0% found this document useful (0 votes)
118 views19 pagesLinear Control Theory Course Overview
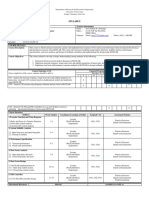
This document provides information about the Linear Control Theory course taught at Muzaffarpur Institute of Technology, Muzaffarpur. It includes the course objectives, outcomes, syllabus, textbook references, and mapping of course outcomes to program outcomes. The course aims to introduce fundamentals of modeling and controlling linear time-invariant systems using Laplace transforms. Key topics covered include time and frequency response analysis, stability criteria, root locus, and compensation techniques. Assessment includes weekly tests, assignments, and a final university examination.
Uploaded by
Lalita KumariCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
118 views19 pagesLinear Control Theory Course Overview
This document provides information about the Linear Control Theory course taught at Muzaffarpur Institute of Technology, Muzaffarpur. It includes the course objectives, outcomes, syllabus, textbook references, and mapping of course outcomes to program outcomes. The course aims to introduce fundamentals of modeling and controlling linear time-invariant systems using Laplace transforms. Key topics covered include time and frequency response analysis, stability criteria, root locus, and compensation techniques. Assessment includes weekly tests, assignments, and a final university examination.
Uploaded by
Lalita KumariCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd