Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Possible Mechanisms of Pathogenesis For The Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of COVID
Uploaded by
Hyacinth Manood0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesPossible mechanisms of neuropsychiatric manifestations of COVID-19 include direct injury to the brain through an exaggerated immune response or neuronal infection, hypoxic injury from impaired pulmonary function, dysregulated immunomodulation causing cytokine storms and inflammation, immune cell transmigration into the CNS, interaction of the virus's ACE-2 receptor and spike protein causing vascular damage, autoimmunity through molecular mimicry, and viral latency or reactivation in the brain leading to persistent neurological or psychiatric effects.
Original Description:
For possible mechanism of relationship of mental illness and covid
Original Title
Possible Mechanisms of Pathogenesis for the Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of COVID
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPossible mechanisms of neuropsychiatric manifestations of COVID-19 include direct injury to the brain through an exaggerated immune response or neuronal infection, hypoxic injury from impaired pulmonary function, dysregulated immunomodulation causing cytokine storms and inflammation, immune cell transmigration into the CNS, interaction of the virus's ACE-2 receptor and spike protein causing vascular damage, autoimmunity through molecular mimicry, and viral latency or reactivation in the brain leading to persistent neurological or psychiatric effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesPossible Mechanisms of Pathogenesis For The Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of COVID
Uploaded by
Hyacinth ManoodPossible mechanisms of neuropsychiatric manifestations of COVID-19 include direct injury to the brain through an exaggerated immune response or neuronal infection, hypoxic injury from impaired pulmonary function, dysregulated immunomodulation causing cytokine storms and inflammation, immune cell transmigration into the CNS, interaction of the virus's ACE-2 receptor and spike protein causing vascular damage, autoimmunity through molecular mimicry, and viral latency or reactivation in the brain leading to persistent neurological or psychiatric effects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
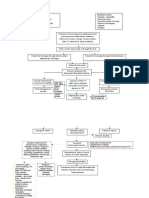
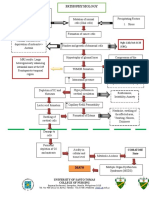
Possible mechanisms of pathogenesis for the neuropsychiatric manifestations of COVID-19.
Mechanism of Details Neuropsychiatric effects
pathogenesis
• Exaggerated immune response • Encephalopathy
Direct injury (Blood • Cytokines increasing blood- • Delirium and acute
circulation) brain-barrier (BBB) confusional state
Koyuncu et al., 2013 Desforges et al.,
( ; permeability
2020
)
Direct injury (Neuronal • Predilection for olfactory • Anosmia
route) epithelium, bulb and vagal • Dysguesia
(Mori, 2015; Bohmwald et al., 2018) centers • Psychiatric disorders
• Anterograde and retrograde
neural proliferation via dynein
and kinesin
• Structural preference for the
forebrain, basal ganglia and
hypothalamus
Hypoxic injury • Impaired pulmonary exchange • Encephalopathy
(Abdennour et al., 2012; Guo et al., and pulmonary oedema can • Somnolence
2020
) cause cerebral hypoxia • Coma
• Cerebral oedema, vasodilation, • Headache
ischaemia and vascular • Confusion
congestion
• Increased intracranial pressure
Dysregulated • Cytokine storm (surge of • Encephalitis
immunomodulation peripheral IL-6,8,10,18, TNF- • MODS
Mechanism of Details Neuropsychiatric effects
pathogenesis
(Fu et al., 2020; Mehta et al., alpha, etc.) • Acute psychosis
2020 Wan et al., 2020
; ) • Systemic Inflammatory • Seizures
Response Syndrome (SIRS)
• Upregulation of
oligodendrocytes and astrocytes
(increased release of IL-15,
TNF-alpha)
• Leaky BBB
• Disturbed neurotransmission
Immune cell • Increased neuro-inflammation • Both acute and chronic
