Different buffer systems assume dominant roles in different parts of Metabolic Alkalosis Increased pH, normal PaCO2, increased
the body: HCO3
Extracellular Fluid Major buffer: Bicarbonate buffer system Normal ABG figures
(ECF) pH 7.35-7.45
Minor buffers: Intracellular problems, PO2 80-100
Phosphate buffer system PCO2 35-45
Blood Major buffers: Bicarb buffer system, HCO3 22-28
Hemoglobin
Minor buffers: Plasma proteins, Phosphate Acid-base homeostasis
buffer system
How is it maintained?
Intracellular fluid Major buffers: Proteins, Phosphate
Buffers Bicarbonate (HCO3) - reacts rapidly, less than an second.
(ICF)
Chemically change strong aicds to weaker acids or bind to
Minor buffers: None neutralise effect
Urine Major buffers: Ammonia, Phosphate Resipr Reacts rapidly - seconds to minutes
Minor buffers: None atory
system
Renal Reacts slowly - hours
system
By felixcharlie (felixcharlie) Published 5th March, 2022. Sponsored by Readable.com
cheatography.com/felixcharlie/ Last updated 5th March, 2022. Measure your website readability!
Page 1 of 2. https://readable.com
Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 4 Cheat Sheet
by felixcharlie (felixcharlie) via cheatography.com/142439/cs/31032/
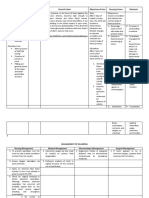
Respiration
CO2 formed and excreted in lungs
Lungs excrete CO2 + H2O as by-products of cellular metabolism
CO2 is regarded as an acid
Homeostasis cycle of CO2 in the body:
During exercise or other activity, cell metabolism increases and
produces more CO2, then:
More CO2 dissolves in blood, forming carbonic acid which lowers
blood pH slightly, then:
Receptors in the brain sense the drop in pH and send nerve signals
to increase breathing rate, then:
Increased breathing rate quickly removes more CO2 from blood.
Blood pH rises slightly, returning to normal - cycle starts again
Continuous mixing of body fluids/gases
By felixcharlie (felixcharlie) Published 5th March, 2022. Sponsored by Readable.com
cheatography.com/felixcharlie/ Last updated 5th March, 2022. Measure your website readability!
Page 2 of 2. https://readable.com
You might also like
- Filipino Management StylesDocument18 pagesFilipino Management StylesNur Fatima Sanaani100% (1)
- MCQ CPRDocument2 pagesMCQ CPRAzmal Kabir Sarker75% (16)
- Fe 4Document36 pagesFe 4api-3697326No ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance and ImbalanceDocument42 pagesAcid Base Balance and ImbalanceBaylon, MarkNo ratings yet
- CC Acid and Base Balance and ImbalanceDocument7 pagesCC Acid and Base Balance and ImbalanceGianna SablanNo ratings yet
- Acid Base PhysiologyDocument12 pagesAcid Base PhysiologyaequNo ratings yet
- 9 - (D) Acid Base Balance Dec 4.17Document61 pages9 - (D) Acid Base Balance Dec 4.17khaledNo ratings yet
- Abg - MLT 4th Semester.Document146 pagesAbg - MLT 4th Semester.Sanjeev walvekarNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Hydroxide: Acid-Base Balance Overview of Acids and Bases DescriptionDocument15 pagesHydrogen Hydroxide: Acid-Base Balance Overview of Acids and Bases DescriptionElisha WorworNo ratings yet
- Clinical BiochemistryDocument11 pagesClinical BiochemistryKrushna SaiNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument10 pagesAcid BaseFiona Marie Kyla TunayNo ratings yet
- Acid Base ImbalanceDocument15 pagesAcid Base ImbalanceIoana SanduNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biochemistry Proteins Buffers in Blood Plasma and CellsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistry Proteins Buffers in Blood Plasma and CellsGwyn Louise CarolinoNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance: Normal PH of Body FluidsDocument30 pagesAcid-Base Balance: Normal PH of Body FluidsAnnDianaJaiminNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance Lecture - Part 1Document43 pagesAcid-Base Balance Lecture - Part 1yigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- Clinical BiochemistryDocument73 pagesClinical BiochemistryEslam NassarNo ratings yet
- Nutri Diet 6Document6 pagesNutri Diet 6jellybeandumpppNo ratings yet
