Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4.2 Collisions: Xamp Es
Uploaded by
alamphyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4.2 Collisions: Xamp Es
Uploaded by
alamphyCopyright:
Available Formats
The unit of momentum is kgm s- 1 , but this can also be expressed as N s.
N s = kgms- 1
Be careful when writing the unit for
Because II stands for velocity and not speed in this definition, momentum is newton seconds to leave a gap
a vector. between N and s, otherwise it looks a
bit like newtons (plural). Similarly, when
Examples writing metres/second, leave a gap to
avoid confusion with milliseconds.
1 How big is the momentum of a child of mass 25kg walking at 0.38ms-1?
2 What is the momentum of a Eurostar train of mass 650 tonnes moving
due South at a speed of 60 m s-1?
Answers
1 Child's momentum = 25kg x 0.38ms-1 = 9.5kgms-1
2 Eurostar's momentum is 650 x 103 kg x 60ms-1 = 3.9 x 107 kgms-11
due South.
Test yourself
1 What is the momentum of a body? Be careful to spot the difference
2 Is momentum a scalar or a vector quantity? between a question thtat asks for
the size or magnitude of a body's
3 Write down the unit of momentum.
momentum and one that asks for its
4 Calculate the momentum of a 640g stone thrown with a velocity
(vector) magnitude and direction.
of 25ms-1 •
5 Estimate the momentum of a charging rhinoceros.
I 4.2 Collisions
The reason momentum is important is that it is conserved. In physics it is
quantities like energy or charge or momentum, which are conser ved,
that help enormously in understanding how the world around us behaves.
A study of the histor y of science supports this claim and we will see later,
in the Year 2 Student's book, that it can even lead scientists to suggest the
existence of undiscovered elementary particles.
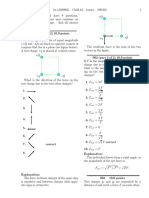
Activity 4.1
A simple collision between trolleys on a to computer
friction-compensated slope ____..and monitor
Trolley A of mass mA is given a push so that, after its release, its
interrupter card cuts through a light beam with the trolley moving
at a constant velocity down the friction-compensated slope. The
time the light beam is interrupted is recorded electronically and
the (constant) velocity, u, of trolley A is calculated.
Trolley A has a cork attached with a pin sticking out of it that
'couples' to a cork attached to trolley B of mass m8 when A hits
B. The two now move off together at a constant velocity, v, down
the slope; a velocity that is calculated as the interrupter card on friction-compensated runway
trolley A passes through the second light beam. Figure 4.2
4 .2 Colli si ons •
You might also like
- Answer Notes Marks NumberDocument1 pageAnswer Notes Marks NumberalamphyNo ratings yet
- Accuracy Will Be Poor. Ystemati Random: Precision, Error. ErrorsDocument1 pageAccuracy Will Be Poor. Ystemati Random: Precision, Error. ErrorsalamphyNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam Questions: Unit 4Document2 pagesPractice Exam Questions: Unit 4alamphyNo ratings yet
- How To Use This Book: Kinematics - Describing MotionDocument1 pageHow To Use This Book: Kinematics - Describing MotionalamphyNo ratings yet
- Method: 02. Use A Falling-Ball Method To Determine The Viscosity of A LiquidDocument1 pageMethod: 02. Use A Falling-Ball Method To Determine The Viscosity of A LiquidalamphyNo ratings yet
- Activity 3.2: Monkey and HunterDocument1 pageActivity 3.2: Monkey and HunteralamphyNo ratings yet
- Class-X Magnetism QuestionsDocument3 pagesClass-X Magnetism QuestionsalamphyNo ratings yet
- Certificate For BSS-2Document1 pageCertificate For BSS-2alamphyNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh School Sohar: Sultanate of OmanDocument1 pageBangladesh School Sohar: Sultanate of OmanalamphyNo ratings yet
- WPH13Document14 pagesWPH13alamphyNo ratings yet
- 4301132Document61 pages4301132alamphyNo ratings yet
- October 2019 Timetable ProvisionalDocument17 pagesOctober 2019 Timetable ProvisionalalamphyNo ratings yet