transmigration to CNS • Microglial activation neuropsychiatric effects
(Wohleb et al., 2015; Desforges et al., • Neural and glial cells as latent
2020
) ‘viral-carriers’
ACE-2 and CoV spike • Vascular and endothelial • Cerebro-vascular
protein interaction damage accidents
(Miller and Arnold, 2019; Wrapp et al., • Hyper-coagulability • Pulmonary and cerebral
2020
) • Increased blood-pressure venous
• Microangiopathy thromboembolism
• Risk of chronic
neurodegeneration
Autoimmunity • Molecular mimicry (cross- • Demyelination
(Kim et al., 2017; Rose, 2017) reaction of myelin, glia and • GBS
beta-2 glycoprotein with viral • Neuropathy
epitopes
Mechanism of Details Neuropsychiatric effects
pathogenesis
Miscellaneous • High ‘viral-latency’ in CNS • Persistent or relapsing-
(Reinhold and Rittner, 2017) • Lack of MHC in brain remitting neurological
• Homeostasis of neural issue sequelae
• Reactivation of seizures
• Chronic psychiatric
conditions
You might also like
- The Healing Power of The Drum - Workshop OutlineDocument2 pagesThe Healing Power of The Drum - Workshop OutlinegerrigongNo ratings yet
- Grand RevalidaDocument342 pagesGrand RevalidaJoeNo ratings yet
- Types of DepressionDocument12 pagesTypes of DepressionKADAMBARINo ratings yet
- Neurocognitive DisordersDocument85 pagesNeurocognitive Disordersadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- CNS PathologyDocument10 pagesCNS Pathologysarguss1483% (6)
- Requirement in PathophysiologyDocument38 pagesRequirement in PathophysiologyckathreenahNo ratings yet
- Emergency Care Emt 13th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesEmergency Care Emt 13th Edition Ebook PDFadolfo.milliken17894% (50)
- Siegelman Online Advantage 1.1 PDFDocument39 pagesSiegelman Online Advantage 1.1 PDFDana Ysabelle Ibarra100% (1)
- CNS Pathology SummaryDocument38 pagesCNS Pathology Summaryimeds100% (2)
- PyomeningitisDocument54 pagesPyomeningitisRiya BagdiNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesBacterial Meningitisjennielunay00No ratings yet
- Seizure Associated With Corona Virus Infection: Meiti Frida PERDOSSI Cabang PadangDocument23 pagesSeizure Associated With Corona Virus Infection: Meiti Frida PERDOSSI Cabang Padangzefri suhendarNo ratings yet
- BoeEoiATKXmvogGcWqYr1601439144 PDFDocument41 pagesBoeEoiATKXmvogGcWqYr1601439144 PDFsrisabrina christiaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Calcifications As A Differential Diagnosis of Psychiatric DisordersDocument17 pagesCerebral Calcifications As A Differential Diagnosis of Psychiatric DisordersMurillo NevesNo ratings yet
- Sleep Problems During The Covid19 Pandemic - Dr. Zamroni Afif, SP.S (K), M. BiomedDocument21 pagesSleep Problems During The Covid19 Pandemic - Dr. Zamroni Afif, SP.S (K), M. BiomedannnisaNo ratings yet
- PP MorbidityDocument65 pagesPP MorbidityRaymart MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Exámenes Auxiliares: NeurologíaDocument12 pagesExámenes Auxiliares: NeurologíaHugo CardenasNo ratings yet
- Neuro TraumaDocument13 pagesNeuro TraumaFikri IchsanNo ratings yet
- Mengapa Didapatkan Keluhan Sakit Kepala Dan Panas Tinggi?: LBM 5 Demam Dan KejangDocument14 pagesMengapa Didapatkan Keluhan Sakit Kepala Dan Panas Tinggi?: LBM 5 Demam Dan KejangVivie Tirany SoediroNo ratings yet
- UMNLand AHCDocument27 pagesUMNLand AHCdrmamodoNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesBacterial Meningitisjennielunay00No ratings yet
- Trauma Medular Dra LucyDocument41 pagesTrauma Medular Dra LucySakuraclowNo ratings yet
- Unconscious and Comatose Patients DR Moses KazevuDocument17 pagesUnconscious and Comatose Patients DR Moses KazevuMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Neimy Kuliah Cedera OtakDocument45 pagesNeimy Kuliah Cedera OtakCahya RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Basis Neurobiologi DepresiDocument24 pagesBasis Neurobiologi DepresiAhmad Shafwan NatsirNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument17 pagesMeningitisKyla Marie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Monard Et Al-2022-Intensive Care MedicineDocument4 pagesMonard Et Al-2022-Intensive Care MedicinePaulHerreraNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and Mental HealthDocument41 pagesInflammation and Mental HealthanindyaguptaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of MENINGITISDocument30 pagesPathogenesis of MENINGITISPrachi TeteNo ratings yet