- Water: PH and BuffersDocument63 pagesWater: PH and BuffersSoffa ShmuelNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance - Physiology: Dr. Preethy DR - Vikas Dr. Vidhya DR - NitashaDocument28 pagesAcid Base Balance - Physiology: Dr. Preethy DR - Vikas Dr. Vidhya DR - NitashaParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Final MCW .ABDpptxDocument124 pagesFinal MCW .ABDpptxFazlul KarimNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance: Editor: Dr. Husnil Kadri, MkesDocument66 pagesAcid-Base Balance: Editor: Dr. Husnil Kadri, MkesDwi SiregarNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Physiology HSFDocument14 pagesAcid Base Physiology HSFGeorge DanceNo ratings yet
- Lect 04Document4 pagesLect 04الحاج كاملNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument43 pagesAcid Base Balanceanju KvNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Balance - Physiology: Dr. Preethy DR - Vikas Dr. Vidhya DR - NitashaDocument28 pagesAcid Base Balance - Physiology: Dr. Preethy DR - Vikas Dr. Vidhya DR - NitashaParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Ivma Ce Acid BaseDocument11 pagesIvma Ce Acid BaseGhozy IANo ratings yet
- BCH 201 ModuleDocument15 pagesBCH 201 ModuleJoyNo ratings yet
- Blood BufferDocument5 pagesBlood Bufferশাহ্ রিয়ারNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas Analysis4231 PDFDocument84 pagesBlood Gas Analysis4231 PDFEng-Mugahed AlmansorNo ratings yet
- PH Acid Base - Lecture 1Document38 pagesPH Acid Base - Lecture 1HumrazNo ratings yet
- (Week 1 BIOCHEM) Introduction To BiomoleculeDocument4 pages(Week 1 BIOCHEM) Introduction To BiomoleculeKatalina Estelle LaurierNo ratings yet
- Pengaturan Asam Basa ElektrolitdasDocument35 pagesPengaturan Asam Basa ElektrolitdasSiti RahmaniNo ratings yet
- School of Physiology: University of The Witwatersrand, JohannesburgDocument19 pagesSchool of Physiology: University of The Witwatersrand, JohannesburgJoel AmoniNo ratings yet
- LGIS. PH and BuffersDocument25 pagesLGIS. PH and Buffershasaanmushtaq98765No ratings yet
- 9975 - Tutorial 4 Blok 1.3 (Akibat Diare)Document37 pages9975 - Tutorial 4 Blok 1.3 (Akibat Diare)sri rahma lizaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base ImbalanceDocument32 pagesAcid Base ImbalanceIftikhar AliNo ratings yet
- Blood Buffer SystemDocument10 pagesBlood Buffer Systemmd hasib munsiNo ratings yet
- Acid Base GHDocument23 pagesAcid Base GHThayalan AllanNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument28 pagesAcid Base BalanceAnis BonitaNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument89 pagesAcid BaseEdouinaNo ratings yet
- Human Biology: Grade 12: A6 - Biological PH and Buffer Systems A7 - Significant Carbohydrates in Biological SystemsDocument8 pagesHuman Biology: Grade 12: A6 - Biological PH and Buffer Systems A7 - Significant Carbohydrates in Biological SystemsShaimaa SalamaNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Asam BasaDocument51 pagesGangguan Asam BasaYudhistira YuliandraNo ratings yet
- "If One Advances Confidently in The Direction of His Dreams, He Will Meet With A Success Unexpected in Common HoursDocument44 pages"If One Advances Confidently in The Direction of His Dreams, He Will Meet With A Success Unexpected in Common Hourssantana2007No ratings yet
- 7 Acidbase-ImbalanceDocument5 pages7 Acidbase-ImbalanceMarie Louise Nicole TuvillaNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Learning Objectives:: Introduction/ OverviewDocument5 pagesArterial Blood Gas Analysis Learning Objectives:: Introduction/ OverviewjanorberteNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Buffers, Carbohydrates Metabolic PathwaysDocument16 pagesWeek 4 Buffers, Carbohydrates Metabolic PathwaysangeliaNo ratings yet
- Acid Base ImbalancesDocument4 pagesAcid Base ImbalancesSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- 1st Chap-2Document40 pages1st Chap-2RJ Noor JanNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base BalanceDocument38 pagesAcid-Base BalanceNym Angga SantosaNo ratings yet
- PHYSIO MODULE 8 - Acid and Base BalanceDocument14 pagesPHYSIO MODULE 8 - Acid and Base BalanceAlexNo ratings yet
- Fluids & Electrolytes AssDocument6 pagesFluids & Electrolytes AssDudil GoatNo ratings yet
- Acide Base Physiology New Concepts 2015Document6 pagesAcide Base Physiology New Concepts 2015luisemisasc1990No ratings yet
- Buffer System For NursingDocument2 pagesBuffer System For NursingjasonNo ratings yet
