Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enumerate The Nursing Management of Each Diagnostic Procedure To Detect Cancer
Uploaded by
Akira A. AtomarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enumerate The Nursing Management of Each Diagnostic Procedure To Detect Cancer
Uploaded by
Akira A. AtomarCopyright:
Available Formats
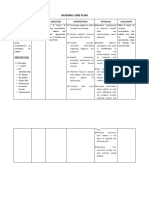
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE NURSING MANAGEMENT
TO DETECT CANCER
- Examine the patient's medical
history.
- Assess and monitor the patient’s
physical and emotional status.
- Keeping track of laboratory,
pathology and imaging studies.
- Safely administering medications,
fluids and cancer treatments, such
as chemotherapy.
Cancer screening - Collaborate with the patient’s
doctors and other clinicians about
the treatment plan.
- Help patients understand the
disease and their treatment plan.
- Help translate complex medical
terminology and answering
questions.
- Communicate with the doctors and
other clinicians on the patient’s
behalf.
- Help the patient plan for and
manage symptoms throughout
treatment.
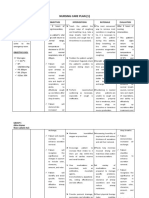
- A structured physical examination
allows the nurse to obtain a
complete assessment of the
patient. Observation/inspection,
Physical exam palpation, percussion and
auscultation are techniques used
to gather information. Clinical
judgment should be used to decide
on the extent of assessment
required.
- Check the equipment to assure it
is working properly and is ready for
use on patients.
Laboratory tests - Drawing blood or administering
medication prior to testing.
- Provide patient care during the test
which may include administering
medicines when needed.
- Monitor their current medical
condition, especially in those
patients deemed unstable.
- Test results are reported to the
patient's doctor, specialists and
others in need of the information
by nurses.
- Check the test results often and
note any abnormal findings.
- Notify the physician of significant
abnormal results.
- Obtain an informed consent
properly signed.
- Assess for any history of allergies
to iodinated dye or shellfish if
contrast media is to be used.
- Ask the patient about any recent
Imaging tests illnesses or other medical
conditions and current medications
being taken.
- Before imaging tests/exam, eat
normally and continue to take your
usual medications, unless
otherwise instructed. You will
typically be asked to change into a
gown and to remove things that
might affect the magnetic imaging,
such as: Jewelry, Hairpins,
Eyeglasses, Watches, Wigs,
Dentures, Hearing aids, Underwire
bras and Cosmetics that contain
metal particles.
- Instruct the patient to wear
comfortable, loose-fitting clothing
during the exam.
- Provide information about the
contrast medium.
- During the examination, tell the
patient to remain still and to
immediately report symptoms of
itching, difficulty breathing or
swallowing, nausea, vomiting,
dizziness, and headache.
- Inform about the duration of the
procedure.
- Prepare and educate the patient.
- Assess them for complications
- Support them during the
procedure.
- The nurse should check vital signs
every 15 minutes for 1 hour, then
Biopsy every hour for four hours. Assess
for any bleeding, dyspnea,
elevated pulse rate, diminished
breath sounds on the biopsy side,
and eventually, cyanosis. Also,
remember to keep the patient calm
and quiet. Coughing and
movement during biopsy may
cause tearing of the lung by the
biopsy needle.
- Prepare sedation. Monitor the
patient during the procedure, and
provide after-care and instructions.
The nurse's management may
involve emergency measures
during or after the procedure.
Endoscopy - Inform the patient to stop drinking
and eating four to eight hours
before endoscopy to ensure
stomach is empty for the
procedure.
- Inform the patient to stop taking
certain blood-thinning medications
in the days before your
endoscopy.
