Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Questions For Review: Jasriel Vera Hilary S. Maquiling
Uploaded by
Jasriel Vera Hilary0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Review Questions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesQuestions For Review: Jasriel Vera Hilary S. Maquiling
Uploaded by
Jasriel Vera HilaryCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Questions for Review
Jasriel Vera Hilary S. Maquiling
1. What are the main characteristics of a competitive market?
Many Competing Firms.
Similar Products Sold.
Equal Market Share.
Buyers have full information.
Ease of Entry and Exit.
2. Explain the difference between a firm's revenue and its profit? Which
do firms Maximize?
Revenue is the overall income made by the sale of goods or
services related to the company's primary operations.
Profit is the number of income that stays after recording financial
transactions for all expenses, debts, additional income streams,
and operating costs.
The general rule is that the firm maximizes profit by processing
that amount of output where marginal revenue = marginal cost.
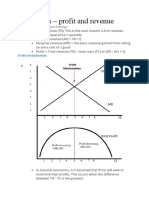
3. Draw the cost curves for a typical firm. Explain how a competitive firm
chooses the level of output that maximizes profit.
Total cost Average fixed cost
Total Fixed cost Total Variable cost
Average Variable cost Average cost
Total Revenue
Marignal Cost
Cost Curves:
Total Fixed costs
do not change with output. It is run up when the return is
zero.
Total Variable costs
change with the change in the output.
Total costs
the addition of total fixed costs and total variable costs.
Average fixed costs
total fixed costs per output.
Average variable costs
total variable costs per output.
Average costs
total costs per output.
Marginal cost
the cost incurred by producing an extra unit of output.
A firm is in equilibrium when:
Distance between TR and TC should be maximum.
Total revenue is greater than total cost.
It maximizes its profit at that level of output when total
revenue (TR) is maximum than total cost (TC)which is
shown graphically below:
4. Under what condition will a firm shut down temporarily? Explain.
In the short run
For a firm that can't retrieve its fixed costs, firm will have no
choice but to shut down temporarily if the price of the good
is less than the average variable cost.
In the long run, when the firm could still recover both fixed
and variable costs, it will choose to exit if the price is less
than the average total cost.
5. Under what condition will a firm exit a market? Explain.
Firms will enter or exit the market until profit is driven to zero. In
the long run, price equals the minimum of average total cost.
6. Does a competitive firm's price equal its marginal cost in the short run,
in the long run, or both? Explain.
Both. A firm's price = marginal cost in the two, the short run and
the long run. In both the short run and the long run, price =
marginal revenue. The firm should expand output as long as
marginal revenue outrun the marginal cost, and reduce output if
marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
7. Does a competitive firm's price equal the minimum of its average total
cost in the short run, in the long run, or both? Explain.
In the long run. The firm's price = the minimum of the average
total cost.
In the short run. The price may be bigger than the average total
cost, where the firm is gaining profits, or the price may be less
than the average total cost, in which case the firm is making
losses.
8. Are market supply curves typically more elastic in the short run or in
the long run? Explain.
The market supply is often more elastic in the long run. It is
supposed that in the long run, a firm can utilize all production
factors to higher the supply, considering, in the short run, the
firm can increase only labor.
You might also like
- Profits of Firms in The Short Ru1Document4 pagesProfits of Firms in The Short Ru1Let it beNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document2 pagesChapter 14usama farooqNo ratings yet
- Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply: Review QuestionsDocument14 pagesProfit Maximization and Competitive Supply: Review QuestionsTonoy Peter CorrayaNo ratings yet
- Maeco - Midterm ReviewerDocument2 pagesMaeco - Midterm ReviewerAngel PasaholNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Chapter 7 Q&ADocument6 pagesModule 5 - Chapter 7 Q&ABusn DNo ratings yet
- Business Economics - Neil Harris - Summary Chapter 3Document2 pagesBusiness Economics - Neil Harris - Summary Chapter 3Nabila HuwaidaNo ratings yet
- 5perfect CompetitionDocument19 pages5perfect CompetitionSHERIF GABERNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Profit and Revenue Learning CompetenciesDocument4 pagesLesson 8 Profit and Revenue Learning CompetenciesDianne Jane LirayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply: Review QuestionsDocument9 pagesChapter 8 Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply: Review QuestionsAnisaNo ratings yet
- Learning Unit - 8 Profit MaximisationDocument7 pagesLearning Unit - 8 Profit Maximisationbohlale.mahlangu18No ratings yet
- Analysis of Perfectly Competitive MarketDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Perfectly Competitive MarketSharif HassanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Perfectly Competitive MarketDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Perfectly Competitive MarketSharif HassanNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - Theory of D Firm - 2Document22 pagesTopic 7 - Theory of D Firm - 2Aina NajihahNo ratings yet
- The Production ProcessDocument4 pagesThe Production ProcessOh MyNo ratings yet
- Market Structure Notes & QuestionsDocument3 pagesMarket Structure Notes & Questionsafrocircus09No ratings yet
- 7 The Production ProcessDocument4 pages7 The Production ProcessOh MyNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Output and CostsDocument16 pagesMicroeconomics: Output and CostsArmin RidžalovićNo ratings yet
- Profit Maximization and Competitive SupplyDocument4 pagesProfit Maximization and Competitive SupplyRodney Meg Fitz Balagtas100% (1)
- Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1Syaimma Syed AliNo ratings yet
- Econ4 Side NotesDocument2 pagesEcon4 Side NotesjeanneNo ratings yet
- Production Process PDFDocument18 pagesProduction Process PDFMarcus Andrei J RamosNo ratings yet
- PomDocument63 pagesPomAllen Fourever50% (2)
- Perfect CompetitionDocument21 pagesPerfect Competitionkingsleymay08No ratings yet
- Be - Tutorial 5 - Stu 2Document16 pagesBe - Tutorial 5 - Stu 2Gia LinhNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis & Decision MakingDocument67 pagesCVP Analysis & Decision MakingcmukherjeeNo ratings yet
- HSS01-competitive Market and PricingDocument14 pagesHSS01-competitive Market and PricingRiteshNo ratings yet
- Firms in Competitive MarketsDocument1 pageFirms in Competitive MarketsrpfaervNo ratings yet
- Pure Competition in The Short Run Four Market Models: Very Large Numbers of Independent Sellers EachDocument2 pagesPure Competition in The Short Run Four Market Models: Very Large Numbers of Independent Sellers EachAriane Jane CachoNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics - Short Answer CHDocument4 pagesManagerial Economics - Short Answer CHAnkita T. MooreNo ratings yet
- 1.5.perfect Competition-2Document19 pages1.5.perfect Competition-2Manhin Bryan KoNo ratings yet
- 08-LECTURE NOTES - Difference Between Economic and Accounting Profit - MANAGERIAL ECONOMICSDocument11 pages08-LECTURE NOTES - Difference Between Economic and Accounting Profit - MANAGERIAL ECONOMICSreagan blaireNo ratings yet
- Finance-Accounting Nam 3 CNTH11Document65 pagesFinance-Accounting Nam 3 CNTH11Nongstan Jie Jie ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Economics - Profit and RevenueDocument23 pagesEconomics - Profit and Revenuejinnah kayNo ratings yet
- Profits: The Meaning of Profit and Different Profit ConceptsDocument10 pagesProfits: The Meaning of Profit and Different Profit ConceptsRitesh MultaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 SUMMARY SECTION CDocument4 pagesChapter 9 SUMMARY SECTION ClalesyeuxNo ratings yet
- Pure CompetitionDocument9 pagesPure Competitioncindycanlas_07No ratings yet
- A3 - ECON 119-1 - Osunero, LeanzyDocument6 pagesA3 - ECON 119-1 - Osunero, Leanzyleanzyjenel domiginaNo ratings yet
- Lec 15,16,17perfect CompetitionDocument19 pagesLec 15,16,17perfect CompetitionSabira RahmanNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Saq 3 LatestDocument3 pagesJawapan Saq 3 LatestAre HidayuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Perfect CompetitionDocument10 pagesChapter 8 Perfect CompetitionXandae MempinNo ratings yet
- PC 2Document6 pagesPC 2Μιχάλης ΘεοχαρόπουλοςNo ratings yet
- Perfect CompetitionDocument71 pagesPerfect CompetitionSumedha SunayaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics For Non-Major - CHAPTER 6 (2) - 1Document18 pagesManagerial Economics For Non-Major - CHAPTER 6 (2) - 1endiolalain aNo ratings yet
- Unit1. Kind of CostDocument2 pagesUnit1. Kind of CostPhương Thảo Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Perfect CompetitionDocument73 pages2.1. Perfect Competitionapi-3696178100% (5)
- Cost Analysis: 2. Explicit and Implicit CostsDocument22 pagesCost Analysis: 2. Explicit and Implicit CostsKrishna PramodNo ratings yet
- Aec 001-Bacc 001 (Econ) - Week 15 ModuleDocument3 pagesAec 001-Bacc 001 (Econ) - Week 15 ModuleNicole ValentinoNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document12 pagesCH 06LinNo ratings yet
- Perfect Competition, Cost & Output DeterminationDocument70 pagesPerfect Competition, Cost & Output DeterminationVũ TrangNo ratings yet
- Key Takeaways On CostsDocument6 pagesKey Takeaways On CostsEsha ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- FSA - RatiosDocument27 pagesFSA - RatiosMahasweta RoyNo ratings yet
- Managerial Decisions in Competitive Markets: Essential ConceptsDocument8 pagesManagerial Decisions in Competitive Markets: Essential ConceptsRohit SinhaNo ratings yet
- Econ Microeconomics 4 4Th Edition Mceachern Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesEcon Microeconomics 4 4Th Edition Mceachern Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFeric.herrara805100% (11)
- ECON Microeconomics 4 4th Edition McEachern Solutions Manual 1Document14 pagesECON Microeconomics 4 4th Edition McEachern Solutions Manual 1debra100% (38)
- Lecture 11Document1 pageLecture 11Sneh MittalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document21 pagesLecture 3Black DevilNo ratings yet
- 1) ANS: Profit Maximization Objective of A Firm: Total Revenue (TR) - Total Cost (TC) ApproachDocument6 pages1) ANS: Profit Maximization Objective of A Firm: Total Revenue (TR) - Total Cost (TC) ApproachAhim Raj JoshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Seminar AnswerDocument7 pagesChapter 11 - Seminar AnswerMisheel MinannNo ratings yet
- Submitted To Submitted by Prof. Pooja Choubey Monika Soniya Mbaiyr SirtDocument14 pagesSubmitted To Submitted by Prof. Pooja Choubey Monika Soniya Mbaiyr SirtMonica SoniyaNo ratings yet
- The Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)From EverandThe Profit Zone (Review and Analysis of Slywotzky and Morrison's Book)No ratings yet
- Economic Models Explained With CowsDocument2 pagesEconomic Models Explained With CowsKhyel Patrick VillasenorNo ratings yet
- New Provision For NBFCDocument4 pagesNew Provision For NBFCpratikshaNo ratings yet
- Final Financial Assessment - 2023Document9 pagesFinal Financial Assessment - 2023Weldu GebruNo ratings yet
- Market Leader Test 2Document2 pagesMarket Leader Test 2Deniss De AnissNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Essay - Project 4Document6 pagesPersuasive Essay - Project 4api-302893696No ratings yet
- EduFin Position PaperDocument88 pagesEduFin Position PaperComunicarSe-ArchivoNo ratings yet
- Capital Mobility in Developing CountriesDocument41 pagesCapital Mobility in Developing CountriesEmir TermeNo ratings yet
- MPSC State Service Preliminary Exam 2018 Paper 1@govnokri - in PDFDocument44 pagesMPSC State Service Preliminary Exam 2018 Paper 1@govnokri - in PDFShwetaNo ratings yet
- Rules in Holding Period in Capital GainsDocument39 pagesRules in Holding Period in Capital GainsTrine De LeonNo ratings yet
- Decoled FR Sas: Account MovementsDocument1 pageDecoled FR Sas: Account Movementsnatali vasylNo ratings yet
- Reserves Proved Indicated Inferred Please Enter Reserves (Million Tonnes) Plese Enter Seam/Ore CharacteresticsDocument35 pagesReserves Proved Indicated Inferred Please Enter Reserves (Million Tonnes) Plese Enter Seam/Ore Characteresticsashishgadgil2011No ratings yet
- JSW Steel - WikipediaDocument28 pagesJSW Steel - WikipediaPawan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 308 Class3Document23 pages308 Class3Bokul HossainNo ratings yet
- Company Formation - ST-IDocument5 pagesCompany Formation - ST-IAlexandra GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- Globalisation Effect Globalisation in Indian Economy Advantages Impact Debate FaqsDocument5 pagesGlobalisation Effect Globalisation in Indian Economy Advantages Impact Debate Faqssridharvchinni_21769No ratings yet
- RPP Infra Projects Limited Bags Order From TNCSC Worth Rs. 254 Millions (Company Update)Document2 pagesRPP Infra Projects Limited Bags Order From TNCSC Worth Rs. 254 Millions (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Order Id Client Name Shipping Phon Order Date Payment Methshipping TaxDocument33 pagesOrder Id Client Name Shipping Phon Order Date Payment Methshipping Taxionut stavarNo ratings yet
- Journal of Business Research: SciencedirectDocument9 pagesJournal of Business Research: Sciencedirectallysa gayle balisongNo ratings yet
- Chemical Industry Outlook 2022Document180 pagesChemical Industry Outlook 2022Err DatabaseNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Document1 pageTax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Mahesh DasarNo ratings yet
- Economic Drain PRCDocument48 pagesEconomic Drain PRCSubhadip Saha ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Solar Street Ligh Province BidDocument5 pagesSolar Street Ligh Province BidHarold MontesNo ratings yet
- Approved List of Securities at Zerodha.Document204 pagesApproved List of Securities at Zerodha.Hemanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Elephant by Raymond CarverDocument5 pagesElephant by Raymond Carverfaisal jahangeerNo ratings yet
- Sole Trader A4 FDocument81 pagesSole Trader A4 FalizaNo ratings yet
- js3 Bus Study 2nd TermDocument2 pagesjs3 Bus Study 2nd TermAyobami onifadeNo ratings yet
- Form Gstr-2B: 3. ITC Available SummaryDocument7 pagesForm Gstr-2B: 3. ITC Available SummaryRohit GoyalNo ratings yet
- USydney Salary Scales FT16 Sydney Salary ScalesDocument6 pagesUSydney Salary Scales FT16 Sydney Salary ScalesPreyashNo ratings yet
- Charged CCDocument5 pagesCharged CCOggy Loves Cockroaches75% (4)
- The SOPL of An Entity Shows The Financial Performance of It For A Specific PeriodDocument2 pagesThe SOPL of An Entity Shows The Financial Performance of It For A Specific PeriodAdesina OlufemiNo ratings yet