Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Business Finance: Final
Uploaded by
BryanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Business Finance: Final
Uploaded by
BryanCopyright:
Available Formats
BUSINESS FINANCE
FINAL
MODULE 2
Ms. CHRYSANTHEMUM B. DURO
Self-Learning Module Business Finance
Final - Module 2 Page 1 of 8
Module
2 Types of Financial
Statements
I. Curriculum Standards:
Content Standards The learners the financial planning process, including budget
preparation, cash management, and working capital management.
Performance The learners are able to
Standards 1. illustrate the financial planning process
2. prepare budgets such as projected collection, sales budget,
production budget, income projected statement of
comprehensive income, projected of financial position, and
projected cash flow statement
3. describe concepts and tools in working capital management
Learning The learner:
Competencies 1. define the measurement levels, namely, liquidity, solvency,
stability, and profitability: ABM_BF12-IIIb-7;
2. perform vertical and horizontal analyses of financial
statements of a single proprietorship: ABM_BF12-IIIb-8;
3. compute, analyze, and interpret financial ratios such as
current ratio, working capital, gross profit ratio, net profit
ratio, receivable turnover, inventory turnover, debtto- equity
ratio, and the like: ABM_BF12-IIIb-9
Damean’s Beat and Competent Professionals, Critical Thinking Skills and Career and
Related Values Learning Self-Reliance
Time Frame 4 days
II. Learning Objectives:
At the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
1. discuss the different types of financial statements;
2. determine how each type are presented;
3. identify which financial statement is more important for investors;
III. Resources:
a. Materials:
Module, Answer Sheet, Laptop, Powerpoint, Laptop
b. References:
Aduana, N. L. (2017) Business Finance in the Philippine Setting .C&E Publishing.
Quezon City., Pp. 54 – 75
Medina, R. G. (2007) Business Finance. Rex Book Store, Inc., Sampaloc,
Manila., Pp. 113 – 120
Self-Learning Module Business Finance
Final - Module 2 Page 2 of 8
IV. Lesson Proper:
INTRODUCTION
This module will discuss the relationship between finance and accounting and dealt with
how financial statements help the financial accountant, managerial accountant, and finance
manager in their decision-making to guide the business toward its goal attainment. Financial
statements are tools that managers use to help them in their decision-making considering
financial implications.
The decision to increase the salary of employees has financial implications because it
requires financing or funding in the long run. The decision to purchase land or any other asset
imp the need for financing. The decision to grant overtime to employees also requires funding.
The decision to increase sales will increase revenue but will also require increased funding for
purchases or manufacturing. The decision to borrow money from a bank will provide funding, but
will involve interest cost. The decision to sell some of the unused or idle machinery will be a source
of funds. The decision whether to lease or to buy has financial implications as well and can affect
profitability and wealth maximization.
Financial statements are the key source of information for most financial decision-making
purposes. For these reasons, the information contained in the financial statements is of utmost
importance to financial officers.
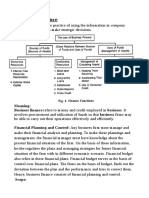
Statement of Financial Position
Statement of Financial Position is a structured financial statement that shows the assets,
liabilities, and equity of a business entity as of a given date
“as of a given date” indicates that the statement of financial position can be prepared
anytime of the year. The assets, liabilities, and equity are the three accounting elements found in
the statement of financial position. These elements are directly related to the measurement of
financial position.
Assets are resources controlled by the entity as a result of past events and from which future
economic benefits are expected to flow to the entity.
Liabilities are present obligations of the entity arising from past events, the settlement of which is
expected to result in an outflow from the entity of resources embodying economic benefits
Equity is the residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting all its liabilities.
The financial position of a business entity is usually expressed in terms of its liquidity, solvency,
financial structure, and capacity for adaptation.
Liquidity refers to the ability of a business entity to settle its currently maturing financial obligations.
Obligations are currently maturing if they become due within one year from the date of the
statement of financial position notwithstanding the normal operating cycle of a business.
Solvency is the ability of a business to pay its long-term financial obligations. Financial obligations
are classified long-term if they mature beyond one year from the date of the statement of financial
position.
Financial structure indicates the amount of capital or resources financed by creditors and the
amount provided by owners. The analysis of the financial structure of the business focuses on the
right side of the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Capital).
ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNER`S EQUITY
Self-Learning Module Business Finance
Final - Module 2 Page 3 of 8
Capacity for adaptation refers to the ability of a business to invest excess available resources or
raise needed funds through borrowings without difficulty in times of need. When the business has
a very high capacity for adaptation, it can easily find funding sources when the need arises.
