Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Chemistry Module 2 - Spectroscopy SY-1 Semester AY - 2021-2021-PSU Balabac Campus
Uploaded by
Farhadz Sailama Barahama0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesModule 2 organic chemistry
Original Title
MOULE 2 CHEM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentModule 2 organic chemistry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesOrganic Chemistry Module 2 - Spectroscopy SY-1 Semester AY - 2021-2021-PSU Balabac Campus
Uploaded by
Farhadz Sailama BarahamaModule 2 organic chemistry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Module 2 –Spectroscopy
SY- 1st Semester AY- 2021-2021-PSU Balabac Campus
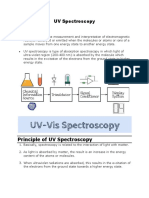
The Principle of UV-
Visible Spectroscopy
is based on the
absorption of ultraviolet light or visible light by chemical
compounds, which results in the production of distinct
spectra. ... When the matter absorbs the light, it undergoes
excitation and de-excitation, resulting in the production of a
spectrum.
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Module 2 –Spectroscopy
SY- 1st Semester AY- 2021-2021-PSU Balabac Campus
In theoretical physics, ultraviolet completion, or UV
completion, of a quantum field theory is the passing from a
lower energy quantum field theory to a more general quantum
field theory above a threshold value known as the cutoff.
A UV-Vis spectrophotometer measures the intensity of light
transmitted through a sample compared to a reference
measurement of the incident light source. ... The transmitted
light is acquired by a CCD optical detector with a wavelength
accuracy of within 0.5nm
Principle of ultraviolet–visible absorption
Molecules containing bonding and non-bonding electrons (n-
electrons) can absorb energy in the form of ultraviolet or visible
light to excite these electrons to higher anti-bonding molecular
orbitals.
There is no difference between UV and visible
spectrophotometer because both names refer to the same
analytical instrument.
UV Spectroscopy uses ultraviolet light to determine the
absorbency of a substance. In simple terms, the technique
maps the interaction between light and matter and measures.
As matter absorbs light it undergoes either excitation or de-
excitation, which generates what is known as a spectrum
UV-Vis Spectroscopy (or Spectrophotometry) is a quantitative
technique used to measure how much a chemical substance
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Module 2 –Spectroscopy
SY- 1st Semester AY- 2021-2021-PSU Balabac Campus
absorbs light. This is done by measuring the intensity of
light that passes through a sample with respect to the intensity
of light through a reference sample or blank.
The UV region covers the wavelength range 100-400 nm and is
divided into three bands: UVA (315-400 nm) UVB (280-315 nm)
UVC (100-280 nm).
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Module 2 –Spectroscopy
SY- 1st Semester AY- 2021-2021-PSU Balabac Campus
Principle of UV-Visible Spectroscopy
The Principle of UV-Visible Spectroscopy is based on the
absorption of ultraviolet light or visible light by chemical
compounds, which results in the production of distinct
spectra. Spectroscopy is based on the interaction between light
and matter. When the matter absorbs the light, it undergoes
excitation and de-excitation, resulting in the production of a
spectrum.
When matter absorbs ultraviolet radiation, the electrons
present in it undergo excitation. This causes them to jump from
a ground state (an energy state with a relatively small amount
of energy associated with it) to an excited state (an energy
state with a relatively large amount of energy associated with
it). It is important to note that the difference in the energies of
the ground state and the excited state of the electron is always
equal to the amount of ultraviolet radiation or visible radiation
absorbed by it.
UV-Visible Spectroscopy and the Beer-Lambert Law
The statement of the Beer-Lambert law can be written as
follows: When a beam of monochromatic light is made incident
on a solution that contains a substance that absorbs the
monochromatic light, the rate at which the intensity of the
beam decreases along the thickness of the solution is directly
proportional to the concentration of the absorbing substance in
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Module 2 –Spectroscopy
SY- 1st Semester AY- 2021-2021-PSU Balabac Campus
the solution and is also directly proportional to the
intensity of the incident monochromatic radiation.
As per the Beer-Lambert law, the greater the number of
absorbing molecules (that have the ability to absorb light of a
specific wavelength), the greater the extent of absorption of
the radiation.
To learn more about the principle of UV-Visible spectroscopy
and other related concepts such as infrared spectroscopy,
register with BYJU’S and download the mobile application on
your smartphone.
Frequently Asked Questions on the Principle of UV Visible
Spectroscopy
What are the Applications of UV-Visible Spectroscopy?