- Neuro NotesDocument15 pagesNeuro NotesClyde CapapasNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) : 1. Anatomical ClassificationDocument4 pagesPeripheral Nervous System (PNS) : 1. Anatomical ClassificationShafiq ZahariNo ratings yet
- Medicine GBS: Guillain Barre SyndromeDocument4 pagesMedicine GBS: Guillain Barre SyndromedinakarNo ratings yet
- Meningitis and Fractures Concept MapDocument4 pagesMeningitis and Fractures Concept MapNamayanja SumayiyahNo ratings yet
- Meningitis: Neonates (65)Document5 pagesMeningitis: Neonates (65)Eugina Naiborhu08No ratings yet
- PHCP - Unit 5 - NEUROLOGIC NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERDocument10 pagesPHCP - Unit 5 - NEUROLOGIC NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERDuh realNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument2 pagesMeningitisedrian02No ratings yet
- Critical Care Management of Adult Traumatic Brain Injury: Dr. Hj. Liliriawati Ananta Kahar, SP - An, KICDocument28 pagesCritical Care Management of Adult Traumatic Brain Injury: Dr. Hj. Liliriawati Ananta Kahar, SP - An, KICfirdainiNo ratings yet
- Emerging Cns InfectionDocument18 pagesEmerging Cns InfectionDedy SavradinataNo ratings yet
- LEC 3 - Nerve, Neuromuscular and Muscle Disorders (Dr. Lim) PDFDocument101 pagesLEC 3 - Nerve, Neuromuscular and Muscle Disorders (Dr. Lim) PDFErald PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Chediak Higashi Sydrome: Diseases of Immune DysregulationDocument2 pagesChediak Higashi Sydrome: Diseases of Immune DysregulationCarla García TorresNo ratings yet
- ObobDocument1 pageObobNikkie SalazarNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Classification of NMD PDFDocument6 pagesEpidemiology and Classification of NMD PDFnita prmtasariNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology FinalDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Finaljustineneri324No ratings yet
- HIV-associated Opportunistic Infections of The CNSDocument48 pagesHIV-associated Opportunistic Infections of The CNSclaudio RivasNo ratings yet
- Fisiología Renal y Equilibrio ElectrolíticoDocument99 pagesFisiología Renal y Equilibrio ElectrolíticofvidalinostrozaNo ratings yet
- Medsurg Finals TheoryDocument27 pagesMedsurg Finals TheoryKAYE PAULINE SERVIDADNo ratings yet
- Synapse Neurobiology: Week 5 - Part 2Document20 pagesSynapse Neurobiology: Week 5 - Part 2bobobNo ratings yet
- Dams - DVT (New)Document48 pagesDams - DVT (New)Msd KishorNo ratings yet
- Therapy of Migraine: An Overview: By-Parul Dixit Iind Trimester, M.Pharm (Pharmacology), SPTM, NmimsDocument29 pagesTherapy of Migraine: An Overview: By-Parul Dixit Iind Trimester, M.Pharm (Pharmacology), SPTM, NmimsParul DixitNo ratings yet
- Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating PolyradiculoneuropathDocument13 pagesChronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathrafael rocha novaesNo ratings yet
- AAAA2Document142 pagesAAAA2Sruthi SruthiNo ratings yet
- To Neurology: Rini AndrianiDocument46 pagesTo Neurology: Rini Andrianiwaraney palitNo ratings yet
- Sazgar CKD and Epilepsy 5 8 2020 v02 WM PWDocument13 pagesSazgar CKD and Epilepsy 5 8 2020 v02 WM PWDita Paramita HaryatiNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY ASSESSMENT ON IMMUNE SYSTEM DYSFUNCTION AND INFLAMMATION IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE - Dr. Dian Ariningrum, M.Kes., SP - PK (K)Document24 pagesLABORATORY ASSESSMENT ON IMMUNE SYSTEM DYSFUNCTION AND INFLAMMATION IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE - Dr. Dian Ariningrum, M.Kes., SP - PK (K)EllenNo ratings yet
