Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BGP Cheatsheet PDF
Uploaded by
Arya NADA SENTOSAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BGP Cheatsheet PDF
Uploaded by
Arya NADA SENTOSACopyright:
Available Formats
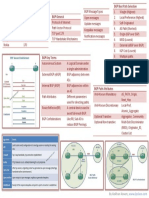
BGP CHEATSHEET – PAGE 1/2
BGP TABLE TYPES BGP NEIGHBOR STATES BGP TERMINOLOGY BGP BASICS
For BGP Routing Information Base (RIB) to learn BGP routes through When BGP is configured
its neighbours, store the best BGP routes and then advertise the best with a neighbour IP
routes to neighbours/peers, there is need for multiple BGP tables address, it goes through a
BGP Routing Information Base consists of three parts: Adj-RIBs-In , series of stages before it
Loc-RIB and Adj-RIBs-Out reaches the desired
Established state. Per RFC
1771, BGP goes through
the following stages of a BGP PATH ATTRIBUTES
neighbour relationship – https://ipwithease.com
https://ipwithease.com
Following are the commands to find output for 3 BGP tables
(Adj-RIBs-Out,Loc-RIB andAdj-RIBs-In) :
BGP MESSAGE TYPES
https://ipwithease.com
EXAMPLE TOPOLOGY TO UNDERSTAND THE USE OF TABLE-MAPS: All BGP message are unicast to the one neighbour over the TCP
connection. BGP BEST PATH SELECTION How does BGP choose the best
R1 is advertising a route of its
loopback 1 i.e. 1.1.1.1 to Route path?
Reflector. We have applied a Using the best path selection
route-map on Route-Reflector algorithm, BGP works through
to deny everything and then this each attribute until it finds one
route-map is called in the table- to that gives a preference. If
map command so as to avoid the there is no preferred attribute
installation of the route in the BGP will always route over the
RIB and FIB on the RR. Though RR shortest AS path.
doesn’t install the route in its RIB
https://ipwithease.com & FIB it still reflects the route to R2. https://ipwithease.com
https://ipwithease.com
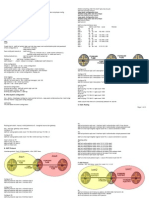
BGP CHEATSHEET - PAGE 2/2
SAMPLE SCENARIO eBGP MULTIHOP BGP TYPES – eBGP and iBGP
R1#
router bgp 1
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 192.168.12.0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 1 TROUBLE SHOOTING COMMANDS
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source
R3#sh run
Loopback0 ——–>R1 to use Loopback 0
router bgp 3
as source for BGP neighborship and
no synchronization
updates
network 192.168.23.0
no auto-summary
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 1
!
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source
ip route 2.2.2.0 255.255.255.0
Loopback0——–>R3 to use Loopback
192.168.12.2 ——->Static Route to
0 as a source for BGP neighborship
reach Loopback0 of R2
and updates with R2
R2#sh run no auto-summary
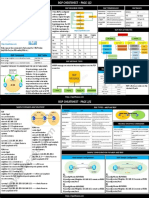
router bgp 1 ! SAMPLE CONFIGURATION FOR eBGP AND iBGP
no synchronization ip route 2.2.2.0 255.255.255.0
network 192.168.12.0 192.168.23.2——->Static Route to eBGP Sample Configuration: iBGP Sample Configuration:
network 192.168.23.0 reach Loopback0 of R2
neighbour 1.1.1.1 remote-as 1
neighbour 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0 ——–>R2 to use
Loopback 0 as a source for BGP neighborship and updates with R1
neighbor 1.1.1.1 next-hop-self
neighbour 3.3.3.3 remote-as 3
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback0——–>R2 to use Loopback R1 R1
0 as a source for BGP neighborship and updates with R3 R1(config)#Router BGP 65001 R1(config)#Router BGP 65001
no auto-summary R1(config-router)#Neighbor 192.168.10.2 remote-as 65002 R1(config-router)#Neighbor 192.168.10.2 remote-as 65001
! R1(config-router)#exit R1(config-router)#exit
ip route 1.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.12.1 ——->Static Route to R2 R2
