Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
Uploaded by
Julie Marie Pavadora0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
133 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
133 views3 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion
Uploaded by
Julie Marie PavadoraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Nursing
Needs/Problems/Cues Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Nursing Actions Rationale
Diagnosis
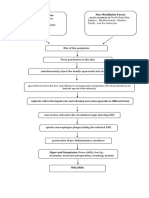
I. Physiologic Ineffective The blood pressure, or the force of blood against the Goal: Measures to
Overload tissue walls of your arteries, becomes high enough to After 5 days of improve circulation
perfusion: damage your arteries and other blood vessels. holistic nursing and maintain the
A. Ineffective tissue Edema Damage to your arteries may restrict blood flow. It can care, the client will normal range of
perfusion related to produce swelling in the blood vessels in your brain, be able to blood pressure:
elevated extremities and to your growing baby. If this abnormal demonstrate 1. Encourage To lessen in
Subjective Cues: blood blood flow through vessels interferes with your brain’s behaviors and client to limit contributing
Verbalization pressure. ability to function, seizures may occur. lifestyle changes salt intake and to edema.
of worry over Source: to improve protein intake.
the obvious https://www.healthline.com/health/eclampsia#causes circulation and 2. Instruct in To facilitate
sign of maintain the blood pressure management
swelling. normal range of monitoring at of
blood pressure. home. hypertension,
Objective Cues: which is a
Blood pressure Objectives: major risk
of 140/110 After 8 hours of factor for
mmHg nurse-client damage to
Presence of interaction, the blood vessel
protein in client will be to: organ
urine function.
Pitting and 1. decrease 3. Collaborate in To maximize
general edema blood treatment of systemic
at the upper pressure hypertension. circulation
and lower from and organ
extremities 140/110 perfusion
and face mmHg to 4. Administer To improve
120/90 medications tissue
mmHg such as perfusion or
below. antiplatelets organ
2. Improve agents or function.
tissue thrombolytics.
perfusion
as
evidenced
by
absence of
edema.
5. Administer To promote
fluids, optimal
electrolytes, blood flow,
nutrients, and organ
oxygen, as perfusion,
indicated and function.
0
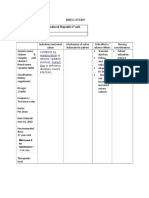
MANAGEMENT OF ECLAMPSIA
Nursing Management Medical Management Pharmacologic Management Surgical Management
1. To prevent aspiration, turn her 1. Administer oxygen by face mask 1. Magnesium sulfate or diazepam 1. If fetus appears to be in
onto her side to allow secretions as needed to protect fetal (Valium) may be administered imminent danger, cesarean birth
to drain from her mouth. oxygenation. intravenously as emergency becomes birth of choice.
measures.
2. Assess oxygen saturation via 2. Preferred method of birth is
pulse oximeter. vaginal because of the minimal
use of anesthesia.
3. Apply an external fetal heart
monitor if one is not already in
place to assess the FHR.
4. Check for vaginal bleeding to
detect placental separation,
although evidence placental
separation has occurred will
probably appear first on the
fetal heart record; vaginal
bleeding will strengthen
presumption.
5. Be certain to
assess for uterine
contractions
during the
postictal stage
because if labor
begins during
this period, the
woman will be
unable to report
the sensation of
contractions.
Pain stimulus can
initiate seizures.
6. Give her nothing
to eat.
7. Conversation is
limited to those
things you would
say if she were
awake.
You might also like
- Drug Study SyntocinonDocument2 pagesDrug Study SyntocinonPrinceNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDiana MuañaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudylouiseordonoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Iron Deficiency AnemiaChielee Anne PayongayongNo ratings yet
- NCP1 - EpisiotomyDocument2 pagesNCP1 - EpisiotomyCarmel Joy DifuntorumNo ratings yet
- Case 1Document7 pagesCase 1Jullienne Ysabelle AngNo ratings yet
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDocument2 pagesNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitNo ratings yet
- ICS Pedia WardDocument8 pagesICS Pedia Wardsweet061991No ratings yet
- NCP Drug Study Group 1Document21 pagesNCP Drug Study Group 1Cassandra Grace Muerong Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Duphaston PDFDocument4 pagesDuphaston PDFmarcusjanaNo ratings yet
- Acyclovir (Acycloguanosi Ne) : Systemic Administration History: AllergyDocument3 pagesAcyclovir (Acycloguanosi Ne) : Systemic Administration History: AllergyAnnahNo ratings yet
- NCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyDocument7 pagesNCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyD CNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Rifadin RifampinDocument4 pagesCollege of Nursing: Rifadin RifampinAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Brokenshire College Madapo, Davao CityDocument1 pageDrug Study: Brokenshire College Madapo, Davao CityHera Pamela Buelis BatoyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SummaryDocument7 pagesDrug Study SummaryKateLayaogNo ratings yet
- Anti Tetanus Serum IDocument2 pagesAnti Tetanus Serum IRobby EffendyNo ratings yet
- Beta ThalaDocument2 pagesBeta ThalaAngie LamoNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument4 pagesAbruptio PlacentaChelzie LasernaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Bigleap - Immediate Care of The Newborn (Updated)Document5 pagesActivity 2 - Bigleap - Immediate Care of The Newborn (Updated)Cameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Baby Jason with Cleft Lip and PalateDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Baby Jason with Cleft Lip and PalatePatricia Ellyne DizonNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument33 pagesDrug Studyjefwy8No ratings yet
- Promoting Proper BreastfeedingDocument12 pagesPromoting Proper BreastfeedingAmal MUTIANo ratings yet
- Abortion BSN 0PR-2: Case Study of BelleDocument27 pagesAbortion BSN 0PR-2: Case Study of BellekervinNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Interrupted Breastfeeding: Student Nurses' CommunityDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Interrupted Breastfeeding: Student Nurses' CommunitySaira SucgangNo ratings yet
- Problem # 3: Threat of Cross Infection From A Communicable Disease CaseDocument3 pagesProblem # 3: Threat of Cross Infection From A Communicable Disease CaseRolandNo ratings yet
- Managing Premature Cervical DilatationDocument10 pagesManaging Premature Cervical DilatationRaiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPLSG ApprenticeNo ratings yet
- Nrg203: Care of Mother, Child, and Adolescent: (StudentDocument6 pagesNrg203: Care of Mother, Child, and Adolescent: (Studentmikhaela sencilNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Jaundice: Causes, Evaluation and ManagementDocument22 pagesNeonatal Jaundice: Causes, Evaluation and ManagementAnkur WadheraNo ratings yet
- NCP Case 1Document6 pagesNCP Case 1boomer SeargeNo ratings yet
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Document3 pagesElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypertension ManagementDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for Hypertension Managementbhavana100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Magda with EpisiotomyDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Magda with EpisiotomyRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyGAYOL BREEN IRAH A.No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Core CompetenciesDocument13 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Core CompetenciesMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- Zocor (Simvastatin)Document3 pagesZocor (Simvastatin)E100% (1)
- OB - NCP (Episiotomy)Document3 pagesOB - NCP (Episiotomy)eosNo ratings yet
- Learning Objective Content Teaching Strategy Time Alloted EvaluationDocument3 pagesLearning Objective Content Teaching Strategy Time Alloted EvaluationAmera DimatingcalNo ratings yet
- Drugs Post PartumDocument3 pagesDrugs Post PartumanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document7 pagesExperiment 7kimber_gado100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studybkr_wltr100% (2)
- Head To Toe Assessment of Infant CsepreDocument5 pagesHead To Toe Assessment of Infant CsepreteuuuuNo ratings yet
- Managing Labor Pain NaturallyDocument2 pagesManaging Labor Pain Naturallyjay kusainNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument3 pagesTetralogy of FallotJohn Mark PocsidioNo ratings yet
- NCP - Gestational HypertensionDocument3 pagesNCP - Gestational HypertensionCameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Brent Hospital and Colleges IncorporatedDocument4 pagesBrent Hospital and Colleges Incorporateddaniel gariandoNo ratings yet
- Post C-Section Delivery Care PlanDocument5 pagesPost C-Section Delivery Care Planᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCPDocument4 pagesCase Study NCPKelly OstolNo ratings yet
- NCP - Preeclampsia (A)Document6 pagesNCP - Preeclampsia (A)Ronel ResurricionNo ratings yet
- TSU Nursing Case Analysis PneumoniaDocument4 pagesTSU Nursing Case Analysis PneumoniaKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- ThalassemiaDocument1 pageThalassemiaJobelle Fernandez-SantosNo ratings yet
- Components of Foood Home Work AdhritDocument3 pagesComponents of Foood Home Work AdhritMrudula GummuluriNo ratings yet
- The Lived Experiences of Thriving Family Caregivers of Persons With Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument11 pagesThe Lived Experiences of Thriving Family Caregivers of Persons With Autism Spectrum DisorderPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous AbortionDocument8 pagesSpontaneous Abortionsaber_fate_11No ratings yet
- NCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Document5 pagesNCP & Drug Study (Tondo Med)Kevin_Remollo_2431No ratings yet
- Nursing Drug StudyDocument12 pagesNursing Drug StudyJoshkorro Geronimo100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan for AmebiasisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for AmebiasiskristennemarieNo ratings yet
- Managing Eclampsia Through Holistic Nursing CareDocument3 pagesManaging Eclampsia Through Holistic Nursing CareJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tubes: Michael J. Klamut, M.D. Division of GastroenterologyDocument11 pagesGastrointestinal Tubes: Michael J. Klamut, M.D. Division of GastroenterologyJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- PAVADORA Prevac LetterDocument1 pagePAVADORA Prevac LetterJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Organization of A Research PaperDocument14 pagesOrganization of A Research PaperKevin CabigtingNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument2 pagesCase StudyJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Kaileigh Sweeney, SN University of Rhode Island Mentor: Carolyn HamesDocument30 pagesKaileigh Sweeney, SN University of Rhode Island Mentor: Carolyn HamesJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Discussion ForumDocument1 pageDiscussion ForumJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- ThemesDocument1 pageThemesJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research: Cebu Doctors University College of NursingDocument31 pagesNursing Research: Cebu Doctors University College of NursingJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Watch Your Health Always!: Get The Knowledge You NeedDocument2 pagesWatch Your Health Always!: Get The Knowledge You NeedJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tubes: Michael J. Klamut, M.D. Division of GastroenterologyDocument11 pagesGastrointestinal Tubes: Michael J. Klamut, M.D. Division of GastroenterologyJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Management Guidelines for PreeclampsiaDocument3 pagesFluid Management Guidelines for PreeclampsiaJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Dark Green Cute Party Hat Funny Birthday Folded CardDocument2 pagesDark Green Cute Party Hat Funny Birthday Folded CardJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Student Stress Aid For Theory 1Document83 pagesNursing Student Stress Aid For Theory 1Julie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Correlations Between Stress and Anxiety Levels in Nursing StudentsDocument7 pagesCorrelations Between Stress and Anxiety Levels in Nursing StudentsJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3Julie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Academic PosterDocument4 pagesAcademic PosterJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- 5 PDFDocument2 pages5 PDFJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Needs/Problems/Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Nursing Actions RationaleDocument3 pagesNeeds/Problems/Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Objectives of Care Nursing Actions RationaleJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- WHO guidelines for standardization of herbal drugsDocument7 pagesWHO guidelines for standardization of herbal drugsJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Managing Eclampsia Through Holistic Nursing CareDocument3 pagesManaging Eclampsia Through Holistic Nursing CareJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Replace With First Name(s) Surname(s)Document2 pagesCurriculum Vitae Replace With First Name(s) Surname(s)Valentina100% (1)
