Professional Documents
Culture Documents
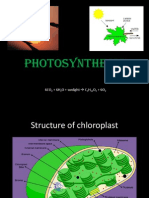
Light Dependant Reaction: Photosynthesis Summary Notes
Uploaded by
Ali Ali AliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Light Dependant Reaction: Photosynthesis Summary Notes
Uploaded by
Ali Ali AliCopyright:
Available Formats
CHARLIE COOPER StudyWise.co.
uk
PHOTOSYNTHESIS SUMMARY NOTES
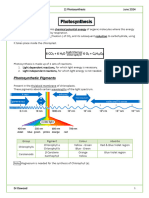
1. LIGHT DEPENDANT REACTION
In Thylakoid membranes
1. Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll
2. This boosts the electrons’ energy level so they escape chlorophyll and are taken up by an
electron carrier
3. Electrons are passed along the carrier (by oxidisation-reduction reactions), losing energy as
they do so and this lost energy helps produce ATP.
4. Meanwhile water undergoes photolysis to give rise to hydrogen ions (plus electrons and
oxygen)
5. These hydrogen ions are taken up by NADP to form REDUCED NADP.
2. LIGHT INDEPENDANT REACTION
In the stroma of chloroplasts
1. Co2 diffuses into leaf and into the stroma
2. Co2 combines with RuBP using an enzyme to produce two molecules of GP
3. GP is reduced to TP using ATP and REDUCED NADP
4. The TP has taken the hydrogen to NADP is reformed
5. Some TP molecules are converted into useful substances or are regenerated into RuBP.
StudyWise: A-Level Biology Revision
CHARLIE COOPER StudyWise.co.uk
LIMITING FACTORS:
The effect of light intensity
• As light intensity increases there comes a “light compensation point” (where the
volume of oxygen produced and carbon dioxide absorbed will increase to a point
where it is balanced by the oxygen absorbed and carbon dioxide produced by
respiration)
• When light is a limiting factor, the rate of photosynthesis is proportional to light
intensity.
The effect of carbon dioxide on the rate of photosynthesis
• High CO2 concentrations can affect the enzyme catalysed reactions that combine
ribulose biphosphate with CO2.
The effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis
• Higher temperatures often cause the rate of photosynthesis to decrease since enzymes
become denatured.
StudyWise: A-Level Biology Revision
You might also like
- 5.2. Energy For Biological ProcessesDocument5 pages5.2. Energy For Biological ProcessesAdwaar HassanNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis T5-1Document9 pagesPhotosynthesis T5-1Kyile FernandoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Bio Topic 5Document6 pagesEdexcel Bio Topic 5quesntinmoorsNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Photosynthesis Text ExplanationDocument14 pagesDokumen - Tips Photosynthesis Text ExplanationRamotSilabanNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesissteven7 IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Biomass PresentationDocument18 pagesBiomass PresentationvnyshreyasNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument43 pagesPhotosynthesisOussema Ben KasdallahNo ratings yet
- Life 112 PhotosynthesisDocument38 pagesLife 112 Photosynthesiskarabontu35No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 5.2.1Document5 pagesPhotosynthesis 5.2.1bexNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis LabDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis LabWalwin HareNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument10 pagesCalvin CycleAthena Joyce SambolanayNo ratings yet
- Light-Dependent ReactionDocument20 pagesLight-Dependent ReactionazwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument43 pagesPhotosynthesisKumaran Jothiram100% (1)
- BOT HW Chapter 8Document11 pagesBOT HW Chapter 8albelqinNo ratings yet
- 13 Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument9 pages13 Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsAarushi GoyalNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument24 pagesPhotosynthesisDexter Armamento Sulit100% (3)
- 28 PhotosynthesisDocument20 pages28 PhotosynthesisAngelNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis WorksheetAshley JohnsNo ratings yet
- Class-Xi Biology Study Material 2022-23Document21 pagesClass-Xi Biology Study Material 2022-23devil luciferNo ratings yet
- L6 PhotosynthesisDocument28 pagesL6 PhotosynthesisNaomi AceroNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 13 PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesBiology Chapter 13 PhotosynthesisSokuntheary SrunNo ratings yet
- Ch. 8 Photosynthesis F17Document70 pagesCh. 8 Photosynthesis F17bae loonaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5Document12 pagesTopic 5Joji KolangadaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 9700 Biology A-Level RevisionDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis 9700 Biology A-Level RevisionMehreen SyedNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument55 pagesPhotosynthesischezkanoelleangeliebalolongNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesisDavid PetalcurinNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 2: ChloroplastsDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis 2: ChloroplastsBonny Ya SakeusNo ratings yet
- BiomassNotes 2019Document155 pagesBiomassNotes 2019Jonathan WrightNo ratings yet
- Edexcel B A Level Biology 2015 Topics 5-10 Revision Notes PDFDocument120 pagesEdexcel B A Level Biology 2015 Topics 5-10 Revision Notes PDFMaha NaserNo ratings yet
- Raven, P. H. Et Al. 1992Document73 pagesRaven, P. H. Et Al. 1992Teflon SlimNo ratings yet
- Coupled Reaction ProcessesDocument6 pagesCoupled Reaction Processesmamariljasmine03No ratings yet
- Ch10 PhotosynthesisDocument23 pagesCh10 Photosynthesiscorygunther6451No ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument26 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISvictoire BadoNo ratings yet
- Function of PhotosynthesisDocument58 pagesFunction of PhotosynthesisJulian ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Cellular Physiology and BiochemistryDocument13 pagesCellular Physiology and BiochemistryNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- 11.1 PhotosynthesisDocument3 pages11.1 PhotosynthesisJane EmminsNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesCH 2 - PhotosynthesisnawarakanNo ratings yet
- 3 4 Group 6 Written Report With CommentsDocument7 pages3 4 Group 6 Written Report With CommentsJanine Abiegale PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document11 pagesChapter 13ririrachma fitriahNo ratings yet
- Photophosphorylation:: PhotoactivationDocument1 pagePhotophosphorylation:: Photoactivationapi-296833859No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument3 pagesBiologyKamran SaleemNo ratings yet
- 9 1photosynthesis-FinalDocument36 pages9 1photosynthesis-FinalHara Vienna ClivaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - Simple English Wikipedia The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis - Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopediaapi-253604375No ratings yet
- Outline For PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesOutline For Photosynthesiswitzy11No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 1Document32 pagesPhotosynthesis 1Allihannah PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Cellular Respiration 2018Document96 pagesChapter 2 Cellular Respiration 2018aliaNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes Topic 5 Energy Flow Ecosystems and The Environment Edexcel (IAL) Biology A LevelDocument9 pagesSummary Notes Topic 5 Energy Flow Ecosystems and The Environment Edexcel (IAL) Biology A LevelLulwa KhaskiehNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis PPDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesis PPDandena Gelmesa SobokaNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument52 pagesPhotosynthesisAdelaide CNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument39 pagesPhotosynthesisAnonymous puLHa9No ratings yet
- Bio AP CHP 9 NotesDocument13 pagesBio AP CHP 9 Noteslauren roNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 4 Q4Document32 pagesLesson 3 4 Q4Joshua DurogaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesChapter-4 Photosynthesiskavitaruby1980No ratings yet
- Light Independent Reaction - BiologyDocument3 pagesLight Independent Reaction - BiologyHidayah SakinahNo ratings yet
- Biology CH 8 and 9Document31 pagesBiology CH 8 and 9Ann QuiranteNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 12 CIE Biology A-LevelDocument5 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 12 CIE Biology A-LevelbeiyuNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 5 Energy Flow, Ecosystems and The Environment - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-Level PDFDocument9 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 5 Energy Flow, Ecosystems and The Environment - Edexcel (IAL) Biology A-Level PDFsammam mahdi samiNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument55 pagesEnergy Transformationelyza gwenNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Dynamics Part Two - KeyDocument4 pages4.2 Dynamics Part Two - KeyAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Relative Motion - KeyDocument4 pagesRelative Motion - KeyAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Law of Conservation of Energy - KeyDocument7 pagesLaw of Conservation of Energy - KeyAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- GR 12 Term 2 2018 Ps Worksheet BookletDocument64 pagesGR 12 Term 2 2018 Ps Worksheet BookletAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Basic Motion - KeyDocument7 pagesBasic Motion - KeyAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Vectors - KeyDocument7 pagesVectors - KeyAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Law of Conservation of Momentum - KeyDocument4 pagesLaw of Conservation of Momentum - KeyAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- 1-d Momentum and Impulse - KeyDocument6 pages1-d Momentum and Impulse - KeyAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- CH 1 FreshmanDocument45 pagesCH 1 FreshmanAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Richeese Updated OffersDocument7 pagesRicheese Updated OffersAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- DerivativesDocument42 pagesDerivativesAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- 2242 - Unit 4 TCA CycleDocument18 pages2242 - Unit 4 TCA CycleAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Richeese Updated MenuDocument11 pagesRicheese Updated MenuAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- C454 Lect3 ViewDocument66 pagesC454 Lect3 ViewAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- BOTPG2201 - PG 2nd Sem - GlycolysisDocument16 pagesBOTPG2201 - PG 2nd Sem - GlycolysisAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid Cycle: Step 1 Step 2 Step 8Document3 pagesCitric Acid Cycle: Step 1 Step 2 Step 8Ali Ali AliNo ratings yet
- 2.photosynthesis QusDocument7 pages2.photosynthesis QusAli Ali AliNo ratings yet
- 1 1 Revision Guide Atomic Structure Aqa PDFDocument9 pages1 1 Revision Guide Atomic Structure Aqa PDFItai Nigel ZembeNo ratings yet
- 7 Glycolysis Notes GanapathyDocument16 pages7 Glycolysis Notes GanapathyAli Ali AliNo ratings yet