Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CIVE 306 - Syllabus v5
Uploaded by
jean paulCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CIVE 306 - Syllabus v5
Uploaded by
jean paulCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSITY OF BALAMAND
Faculty Of Engineering
Civil Engineering Department
COURSE SYLLABUS (v5)
SECTION I: Course Information and Learning Outcomes
Course Name (Title): Soil Mechanics Laboratory Required/Elective: R
Course Code: CIVE306 Nb. of credits:1 Co/Pre-Requisite(s): CIVE 301
Academic Year: 2021-2022 Semester: Fall
Course Time TH 14:00-17:00 Section: 1 Bldg/Room: SHIKHANI
Instructor Name / Title:Nina Helal Office: Shikhani Tel/Ext: 3444
Emailnina.helal@balamand.edu.lb Office Hours: T-TH 10:00-11:30
Coordinator Name:
Course (Catalogue) Description:
In this course, students will perform several field and laboratory test methods that are
commonly used to determine the mechanical properties of soils. These properties are
crucial for the design of the foundation of each construction.
The course includes determination of critical soils index, classification of soils, moisture-
density relationship, California bearing ratio and hydraulic conductivity tests.
Course Learning Outcomes and degree of emphasis w.r.t. Student Outcomes SO’s (3, 5,
6): (1) = Some emphasis; (2) = Moderate emphasis; and (3) = Substantial emphasis
Upon successful completion of the course, students must be able to:
1. Analyse particle size distribution using mechanical and hydrometer method [SO6
(3), SO5 (3)]
2. Measure the specific gravity of soil solids [SO6 (3), SO5 (3)]
3. Conduct and identify the liquid and plastic limits of soil [SO6 (3), SO5 (3)]
4. Determine the relative density, and the field density of compacted soil [SO6 (3),
SO5 (3)]
5. Conduct modified proctor test and evaluate the moisture density relationship [SO6
(3), SO5 (3)]
6. Calculate the shearing resistance of soil through california bearing ratio [SO6 (3),
SO5 (3), SO3 (2) ]
7. Analyze the cleanliness of sand by the sand equivalent experiment [SO6 (3), SO5
(3)]
8. Participate effectively in laboratory based teams [SO5 (3) ].
Required Textbooks:
Bowles Joseph E., “Engineering Properties of Soils and their measurements”, McGraw-Hill,
4th edition.
References (readings, technical articles, hard copy and e-resources, etc.):
Liu Cheng and Evett Jack B., “Soil Properties: Testing, Measurement, and Evaluation”,
Prentice-Hall, 4th edition.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Section 4; Construction: Vol. 04.08; Soil and Rock (I).
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Section 4; Construction: Vol. 04.09; Soil and Rock (II).
Required Tools/Software/Skills:
None
SECTION II: Course Content and Timetable
Contribution of Course to Meeting the Professional Component:
Professional Component Credits
Mathematics and Basic Sciences 0
Engineering Topic 1
General Education 0
Course Structure:
Description
Lecture During the lab session
Laboratory 1 lab session -180 min per week
Medium all material explained in class and on the blackboard
Tests Midterm, 45 minutes, closed book
Final 60 minutes, closed book
Homework/Project Lab reports
Course Timetable
Week(s) Chapters/Topics/Coverage
Week #1 Introduction: Soil properties, water content determination,
representative soil samples, use of balances, safety, and reports writing.
Week # 2-3 Lecture + Experiment: Relative density determination and Particle size
analysis – mechanical method
Week #4 Lecture + Experiment: Sand equivalent test
Week # 5 Lecture + Experiment: Specific Gravity of Soil Solids
Week # 6 Lecture: Moisture- density relationship (Proctor), in-place soil density
and CBR
Week # 7- 8- 9 Experiment: Moisture- density relationship (Proctor), in-place soil
density and CBR
Week # 10 Lecture + Experiment: Atterberg limits
Week # 11-12 Lecture + Experiment: Hydrometer Analysis , Revision
Student Work Evaluation
These are called assessment methods whose purpose is to provide evidence of the level or
extent of learning. These methods are to be designed to measure stated Learning Outcomes
and must be consistent with the instructional approach or strategy.
