Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SCM Assignment No 1
Uploaded by
46 Gaurav Pawar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views5 pagesSCM Assignment No 1
Uploaded by
46 Gaurav PawarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
SCM Assignment No.
1
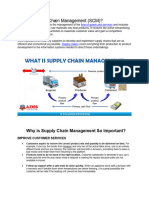
Q1. Define Supply chain management. Explain the significance and limitations of SCM.
Answer :-
Supply chain management is the management of the flow of goods and services and
includes all processes that transform raw materials into final products. It involves the active
streamlining of a business's supply-side activities to maximize customer value and gain a
competitive advantage in the marketplace.
The Significance of Supply Chain Management :
It is well known that supply chain management is an integral part of most businesses
and is essential to company success and customer satisfaction.
1. Boost Customer Service
Customers expect the correct product assortment and quantity to be delivered.
Customers expect products to be available at the right location. (i.e., customer
satisfaction diminishes if an auto repair shop does not have the necessary parts in
stock and can’t fix your car for an extra day or two).
Right Delivery Time – Customers expect products to be delivered on time (i.e.,
customer satisfaction diminishes if pizza delivery is two hours late or Christmas
presents are delivered on December 26).
Right After Sale Support – Customers expect products to be serviced quickly. (i.e.,
customer satisfaction diminishes when a home furnace stops operating in the winter
and repairs can’t be made for days)
2. Reduce Operating Costs
Decreases Purchasing Cost – Retailers depend on supply chains to quickly deliver
expensive products to avoid holding costly inventories in stores any longer than
necessary. For example, electronics stores require fast delivery of 60” flat-panel
plasma HDTV’s to avoid high inventory costs.
Decreases Production Cost – Manufacturers depend on supply chains to reliably
deliver materials to assembly plants to avoid material shortages that would
shutdown production. For example, an unexpected parts shipment delay that causes
an auto assembly plant shutdown can cost $20,000 per minute and millions of
dollars per day in lost wages.
Decreases Total Supply Chain Cost – Manufacturers and retailers depend on supply
chain managers to design networks that meet customer service goals at the least
total cost. Efficient supply chains enable a firm to be more competitive in the market
place.
3. Improve Financial Position
Increases Profit Leverage – Firms value supply chain managers because they help
control and reduce supply chain costs. This can result in dramatic increases in firm
profits. For instance, U.S. consumers eat 2.7 billion packages of cereal annually, so
decreasing U.S. cereal supply chain costs just one cent per cereal box would result in
$13 million dollars saved industry-wide as 13 billion boxes of cereal flowed through
the improved supply chain over a five year period.
Decreases Fixed Assets – Firms value supply chain managers because they decrease
the use of large fixed assets such as plants, warehouses and transportation vehicles
in the supply chain. If supply chain experts can redesign the network to properly
serve U.S. customers from six warehouses rather than ten, the firm will avoid
building four very expensive buildings.
Increases Cash Flow – Firms value supply chain managers because they speed up
product flows to customers. For example, if a firm can make and deliver a product to
a customer in 10 days rather than 70 days, it can invoice the customer 60 days
sooner.
The Limitations of Supply Chain Management :
Supply chains continue to increase in complexity as they are leveraged to drive
higher value through increased output at lower costs. The more intricate supply chains
become, the more difficult (and necessary) it becomes to analyse risks simultaneously.
Risk analysis becomes more difficult as risk visibility decreases and complexity
increases. It is quite easy to see risk drivers in simple supply chains, but as additional
departments and components are added, risks become obscured.
Despite categorizations that make your supply chain seem like independently run
departments, the entire chain is still interconnected, and each division is dependent on all
others for overall success. Disruptive events in one area of a supply chain can have
damaging effects on other areas if the event is not controlled properly. Even worse, events
in your supply chain can disrupt departments outside of your supply chain, like Sales and
Marketing.
The probability of extensive damage is significantly increased when these disruptive
events occur unexpectedly. While these events can’t always be predicted, advanced
planning, forecasting of risk events and adopting a more holistic representation of your
business can prepare planners to react quickly and intelligently to mitigate damages.