UV-Visible spectroscopy is widely used in the field of analytical
chemistry, especially during the quantitative analysis of a
specific analyte. For example, the quantitative analysis of
transition metal ions can be achieved with the help of UV-
Visible spectroscopy. Furthermore, the quantitative analysis of
conjugated organic compounds can also be done with the help
of UV-Visible spectroscopy. It can also be noted that this type of
spectroscopy can also be carried out on solid and gaseous
analytes in some conditions.
What kinds of detectors are used in UV-Visible spectroscopy?
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Module 2 –Spectroscopy
SY- 1st Semester AY- 2021-2021-PSU Balabac Campus
A widely used detector in UV-Vis spectroscopy is the
Photomultiplier tube. It consists of a photoemissive cathode
(which is a cathode that releases electrons when it is hit by
radiation photons), multiple dynodes (which is a device that
emit multiple electrons for each striking electron), and an
anode.
What is UV-Visible spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet and visible (often abbreviated to UV-Vis) absorption
spectroscopy is a type of spectroscopy which involves the
calculation of a light beam’s attenuation (strength/intensity
weakening) after it passes through a sample or reflects from a
sample surface
You might also like
- EAU2 - I - 04 - Ruins of The Lost RealmDocument127 pagesEAU2 - I - 04 - Ruins of The Lost RealmHache73% (15)
- m1340008 Dark FutureDocument220 pagesm1340008 Dark Futurejkj1176100% (1)
- AD GT3000 Catalogue en 12-07 CDocument52 pagesAD GT3000 Catalogue en 12-07 CMohamed AlkharashyNo ratings yet
- Magic HRC Scarf 1: by Assia BrillDocument6 pagesMagic HRC Scarf 1: by Assia BrillEmily HouNo ratings yet
- Amc Offer 500 Kva & 380 Kva DGDocument8 pagesAmc Offer 500 Kva & 380 Kva DGabhibawa100% (3)
- DR Tian Sing NG, BOSFA Fibres For Crack Control PDFDocument68 pagesDR Tian Sing NG, BOSFA Fibres For Crack Control PDFsaiNo ratings yet
- Classification of AntibioticsDocument5 pagesClassification of AntibioticsdenaNo ratings yet
- Okuma GENOS M560R-V TECHNICAL SHEET (4th Edition)Document79 pagesOkuma GENOS M560R-V TECHNICAL SHEET (4th Edition)Ferenc Ungvári100% (1)
- Spectrophotometry and ColorimetryDocument5 pagesSpectrophotometry and ColorimetryHarish.UNo ratings yet
- UV Spectroscopy - Principle, Instrumentation, Applications - Instrumentation - Microbe NotesDocument5 pagesUV Spectroscopy - Principle, Instrumentation, Applications - Instrumentation - Microbe NotesIJAJ-PHARMA TUTOR100% (1)
- Principles and Application of Spectroscopic Techniques: Chapter ThreeDocument113 pagesPrinciples and Application of Spectroscopic Techniques: Chapter ThreeKetsela YirdawNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Light Trapping in Solar Cell and Photo-detector DevicesFrom EverandIntroduction to Light Trapping in Solar Cell and Photo-detector DevicesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SpectrosDocument24 pagesIntroduction To SpectrosPIRZADA TALHA ISMAIL100% (1)
- Introduction To Molecular Spectroscopy: By: M.Z.IqbalDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Molecular Spectroscopy: By: M.Z.IqbalMuhammad TausifNo ratings yet
- Rieter k42 Brochure 2539 v3 - 89691 en PDFDocument28 pagesRieter k42 Brochure 2539 v3 - 89691 en PDFAjay Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- SpectrosDocument35 pagesSpectrosLoren Victoria AgbayNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Uv-Visible Determination of An Unknown Concentration of Kmno Solution Theory/BackgroundDocument13 pagesExperiment 2 Uv-Visible Determination of An Unknown Concentration of Kmno Solution Theory/BackgroundMuhammad Azri HaziqNo ratings yet
- Uv Visible SpectrosDocument28 pagesUv Visible Spectrosjoshishravan3003No ratings yet
- UV-Vis InstrumentDocument7 pagesUV-Vis InstrumentNorizzatul Akmal100% (1)
- EEDI FormulaDocument67 pagesEEDI Formulawaleed yehiaNo ratings yet
- Photoluminescence Spectroscopy and Its Applications 2Document11 pagesPhotoluminescence Spectroscopy and Its Applications 2RohithNo ratings yet
- Uv-Vis Spectroscopy ThesisDocument4 pagesUv-Vis Spectroscopy ThesisCustomCollegePaperUK100% (2)
- What Is UV SpectrosDocument20 pagesWhat Is UV SpectrosSimranNo ratings yet
- Principle of UV SpectrosDocument10 pagesPrinciple of UV SpectrosHesham AlsoghierNo ratings yet
- Uv Visible RadiationDocument6 pagesUv Visible RadiationNimra LiaqatNo ratings yet
- SKL DiscussionDocument3 pagesSKL DiscussionLingesswari NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 UV-Visible SpectrometryDocument32 pagesUnit 2 UV-Visible SpectrometryKrishnanand NagarajanNo ratings yet
- UV SpectrosDocument4 pagesUV SpectrosCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- Electronic SpectrosDocument82 pagesElectronic SpectrosEub EuNo ratings yet
- UV-Vis NoteDocument3 pagesUV-Vis Noteknowledge updatesNo ratings yet
- UVSpectrosDocument22 pagesUVSpectrosAbu Tareq SarkerNo ratings yet
- UV SpectrosDocument15 pagesUV Spectrosjatt da mukabalaNo ratings yet
- UV Vis SpectrosDocument19 pagesUV Vis Spectrosbharatsinhparmartithor7777No ratings yet
- Report On UV Visible Spectroscopy - CEP 506Document11 pagesReport On UV Visible Spectroscopy - CEP 506showravNo ratings yet
- Development and Optimization of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy - A ReviewDocument11 pagesDevelopment and Optimization of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy - A ReviewJafar MohammadNo ratings yet
- Module-6 Unit-4 UV-Vis Spectroscopy SpectrosDocument11 pagesModule-6 Unit-4 UV-Vis Spectroscopy SpectrosManikandan KKNo ratings yet
- Report Ni RizaDocument8 pagesReport Ni RizaInga Budadoy NaudadongNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 1 Name Rishabh Raj Prasad REG-NO 18BEE0069Document7 pagesDigital Assignment 1 Name Rishabh Raj Prasad REG-NO 18BEE0069Kumar RishabhNo ratings yet
- Uv VisDocument4 pagesUv VisohoreyNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document34 pagesUnit 4sankar velisettyNo ratings yet
- M AsadullahDocument22 pagesM AsadullahMehtab Ahmed AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation: Sources of UV RadiationDocument16 pagesInstrumentation: Sources of UV Radiationexample2000No ratings yet
- Comparison Between Spectrophotometry and Spectrofluorimetry, Its Application in Agriculture and Medicine.Document8 pagesComparison Between Spectrophotometry and Spectrofluorimetry, Its Application in Agriculture and Medicine.Ayolotu Muyiwa100% (2)
- Sathyabama University Department of Biomedical EngineeringDocument17 pagesSathyabama University Department of Biomedical EngineeringMathavaraja JeyaramanNo ratings yet
- Ultra Violet - Visible SpectrosDocument13 pagesUltra Violet - Visible SpectrosSherin SunnyNo ratings yet
- Principle of UV SpectrosDocument2 pagesPrinciple of UV SpectrosJohn BobNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of Uv SpectrosDocument6 pagesLiterature Review of Uv Spectroseeyjzkwgf100% (1)
- Chapter 17Document78 pagesChapter 17Romar PanopioNo ratings yet
- Uv-Visible Spectroscopy TheoryDocument8 pagesUv-Visible Spectroscopy TheoryHamdan afzalNo ratings yet
- UV Visible SpectrosDocument12 pagesUV Visible SpectrosAbdullah Bin TariqNo ratings yet
- MFSN 802 PresentationDocument27 pagesMFSN 802 PresentationGibsonNo ratings yet
- Polymer Analysis by UVDocument10 pagesPolymer Analysis by UVnethumini GunawardanaNo ratings yet
- B Pharm Sem 2Document34 pagesB Pharm Sem 2prajwalshende916No ratings yet
- Research Paper On Uv Visible SpectrosDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Uv Visible Spectrosj0lemetalim2100% (1)
- Group 2 - ch117l - Final Lab Report 4Document10 pagesGroup 2 - ch117l - Final Lab Report 4Luis Alfonso DañezNo ratings yet
- UV VisDocument2 pagesUV Vist4424914No ratings yet
- Introduction To Molecular Spectroscopy Lecture 1 - GammaDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Molecular Spectroscopy Lecture 1 - GammaLindsayPat8911No ratings yet
- Introduction To SpectrosDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Spectross11925877No ratings yet
- UV SpectrosDocument7 pagesUV Spectrosbszool006No ratings yet
- Spektro (1,2)Document16 pagesSpektro (1,2)Asnita HfsaniNo ratings yet
- Bab IDocument16 pagesBab IimalaNo ratings yet
- A StudyDocument6 pagesA StudySunanda VashishatNo ratings yet
- Uv Vis & FtirDocument15 pagesUv Vis & FtirVannessa Shallomy100% (2)
- Group 4 Ultraviolet Visible SpectrosDocument6 pagesGroup 4 Ultraviolet Visible SpectrosJane Frances JabricaNo ratings yet
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy - Principle, Strengths and Limitations and ApplicationsDocument19 pagesUV-Vis Spectroscopy - Principle, Strengths and Limitations and ApplicationsSajjad AliNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet and Visible (UV-Vis) Absorption Spectroscopy: A Ecl /I)Document17 pagesUltraviolet and Visible (UV-Vis) Absorption Spectroscopy: A Ecl /I)Des MamNo ratings yet
- Uv Spectroscopy 5Document11 pagesUv Spectroscopy 5Emmanuella OffiongNo ratings yet
- Shining a Light on Cool Standards: Infrared Spectroscopy Theory Explored.From EverandShining a Light on Cool Standards: Infrared Spectroscopy Theory Explored.No ratings yet
- Laser Metrology in Fluid Mechanics: Granulometry, Temperature and Concentration MeasurementsFrom EverandLaser Metrology in Fluid Mechanics: Granulometry, Temperature and Concentration MeasurementsNo ratings yet
- Photoelectron Spectroscopy: Bulk and Surface Electronic StructuresFrom EverandPhotoelectron Spectroscopy: Bulk and Surface Electronic StructuresNo ratings yet
- Medications: Jason Yu Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesMedications: Jason Yu Discharge PlanPhilip Royce EmpeñoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22-The Pre Cam Brian EarthDocument38 pagesChapter 22-The Pre Cam Brian Earthncl12142No ratings yet
- Elf-Micro Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (Smedds) : A Review On Physico-Chemical and Biopharmaceutical AspectsDocument11 pagesElf-Micro Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (Smedds) : A Review On Physico-Chemical and Biopharmaceutical AspectsMenoddin shaikhNo ratings yet
- Echo SounderDocument2 pagesEcho SounderDimas AnggaNo ratings yet
- K-90-1900 FM-200 AgentDocument1 pageK-90-1900 FM-200 AgentPutra LangitNo ratings yet
- Zener Diodes and Transient Voltage Suppressors Quarter 3, 1998 SG274 - D Rev 16Document8 pagesZener Diodes and Transient Voltage Suppressors Quarter 3, 1998 SG274 - D Rev 16Imraan RamdjanNo ratings yet
- PHontDawg Vol.2 2007Document8 pagesPHontDawg Vol.2 2007Tanczos AndrasNo ratings yet
- OCDM2223 Tutorial7solvedDocument5 pagesOCDM2223 Tutorial7solvedqq727783No ratings yet
- Consumer Studies GR 11 Revision Term 1 2023 FinalDocument20 pagesConsumer Studies GR 11 Revision Term 1 2023 FinalCerboh MazibukoNo ratings yet
- A Green Chemistry Approach To Mercury ControlDocument7 pagesA Green Chemistry Approach To Mercury ControlDennis Daniel Condori EspilcoNo ratings yet
- 10th PET POW EM 2023 24Document6 pages10th PET POW EM 2023 24rpradeepa160No ratings yet
- Sealand Equipment GuideDocument5 pagesSealand Equipment GuidePool Jaime Quispe CordovaNo ratings yet
- MonkayoDocument12 pagesMonkayoJabezNo ratings yet
- Mua prc007 en - 12042009Document73 pagesMua prc007 en - 12042009sachinsaklani23No ratings yet
- 20240119-AC MV Cable Schedule - R1Document1 page20240119-AC MV Cable Schedule - R1newattelectricNo ratings yet
- Milestone Math Review Part 1Document16 pagesMilestone Math Review Part 1api-249548920No ratings yet
- Weapon Type Code Range L M H Traits Category: Wong Rong Jing (Order #7811643)Document1 pageWeapon Type Code Range L M H Traits Category: Wong Rong Jing (Order #7811643)John SmithNo ratings yet
- BS en 480-6-2005Document5 pagesBS en 480-6-2005Abey Vettoor0% (1)
- Aiwa CX jn5 ETDocument78 pagesAiwa CX jn5 ETluzmarospiNo ratings yet
- Essay Test 2021 (Practice Test)Document3 pagesEssay Test 2021 (Practice Test)Philani HadebeNo ratings yet