- Acid - Base DisturbancesDocument3 pagesAcid - Base DisturbancesMarie Antionette MondragonNo ratings yet
- Metabolic AcidosisDocument102 pagesMetabolic AcidosisShajahan SideequeNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Regulation - ppt@BVSCAH-6th SemDocument95 pagesAcid Base Regulation - ppt@BVSCAH-6th SemDr. Prakash PanthiNo ratings yet
- BuffersDocument5 pagesBuffersCarol SimonNo ratings yet
- Zuku Visual Flashnotes Blood Gas EvalDocument10 pagesZuku Visual Flashnotes Blood Gas EvalvetthamilNo ratings yet
- Mtap421 BloodgasesDocument11 pagesMtap421 BloodgasesNhelomar ManlinconNo ratings yet
- Acid Base BalanceDocument56 pagesAcid Base BalanceBhumika ghimireNo ratings yet
- (Case Week 5-6) With DaranginaDocument3 pages(Case Week 5-6) With DaranginaNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- NCM119QUIZDocument3 pagesNCM119QUIZNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Gentamicin Sulfate Drug Study 1 2Document3 pagesGentamicin Sulfate Drug Study 1 2Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Nurco-2 (Deliverables) Group 4-2Document3 pagesNurco-2 (Deliverables) Group 4-2Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Kardex VS Monitoring Sheet SanaaniDocument2 pagesKardex VS Monitoring Sheet SanaaniNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Basic Guides To Conduct Effective MeetingDocument3 pagesBasic Guides To Conduct Effective MeetingNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Individual Work 15Document5 pagesIndividual Work 15Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- EINC Essential Intrapartim NC ChecklistDocument7 pagesEINC Essential Intrapartim NC ChecklistNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Continuing Professional Development Handout 2Document19 pagesContinuing Professional Development Handout 2Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- 7 Bates Assessment ToolDocument10 pages7 Bates Assessment ToolNur Fatima Sanaani0% (1)
- Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 1Document2 pagesFelixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 1Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Manifestations of Altered F e Balance Part 2Document2 pagesFelixcharlie Manifestations of Altered F e Balance Part 2Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 3Document3 pagesFelixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 3Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Manifestations of Altered F e BalanceDocument2 pagesFelixcharlie Manifestations of Altered F e BalanceNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Felixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 2Document1 pageFelixcharlie Electrolyte Homeostasis Part 2Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- (SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA, M.) Plan-Of-ActivitiesDocument3 pages(SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA, M.) Plan-Of-ActivitiesNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Aina ArrhytmiaDocument2 pagesAina ArrhytmiaNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study (SANAANI, NUR) LOSARTANDocument11 pagesDrugs Study (SANAANI, NUR) LOSARTANNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- BL NurChem Activity 5 Physical Chemical ChangesDocument4 pagesBL NurChem Activity 5 Physical Chemical ChangesNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- POST TEST FUNDA - StudentDocument4 pagesPOST TEST FUNDA - StudentNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- COURSE OUTLINE For STUDENT 1Document5 pagesCOURSE OUTLINE For STUDENT 1Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- BL NurChem Activity 4 Physical Properties - Density FINALDocument6 pagesBL NurChem Activity 4 Physical Properties - Density FINALNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- NCP (Sanaani, Nur)Document5 pagesNCP (Sanaani, Nur)Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bondinggg 1Document2 pagesChemical Bondinggg 1Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- NCM 120J Handout # 1: 2.decent Work Is Employment That "Document10 pagesNCM 120J Handout # 1: 2.decent Work Is Employment That "Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Attachment