For these reasons, supply chain network design tools are simply not enough when it
comes to risk management. Unfortunately, many such solutions only provide limited insight
rather than a holistic view of risk drivers and effective risk management options.
Q2. Explain the Bull whip effect. What are the measures to control this effect?
Answer :
Imagine a person having a long whip in his hand, and if he gives a little nudge to the
whip at the handle, it creates little movements in the parts closest to the handle, but parts
further away would move more in an increasing fashion.
Similarly, in the supply chain world, the end customers have the whip handle and
they create a little movement in the demand which travels up the supply chain in increasing
fashion. As we move away from the customer, we can see bigger movements. On average,
there are six to seven inventory points between the end customer and raw material supplier
(as shown below in figure 1). Everyone tries to protect themselves from stock-out situations
and missed customer orders, by keeping extra inventory to hedge against variability in the
supply chain. Hence, huge buffers of inventories up to six months can exist between the end
customer and raw material supplier.
The bullwhip effect is a concept for explaining inventory fluctuations or inefficient
asset allocation as a result of demand changes as you move further up the supply chain. As
such, upstream manufacturers often experience a decrease in forecast accuracy as the
buffer increases between the customer and the manufacturer.
Measures to control this Bull whip effect
Every industry has its own unique supply chain, inventory placements, and
complexities. However, after analysing the bullwhip effect and implementing improvement
steps, inventories in the range of 10 to 30 percent can be reduced and 15 to 35 percent
reduction in instances of stock out situations and missed customer orders can be achieved.
Below are some of the methods to minimize the bullwhip effect.
1. Accept and understand the bullwhip effect
The first and the most important step towards improvement is the recognition of the
presence of the bullwhip effect. Many companies fail to acknowledge that high buffer
inventories exist throughout their supply chain. A detailed stock analysis of the inventory
points from stores to raw material suppliers will help uncover idle excess inventories. Supply
chain managers can further analyze the reasons for excess inventories, take corrective
action and set norms.
2. Improve the inventory planning process
Inventory planning is a careful mix of historical trends for seasonal demand, forward-looking
demand, new product launches and discontinuation of older products. Safety stock settings
and min-max stock range of each inventory point need to be reviewed and periodically
adjusted. Inventories lying in the entire network need to be balanced based on regional
demands. Regular reporting and early warning system need to be implemented for major
deviations from the set inventory norms.
3. Improve the raw material planning process
Purchase managers generally tend to order in advance and keep high buffers of raw
material to avoid disruption in production. Raw material planning needs to be directly linked
to the production plan. Production plan needs to be released sufficiently in advance to
respect the general purchasing lead times. Consolidation to a smaller vendor base from a
larger vendor base, for similar raw material, will improve the flexibility and reliability of the
supplies. This, in turn, will result in lower raw material inventories.
4. Collaboration and information sharing between managers
There might be some inter-conflicting targets between purchasing managers, production
managers, logistics managers and sales managers. Giving more weight to common company
objectives in performance evaluation will improve collaboration between different
departments. Also providing regular and structured inter-departmental meetings will
improve information sharing and decision-making process.
5. Optimize the minimum order quantity and offer stable pricing
Certain products have high minimum order quantity for end customers resulting in overall
high gaps between subsequent orders. Lowering the minimum order quantity to an optimal
level will help provide create smoother order patterns. Stable pricing throughout the year
inset.
Name :- Gaurav Pawar
SY BBA ( IB)
Roll No. 14646
You might also like
- An Introduction to Global Supply Chain Management: What Every Manager Needs to UnderstandFrom EverandAn Introduction to Global Supply Chain Management: What Every Manager Needs to UnderstandNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain 2Document8 pagesSupply Chain 2fayzaaj10No ratings yet
- Indroduction To Supply Chain 1Document38 pagesIndroduction To Supply Chain 1Tansen John100% (2)
- Report on SCM, TQM and Six SigmaDocument15 pagesReport on SCM, TQM and Six SigmaKarthika SasikumarNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument19 pagesSupply Chain ManagementKaran MehtaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Supply Chain ManagementDocument47 pagesIntroduction to Supply Chain ManagementEmanuelle BakuluNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument9 pagesSupply Chain ManagementRupesh SinghNo ratings yet
- SC MGT - Supply Chain Management in Hospitality Industry (PRELIM NOTES)Document13 pagesSC MGT - Supply Chain Management in Hospitality Industry (PRELIM NOTES)chloekent loreNo ratings yet
- SCM - Module 1Document8 pagesSCM - Module 1May AlmendraNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument6 pagesChapter IBuena flor AñabiezaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Designing and Managing The Supply Chain 3rd Edition by David Simchi LeviDocument56 pagesSolution Manual For Designing and Managing The Supply Chain 3rd Edition by David Simchi LeviOmnia MustafaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management Techniques and Decision PhasesDocument4 pagesSupply Chain Management Techniques and Decision PhasesMurugan SaravananNo ratings yet
- Logistics & Supply Chain ManagementDocument53 pagesLogistics & Supply Chain Managementsneha bhongadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1harleycrispino.eduNo ratings yet
- Important Question and AnswersDocument7 pagesImportant Question and Answersshamal0392% (25)
- 7 Ways Everyone Can Cut Supply Chain CostsDocument7 pages7 Ways Everyone Can Cut Supply Chain CostsbumbiazarkaNo ratings yet
- Simchi Levi3E SMDocument56 pagesSimchi Levi3E SMKhang HuynhNo ratings yet
- 13.1 The Importance of The Level of Product AvailabilityDocument3 pages13.1 The Importance of The Level of Product AvailabilityMeo OlaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document7 pagesUnit 5Sheela AngelNo ratings yet
- DMC 216Document4 pagesDMC 216sailesh chaudhary0% (1)
- Supply Chain TerminologyDocument5 pagesSupply Chain TerminologyMehroz KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Strategies Improve Supply ChainDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Strategies Improve Supply ChainAnup DasNo ratings yet
- Samples Solution Manual Designing and Managing The Supply Chain 3rd Edition by David Simchi Levi SLM1060Document11 pagesSamples Solution Manual Designing and Managing The Supply Chain 3rd Edition by David Simchi Levi SLM1060mathimurugan n0% (1)
- Specialist Diploma in Supply Chain Management Distribution and Transportation Management (MA2018) Group Assignment-2Document20 pagesSpecialist Diploma in Supply Chain Management Distribution and Transportation Management (MA2018) Group Assignment-2brijeshgupta457No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Coordination and the Impacts of Lack ThereofDocument11 pagesSupply Chain Coordination and the Impacts of Lack ThereofEdlawit AwegchewNo ratings yet
- Obstacles and Components of E-Business DistributionDocument11 pagesObstacles and Components of E-Business DistributionAkshay DhakanNo ratings yet
- SCM Unit-3Document15 pagesSCM Unit-3Aashish Singh IINo ratings yet
- Final Om Term PaperDocument23 pagesFinal Om Term PaperManisha TekchandaniNo ratings yet
- Thi S Is Also Known As A "Pull System," and It Entails The FollowingDocument4 pagesThi S Is Also Known As A "Pull System," and It Entails The FollowingMinh Anh MinhNo ratings yet
