Professional Documents
Culture Documents
130313
130313
Uploaded by
ARYAN PANDEY0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesOriginal Title
20210424_130313
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pages130313
130313
Uploaded by
ARYAN PANDEYCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
ae
stmmetrical about y- aXts
~
‘Thedomain ofthe function FX) = flog > .
is
2)(0.%) 3(Le) 4)R
Diy
The domain of
x-5 ee
Sg aes
f(x) = log, eloxe 4 v is
1) (45) 2) (6.20)
3)(45)U(6) 4) (45]U(6.)
[si "(lose x?)
The domain of ¢(x)=Ve is
Let f(x)=sec"[1+cos*x] where |.)
denotes the greatest integer function
I: Domain of f(x) is R
Ionlylistrue 2) only IL is true
3) both [and II are true
4) neither Inor Il are true
Observer the following lists
List -1 List - II
Functions Domain
L f(x)= sin" (log, x) a) {-1,1}
IL. g(x)=,cos(sinx) —_b) {1}
IT: Range of f(x) is {sec™'1, se
I, h(x) = sin” 'S OER
TV. f(x) = g(x) + h(x) d) [1,2]
eR
The correct matching of List I to List His
1) Fb; Tea; Hl-c; 1V-d_ 2) L-aslI-bslll-d:IV-c
3)FdT-elllalV-a 4)I-bjl-alll-dIV-c
ion
3+
1(x)=cot (VOr+3)8) +cos"(¥
is defined on the set S, then S is equal to
U{-%0} 2) [-3.0] 3) [0,3] 4) (-3,0)
7. If f(x) is defined on (0.1), then the
domain of /(sin.x) is
1) (2nz,(2n+1) 2). nez
),
3) ((2-I)z,(n41)z) mez
4) (nz,(2n+1)x)nez
8. Thedomain of the function
oe
2 | 2nF Sng neZ
f(x) =V10-Vx*—21,° is
2 [-V21,vai]
1) [5, 20)
9. Domain of )x(1~e*)(x +2)(x-3)'
1)[-2. 3]
3)(-2,-2]U{0, 3}
2)(-2,0]
4)(—», = 2) U[0, 3]
. Range of the function /(x)
7 7
1) [1.2] ranm[ez]o(s
M1. The range of =sin | > is
(04) »[ad)n[a
The image of the interval [1,3] under the
Z)41 [0.1]
2.
mapping /:R > R, given by
f (x) =2x° -24x+107 is
1) [0,89] 2)[75,89] 3)[0.75] 4) [70,80]
einem! SEhi5 i ~
If f:R->R is defined by f(x) =
constants) and /(—7)=7, then the range
of £(7)+17cosx is
1) [-34,0]
3)[-34.34]
2)[0,34]
4) {-34,34}
for y < R, where [x] is the greatest integer
not exceeding x, then the range of / is
2){0.1}
D{ve R05 x51}
3){xeER:x>0} 4){xeR:x <0}
. The range of
| ie tl
sin [: +4] ecos{x?-4],
2] es
where [.] denotes the greatest integer
funeti
n{z x} 2{z} 3)
2
. The function f:R +B is defined by
f(x) =[x]+[-x] where [ .] is GLF is
surjective then B=
DR 2) [01] 3)[-1,0] — 4)f{-1, o}
. Statement I: The range of the function
sin([s]e) ,
(Ose 1)
Statement I : The range of the function
mie)
B(x)=y
1) only 1 is true 2) only Il is true
3) both | and I are true
4) neither I nor II are true
- Let S be the set of all triangles and R be
the set of positive real numbers. Then the
function /:5 > R°,
AcS is
1) injective but not surjective
2) surjective but not injective
3) injective as well as surjective
4) neither injective nor surjective
rv
J (A)=areaof A, where
weet
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
and_f(x)=cos(5x+2) then the mapping
f:A>Bis
1) One - one but not onto
2) Onto but not one - one
3) Both one- one and onto
4) Neither one - one nor onto
If £(x) =sin? x +sin?(x +7/3)*
cosx cos(x +4 /3)and g(5/4)=1
then (gof)(x) =
1 2)0
Hee hen £(6(3))=
3)sinx 4) -cosx
If s(x)
hhr [~1,.0) is
defined by {(x)=x?-4x4+3 then
£ (x)=
1) 2-Vx+1 2) 2+Ve41
jy2cveHl 4) 2eNeed
5 5
Let f(x)=x?-x+1x21/2, then the
solution of the equation f-'(x) = f(x) is
1
x 2)x=2 3X=Z 4x0
Let f:R +R be given by
f(x)=(x4+1) -1,x2-1 Then f'(x) =
VY -t4Ve41 0 2) -1-Vx41
3) does not exist because fis not one-
one
4) does not exist because fis not onto
'S. The inverse of the function
F(x)==
Taw
+2 is given by
2) tos.