Laboratory Reports: 40% (on weekly basis)
PowerPoint Presentation: 10% (October 21st )
Midterm: 20% (October 14th )
Final exam: 30% (TBA BY REGISTRAR)
SECTION III: Policies and Students’ Responsibilities
Academic rules and regulations are to be followed according to the policies and guidelines of
the University, as laid out in the Catalogue (particularly the sections on Attendance and
Academic Behavior).
The following are the Program Outcomes, which are adopted by the Civil Engineering
Program at UOB and are the same as ABET’s “Student Outcomes”, known as SO’s:
1. an ability to identify, formulate, and solve complex engineering problems by applying
principles of engineering, science, and mathematics
2. an ability to apply engineering design to produce solutions that meet specified needs
with consideration of public health, safety, and welfare, as well as global, cultural,
social, environmental, and economic factors
3. an ability to communicate effectively with a range of audiences
4. an ability to recognize ethical and professional responsibilities in engineering situations
and make informed judgments, which must consider the impact of engineering
solutions in global, economic, environmental, and societal contexts
5. an ability to function effectively on a team whose members together provide leadership,
create a collaborative and inclusive environment, establish goals, plan tasks, and meet
objectives
6. an ability to develop and conduct appropriate experimentation, analyze and interpret
data, and use engineering judgment to draw conclusions
7. an ability to acquire and apply new knowledge as needed, using appropriate learning
strategies
You might also like
- Course Pack Soil Laboratory ExperimentDocument124 pagesCourse Pack Soil Laboratory Experimentkrazeecoolguy100% (1)
- CIVE1129 Course Guide Part BDocument3 pagesCIVE1129 Course Guide Part BMike ChanNo ratings yet
- CE 485 Engineering Hydrology Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesCE 485 Engineering Hydrology Course SyllabusOvidiu Genteanu100% (1)
- CIV324 - Geotechnical EngineeringDocument5 pagesCIV324 - Geotechnical EngineeringALIKNFNo ratings yet
- Integrating Research To The Undergraduate Geotechnical Engineering Class-RoomDocument9 pagesIntegrating Research To The Undergraduate Geotechnical Engineering Class-RoomIzam FatimaNo ratings yet
- ENEN20002 Earth Processes For Engineering - 2017Document4 pagesENEN20002 Earth Processes For Engineering - 2017Dilshan JayasuriyaNo ratings yet
- Obe Syllabus HydrologyDocument9 pagesObe Syllabus HydrologyNeil Llacuna PagalaranNo ratings yet
- 1 CHEN401 - First Day Package - Prof. N.S. MainaDocument5 pages1 CHEN401 - First Day Package - Prof. N.S. Mainasaminumusa217No ratings yet
- Guidelines for Final Year Project & Log BookDocument48 pagesGuidelines for Final Year Project & Log BookChristyNo ratings yet
- Btech Acadcivil4Document23 pagesBtech Acadcivil4Tvc TejaNo ratings yet
- Tcs Chemistry Syllabus 2013 2014Document8 pagesTcs Chemistry Syllabus 2013 2014api-235625414No ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument7 pagesHydraulicsBernard PalmerNo ratings yet
- CEE 586 - Rock Mechanics & Behavior: Course SyllabusDocument3 pagesCEE 586 - Rock Mechanics & Behavior: Course Syllabusrivai sargawiNo ratings yet
- ES10 Syllabus 2nd Sem 11-12Document5 pagesES10 Syllabus 2nd Sem 11-12Marianne CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Intro 2020Document38 pagesLecture 1 Intro 2020Rahamim BattenNo ratings yet
- CHM12-3 Gen. Chem 2Document6 pagesCHM12-3 Gen. Chem 2Bien Carlo HaliliNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering Fundamentals SyllabusDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Engineering Fundamentals SyllabusparinjaniNo ratings yet
