Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ieema Transformer Proection Power Plant
Ieema Transformer Proection Power Plant
Uploaded by
ardianto hamonangan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views6 pagesIeema Transformer Proection Power Plant
Ieema Transformer Proection Power Plant
Uploaded by
ardianto hamonanganCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Article
1.0
Introduction
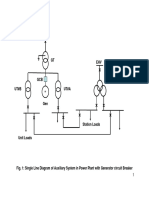
A typical power plant is equipped with following
ower transformers:
4) Generator Transformer (GT)
») Station Transformer (ST)
c) Unit Transformer (UT)
Generator transformer evacuates the generated
power. In a plant with Generator circuit breaker
(GCB), GT can also be used to feed the auxiliaries
vwa Unit transformer. Refer Fig.1. Unit Transformer
feeds the unit auxiliary loads and Station Transformer
feeds the station auxiliary loads. In a plant without
GCB Station Transformer draws power from the grid
to provide startup power.
‘This article discusses the protection philosophy for
the above transformers. it excludes interconnecting
transformer ((CT), HV and LV Auxiliary transformers
Fig. 1- Single Line Diagram of Auxitary System in Power Plant
vith Generator circuit Breaker
84
2.0 Transformer Protections
The protections provided for the power transformers,
are detailed below’
24
2A4
Protection of Generator Transformer (GT)
Electrical protections.
2.1.1.1 GT differential protection (87GT)
2) In case of three phase units, GT differential
typically covers the overhead section of the
switchyard in addition to the transformer,
Refer Fig.2,
Fig, 2. Three Phase GT Protection
b) For a bank of single phase transformer,
the GT differential generally covers only
the transformer. A separate differential
protection (87L) covering the HV winding
and overhead section is also provided
for bank of single phase transformer.
Refer Fig. 3
June 2013 @@M@ journal
Fig, 3 Bank of Single Phase GT Protection
‘) It may be noted that CTs shown in shaded
area in Fig 2 and Fig 8 are bushing CTs.
2.1.1.2) For a bank of single phase transformers,
differential protection is shown in Fig 4
Fig.4- Conventional Differential Scheme for Single phase
transformer bank
b) Two CTs, on either side of LV windings are
provided, intrinsically to cover ground faults
in the delta winding. [Ref (1)]. This scheme
is built on the premise that sufficient current
will flow on occurrence of earth fault.
©) However in a power plant, high resistance
{grounding is provided for generator neutral
The earth fault current on the delta side of
GTis limited within 108.
4) The differential protection of generator
transformer cannot sense the ground fault in
the delta winding. Itcan be sensed only by
voltage based earth fault sensing scheme
provided on generator terminals. (S8N and
64G in Fig.2 and Fig.3)
€) In view of the above, provision of one
CT on delta winding is sufficient. Refer
Fig.5. This philosophy is adopted in all
recently engineered power plants in
authors’ company.
FeemMea journal Juve 2013
Fig: Dilerential scheme with single CT in deta winding
2.1.1.8.) Overhang differential protection (87L) or HV
Restricted earth fault (REF) protection (64)
= Overhang differential protection (87L) is,
a biased three phase differential protection
covering the HV windings as well as the
‘overhead conductors from switchyard to the
transformer. This protection is provided for
fa bank of single phase transformers. This
protection is implemented as a differential
protection of each individual HV winding
and its EHV overhead connection. For
this purpose one CT is provided at the HV
neutral bushing and its corresponding CT
Js provided at the EHV breaker end. Refer
Fig.6. In this case separate REF protection
is not required for Generator transformer.
Alternatively a single pole differential can
act as a REF protection.
Fig.6: Ditlerentia! Protection for Single Phase Generator
Transformer
b) For three phase generator transformer, high
Impedance restricted earth fault protection
(64) is provided. The restricted earth fault
protection usually covers only the HV
windings. Refer Fig.2
‘c) The zone covered by differential protection
and REF protection in case of 3 x single
phase GT bank and three phase GT is
summarised in Table 1.
85
Article
‘Currents from LV
Diterenl bushing ee
protection | Tensformer | compared against | Rt Fig 9
(77) eee ‘currents from HV
busting ot
1 Relig 8
Coents rom ny | 2: Mil espond to pase
axsinge |Ovang —|Transomer tv |oural using cre [=r se at,
Preset | iferontal_ |winangs and EHV | are compared against |. REF Protection (oa
Bank _| Protection (871) | connection suena fem EHV") Fi protect |
provided,
Tet used
1 Rel Fg. @
Sumaiedcuensot | 2 Wi veepond to ear
Transomer HV | metal bushing CF | faults ony
REF prtecton | inane and EHV |e compared azant | 887. protection need
comecton” |aummaed carers ot |not be prone fe
tweets prcacion eroded
I aol used
Caren For tv
bites! |tansiomer iv [bushing Cae
protien | wnnge and EHV. | compared against | Ra Fl 2
‘Thies ph (87GT) connection ‘currents from EHV
fear ots
‘Current on HV
‘neutral bushing CT
REF prtecton |ansomer HY [Tcompared against | Ref Po 2
sumatod cents of
FV phe busing te :
2.114 Overa tert proton (6708) —This b) Pressure ket Device ip
covers the Generator and the GT and
functions as a backup to the GT differential @ Busihole sien end We
protection. 4) Oil level low alarm
2.1.1.5 Instantaneous over current protection acts as a For single phase transformers all the above
‘backup to GT differential protection (5067). Protections are provided for each of the
2.1.1.8 GTHV side over-current protection (51GT) Phase unit
2441.7 GT HV side stand-by earth-ault protection | 213. In addition to the above, fie protection is
(SINGT) also provided for the GT.
24.4.8 GT Oversluxing protection (24) - sensed | 2.1.4 The electrical protections mentioned in Cl
from selected EHV bus voltage (not shown 2.1.1 are suitably grouped in two or three
in figure) ‘numerical relays. The grouping is done in
Protections listed in 2.1.1.6 to 2.1.1.8 are such a manner that each acts as a backup
provided for protection against uncleared to the other.
oid fauits/disturbances.
A typical suggested grouping of functions
24.2 Thermal / Mechanical protections for bank of single phase transformers is
a) OT1/ WTI~ alarm and trip Given in Table -2.
86 June 2013 EMG journal
Article
‘Overal aferomta protection (870A)
Relay -2 (R2): Trafo Protection Relay
‘verhang diferential protection (671)
(GT HY side instantaneous and IDMT phase over
current protection (50/51GT)
Relay. (RS): Tao |
GT Differential Protection (8767)
GTHV sie stanchby eathaut protection (51NGT)
Overining (4)
‘Atypical suggestive grouping of functions for three
phase transformers is given in Table 3
REF protection (4)
GT HV side instantaneous and IDMT phase over
current pretecton (8/6167)
Gr Diferental Protection (@7GT)
GT HV side stand-by earth-fault protection (51NGT)
Overiluxing (24)
2.2 Protection of Station Transformer (ST)
2.2.1 Electrical protections (Refer Fig.7)
ig
Fig. 7 Station Transformer Protection
22.1.1 ST differential protection (87ST) - ST
differential covers the overhead section of
the switchyard in addition to the transformer,
1@MO jOUFNAL June 2013
2212
22.13
2244
22.15
22.16
222
223
224
225
‘and busduct connecting the LY
the switchgear.
ding with
HV winding Restricted Earth
fault, (REF) protection (64HV)
High impedance REF protection is usually
provided for HV side winding
HV phase over-current and directional
earth fault protection (60/51/67N)
The instantaneous (50) stage of phase
and earth fault protection is set to clear
HV side faults instantaneously. The IDMT
stage of phase overcurrent protection
is coordinated with LV side relays. The
overcurrent protection also acts a backup
to differential protection for HV side faut.
The earth fault elomentis directionaised to
ensure pickup for ground faults towards ST
and not in grid
LV winding Restricted Earth
fault (REF) protection (64LV)
Low impedance REF protection is envisaged
for LV side winding. A low impedance REF
scheme provides sensitive protection without
provision of interposing CT and stabilising
resistor as required in high impedance
protection scheme,
LV Stand-by Earth faut protection (51NS)
= This protection is provided to clear
Lncleared earth faults on LV side. tacts as
backup to LY REF protection aso.
‘ST Ovor-fuxing protection (24) ~ This
protection is provided to protect the
transformer against gid over voltages. is
‘sensed from selected EHV bus voltage (not
shown in figure)
‘Thermal / Mechanical protections
8) OT1/ WTI— alarm and trip
») Pressure Relief Device trip
6) Buchholz alarm and tip
4) Oil Surge Relay ~ trip
@) Oil level low alarm
In adcition to the above, fire protection is
also provided for the ST.
It may be noted that CTs shown in shaded
area in Fig 7 are bushing CTs.
‘The electrical protections are grouped in two
‘numerical relays. The grouping is done in
such a manner that each acts as a backup
to the other. The grouping of functions can
be as per Table -4
87
Article
LY side stand-by earth-ault protection (51NS)
HV side phase over current and earth fauit protection
(60/51/67)
HV REF
ST Differential Protection (87ST)
protection (64HV)
LV REF protection (G4LV)
‘Overtiuxing (24)
23
23.1
Protection of Unit Transformer (UT)
Electrical protections (Refer Fig.8)
232
233
234
235
LV side stand-by earth-fault protection (51NS)
Thermal | Mechanical protections
a) OTI/ WTI ~ alarm and trip
) Pressure Relief Device trip
©) Buchholz - alarm and trip,
¢) Oil Surge Relay ~ trip
) Oil level low alarm
In addition to the above, fire protection is
also provided for the UT.
It may be noted that CTs shown in shaded
area in Fig 8 are bushing CTs
‘The electrical protections are grouped in two
numerical relays. The grouping is done in
such a manner that each acts as a backup
to the other. A typical grouping of functions
could be as per Table -5
HV side phase over current protection (50/51)
UT Differential Protection (87UT)
Fig, 8 Unit Tanstonmer Protection
23.1.4
23.1.2
23.1.3
2314
88
UT differential protection (87UT) - UT
differential covers the transformer and
busduct connecting the LV winding with
the switchgear.