- Types of CheeseDocument20 pagesTypes of CheeseJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Developed and Developing CountriesDocument1 pageComparison of Developed and Developing CountriesJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- GUIDELINESDocument3 pagesGUIDELINESJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- EcclampsiaDocument11 pagesEcclampsiaJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- References:: Maternal and Child HealthDocument2 pagesReferences:: Maternal and Child HealthJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- OxygentherapyDocument25 pagesOxygentherapyJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Postpartal FinalDocument57 pagesPostpartal FinalJulie Marie PavadoraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food and Beverage IndustryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Food and Beverage IndustryRhyza BehaveNo ratings yet
- 11 - FORAGERS by Sam BoyerDocument106 pages11 - FORAGERS by Sam BoyerMurtaza HussainNo ratings yet
- 0610 m16 QP 62Document12 pages0610 m16 QP 62faryal khanNo ratings yet
- Erotic MassageDocument113 pagesErotic MassageMahmoud El Mohamdy75% (4)
- Tabcalcs.com general equations sheetDocument2 pagesTabcalcs.com general equations sheetRamadan RashadNo ratings yet
- 5 Variable K-MapDocument15 pages5 Variable K-MapBen SewellNo ratings yet
- NPT Pipe Thread Sizes and TapersDocument1 pageNPT Pipe Thread Sizes and TapersRajesh J BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Barney's Great Adventure - Barney Wiki - WikiaDocument2 pagesBarney's Great Adventure - Barney Wiki - WikiachefchadsmithNo ratings yet
- Guide to Quality Control Arrangements on SeedsDocument15 pagesGuide to Quality Control Arrangements on SeedsArun Kumar100% (1)
- Oxford Reading Tree: The Pet ShopDocument12 pagesOxford Reading Tree: The Pet ShopKanjaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Monitoring of The Humber Bridge UsingDocument7 pagesExperimental Monitoring of The Humber Bridge Using정주호No ratings yet
- Diagrama 4 AMBIENT AIR TEMPER..Document1 pageDiagrama 4 AMBIENT AIR TEMPER..Gustavo PérezNo ratings yet
- 5988-4082EN Designers GuidDocument82 pages5988-4082EN Designers GuidAndreaNo ratings yet
- Preferred Drug ListDocument2 pagesPreferred Drug ListRamNo ratings yet
- Differences in Left Ventricular and Left Atrial FuDocument10 pagesDifferences in Left Ventricular and Left Atrial FueugeniaNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Entry: OSHA Standard 1910.146Document38 pagesConfined Space Entry: OSHA Standard 1910.146SKH CultureNo ratings yet
- STP1236 Eb.1415051 1 PDFDocument208 pagesSTP1236 Eb.1415051 1 PDFpaolaNo ratings yet
- VSD Power Supply Connections and EarthingDocument4 pagesVSD Power Supply Connections and EarthingHumaid ShaikhNo ratings yet
- AABB Accredited DNA Testing FacilitiesDocument2 pagesAABB Accredited DNA Testing Facilitiesjosueduran75No ratings yet
- Beyond Schein DentalDocument9 pagesBeyond Schein DentaltomdietzlerNo ratings yet
- Cse Reviewer - MathDocument58 pagesCse Reviewer - MathLyne LerinNo ratings yet
- A Thing of Beauty Analysis by Sharvaree S. ChavanDocument12 pagesA Thing of Beauty Analysis by Sharvaree S. Chavansharu11No ratings yet
- Ship Construction: Second Mates - HANDOUTDocument117 pagesShip Construction: Second Mates - HANDOUTmaneeshNo ratings yet
- GROHE Specification Sheet 19443000-1Document2 pagesGROHE Specification Sheet 19443000-1Fred PrzNo ratings yet
- 1992SGSDesignersGuidetoPowerProductsApplicationManual2Ed 1182713547Document1,298 pages1992SGSDesignersGuidetoPowerProductsApplicationManual2Ed 1182713547analog changeNo ratings yet
- Tables and Bar ChartsDocument7 pagesTables and Bar ChartsVictoria FedoseevaNo ratings yet
- Violet Flame Clearing of The Heart ServiceDocument16 pagesViolet Flame Clearing of The Heart ServiceMySecret Gardenmdp82% (11)
- Flacs CFD ManualDocument658 pagesFlacs CFD ManualCyanNo ratings yet
- CHS-WWW - Polsteel. TUBOS METALICOS PDFDocument3 pagesCHS-WWW - Polsteel. TUBOS METALICOS PDFEduardo TorreNo ratings yet
- Shat Karma ConciseDocument4 pagesShat Karma ConcisesarikaabhayNo ratings yet