- Neurocritico Nuevos ParadigmasDocument16 pagesNeurocritico Nuevos ParadigmasAlessandraCervantesNo ratings yet
- Anti Nmdar EncephalitisDocument2 pagesAnti Nmdar EncephalitisbugogiNo ratings yet
- DEMENTIAAAADocument24 pagesDEMENTIAAAAOreoluwaNo ratings yet
- Intensive Management of Status EpilepticusDocument41 pagesIntensive Management of Status EpilepticussnyNo ratings yet
- 98419-Normal Aging and Brain Athropy - Meike VernooijDocument11 pages98419-Normal Aging and Brain Athropy - Meike Vernooijdrgaganwahi1971No ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis: BY: Ridhima Daga MPT-2 YearDocument130 pagesMultiple Sclerosis: BY: Ridhima Daga MPT-2 YearDurga BhavaniNo ratings yet
- Gbs (Guillain Barre Syndrome)Document16 pagesGbs (Guillain Barre Syndrome)Mimba Wibiyana100% (1)
- NCC Vs Cns TuberculomaDocument28 pagesNCC Vs Cns TuberculomaAbhinav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Meningitis TutorialDocument9 pagesMeningitis TutorialSara AbdoNo ratings yet
- (HOGH) Dysmenorrhea Ver 1.1 AOFOGDocument16 pages(HOGH) Dysmenorrhea Ver 1.1 AOFOGMai Đặng NgọcNo ratings yet
- Genetics PDFDocument58 pagesGenetics PDFAngelaNo ratings yet
- 1b-Physio-1m-Cvs 4Document12 pages1b-Physio-1m-Cvs 4urvashi rao rajputNo ratings yet
- Goal 1: Eradicate Extreme Poverty and HungerDocument15 pagesGoal 1: Eradicate Extreme Poverty and HungerChege Mbuthia Jr.No ratings yet
- Breast Cancer - Catching Them EarlyDocument11 pagesBreast Cancer - Catching Them EarlyOgbemudia AfamNo ratings yet
- Polio VirusDocument12 pagesPolio VirusNovianaHartikasariNo ratings yet
- Guardant360 Patient BrochureDocument5 pagesGuardant360 Patient BrochureSoca ArrelNo ratings yet
- Philippines RiteMed 2008 PDFDocument24 pagesPhilippines RiteMed 2008 PDFAnonymous 45z6m4eE7pNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Haid - PPT YudisDocument34 pagesGangguan Haid - PPT YudisIde Yudis TiyoNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Brain Tumor Edge Extraction Using Morphological Op PDFDocument89 pagesComputer Aided Brain Tumor Edge Extraction Using Morphological Op PDFChitra VigneshNo ratings yet
- Mr. William's Case StudyDocument2 pagesMr. William's Case StudyChelsea AquinoNo ratings yet
- MCQ Final 1981Document19 pagesMCQ Final 1981JohnSonNo ratings yet
- Brochure On InhalantsDocument2 pagesBrochure On InhalantsMarla DaigneaultNo ratings yet
- МартDocument55 pagesМартLuisAngelPonceTorresNo ratings yet
- مايكرو عملي ٥Document18 pagesمايكرو عملي ٥ManWol JangNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Biology 5090/21Document12 pagesCambridge O Level: Biology 5090/21sadequins3No ratings yet
- Nutrigenomics and Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument19 pagesNutrigenomics and Cardiovascular DiseaseAssignmentLab.comNo ratings yet
- Tackling Prediction Uncertainty in Machine Learning For HealthcareDocument8 pagesTackling Prediction Uncertainty in Machine Learning For HealthcareZQ TANGNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration Form SteftiDocument1 pageHealth Declaration Form SteftiJen-Jen L. ElonaNo ratings yet
- AJOG Modelo Predictivo para Preeclampsia Nicolaides 2019Document13 pagesAJOG Modelo Predictivo para Preeclampsia Nicolaides 2019Ana PadillaNo ratings yet
- Organophosphateand Carbamatepoisoning: Andrew M. King,, Cynthia K. AaronDocument19 pagesOrganophosphateand Carbamatepoisoning: Andrew M. King,, Cynthia K. AaronGufront MustofaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Homeostasis PDFDocument77 pages2.1 Homeostasis PDFtess_15No ratings yet
- Pathoma CH 1 NotesDocument2 pagesPathoma CH 1 NotesjdNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingkimmybapkiddingNo ratings yet
- SunPharmaAR2019 20 PDFDocument288 pagesSunPharmaAR2019 20 PDFAvishkar AvishkarNo ratings yet
- Analyzing COVID-19 With Mixed Test-Type Data: Contagion Trends With Molecular and Serological TestsDocument11 pagesAnalyzing COVID-19 With Mixed Test-Type Data: Contagion Trends With Molecular and Serological TestsMetro Puerto RicoNo ratings yet