HV phase overcurrent protection (50/51)
The instantaneous stage of phase over-
current protection is set to clear HV side
faults instantaneously. The IDMT stage of
phase overcurrent protection is coordinated
with LY side relays. talso acts a backup to
aitferential protection for HV side faults
LV winding Restricted Earth
fault (REF) protection (64LV)
Low impedance REF protection is envisaged
for LV side, The comments made for ST are
applicable here also.
LY Stand-by Earth fault protection (S1NS)
= This protection is provided to clear
uncleared earth faults on LV side. tacts as.
backup to LV REF protection also.
REF protection (64)
3.0 Grouping of Protection functions
34
32
33
‘There is usually an apprehension regarding
provision of LV side REF and differential
protection in one relay (Relay 2 in Table-4
land Table-S) as suggested in Cl 2.2.5 and
235,
‘The vector group of ST is star/star with
EHY side solidly earthed, UT is a delta/star
transformer. On HV side of UT, earth fault
is restricted within 10A. Current based
protections do not respond to earth fauits
on HY side of UT. The earth fault is sensed
only by voltage based earth fault scheme
provided on generator terminals. (59N and
64G in Fig2 and Fig.3)
Usideof UTand STs earthedthroughneutral
{grounding resistor (NGR) restricting the earth
fault current to typically 300A. Operation of
differential protection is doubitul for earth
faults on LV side especially for faults within
the winding (Ref (2)]. Only REF and SEF
protection will definitely respond to LV side
earth faults.
June 2013 ieemea journal
Article
3.4.1 The responses for differential protection, REF and backup over current and earth fault protection under
various fault conditions for ST and UT are tabulated in Table-6A and 6B respectively.
Faults
Table - 6A: Protections for ST
WREF HV side | HV side inst | LV Standby
fault
Diferential Protection | protection | IOMTOC | OC &EF | Earth Fautt
HV side Phase |X Ee ; oe
faut
HY side earth fault |X a x =
WW side Phase |X ay 4 a Ei
LV side earth fault | Operation doubitul due
to limited sensitivity
X— Responds 1 fault
Coe an
Protections
Fauts LW REF HV side | HV side inst | LV Standby
Diferential Protection | eee ae Seren
HV sido
Phase fault D ae eZ 2% a
HV side earth fz? ns a
faut
LV side Phase
fault me a x rE a
LY side earth | Operation doubtful due Pe a y
fault to limited sensitivity
X- Responds to ful
35 As soen from Table-6A and 6B, for phase | 43 Suggestions are given (Tables 2 to 5) for
faults over-current protection acts as grouping protection elements in two or tree
backup to diferontial. For earth faults on humercal relays
Lside, standby earth faultactsabackupto | 4.4 Justification for including LV REF and
REF protection differential protection in the same relay
6 Providing LV REF and dierent protection fr staon transformer / unt wansformer
Inseparate relays has no true value addition, 9
as ferential protection wilnotback up REF | REFERENCES
protection in majority cases, [1] Protective Relaying Principles and Appcatons by
Btackburn
3.7 In addition to the electrical protections,
‘mechanical protections are also provided
for fast fault clearance of transformer
internal fault.
4.0 Conclusions and Recommendations
4a
42
The scheme (Fig 5) suggested inthis article
can be adopted for citferential protection of
‘bank of ingle phase generator transformers.
It eliminates three CTs compared to
conventional scheme without sacrificing
stability and sensitivity of scheme.
The zones covered by each protection
element have been clearly brought out
1@MA jOUFNAl June 2013
[2} “Sensitivity Comparison of Diterential, REF and Over
current Protection’, K Rajamani. EEMA Journal, October
2002, pp 28 - 93.
Rajamani Bina Mita
Allon astra
89
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- NO Cubicle Phasa Core VA Inject (A) Measure (V)Document3 pagesNO Cubicle Phasa Core VA Inject (A) Measure (V)ardianto hamonanganNo ratings yet
- Manual Book - PCI Three PhaseDocument9 pagesManual Book - PCI Three Phaseardianto hamonanganNo ratings yet
- Manual Book - Primary Current Injection Single PhaseDocument9 pagesManual Book - Primary Current Injection Single Phaseardianto hamonanganNo ratings yet
- K Factor Rated Transformer: Venkatesan R Electrical Engineer - Power Projects, Chennai +91 9791560792Document23 pagesK Factor Rated Transformer: Venkatesan R Electrical Engineer - Power Projects, Chennai +91 9791560792ardianto hamonanganNo ratings yet
- Transformer Stability TestsDocument5 pagesTransformer Stability Testsardianto hamonanganNo ratings yet
- Transformer General Test TalkDocument12 pagesTransformer General Test Talkardianto hamonanganNo ratings yet
- IEEMA Transformer Protection FigsDocument8 pagesIEEMA Transformer Protection Figsardianto hamonanganNo ratings yet
- Ground Distance RelaysDocument78 pagesGround Distance Relaysardianto hamonanganNo ratings yet