You might also like
- USMLE Step 3 CCS in ShortDocument4 pagesUSMLE Step 3 CCS in ShortPraneeth Reddy100% (5)
- Fundamentals of Nursing Notes 1Document23 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Notes 1Tin100% (11)
- Vocabulary For NurseDocument12 pagesVocabulary For NurseNecysxIrwan'tzZeghaNo ratings yet
- Frando Final Term Learning Activity Sheet 1Document27 pagesFrando Final Term Learning Activity Sheet 1Ranz Kenneth G. FrandoNo ratings yet
- Assisting in EndosDocument6 pagesAssisting in EndosTheSweetpea501No ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanRenee Palay50% (2)
- Clinical Rotation ManualDocument188 pagesClinical Rotation ManualHafidzoh NajwatiNo ratings yet
- Gnur 405 SuzyDocument6 pagesGnur 405 SuzySeth MensahNo ratings yet
- PreOperative CareDocument9 pagesPreOperative CareYana Pot100% (2)
- Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument3 pagesInflammatory Bowel DiseaseDivine ParagasNo ratings yet
- SURGERY WARD-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesSURGERY WARD-WPS OfficeMary Claire MasoNo ratings yet
- Preoperative CareDocument18 pagesPreoperative Caresho bartNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Evaluation and Considerations in ChildrenDocument24 pagesPreoperative Evaluation and Considerations in ChildrenArshan AliNo ratings yet
- Question 5 Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesQuestion 5 Nursing ResponsibilitiesMichaela JapsayNo ratings yet
- 9 1 EndosDocument6 pages9 1 EndosmghNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound (U.S.G.) : IntroductionDocument4 pagesUltrasound (U.S.G.) : IntroductionAmit MartinNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination of Companion AnimalsDocument6 pagesClinical Examination of Companion AnimalsLouise Alysson OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Imaging - 2) )Document12 pagesImaging - 2) )Susan FNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care in Post Operation Patients SCDocument9 pagesNursing Care in Post Operation Patients SCika dwiNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia-Anesthesia Basics PDFDocument5 pagesAnesthesia-Anesthesia Basics PDFFebbi Iral Bin AgusNo ratings yet
- Wound ManaagementDocument20 pagesWound Manaagementandrewonguka9No ratings yet
- Postoperative Hip Answer SheetDocument19 pagesPostoperative Hip Answer SheetCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Nursing CareDocument42 pagesPreoperative Nursing Careakoeljames8543No ratings yet
- Preoperative PhaseDocument13 pagesPreoperative PhaseNick RealinoNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Perioperative ReviewerDocument18 pagesNCM 112 Perioperative RevieweriamunknownnnnnnnNo ratings yet
- Informed ConsentDocument17 pagesInformed ConsentKenvyne Quides-CalugayNo ratings yet
- Physical Examinations I (JoVE)Document119 pagesPhysical Examinations I (JoVE)Thasya RenaNo ratings yet
- Role of Anesthesia Nurse in Operation TheatreDocument37 pagesRole of Anesthesia Nurse in Operation TheatreZainul SaifiNo ratings yet
- MS Preoperative Part 2Document5 pagesMS Preoperative Part 2Ano NymousNo ratings yet
- 1.01 ClinPath Lec - IntroductionDocument4 pages1.01 ClinPath Lec - IntroductionDETECTIVE CONANNo ratings yet
- Funciones de Enfermeria Ingles-EspañolDocument10 pagesFunciones de Enfermeria Ingles-EspañolSarah Vazquez FranNo ratings yet
- Medical Ward - Discharge PlanDocument5 pagesMedical Ward - Discharge Plandon7dane100% (1)
- Nursong ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesNursong ResponsibilitiesMichaela JapsayNo ratings yet
- Sources of Stress As Per: Student's Academic Performance Effects of StressDocument14 pagesSources of Stress As Per: Student's Academic Performance Effects of StressMacrina PatocNo ratings yet
- Medications: Jason Yu Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesMedications: Jason Yu Discharge PlanPhilip Royce EmpeñoNo ratings yet
- Medical and Allied Health ProfessionDocument30 pagesMedical and Allied Health ProfessionAnalyn QueroNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentEduard GarchitorenaNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Ot and Patient PreparationDocument8 pagesEthics in Ot and Patient Preparationjosphinenthenya001No ratings yet
- Anesthesia and Analgesia Book 1Document104 pagesAnesthesia and Analgesia Book 1JoanneYiNo ratings yet
- NSG 126 Serologic Studies (Part 5-8)Document11 pagesNSG 126 Serologic Studies (Part 5-8)Angelica Charisse BuliganNo ratings yet
- Peri Operative Nursing1Document78 pagesPeri Operative Nursing1Jeon CookyNo ratings yet
- HealthDocument5 pagesHealthColeen BalaccuaNo ratings yet
- 1st Tetanus LAB ANADocument1 page1st Tetanus LAB ANASheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia and Analgesia Book 1Document104 pagesAnesthesia and Analgesia Book 1Alan Alvaro Salazar GarciaNo ratings yet
- Finalpharmacology PART 3Document18 pagesFinalpharmacology PART 3Roshin TejeroNo ratings yet
- Citi ColineDocument1 pageCiti ColinehoneyNo ratings yet
- Practical Manual On Veterinary Clinical Diagnostic Approach 2157 7579 1000337Document10 pagesPractical Manual On Veterinary Clinical Diagnostic Approach 2157 7579 1000337Shravankumar Gaddi100% (1)
- December 2012 Pnle Pearls of Success Part 6: Medical and Surgical Health Nursing (A)Document11 pagesDecember 2012 Pnle Pearls of Success Part 6: Medical and Surgical Health Nursing (A)Haifi HunNo ratings yet
- CRITICALTHINKINGDocument13 pagesCRITICALTHINKINGBrandy JaffarNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching On Ta - HbsoDocument3 pagesHealth Teaching On Ta - Hbsomecz26No ratings yet
- HP May00 Sedat PDFDocument9 pagesHP May00 Sedat PDFSaurabh SatheNo ratings yet
- Week 6 DocsDocument18 pagesWeek 6 DocsSHERMINA HASANNo ratings yet
- w0s$ Qy.8vz) 8 (88j1Document22 pagesw0s$ Qy.8vz) 8 (88j1Kristel AnneNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical ReviewerDocument9 pagesMedical Surgical ReviewerMary Ann Sambo OgoyNo ratings yet
- Pre and Postoperative CareDocument17 pagesPre and Postoperative CaremeghanaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument12 pagesCurriculum VitaeHannah AlmacenNo ratings yet
- Monitoring & Devices Used in ICU CCUDocument48 pagesMonitoring & Devices Used in ICU CCUProf. Ramsharan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Operating RoomDocument81 pagesOperating Roomjaypee01100% (3)
- ADEX. MP Resume Template 0604.12 (NY) .6.24.15 (1) (005) (002) (0B7)Document6 pagesADEX. MP Resume Template 0604.12 (NY) .6.24.15 (1) (005) (002) (0B7)Baniwas Marie AgnesNo ratings yet
- Pre Op SyllabusDocument50 pagesPre Op Syllabusmunira.2707No ratings yet
- 1 Dr. Erwin Astha T - Bpjs Jatim 2016Document41 pages1 Dr. Erwin Astha T - Bpjs Jatim 2016Diah AzarineNo ratings yet
- Maria Odette A. Carpio, COVID Confirmed With Moderate PneumoniaDocument18 pagesMaria Odette A. Carpio, COVID Confirmed With Moderate PneumoniaKeanuNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Reflection (CW)Document2 pagesReflection (CW)Akira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (1) : Group 5 Akira Atomar Shara Lailanie AzisDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan (1) : Group 5 Akira Atomar Shara Lailanie AzisAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Geriatric ToolDocument14 pagesComprehensive Geriatric ToolAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Geriatric ToolDocument14 pagesComprehensive Geriatric ToolAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Realization and Reaction PaperDocument5 pagesRealization and Reaction PaperAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument1 pageCase StudyAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Realization and Reaction PaperDocument5 pagesRealization and Reaction PaperAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective CuesAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (1) : Group 5 Akira Atomar Shara Lailanie AzisDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan (1) : Group 5 Akira Atomar Shara Lailanie AzisAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Realization and Reaction PaperDocument5 pagesRealization and Reaction PaperAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (1) : Group 5 Akira Atomar Shara Lailanie AzisDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan (1) : Group 5 Akira Atomar Shara Lailanie AzisAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentAkira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Webinar Sa Kasaysayan 2021Document2 pagesWebinar Sa Kasaysayan 2021Akira A. AtomarNo ratings yet
- Specification For Training in Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocument14 pagesSpecification For Training in Obstetrics and GynaecologyRAJUNo ratings yet
- HR Interview FormDocument30 pagesHR Interview FormGuyton LoboNo ratings yet
- Company - Business Plan - Benham - Park - HealthcareDocument39 pagesCompany - Business Plan - Benham - Park - HealthcarePeter Davidson0% (1)
- GERIATRIC HEALTH PresentationDocument40 pagesGERIATRIC HEALTH Presentationapi-19712253No ratings yet
- Dengue Death Case Investigation Form (CIF)Document3 pagesDengue Death Case Investigation Form (CIF)Chamee Mallillin100% (1)
- 2s2022 Ncm109 Rle Learn Mat 1Document18 pages2s2022 Ncm109 Rle Learn Mat 1Guia SalandananNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 212022 PIDS Vs COA On Additional Health BenefitsDocument36 pagesG.R. No. 212022 PIDS Vs COA On Additional Health BenefitsChristopher BautistaNo ratings yet
- INC Format For Case StudyDocument31 pagesINC Format For Case StudyRoselineTigga100% (1)
- Medical Certificate: Healthservices@lnu - Edu.phDocument3 pagesMedical Certificate: Healthservices@lnu - Edu.phNiko ChavezNo ratings yet
- Traumatology and Orthopaedics Manual For Students and Practical DoctorsDocument108 pagesTraumatology and Orthopaedics Manual For Students and Practical DoctorsMsa MillaNo ratings yet
- Firefighter Physical Fit MannualDocument42 pagesFirefighter Physical Fit MannualFélix LlamosasNo ratings yet
- HA-RLE-Week 1Document27 pagesHA-RLE-Week 1xander christian raymundoNo ratings yet
- What Is An Immigration DoctorDocument2 pagesWhat Is An Immigration Doctornacholibrae1No ratings yet
- AMR-Annual Medical ReportDocument7 pagesAMR-Annual Medical ReportAlaine SobredoNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Australian MedicalDocument3 pagesGuidelines For Australian MedicalstynapittNo ratings yet
- Focused Study Tips: CHAPTER 10/ Critical Thinking and The Nursing ProcessDocument21 pagesFocused Study Tips: CHAPTER 10/ Critical Thinking and The Nursing Processiannello100% (1)
- BFI-Serviceprospect 2019 EN PDFDocument10 pagesBFI-Serviceprospect 2019 EN PDFChristian Camilo Suarez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesCase AnalysisDebi Bahinting Ouano-RotaNo ratings yet
- Endorsement Letter For PEME (EPI5Document2 pagesEndorsement Letter For PEME (EPI5Nat HernandezNo ratings yet
- 2.UWorld Step2 CS Key To SuccessDocument3 pages2.UWorld Step2 CS Key To SuccessHeinrichKrauseNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 Health Assessment PPT 2Document10 pagesNCM 101 Health Assessment PPT 2Dianna Rose Belen100% (1)
- PD 6 To 9Document103 pagesPD 6 To 9Loai Mohammed IssaNo ratings yet
- Annual Accomplishment Report FinalDocument145 pagesAnnual Accomplishment Report FinalShan Dave TupasNo ratings yet
- Tie UpDocument43 pagesTie UpCres DayagNo ratings yet
- C2 - Evaluarea PretransplantDocument31 pagesC2 - Evaluarea PretransplantIuliia •No ratings yet
- Health Assessment For Nursing Practice Wilson 5th Edition Test BankDocument36 pagesHealth Assessment For Nursing Practice Wilson 5th Edition Test Bankpeelefisc7vnzww100% (37)