reach Loopback0 of R1 R1(config)#Router BGP 65002 R1(config)#Router BGP 65001
ip route 3.3.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.23.3 ——->Static Route to R1(config-router)#Neighbor 192.168.10.1 remote-as 65001 R1(config-router)#Neighbor 192.168.10.1 remote-as 65001
reach Loopback0 of R3 R1(config-router)#exit R1(config-router)#exit
https://ipwithease.com
You might also like
- Interview Questions Topic-BgpDocument21 pagesInterview Questions Topic-BgpMansharam PatidarNo ratings yet
- BGP Short Note FileDocument60 pagesBGP Short Note FileTabarez AhmedNo ratings yet
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) - Port 179: Gateway Protocols (IGP's)Document32 pagesBGP (Border Gateway Protocol) - Port 179: Gateway Protocols (IGP's)Nitesh MulukNo ratings yet
- BGP Path Selection: Selects The Best Path Based On A List of AttributesDocument38 pagesBGP Path Selection: Selects The Best Path Based On A List of Attributeschandrashekar_ganesanNo ratings yet
- BGP Techniques For ISPDocument76 pagesBGP Techniques For ISPmailandrewgNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsFrom EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo ratings yet
- BGP Questions and Answers Vol 1.0Document25 pagesBGP Questions and Answers Vol 1.0Eduardo AguilarNo ratings yet
- Versatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSFrom EverandVersatile Routing and Services with BGP: Understanding and Implementing BGP in SR-OSNo ratings yet
- IP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsFrom EverandIP Routing Protocols All-in-one: OSPF EIGRP IS-IS BGP Hands-on LabsNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsFrom EverandTroubleshooting Campus Networks: Practical Analysis of Cisco and LAN ProtocolsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- BGP Short Notes: Key Concepts and Usage of the Border Gateway ProtocolDocument12 pagesBGP Short Notes: Key Concepts and Usage of the Border Gateway Protocolparveen_1974No ratings yet
- BGP Introduction - Understanding the Border Gateway ProtocolDocument15 pagesBGP Introduction - Understanding the Border Gateway ProtocolPankaj GargNo ratings yet
- Deploying Next Generation Multicast-enabled Applications: Label Switched Multicast for MPLS VPNs, VPLS, and Wholesale EthernetFrom EverandDeploying Next Generation Multicast-enabled Applications: Label Switched Multicast for MPLS VPNs, VPLS, and Wholesale EthernetNo ratings yet
- Cisco BGPDocument82 pagesCisco BGPMohit KumarNo ratings yet
- BGP TutorialDocument157 pagesBGP Tutorialbhavik_babariaNo ratings yet
- BGP Advanced Lab PDFDocument8 pagesBGP Advanced Lab PDFDwi UtomoNo ratings yet
- How To Load Images To The EVEDocument2 pagesHow To Load Images To The EVESergio Tomas SaraviaNo ratings yet
- BGP Best Path Selection Cheat SheetDocument1 pageBGP Best Path Selection Cheat SheetDavi Sadaseeven Saminaden0% (1)
- Lab BGP JuniperDocument20 pagesLab BGP Junipercru55er100% (1)
- Ospf - Study: Saravanan ARDocument52 pagesOspf - Study: Saravanan ARdouglosNo ratings yet
- DMVPN TutorialDocument10 pagesDMVPN TutorialwahyuabadiNo ratings yet
- BGP TroubleshootingDocument191 pagesBGP TroubleshootinglavidolacoNo ratings yet
- Building Data Center Networks With VXLAN EVPN Overlays - Part IIDocument150 pagesBuilding Data Center Networks With VXLAN EVPN Overlays - Part IIPhichitNo ratings yet
- Cisco Unified Communications Manager 8: Expert Administration CookbookFrom EverandCisco Unified Communications Manager 8: Expert Administration CookbookNo ratings yet
- OSPF Part3 - CheatSheet ATech (Waqas Karim)Document1 pageOSPF Part3 - CheatSheet ATech (Waqas Karim)Waqas Karim100% (1)
- CCNP Route: PPP Configuration and Troubleshooting GuideDocument65 pagesCCNP Route: PPP Configuration and Troubleshooting GuideMashud Ashraf BarbhuiyaNo ratings yet
- 1 CCIE RS v5 Step by StepDocument100 pages1 CCIE RS v5 Step by StepTuPro Fessional100% (1)
- Configuring VXLAN BGP EVPNDocument13 pagesConfiguring VXLAN BGP EVPNEmailiftekhar100% (2)
- ASR9000 Troubleshooting ArchitectureDocument165 pagesASR9000 Troubleshooting ArchitectureEllenNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 MulticastDocument1 pageIpv4 MulticastopexxxNo ratings yet
- MPLS Fundamentals ExplainedDocument52 pagesMPLS Fundamentals ExplainedBon Tran HongNo ratings yet
- MPLS (JUNIPER NETWORK) PLANES AND COMPONENTSDocument37 pagesMPLS (JUNIPER NETWORK) PLANES AND COMPONENTSsiddharthNo ratings yet
- BGP Border Gateway Protocol e Book 1Document514 pagesBGP Border Gateway Protocol e Book 1romaric assyNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7.1 Tshoot SaDocument126 pagesCCNPv7.1 Tshoot SaBrandy100% (1)
- MPLS HandbookDocument278 pagesMPLS Handbooksaikyawhtike100% (1)
- CCNP Route ManualDocument60 pagesCCNP Route Manualmansoor.ahmed100100% (1)
- OSPF Demystified With RFC: Request For Comments Translated Into PracticeFrom EverandOSPF Demystified With RFC: Request For Comments Translated Into PracticeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CLI Cheat Sheet: Top CommandsDocument12 pagesCLI Cheat Sheet: Top CommandsmikeNo ratings yet
- OSPF Deep DiveDocument149 pagesOSPF Deep DiveNirmal KumarNo ratings yet
- MSTP ConfigurationDocument42 pagesMSTP ConfigurationLeon DobrzinskyNo ratings yet
- Cisco SDWAN Solution OverviewDocument68 pagesCisco SDWAN Solution Overviewshashwat tiwariNo ratings yet
- VRF, MPLS and MP-BGP FundamentalsDocument55 pagesVRF, MPLS and MP-BGP FundamentalsIVAN TANEV100% (2)
- BGP Route Distinguisher vs Route Target ExplainedDocument2 pagesBGP Route Distinguisher vs Route Target ExplainedMohit MittalNo ratings yet
- Add Certificates To Cisco Sd-Wan Lab (Version 18.4.4) : 1) VmanageDocument21 pagesAdd Certificates To Cisco Sd-Wan Lab (Version 18.4.4) : 1) VmanageNarender GargNo ratings yet
- Tshooting Cisco VPN SolutionsDocument107 pagesTshooting Cisco VPN SolutionsAdrian SoltaniNo ratings yet
- Cisco Nexus 7000Document85 pagesCisco Nexus 7000Roger Jerí100% (1)
- Show Commands XR v1Document1 pageShow Commands XR v1jaynexoNo ratings yet
- Nexus VPCDocument11 pagesNexus VPCNdaru Prakoso100% (1)
- BGP Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesBGP Cheat SheetAndré Stato FilhoNo ratings yet
- Advances in BGP: BRKIPM-3005Document125 pagesAdvances in BGP: BRKIPM-3005Laura IancuNo ratings yet
- Advanced CCIE Routing & Switching: Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SPDocument13 pagesAdvanced CCIE Routing & Switching: Narbik Kocharians CCSI, CCIE #12410 R&S, Security, SPABhiraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Cisco ASA Firewall ConfigurationDocument18 pagesCisco ASA Firewall ConfigurationjbonNo ratings yet
- BGPDocument135 pagesBGPNdahimana EmmyNo ratings yet
- Patrik PDFDocument55 pagesPatrik PDFaldivxNo ratings yet
- Patrik PDFDocument55 pagesPatrik PDFaldivxNo ratings yet
- Patrik PDFDocument55 pagesPatrik PDFaldivxNo ratings yet
- Patrik PDFDocument55 pagesPatrik PDFaldivxNo ratings yet
- Fortinet Fortigate Cli CheatsheetDocument2 pagesFortinet Fortigate Cli CheatsheetAyanNo ratings yet
- Cisco Juniper Cli CheatsheetDocument1 pageCisco Juniper Cli CheatsheetAmit kumarNo ratings yet
- Cisco Juniper Cli CheatsheetDocument1 pageCisco Juniper Cli CheatsheetAmit kumarNo ratings yet
- BGP Cheatsheet PDFDocument2 pagesBGP Cheatsheet PDFSai Rajesh SNo ratings yet
- Fortinet Fortigate Cli CheatsheetDocument2 pagesFortinet Fortigate Cli CheatsheetAyanNo ratings yet
- DEF CON 30 - Hadrien Barral - Emoji Shellcoding ?, ?, and ? - PresentationDocument141 pagesDEF CON 30 - Hadrien Barral - Emoji Shellcoding ?, ?, and ? - Presentationkumar sanjayNo ratings yet
- Drewry Capability StatementDocument9 pagesDrewry Capability Statementmanis_sgsNo ratings yet
- Customer Status Update Report 27th January 2015 ColourDocument20 pagesCustomer Status Update Report 27th January 2015 ColourmaryNo ratings yet
- MATH 499 Homework 2Document2 pagesMATH 499 Homework 2QuinnNgo100% (3)
- Hospital Food Service: October 2019Document28 pagesHospital Food Service: October 2019Shaikh Sobiya 57No ratings yet
- Argacel TCW_enDocument2 pagesArgacel TCW_enUtpalNo ratings yet
- Switchword PairsDocument6 pagesSwitchword PairsLaleKulahli100% (7)
- Loveology: God. Love. Marriage. Sex. and The Never-Ending Story of Male and Female. by John Mark Comer, SamplerDocument32 pagesLoveology: God. Love. Marriage. Sex. and The Never-Ending Story of Male and Female. by John Mark Comer, SamplerZondervan40% (5)
- Wind Energy Services Brochure 4696 3 Da en PDFDocument62 pagesWind Energy Services Brochure 4696 3 Da en PDFghadasaudiNo ratings yet
- Training EvaluationDocument15 pagesTraining EvaluationAklima AkhiNo ratings yet
- Patrick Meyer Reliability Understanding Statistics 2010Document160 pagesPatrick Meyer Reliability Understanding Statistics 2010jcgueinj100% (1)
- BS 0812-114 - 1989Document12 pagesBS 0812-114 - 1989عمر عمرNo ratings yet
- Republic OF THE Philippines Department OF Budget AND Manageme 589 May 25, 2022Document14 pagesRepublic OF THE Philippines Department OF Budget AND Manageme 589 May 25, 2022Juvy BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Orienteering Lesson PlanDocument34 pagesOrienteering Lesson PlanJuan Carlos Guillen BayonNo ratings yet
- R V Akeemly Grant & Andre WilliamsDocument5 pagesR V Akeemly Grant & Andre WilliamsKerry-Ann WilsonNo ratings yet
- Y10 ICT End of TermDocument7 pagesY10 ICT End of TermIvy Atuhairwe BisoborwaNo ratings yet
- Telecom Business Management Systems Net ProjectDocument68 pagesTelecom Business Management Systems Net ProjectRahul RaiNo ratings yet
- Eriopon R LiqDocument4 pagesEriopon R LiqsaskoNo ratings yet
- History All Pictures QuestionsDocument7 pagesHistory All Pictures QuestionsDivyansh RajoriaNo ratings yet
- AMS 2750 E Heat Treatment Standards ComplianceDocument3 pagesAMS 2750 E Heat Treatment Standards ComplianceQualidadeTFNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument44 pagesResearchGwend MemoracionNo ratings yet
- Personal SWOT AnalysisDocument8 pagesPersonal SWOT AnalysisNamNo ratings yet
- Implementing Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure: (Dcaci)Document2 pagesImplementing Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure: (Dcaci)radsssssNo ratings yet
- Math207 Portfolio1 2Document5 pagesMath207 Portfolio1 2api-297797024No ratings yet
- CWI - Part A Fundamentals Examination (Full) PDFDocument43 pagesCWI - Part A Fundamentals Examination (Full) PDFJulian Ramirez Ospina100% (4)
- LESSON PLAN On PancreasDocument4 pagesLESSON PLAN On PancreasShweta Pal100% (1)
- Arnold Jacobs: His Global Influence: Midwest Clinic, Thursday, December 17 12:00-1:00pmDocument17 pagesArnold Jacobs: His Global Influence: Midwest Clinic, Thursday, December 17 12:00-1:00pmAlex MoralesNo ratings yet
- Effect of Grain Boundary Thermal Expansion on Silicon Nitride Fracture ToughnessDocument8 pagesEffect of Grain Boundary Thermal Expansion on Silicon Nitride Fracture Toughnessbrijesh kinkhabNo ratings yet
- Does Cash App Have Business Accounts - Google SeaDocument1 pageDoes Cash App Have Business Accounts - Google SeaAdedayo CrownNo ratings yet