26. If f:R>R is an invertible functiy,
such that f(x)and — S''(x)ayy
symmetric about the line Y= —X, then
1) f(x) is odd
2) £(x)and f-' (x) may not be symmetry,
about the line y=*
3) f(x) may not be odd
4) f'(x)may be odd
27, If f(x) is an odd periodic function with
period 2, then f (4) =
If f(x+y)=f(x)-f(») for all real x,»
and / (0) #0, then the function
- 0).
8)" Ge)
1) even function 2) odd function
3)oddif f(x)>0 4) neither even nor odg
28.
is
. Let the function
f(x) =3x?—4x +8 log(1+|x|) be defined
on the interval [0, 1]. The even extension
of f(x) of the interval |-1, 1] is
1) 3x’ ~4|x|+8log(1+|x|)
2) 3x? -4x +8log(1+|x|)
3) 3x? +4x —8log(1+|x|)
4) 3x" -4x—8log(1 +|x|)
30. Ifthe real valued function
a | |, thi =
F wal) is even, then n
- Let £:[-3,3] > R where
[x?+2]
[a | bean odd
function then the value of a is (where | .|
represents greatest integer function)
I) less than TI 211
3) greater than 11 412
f(x)=x* +sinx +
32. Le
MM.
6.
38.
39.
;. The fundamental period of the function
ray tn
0) Tie ene,
yea
0. If for nonzero x, af(x) +b!) Ly ots,
Lx)
then / is (where |. where a ¥ b, then f (2)=
integer function)
Hanodd function 2) aneven fimet
3) both odd and even ——
4) neith
| represents greatest
odd nor even
The period of the function
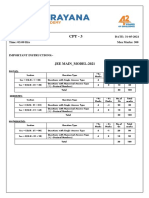
EXERCISE - Il: KEY
O11 02)3,——-03)2— 043. 05)3
06)1 07)1_ 08). 093-104
Mery Fst) 142 15)2
164 173 18)2 1993, 20 |
21)t 2292, 23) 24)1 254 |
261 270 = -28)1_—-29)1 3093 |
32)b-33)3,34)l_ Ss 35)4
37)997.5 38)500 39)3
HINTS
log} is defind fora b> Oand 641
[co
f(x
ny +COS.
= 7
D> De Ye bag
The period of the function
F(x)=cos| = vin EA] is
1) 2(m +1)! 2) 2(m!) 3) (+1) 4) nt
(x-z)
f(s) =4c0s'| 5] -2e0s{ SF
xe
is defined then
is equal to :
eee lox +24"
Nai 2D4e* 3)3n* 4) ant
If /:R— RK isa function satisfying the
property
f(2x+3)+ f(24+7)= 20x Ry then
= >0
Ox+24
F(x) is detined if 1 1<1+cos*x<2,
]
©. Range = {sec’' I,sec ‘2
or2
to lae i. {
(1996, (1996, (1996
If [x] stands for the greatest integer
function, then
ie
=[I + cos” x
(x) isdefined for f(x) has to be define and
[27000 |*
(x-a Ms=) Eder components to be meaningful,
If (x)= ana compone e
we must have
r(x) r(r+3)20 and OS x 43x61
GG rane ,
(x+3)x=0 ie. x=0,-3 -.S ={-3,0}
— He). k then k= Since the domain of fis (0.1
(e—x)e-¥) 9 4 bab “0 Int
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- CPT 3Document9 pagesCPT 3ARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- DPP-11 AlcoholDocument14 pagesDPP-11 AlcoholARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Key Sheet: Sec: IIT-XII-IC-CF CPT-1 Date:17-05-2021 Max - Marks:360Document10 pagesKey Sheet: Sec: IIT-XII-IC-CF CPT-1 Date:17-05-2021 Max - Marks:360ARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- CPT - 3 - Xii Ic 31-05-2021 (Solved)Document13 pagesCPT - 3 - Xii Ic 31-05-2021 (Solved)ARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- CPT - 3 - XII IC CF - Mains Paper - 31-05-2021 - KeyDocument16 pagesCPT - 3 - XII IC CF - Mains Paper - 31-05-2021 - KeyARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Xii Iit CPT-1 Top 100 Students ListDocument2 pagesXii Iit CPT-1 Top 100 Students ListARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Xii Iit CPT-1 Result 17-05-21Document4 pagesXii Iit CPT-1 Result 17-05-21ARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 07-30-2021 09.40.34Document11 pagesCamScanner 07-30-2021 09.40.34ARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Xii Ic Top 100 Students ListDocument3 pagesXii Ic Top 100 Students ListARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- DPP-5 (Grignard Reagents)Document11 pagesDPP-5 (Grignard Reagents)ARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- The Narayana Group: Xii Iit Cpt-8 Result 12-07-2021Document4 pagesThe Narayana Group: Xii Iit Cpt-8 Result 12-07-2021ARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Xii Iit Top 100 Students ListDocument2 pagesXii Iit Top 100 Students ListARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- CPT-9 Xii Top 100 Students ListDocument2 pagesCPT-9 Xii Top 100 Students ListARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument30 pagesSolid StateARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet