Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psychological Disorders I. Defining "Abnormal" and The Prevalence of Disorders
Uploaded by
Krisha Koirala0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesOriginal Title
abnorm outline
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesPsychological Disorders I. Defining "Abnormal" and The Prevalence of Disorders
Uploaded by
Krisha KoiralaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
I. Defining “abnormal” and the prevalence of disorders
A. Prevalence of psychological disorders
B. Defining psychological disorders: the 4 Ds
1. Deviation
a. Statistical (tails of a bell curve)
b. from social norms (this depends on culture, time, etc.)
what if society itself is warped?
2. Distress—is the person unhappy with his/her condition?
3. Dysfunctional behavior—maladaptive behavior; can’t meet personal goals
4. Dangerous—potential harm to self or others (rare)
C. DSM V: why do we classify people, what has changed from DSM IV, role of culture
II. Anxiety Disorders, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders, and PTSD
A. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (see text for details)
B. Panic Disorder (see text for details)
C. Phobias
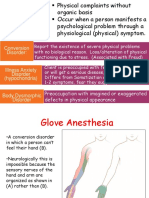
C. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
1. Persistent and unwanted thoughts, often about violence, sex, or contamination
2. Repetitive rituals, such as checking or cleaning
D. Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
E. Possible causes of these disorders
III. Mood disorders
A. Depression—the most common disorder
1. Symptoms include:
a. Emotional, sleep, physical factors
b. Social factors and the vicious cycle
c. Cognitive factors—negative schemas about self, others, the future
Less self-serving bias (taking credit for success but not failure)
Negative internal, stable, global attributions (e.g., “I’m bad at everything”)
B. Bipolar Disorder
1. How it is different from regular depression?
2. Manic episodes and symptoms
C. Possible causes of these disorders
IV. Disorders of Identity & Memory
A. Dissociative Identity Disorder (formerly MPD)
1. Separate and different personalities, “host” usually has no awareness of the other(s)
2. Controversy surrounding dramatic increases in U.S. cases in the ‘80s
V. Schizophrenia
A. Symptoms
1. Positive (present) symptoms
a. Delusions
b. Hallucinations (and other perceptual problems)
c. Emotional abnormalities—inappropriate affect
d. Disorganized thought and speech (e.g., loose associations, clanging, neologisms)
2. Negative (absent) symptoms
a. Poverty of speech
b. Loss of volition
c. Flat affect
d. Social withdrawal
3. Motor abnormalities (e.g., waxy flexibility) and catatonic schizophrenia
4. Chronic versus acute
B. Causes of schizophrenia
1. Biological factors (genetic links, brain abnormalities, excess dopamine activity)
2. Environmental factors may include exposure to virus in utero, birth complications
3. Vulnerability-stress model (also called predisposition model) combines these
VI. Personality Disorders
A. Narcissistic
B. Borderline
C. Antisocial
You might also like
- Student Lecture Dissociative DisorderDocument4 pagesStudent Lecture Dissociative DisorderMarcela DiasNo ratings yet
- Mental Illness Schizophrenia - Greek For "Split" (From Reality) and "Mind"Document7 pagesMental Illness Schizophrenia - Greek For "Split" (From Reality) and "Mind"Alaina AndersonNo ratings yet
- Psy201 Final NotesDocument12 pagesPsy201 Final NotesNagham KDNo ratings yet
- Psy 10Document5 pagesPsy 10Shishir SubbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders.Document9 pagesChapter 14 Psychological Disorders.BorisVanIndigoNo ratings yet
- What Is Normal? What Is Abnormal?Document28 pagesWhat Is Normal? What Is Abnormal?Mehboob ViraniNo ratings yet
- Personality DisordersDocument30 pagesPersonality DisordersSubhashree MohantyNo ratings yet
- Block 5Document59 pagesBlock 5aakash atteguppeNo ratings yet
- Psych DisordersDocument44 pagesPsych DisordersKhadeeja hannaNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorders Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesPersonality Disorders Lesson Planapi-284104206No ratings yet
- Abnormal PsychologyDocument136 pagesAbnormal PsychologyMary Ye Ariola Magsino100% (3)
- Unit 1Document16 pagesUnit 1reeta yadav0% (1)
- Psychiatric History Taking FormatDocument10 pagesPsychiatric History Taking Formatleena_awi100% (3)
- Chapter 13Document7 pagesChapter 13Chin SilverNo ratings yet
- Learn Psychology With Vishal Pandey: Term 2Document35 pagesLearn Psychology With Vishal Pandey: Term 2Labhanshi BhargavaNo ratings yet
- 6-Anxiety DisordersDocument48 pages6-Anxiety DisordersyohanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven: Psychological Disorders and Treatment TechniquesDocument32 pagesChapter Seven: Psychological Disorders and Treatment TechniquesBiniyam TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Prelim ReviewerDocument8 pagesPrelim ReviewerAGNER JASMIN ROSE L.No ratings yet
- SYBA PsychologyDocument22 pagesSYBA PsychologyShivani MaratheNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Dissociative DisordersDocument4 pagesGroup 5 Dissociative DisordersKian HopeNo ratings yet
- Psychologi Cal Disorders: Powerpoint ® PresentationDocument86 pagesPsychologi Cal Disorders: Powerpoint ® PresentationZariyah PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Psychological DisordersREVDocument18 pagesPsychological DisordersREVlucas OmondiNo ratings yet
- Topic7 AbnormalPsych (Students)Document33 pagesTopic7 AbnormalPsych (Students)nickpho21No ratings yet
- SUMMARYDocument8 pagesSUMMARYSJane FeriaNo ratings yet
- RGO PresentationDocument706 pagesRGO PresentationAnonymous okusLz100% (1)
- Patterns of BehaviorDocument8 pagesPatterns of BehaviorKeith AquinoNo ratings yet
- RGO AbPsy Handout2019 PDFDocument24 pagesRGO AbPsy Handout2019 PDFJoshuamadelDelantar100% (3)
- Chapter SevenDocument25 pagesChapter Sevenfunny zoneNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric History TakingDocument6 pagesPsychiatric History TakingNurul Nadzri100% (1)
- Lecture16 Abnormal Fulltext PDFDocument58 pagesLecture16 Abnormal Fulltext PDFGreyie kimNo ratings yet
- Psi. Abnormal PENGANTARDocument29 pagesPsi. Abnormal PENGANTARjatmiko.purwantonoNo ratings yet
- Psychological DisordersDocument21 pagesPsychological DisordersMark100% (2)
- SAD Social Anxiety DisorderDocument5 pagesSAD Social Anxiety Disorderselina shakyaNo ratings yet
- Personality DisordersDocument23 pagesPersonality DisordersAndrew NavarraNo ratings yet
- DISSOCIATIVE DISORDERS - TeachersDocument19 pagesDISSOCIATIVE DISORDERS - TeachersIano IanoNo ratings yet
- AP Psych Prep 12 - Abnormal PsychologyDocument116 pagesAP Psych Prep 12 - Abnormal Psychologydms727No ratings yet
- Dissociative DisorderDocument21 pagesDissociative DisorderAryan Judith DoloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter15 150408174807 Conversion Gate01Document86 pagesChapter15 150408174807 Conversion Gate01Al bertNo ratings yet
- Sychology Actsheets: DepressionDocument4 pagesSychology Actsheets: DepressionLachlan ScholesNo ratings yet
- Psychological Disorders Lecture Notes PDFDocument8 pagesPsychological Disorders Lecture Notes PDFTANUINo ratings yet
- Psychology Chapter SevenDocument25 pagesPsychology Chapter Sevenmelaku zegeyeNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-09-28 at 11.29.26 AMDocument52 pagesScreenshot 2022-09-28 at 11.29.26 AMTheany Be SmilerNo ratings yet
- Psychology: (9th Edition) David MyersDocument75 pagesPsychology: (9th Edition) David MyersMudassirKhanNo ratings yet
- 8Document7 pages8Alejandro AnselmiNo ratings yet
- Disorders RushedDocument40 pagesDisorders Rushedapi-391411195No ratings yet
- Resume 13 Abnormal Psychology "Kleptomania and Obsessive and Compulsive"Document9 pagesResume 13 Abnormal Psychology "Kleptomania and Obsessive and Compulsive"Salsabila RizkaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document42 pagesChapter 4Athira RaghuNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: Disturbances Thinking in Feeling BehaviorDocument26 pagesSchizophrenia: Disturbances Thinking in Feeling BehaviorVaibhav KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Dissociative Identity Disorder, (Multiple Personality Disorder) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDissociative Identity Disorder, (Multiple Personality Disorder) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- SchizopherniaDocument11 pagesSchizopherniaSa Ra Doh0% (1)
- PSYC 1002M Notes Chapter 15-16Document10 pagesPSYC 1002M Notes Chapter 15-16ayd3nmcd0naldNo ratings yet
- Psych 0Document6 pagesPsych 0Joya Ruben CamposNo ratings yet
- DR McDaniel PSYC 3023 Abnormal Psych FA 21 Chapter 8 Dissociative POSTDocument27 pagesDR McDaniel PSYC 3023 Abnormal Psych FA 21 Chapter 8 Dissociative POSTHeather JenkinsNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Plus NEW MyPsychLab 15th Edition Butcher Solutions Manual 1Document21 pagesAbnormal Psychology Plus NEW MyPsychLab 15th Edition Butcher Solutions Manual 1william100% (39)
- Abnormal Psychology Plus NEW MyPsychLab 15th Edition Butcher Solutions Manual 1Document36 pagesAbnormal Psychology Plus NEW MyPsychLab 15th Edition Butcher Solutions Manual 1herbertjacksonjioyzepmaf100% (19)
- Abnormal Psychology Plus New Mypsychlab 15Th Edition Butcher Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesAbnormal Psychology Plus New Mypsychlab 15Th Edition Butcher Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFmary.wiles168100% (18)
- Somatic Symptom Disorders and Personality DisordersDocument15 pagesSomatic Symptom Disorders and Personality Disordersapi-287575009No ratings yet
- 10 1111@j 1460-9568 2006 04785 X PDFDocument13 pages10 1111@j 1460-9568 2006 04785 X PDFTlaloc GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Johari WindowDocument10 pagesJohari WindowjeffreyrakeshNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument4 pagesAssessmentninja ni Rose91% (11)
- Davidson. Mental EventsDocument10 pagesDavidson. Mental EventsMolly FasslerNo ratings yet
- Akhuwat Internship ProgrammeDocument2 pagesAkhuwat Internship ProgrammeAtiya FalakNo ratings yet
- The Methodology of Organizational Diagnosis - Clayton. P. AlderferDocument10 pagesThe Methodology of Organizational Diagnosis - Clayton. P. AlderferRifa AratikaNo ratings yet
- Letters SoundsDocument243 pagesLetters SoundsRivka Share100% (3)
- Mock TrialsDocument121 pagesMock TrialscitizenschoolsNo ratings yet
- Basic IELTS Task 2 Writing Template StructureDocument3 pagesBasic IELTS Task 2 Writing Template StructureANUPAM SHARMA100% (4)
- IntroductionDocument127 pagesIntroductiondiona macasaquitNo ratings yet
- Bertrand RussellDocument23 pagesBertrand RussellNikhil LallNo ratings yet
- All Report Writing Lectures All Report Writing LecturesDocument98 pagesAll Report Writing Lectures All Report Writing LecturesAhmed ButtNo ratings yet
- Aleida Assmann: Esponse To Eter OvickDocument6 pagesAleida Assmann: Esponse To Eter Ovickmateusz dupaNo ratings yet
- NICHQ Vanderbilt Teacher RatingDocument3 pagesNICHQ Vanderbilt Teacher RatingJanine Erica De LunaNo ratings yet
- Do What You Are Handbook 2008Document23 pagesDo What You Are Handbook 2008q12345q6789No ratings yet
- Character Traits Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesCharacter Traits Lesson Planapi-376373807No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Human Exceptionality School Community and Family 12th EditionDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Human Exceptionality School Community and Family 12th Editionsloppy.obsidian.v8ovu100% (46)
- 9b. Semana 2 y 3Document5 pages9b. Semana 2 y 3Aram ConsNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan: Analogy To Show Relationships of WordsDocument2 pagesLearning Plan: Analogy To Show Relationships of WordsMonaliza PawilanNo ratings yet
- (Zeigarnik, B.) Experimental Abnormal PsychologyDocument162 pages(Zeigarnik, B.) Experimental Abnormal PsychologyE Alan CórdovaNo ratings yet
- Topic Workbook - Leading in Digital Disruption 1Document16 pagesTopic Workbook - Leading in Digital Disruption 1ahmedyarkarim63No ratings yet
- 103ppt Develop Your Leaders From WithinDocument12 pages103ppt Develop Your Leaders From WithinA Aezat LKNo ratings yet
- Transformational LeadershipDocument24 pagesTransformational LeadershipĐăng Lưu100% (2)
- Student Teaching ReflectionDocument2 pagesStudent Teaching Reflectionapi-453445899100% (1)
- The 5 Leadership Learning PrinciplesDocument2 pagesThe 5 Leadership Learning PrinciplesMardhiah RamlanNo ratings yet
- Team Management: By:-Akshara Saxena B.A.S.L.P Second YearDocument18 pagesTeam Management: By:-Akshara Saxena B.A.S.L.P Second YearAkshara SaxenaNo ratings yet
- The Structure of ConversationsDocument42 pagesThe Structure of ConversationsCarlos RojasNo ratings yet
- The Primary Years Programme (PYP)Document5 pagesThe Primary Years Programme (PYP)Sorin Iordache100% (1)
- SPECIALIST TECHNICIAN IN ENGLISH LANGUAGE TEACHING-DiagnosisDocument4 pagesSPECIALIST TECHNICIAN IN ENGLISH LANGUAGE TEACHING-DiagnosisCarlos SalgadoNo ratings yet
- New Year'S ResolutionsDocument10 pagesNew Year'S ResolutionsChiaraMazzoleniNo ratings yet