B SAMPLE Laboratory Report EDITABLE WORD VERSIONDocument3 pagesAttachment B SAMPLE Laboratory Report EDITABLE WORD VERSIONNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - MCH Course 2019 FINAL 1 1Document8 pagesSyllabus - MCH Course 2019 FINAL 1 1Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- BL NurChem Activity 3 Measurement - REVISED 081920Document8 pagesBL NurChem Activity 3 Measurement - REVISED 081920Nur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Plavix Clopidogrel Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPlavix Clopidogrel Drug StudyNur Fatima SanaaniNo ratings yet
- SDL Respiratory Care Modalities LOPEZ BSN 3CDocument3 pagesSDL Respiratory Care Modalities LOPEZ BSN 3CMaria Niña Angela LopezNo ratings yet
- Clinical Cheat Sheet: Radiographic AssessmentDocument1 pageClinical Cheat Sheet: Radiographic AssessmentTracy PopeNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- High Altitude Anaesthesia PDFDocument7 pagesHigh Altitude Anaesthesia PDFK.krishna PriyaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 First Quarter Exam SY 2021-2022Document5 pagesScience 9 First Quarter Exam SY 2021-2022Encluna Lindon JayNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TherapyDocument31 pagesOxygen TherapyChayan BhowmikNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Bio Starter 21.03.23 Malak PDFDocument4 pages2.8 Bio Starter 21.03.23 Malak PDFMalak ANo ratings yet
- Toolkit For Sleep: Andrew D. Huberman, PH.DDocument6 pagesToolkit For Sleep: Andrew D. Huberman, PH.DFlori100% (1)
- CHAPTER 29 Instructor Notes From JarvisDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 29 Instructor Notes From JarvisAhata Sham NewazNo ratings yet
- Physiology SpottingDocument51 pagesPhysiology SpottingShruti RautNo ratings yet
- Biological-Approach-Key-Terms IB PsychologyDocument2 pagesBiological-Approach-Key-Terms IB PsychologySupriyaa ChordiaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument11 pagesCardiac ArrhythmiasChino Paolo SamsonNo ratings yet
- Hormones: Siti Zulaika Binti KasmatDocument21 pagesHormones: Siti Zulaika Binti KasmatikaNo ratings yet
- Web of Science - Science Citation Index ExpandedDocument149 pagesWeb of Science - Science Citation Index ExpandedHo Ngoc VinhNo ratings yet
- Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems: Chapter TestDocument6 pagesCirculatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems: Chapter TestJunior SencionNo ratings yet
- Ask An Expert: The Benefits of Aerobic ExerciseDocument3 pagesAsk An Expert: The Benefits of Aerobic ExercisePrincess Villasis BaciaNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Synchronous Demand Pacemaker IJERTV2IS4162Document8 pagesVentricular Synchronous Demand Pacemaker IJERTV2IS416221 Yash RewaleNo ratings yet
- Maniba Bhula Nursing College: Subject: TopicDocument6 pagesManiba Bhula Nursing College: Subject: TopicRinal BaradNo ratings yet
- Topic-5A (Homework) PDFDocument5 pagesTopic-5A (Homework) PDFShayna NaserNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement Sleeping DisordersDocument7 pagesThesis Statement Sleeping DisordersBrandi Gonzales100% (2)
- Control of Internal EnvironmentDocument29 pagesControl of Internal EnvironmentVandini LohanaNo ratings yet
- CH-21 Neural Control and Coordination.......Document16 pagesCH-21 Neural Control and Coordination.......Irmin HasanNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamics The Study of The Movement of Blood and The Physical Principles Governing This MovementDocument46 pagesHemodynamics The Study of The Movement of Blood and The Physical Principles Governing This MovementwayneNo ratings yet
- Irritability Part IDocument18 pagesIrritability Part IYanique JonesNo ratings yet
- NfiDocument41 pagesNfiKristine Singson0% (1)
- Sleep Strategies To Improve Your Sleep The Importance of SleepDocument3 pagesSleep Strategies To Improve Your Sleep The Importance of SleepEmanNo ratings yet
- Capnography 1Document125 pagesCapnography 1tamikanjiNo ratings yet
- Pato Insomnia PDFDocument14 pagesPato Insomnia PDFdilaNo ratings yet
- Loving Kindness Therapy - HPHI Ns. MukhlisDocument20 pagesLoving Kindness Therapy - HPHI Ns. MukhlisNursida AbudNo ratings yet