- Course Description: Syllabus, GLG362 Geomorphology Instructor: K. WhippleDocument7 pagesCourse Description: Syllabus, GLG362 Geomorphology Instructor: K. WhippleS Hashim RizviNo ratings yet
- AMME2261 2015 Semester 1 StudentDocument3 pagesAMME2261 2015 Semester 1 StudentqianjixinNo ratings yet
- MICR3071 Course Outline Summary S1 2012Document11 pagesMICR3071 Course Outline Summary S1 2012david_physiologyNo ratings yet
- 2013 Lab ManualDocument92 pages2013 Lab Manualaumi77No ratings yet
- National University of Engineering College of Geological, Mining and Metallurgical Engineering Metallurgical Engineering ProgramDocument3 pagesNational University of Engineering College of Geological, Mining and Metallurgical Engineering Metallurgical Engineering ProgramJhair JhamidhNo ratings yet
- Ce 442 Foundation Engineering II - Tedu s1617 - SyllabusDocument8 pagesCe 442 Foundation Engineering II - Tedu s1617 - SyllabusRex MayabangNo ratings yet
- SECTION I: Course Information and Learning Outcomes: Substantial EmphasisDocument4 pagesSECTION I: Course Information and Learning Outcomes: Substantial Emphasislaura sageNo ratings yet
- Syllabus CGN 4851 CCM Fall 2022Document6 pagesSyllabus CGN 4851 CCM Fall 2022Luis AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Marine Pollution Code: MR332: Theoretical: 2 Practical: 2Document3 pagesCourse Title: Marine Pollution Code: MR332: Theoretical: 2 Practical: 2mtarequeali5836No ratings yet
- Integrating Research To The Undergraduate Geotechnical Engineering Class-RoomDocument9 pagesIntegrating Research To The Undergraduate Geotechnical Engineering Class-Roomjohncruz32No ratings yet
- Chem 1 Subject-OutlineDocument10 pagesChem 1 Subject-OutlineFoo FuuNo ratings yet
- 3rd Year Eng - Outline PDFDocument7 pages3rd Year Eng - Outline PDFkingNo ratings yet
- MEC30Document4 pagesMEC30Christelle ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument4 pagesSyllabusRea AbuanNo ratings yet
- Course Outline CIV4112Document2 pagesCourse Outline CIV4112narutoNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Engineering 663: Formation Evaluation and The Analysis of Reservoir PerformanceDocument5 pagesPetroleum Engineering 663: Formation Evaluation and The Analysis of Reservoir PerformancemanningamanningaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements and Instrumentation KG ReddyDocument158 pagesElectrical Measurements and Instrumentation KG Reddyabhaymehta67No ratings yet
- 22ESC141 - SyllabusDocument4 pages22ESC141 - SyllabusW03 AKASHNo ratings yet
- Course Content CLOS Geotech I THDocument11 pagesCourse Content CLOS Geotech I THBilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- LM - Dr. Jitesh OzaDocument94 pagesLM - Dr. Jitesh OzaDakshraj RathodNo ratings yet
- CHBE370 Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesCHBE370 Course Syllabusjpcobucci58No ratings yet
- EHS 140 Introduction to Environmental SciencesDocument7 pagesEHS 140 Introduction to Environmental SciencesAndres AzanaNo ratings yet
- Ce 401Document2 pagesCe 401MæbēTh CuarterosNo ratings yet
- Analytical ChemistryDocument14 pagesAnalytical ChemistryHarrizul Rivai100% (1)
- GT Materials Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesGT Materials Course SyllabusXingjian LiuNo ratings yet
- GEM 2105 and 2105L Course Outlines As Recommended by UWI March 2016Document4 pagesGEM 2105 and 2105L Course Outlines As Recommended by UWI March 2016Callista StephenNo ratings yet
- CE 401 Course OrientationDocument16 pagesCE 401 Course OrientationMarjorie AbendañoNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering - Course Outline Cegb333Document6 pagesGeotechnical Engineering - Course Outline Cegb333MuhammadFarhanGulNo ratings yet
- CHNG2801 2014 Semester 1 StudentDocument4 pagesCHNG2801 2014 Semester 1 StudentRiley Murray RumingNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument4 pagesSyllabusIan HoldemanNo ratings yet
- Gopikrishna FileDocument99 pagesGopikrishna FileB. Tipraj CivilNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 5 Unit 2 Guide 2010Document268 pagesScience Grade 5 Unit 2 Guide 2010sasnewsNo ratings yet
- StudyGuide SGM 311_2024Document14 pagesStudyGuide SGM 311_2024tusopulaNo ratings yet
- 55-500314 Applied Thermodynamics and Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pages55-500314 Applied Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanicszinou68No ratings yet
- EVS Lab Course File BS162Document37 pagesEVS Lab Course File BS162gstarNo ratings yet
- ARC2043 Building Science CourseDocument5 pagesARC2043 Building Science Coursekulov1592No ratings yet
- Scientific Integrity and Ethics in the GeosciencesFrom EverandScientific Integrity and Ethics in the GeosciencesLinda C. GundersenNo ratings yet
- Designing with Geosynthetics - 6Th Edition Vol. 1From EverandDesigning with Geosynthetics - 6Th Edition Vol. 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Soil Improvement and Ground Modification MethodsFrom EverandSoil Improvement and Ground Modification MethodsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Geotechnical Interpretations in Field Practice: An IntroductionFrom EverandGeotechnical Interpretations in Field Practice: An IntroductionNo ratings yet
- Building Professionals Facing the Energy Efficiency ChallengeFrom EverandBuilding Professionals Facing the Energy Efficiency ChallengeNo ratings yet
- Microfluidics and Nanofluidics: Theory and Selected ApplicationsFrom EverandMicrofluidics and Nanofluidics: Theory and Selected ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Relative Density GR 1 ReportDocument8 pagesRelative Density GR 1 Reportjean paulNo ratings yet
- General Rules:: No Sandals!Document8 pagesGeneral Rules:: No Sandals!jean paulNo ratings yet
- CIVE306 - Soil Mechanics Laboratory: Experiment TitleDocument1 pageCIVE306 - Soil Mechanics Laboratory: Experiment Titlejean paulNo ratings yet
- Calcium chloride soil test procedureDocument2 pagesCalcium chloride soil test procedurejean paulNo ratings yet
- Tentative Schedule CIVE306 Fall21-22Document2 pagesTentative Schedule CIVE306 Fall21-22jean paulNo ratings yet
- CIVE306-report 1 - Specific Gravity-Group1Document4 pagesCIVE306-report 1 - Specific Gravity-Group1jean paulNo ratings yet
- CIVE306 - Sieve Analysis-Report2 - GROUP 1Document6 pagesCIVE306 - Sieve Analysis-Report2 - GROUP 1jean paulNo ratings yet
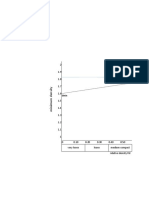
- 2 1.9 D Field 1.8 1.7 1.6 Dmin 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 1.1 1 0 0.10 0.20 0.30 0.40 0.50 Very Loose Loose Medium Compact Relative Density RDDocument2 pages2 1.9 D Field 1.8 1.7 1.6 Dmin 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 1.1 1 0 0.10 0.20 0.30 0.40 0.50 Very Loose Loose Medium Compact Relative Density RDjean paulNo ratings yet
- Experiment Report: Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument4 pagesExperiment Report: Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Departmentjean paulNo ratings yet
- Oshas Technical Maual Part 1Document317 pagesOshas Technical Maual Part 1koteshwararaoNo ratings yet
- Assessing rock rippability using specific energy and production rateDocument9 pagesAssessing rock rippability using specific energy and production rateelson siraitNo ratings yet
- Draft CHED - MARINA OB Monitoring InstrumentDocument15 pagesDraft CHED - MARINA OB Monitoring InstrumentRobert M. MaluyaNo ratings yet
- 730C-725C T4F SVC ITTP M02 MonSys EN INSDocument20 pages730C-725C T4F SVC ITTP M02 MonSys EN INScesarcaterpillar100% (1)
- 2018 Assessment Tool BSFDocument24 pages2018 Assessment Tool BSFRugay LaboratoryNo ratings yet
- COT1 Science5 Lesson Plan 2021Document11 pagesCOT1 Science5 Lesson Plan 2021jimsonNo ratings yet
- FMLA-Automation Improves Lab Productivity 185Document31 pagesFMLA-Automation Improves Lab Productivity 185Jean-paul SusiniNo ratings yet
- Lab Report FormatDocument1 pageLab Report Formatapi-260702228No ratings yet
- ASTM C1077 (English) PDFDocument9 pagesASTM C1077 (English) PDFfabiomorales100% (1)
- T6 Course Specifications 10-6-2017Document7 pagesT6 Course Specifications 10-6-2017Khalid M. HafezNo ratings yet
- California Test 504 Method for Determining Air Content of Fresh ConcreteDocument3 pagesCalifornia Test 504 Method for Determining Air Content of Fresh ConcretePritha DasNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Physics Class 12 Cbse PDFDocument2 pagesLab Manual Physics Class 12 Cbse PDFDev Printing SolutionNo ratings yet
- 2 Assessment of In-Place Cleanability 2004 - Updated 07Document17 pages2 Assessment of In-Place Cleanability 2004 - Updated 07Mtto y Proyecto VerterquimNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Design & Construction Guidelines: Environmental Health & Safety Research Safety BureauDocument12 pagesLaboratory Design & Construction Guidelines: Environmental Health & Safety Research Safety BureauAli RizviNo ratings yet
- Chem 120.1 Lab Sheet (Exercise No. 1)Document2 pagesChem 120.1 Lab Sheet (Exercise No. 1)Giema OrocNo ratings yet
- Melbourne Quality Procedure ManualDocument61 pagesMelbourne Quality Procedure Manualsurangaguna100% (1)
- Floor Plan of LaboratoryDocument5 pagesFloor Plan of LaboratoryNorhida PantaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 SummaryDocument6 pagesChapter 17 Summaryapi-550249882No ratings yet
- Procedure For Processing The Proposal For Utilization of Hazardous Waste Under Rule 9, of HWM Rules 2016Document9 pagesProcedure For Processing The Proposal For Utilization of Hazardous Waste Under Rule 9, of HWM Rules 2016LoveinderNo ratings yet
- Lab - Report - PPT 2Document12 pagesLab - Report - PPT 2WaterNo ratings yet
- Heraguard ECO Clean Bench BrochureDocument8 pagesHeraguard ECO Clean Bench BrochureDivisión Laboratorio INo ratings yet
- ORA LAB Manual-TocDocument2 pagesORA LAB Manual-TocSougata PramanickNo ratings yet
- ETHOS EASY-brochureDocument8 pagesETHOS EASY-brochureMichael MichaelidesNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance Program PlanDocument128 pagesQuality Assurance Program PlanVictor50% (2)
- Bilogia Laboratorios Compressed 1 40Document40 pagesBilogia Laboratorios Compressed 1 40kevin oliverosNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual-Aircon System-Level 2-TrendlineDocument2 pagesLab Manual-Aircon System-Level 2-TrendlinetashaNo ratings yet
- Management: Chapter 1: Introduction To Laboratory ManagementDocument9 pagesManagement: Chapter 1: Introduction To Laboratory ManagementREGINE COELI LANSANGANNo ratings yet
- Wajid NewDocument2 pagesWajid Newwajidalikhan822No ratings yet
- Dental Lab Site Inspection ChecklistDocument2 pagesDental Lab Site Inspection ChecklistRAZNAS ASLAM A K100% (1)
- Cven 342 Lab Manual - Msf-Rev-2014Document117 pagesCven 342 Lab Manual - Msf-Rev-2014Nathan MillerNo ratings yet