- Ice 19-20Document67 pagesIce 19-20alamphyNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Forces and MotionDocument75 pagesTopic 1 - Forces and Motionalamphy100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Mathematics: Sequences and Series of Real NumbersDocument2 pagesMathematics: Sequences and Series of Real Numbersaishwarya asawaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 18 Eletric Force and Electric Field PDFDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 18 Eletric Force and Electric Field PDFmasemola koketsoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Differential ApproachDocument45 pagesChapter 5 Differential ApproachAadarshPotluruNo ratings yet
- Quaternions, Torsion and The Physical Vacuum Theories of M. Sachs and G. Shipov ComparedDocument8 pagesQuaternions, Torsion and The Physical Vacuum Theories of M. Sachs and G. Shipov ComparedOdessa FileNo ratings yet
- Test-03 Quantum Numbers: B. C. D. E. F. GDocument2 pagesTest-03 Quantum Numbers: B. C. D. E. F. GNishali Sam100% (1)
- Area Under The Curve & Differential Equation: Theory and Exercise BookletDocument8 pagesArea Under The Curve & Differential Equation: Theory and Exercise BookletEr. Narender SinghNo ratings yet
- Code No.: Time Allowed: 3 Hours) (Maximum Marks: 100Document8 pagesCode No.: Time Allowed: 3 Hours) (Maximum Marks: 100alex25No ratings yet
- Qiskit: First CircuitDocument23 pagesQiskit: First CircuitL. David Cruz-DiosdadoNo ratings yet
- Angular MomentumDocument9 pagesAngular MomentumSambid parajuli2002No ratings yet
- The Concept of The PhotonDocument10 pagesThe Concept of The PhotonDouglas Delgado de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1, Grade 10Document2 pagesWorksheet 1, Grade 10Maher SuccarNo ratings yet
- Math TurkDocument7 pagesMath TurkMəhəmməd BayramovNo ratings yet
- File 481bbDocument3 pagesFile 481bbSNo ratings yet
- Electric FieldDocument4 pagesElectric Fieldsebut saja anonimNo ratings yet
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument2 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksAdhikari SushilNo ratings yet
- Complex Analytic FunctionsDocument60 pagesComplex Analytic FunctionsKiran YadavNo ratings yet
- Isaev ZaitsevDocument30 pagesIsaev ZaitsevDmitri ZaitsevNo ratings yet
- PHY 711 Classical Mechanics and Mathematical Methods 10-10:50 AM MWF Olin 103 Plan For Lecture 7Document19 pagesPHY 711 Classical Mechanics and Mathematical Methods 10-10:50 AM MWF Olin 103 Plan For Lecture 7Vishnu WishNo ratings yet
- Ch22 h3 Solutions PDFDocument4 pagesCh22 h3 Solutions PDFld393563No ratings yet
- Constitutive Relations and Conditions For Reciprocity in Bianisotropic Media (Macroscopic Approach)Document5 pagesConstitutive Relations and Conditions For Reciprocity in Bianisotropic Media (Macroscopic Approach)aldoNo ratings yet
- SmitWijn Ferrites TextDocument387 pagesSmitWijn Ferrites TextPatitoNo ratings yet
- Fiziks: Institute For NET/JRF, GATE, IIT JAM, M.Sc. Entrance, JEST, TIFR and GRE in PhysicsDocument8 pagesFiziks: Institute For NET/JRF, GATE, IIT JAM, M.Sc. Entrance, JEST, TIFR and GRE in Physicssreejitha KNo ratings yet
- Tables and FormulasDocument3 pagesTables and FormulasYA uzNo ratings yet
- Chem Quiz PTRDocument3 pagesChem Quiz PTRniloNo ratings yet
- Relativity108a Schwarzschild Metric DerivationDocument98 pagesRelativity108a Schwarzschild Metric DerivationAbhinav RaghavanNo ratings yet
- EM Fields Lecture SlidesDocument89 pagesEM Fields Lecture SlidesDominic LadesmaNo ratings yet
- Flavio Abdenur, Sylvain Crovisier (Auth.), Panos M. Pardalos, Themistocles M. Rassias (Eds.) - Essays in Mathematics and Its Applications - in Honor of Stephen Smale S 80th Birthday-Springer BerDocument500 pagesFlavio Abdenur, Sylvain Crovisier (Auth.), Panos M. Pardalos, Themistocles M. Rassias (Eds.) - Essays in Mathematics and Its Applications - in Honor of Stephen Smale S 80th Birthday-Springer BerIvan AguilarNo ratings yet
- Particle Physics Mind Map by Saad (Edexcel) PDFDocument1 pageParticle Physics Mind Map by Saad (Edexcel) PDFAhmedHassanIsmail100% (1)
- L11 Hermite Bicubic Surface PatchDocument15 pagesL11 Hermite Bicubic Surface PatchAnonymous dGnj3bZNo ratings yet
- (Physics) R Gupta's Popular Master Guide 2022Document150 pages(Physics) R Gupta's Popular Master Guide 2022beniiiNo ratings yet