- Coordination in Supply ChainDocument8 pagesCoordination in Supply ChainWaqqar ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- 8 Benefits of Effective Supply Chain ManagementDocument4 pages8 Benefits of Effective Supply Chain ManagementOkorie SundayNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 NoteDocument9 pagesUnit 3 NoteRavi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ome752 Supply Chain Management Unit - I IntroductionDocument21 pagesOme752 Supply Chain Management Unit - I Introductionjeeva santhiyaNo ratings yet
- Oscm Module - IvDocument10 pagesOscm Module - IvRadha Krishna - with youNo ratings yet
- 1-Thiết kế chuỗi cung ứng (xác định có những bên nào tham gia vào chuỗi cung ứng, nhiệm vụ của họ là gì) Producers Document8 pages1-Thiết kế chuỗi cung ứng (xác định có những bên nào tham gia vào chuỗi cung ứng, nhiệm vụ của họ là gì) Producers Trung TrinhNo ratings yet
- Distribution & Logistics Management V3Document5 pagesDistribution & Logistics Management V3solvedcareNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Supply Chain Management: Customer Satisfaction: How To Measure and Tips For ImprovementDocument5 pagesBenefits of Supply Chain Management: Customer Satisfaction: How To Measure and Tips For ImprovementPritchard MatamboNo ratings yet
- The 7 Principles of Supply Chain ManagementDocument10 pagesThe 7 Principles of Supply Chain Managementmela917No ratings yet
- ONM4201E. I22022258 .JUN2022.Document8 pagesONM4201E. I22022258 .JUN2022.Joan 夏No ratings yet
- Global Supply Chain Management Notes-Msc Procurement and Logistics-Sept, 2023Document85 pagesGlobal Supply Chain Management Notes-Msc Procurement and Logistics-Sept, 2023hassan28sepNo ratings yet
- Homeworksimchi Levidesigningandmanagingsupplychain 140401173556 Phpapp01Document50 pagesHomeworksimchi Levidesigningandmanagingsupplychain 140401173556 Phpapp01Anish Mathew88% (32)
- Chain Decisions On The Success of A Firm. The Goal of A Supply Chain Should Be To Grow OverallDocument8 pagesChain Decisions On The Success of A Firm. The Goal of A Supply Chain Should Be To Grow OverallmelihNo ratings yet
- Aditonal Notes - 1Document8 pagesAditonal Notes - 1yeteday615No ratings yet
- Faculty of Business and Management Individual AssignmentDocument9 pagesFaculty of Business and Management Individual Assignment静思No ratings yet
- FinalAssignmentDocument5 pagesFinalAssignmentAB BANo ratings yet
- SCLM Unit 3Document35 pagesSCLM Unit 3VedikaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument26 pagesSupply Chain ManagementLinh LêNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Performance: The Supplier's Role: Executive Brief Industry Directions Inc. March 2005Document6 pagesSupply Chain Performance: The Supplier's Role: Executive Brief Industry Directions Inc. March 2005Himura SanzouNo ratings yet
- IT Enabled Supply Chain Management.Document46 pagesIT Enabled Supply Chain Management.anampatelNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management of Coca-ColaDocument20 pagesSupply Chain Management of Coca-ColaAditya Dethe85% (33)
- Midterm NotesDocument5 pagesMidterm NotesGupta KiraNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Logistics Management 4th Edition Bowersox Solutions ManualDocument3 pagesSupply Chain Logistics Management 4th Edition Bowersox Solutions Manuala37113077575% (4)
- Reflective_Assignment_EA23onl013Document8 pagesReflective_Assignment_EA23onl013Saurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Right Supply Chain for Your ProductDocument15 pagesRight Supply Chain for Your ProductEmile JanssensNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Business Startup Guide: Step-by-Step Tips for SuccessFrom EverandSupply Chain Business Startup Guide: Step-by-Step Tips for SuccessNo ratings yet
- How to Optimise Your Supply Chain to Make Your Firm Competitive!From EverandHow to Optimise Your Supply Chain to Make Your Firm Competitive!Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Project On Environment ScienceDocument8 pagesProject On Environment Science46 Gaurav PawarNo ratings yet
- SCM Assignment No. 2 Q 1. Importance of Workflow Automation. AnswerDocument3 pagesSCM Assignment No. 2 Q 1. Importance of Workflow Automation. Answer46 Gaurav PawarNo ratings yet
- Typesreasons ScopusDocument8 pagesTypesreasons Scopus46 Gaurav PawarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Frauds in Indian Banking SectorDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Frauds in Indian Banking SectorEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- Banking Fraud Case Analysis in IndiaDocument7 pagesBanking Fraud Case Analysis in India46 Gaurav PawarNo ratings yet
- Banking FraudsDocument24 pagesBanking FraudsKenith Castelino100% (1)
- Liquid Analysis v3 Powell-Cumming 2010 StanfordgwDocument28 pagesLiquid Analysis v3 Powell-Cumming 2010 StanfordgwErfanNo ratings yet
- Time Table Semester II 2019-2020Document18 pagesTime Table Semester II 2019-2020Shiv Kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- 2 Druid StreetDocument4 pages2 Druid StreetthamestunnelNo ratings yet
- Daily Assessment RecordDocument4 pagesDaily Assessment Recordapi-342236522100% (2)
- Timber, PVCu and aluminium window and door hardware systemsDocument24 pagesTimber, PVCu and aluminium window and door hardware systemsOmul Fara NumeNo ratings yet
- How To Pass in University Arrear Exams?Document26 pagesHow To Pass in University Arrear Exams?arrearexam100% (6)
- Early Diabetic Risk Prediction Using Machine Learning Classification TechniquesDocument6 pagesEarly Diabetic Risk Prediction Using Machine Learning Classification TechniquesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Chanel SWOT AnalysisDocument5 pagesChanel SWOT AnalysisJeish KimNo ratings yet
- Final Annotated BibiliographyDocument4 pagesFinal Annotated Bibiliographyapi-491166748No ratings yet
- Komatsud65ex 16dozerbulldozerservicerepairmanualsn80001andup 200727063646Document26 pagesKomatsud65ex 16dozerbulldozerservicerepairmanualsn80001andup 200727063646juan santa cruzNo ratings yet
- I Button Proper TDocument4 pagesI Button Proper TmariammariaNo ratings yet
- Types of NumbersDocument11 pagesTypes of NumbersbrajanosmaniNo ratings yet
- Load Frequency Control of Hydro and Nuclear Power System by PI & GA ControllerDocument6 pagesLoad Frequency Control of Hydro and Nuclear Power System by PI & GA Controllerijsret100% (1)
- S06 - 1 THC560 DD311Document128 pagesS06 - 1 THC560 DD311Canchari Pariona Jhon AngelNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Steel Structures: Updates of Eurocode 8Document107 pagesSeismic Design of Steel Structures: Updates of Eurocode 8antonio111aNo ratings yet
- People v. Lagarto, 326 SCRA 693 (2000)Document43 pagesPeople v. Lagarto, 326 SCRA 693 (2000)GioNo ratings yet
- Victor Mejia ResumeDocument1 pageVictor Mejia Resumeapi-510300922No ratings yet
- Mad LabDocument66 pagesMad LabBalamurugan MNo ratings yet
- Service Parts List: 54-26-0005 2551-20 M12™ FUEL™ SURGE™ 1/4" Hex Hydraulic Driver K42ADocument2 pagesService Parts List: 54-26-0005 2551-20 M12™ FUEL™ SURGE™ 1/4" Hex Hydraulic Driver K42AAmjad AlQasrawi100% (1)
- Answer Questions Only: Chemical Engineering DeptDocument2 pagesAnswer Questions Only: Chemical Engineering DepthusseinNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Opportunities in SwitzerlandDocument5 pagesAerospace Opportunities in SwitzerlandBojana DekicNo ratings yet
- Durand Et Al JHRC 1997 Experimental Design Optimization of The Analysis of Gasoline by Capillary Gas ChromatographyDocument6 pagesDurand Et Al JHRC 1997 Experimental Design Optimization of The Analysis of Gasoline by Capillary Gas ChromatographyCatalinaSalamancaNo ratings yet
- One - Pager - SOGEVAC SV 320 BDocument2 pagesOne - Pager - SOGEVAC SV 320 BEOLOS COMPRESSORS LTDNo ratings yet
- English Extra Conversation Club International Women's DayDocument2 pagesEnglish Extra Conversation Club International Women's Dayevagloria11No ratings yet
- Fehniger Steve-Pump VibrationDocument35 pagesFehniger Steve-Pump VibrationSheikh Shoaib100% (1)
- Icelandic Spells and SigilsDocument16 pagesIcelandic Spells and SigilsSimonida Mona Vulić83% (6)
- EPISIOTOMYDocument17 pagesEPISIOTOMYKaye Arriane TenorioNo ratings yet
- Travis Walton Part 1 MUFON Case FileDocument346 pagesTravis Walton Part 1 MUFON Case FileClaudio Silva100% (1)
- SCJP 1.6 Mock Exam Questions (60 QuestionsDocument32 pagesSCJP 1.6 Mock Exam Questions (60 QuestionsManas GhoshNo ratings yet
- L Williams ResumeDocument2 pagesL Williams Resumeapi-555629186No ratings yet