STATEMENT COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
The statement of comprehensive income (new title for income statement) is a structured
financial statement that shows the financial performance of a business entity for a given period.
The term "period" indicates that the statement covers a month, a quarter, six months, or a
year. The accounting elements comprising the statement of comprehensive income are the
following:
a. Income is the summary of increases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the
form of inflows or enhancement of assets or decreases of liabilities that result in increases in equity
other than those relating to contributions from equity participants.
b. Expenses are decreases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of
outflows or depletion of assets or incurrences of liabilities that result in decreases in equity, other
than those relating to distribution to equity participants.
The definitions of income and expenses identify their essential features but do not attempt
to satisfy the criteria that needed to be met before they are recognized in the income statement.
Thus, the item of income and expense is included in the statement of comprehensive income if it
meets the criteria for recognition. Profit is frequently used as a measure of performance or the
basis of other measures such as determination of return on investment (ROI) or earnings per share
(EPS).
Income and expenses may be presented in the statement of comprehensive income in
different ways in order to provide information relevant to economic decision-making. For example,
it is a common practice to distinguish between items of income and expenses arising from the
ordinary course of the business of the entity and those that do not.
Self-Learning Module Business Finance
Final - Module 2 Page 4 of 8
STATEMENT OF CHANGES EQUITY
The statement of changes in owners' equity details the changes that occurred in the owner(s)'
equity. It shows the beginning owner(s)' equity with additional investments for a sole proprietorship
or partnership or, for a corporation, additional issues of corporate stock. Also, it shows the
withdrawals made by a sole proprietor or partner(s) or declaration of dividends of a corporation. It
shows profit for the sole proprietorship or partnership or changes in the retained earnings account
if a separate statement of retained earnings is not made.
The statement of changes in equity is a financial statement showing the following:
a. net income or loss for the period
b. each item of income and expense for the period that is recognized directly in equity and the total
of these as required by the Standards
c. total income and expense for the period showing separately the total amounts attributable
to equity holders of the parent company and to minority interest in a corporation
d. for each component of equity, the effect of changes in accounting policies and corrections of
errors
The statement of changes in equity, stated otherwise, is a statement that reflects all the elements
that caused changes in an entity's equity between two dates of the statement of financial position.
Share capital represents funds contributed by shareholders. An entity's shares capital may be in
the form of ordinary shares capital or preference shares capital. Shareholders holding ordinary
shares capital have the same rights and privileges and enjoy no preference over each other.
However, shareholders holding preference shares capital have preference over ordinary
shareholders on the dividends and net assets of an entity in the event of liquidation.
Retained earnings is a line item in the equity that represents the accumulated amount of net
income or loss, errors of prior periods, dividends distributions, changes in accounting policy, and
other equity adjustments other than those arising from contributions from shareholders.
Reserves are a line-item in the equity section that includes the following:
Self-Learning Module Business Finance
Final - Module 2 Page 5 of 8
1. appropriation reserve
2. share premium
3. revaluation adjustment
4. foreign currency translation reserve
Appropriation reserve is the appropriation reserve is a transfer of an amount from the retained
earnings. The creation of reserves may be required by law in order to give the entity and its creditors
an added measure of protection from the effects of losses, voluntary action of the management, or
contractual obligations.
Share premium represents the excess amount contributed by the shareholders over the par value.
The par value is the minimum issue price of the shares appearing in the certificate of stock.
The revaluation adjustment represents the excess of the depreciated replacement cost or sound
value of the revalued property, plant, and equipment over the book value. There will be a
revaluation adjustment only when the entity adopts the revaluation model of measuring the
property, plant, and equipment after initial recognition. The fair values or revalued values less any
subsequent depreciation and subsequent impairment losses are not equal to the net book value of
the assets.
STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
The statement of cash flows is a financial statement that provides information about the historical
change-inflows and outflows-in cash and cash equivalents of an entity during the period from
operating, investing, and financing activities.
Cash comprises cash on hand and demand deposits.
Cash equivalents are short-term, highly liquid investments that are readily convertible into known
amounts of cash near their maturity that they present insignificant risk of changes in value or
interest rates.
Operating activities are the principal revenue-producing activities of the entity and other activities
that are neither investing nor financing. Operating activities are all operation-related earning
activities of the company-rendering service for a service firm, selling goods for a trading concern,
and manufacturing and selling activities for a manufacturing company. They include the income
and expense items found in the income statement and all other activities of the enterprise related
to extension of credit to customers, investment in inventories, obtaining credit from suppliers. They
are concerned with the working capital accounts (current assets and current liabilities).
Self-Learning Module Business Finance
Final - Module 2 Page 6 of 8
Investing activities are the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets and other investments
not included in cash equivalents.
Financing activities are activities that result in changes in the size and composition of the
contributed equity and liabilities of the entity. It involves obtaining resources from owners
(issuances of capital stock) and paying them dividends as their share in the profit of the company.
They also include obtaining resources from creditors and repaying the amounts borrowed.
Information about the cash flows of an entity is useful in providing users of financial statements
with a basis to assess the ability of the entity to generate cash and cash equivalents and the needs
of the entity to utilize those cash flows. The economic decisions made by users require an
evaluation of the ability of an entity to generate cash and cash equivalents and the timing and
certainty of their generation. The statement of cash flow, therefore, is a mere accounting of the
cash flows of a business entity. Cash flows are inflows and outflows of cash and cash equivalents.
Activity 1: Let`s Check Your Understanding
True or False. Write TRUE if the statement is correct and write FALSE if wrong.
1. Assets are resources controlled by the entity as a result of future events and from
which the entity expects future economic benefits.
2. Non-current assets include only tangible financial assets that are considered
permanent or long-term in nature.
3. Funds contributed by shareholders are called share capital.
.
4. The statement of financial position is a structured financial statement that
shows the assets, liabilities, equity, revenues and expenses of a business
entity.
5. A statement of cash flows is useful in providing users information about the
ability of the entity to generate and utilize cash and cash equivalents.
Self-Learning Module Business Finance
Final - Module 2 Page 7 of 8
Activity 2: Identification
Identify the statements below.
1. The ability of a business to pay its long-term financial obligations.
2. The key source of information for most financial decision-making purposes.
3. Is frequently used as a measure of performance or the basis of other measures such as
determination of return on investment.
4. Indicates the amount of capital or resources financed by creditors and the amount provided by
owners.
5. It shows the net income or loss for the period.
Activity 3: ESSAY…
Essay. Answer the question in not less than 5 sentences. 10 points.
This is the criteria:
Content(Relevant, focused and thorough explanation): 6 pts
Organization (Logical sequencing, effective transition): 2 pts
Conventions (Spelling and Grammar): 2 pt
10 pts
Which financial statement is most important to investors? Why?
Self-Learning Module Business Finance
Final - Module 2 Page 8 of 8
You might also like
- 03 BSAIS 2 Financial Management Week 5 6Document8 pages03 BSAIS 2 Financial Management Week 5 6Ace San GabrielNo ratings yet
- Course Financial Management Developer and Their Background: See Assignment / Agreement SectionDocument33 pagesCourse Financial Management Developer and Their Background: See Assignment / Agreement SectionHazel Jane Esclamada100% (1)
- Module 3 Conceptual Frameworks and Accounting StandardsDocument10 pagesModule 3 Conceptual Frameworks and Accounting StandardsJonabelle DalesNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document11 pagesModule 1Karelle MalasagaNo ratings yet
- Final AccountsDocument91 pagesFinal AccountsKartikey swami0% (1)
- 03 BSIS 2 Financial Management Week 5 6Document5 pages03 BSIS 2 Financial Management Week 5 6Ace San GabrielNo ratings yet
- Actg 4 PDFDocument13 pagesActg 4 PDFHo Ming LamNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Pre - Test and Lesson 1Document29 pagesBusiness Finance Pre - Test and Lesson 1Iekzkad RealvillaNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Final PrintDocument61 pagesCash Flow Final PrintGeddada DineshNo ratings yet
- G 12 Fabm 2 Q1 G. BruanDocument33 pagesG 12 Fabm 2 Q1 G. BruanDark SideNo ratings yet
- Week 10 (Learning Materials)Document8 pagesWeek 10 (Learning Materials)CHOI HunterNo ratings yet
- Unit - 10 Financial Statements and Ratio AnalysisDocument18 pagesUnit - 10 Financial Statements and Ratio AnalysisAayushi Kothari100% (1)
- MB0045 - Mba 2 SemDocument19 pagesMB0045 - Mba 2 SemacorneleoNo ratings yet
- Prelim ModuleDocument5 pagesPrelim ModuleJenefer GwmpesawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 (FSA)Document3 pagesChapter 01 (FSA)Prasenjit SahaNo ratings yet
- (Chapter 4) Advance (Chapter 5) Working Capital Chapter 1: Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument92 pages(Chapter 4) Advance (Chapter 5) Working Capital Chapter 1: Introduction To Financial ManagementYukiNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Business ManagementDocument5 pagesAgricultural Business ManagementAreicra NutNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document45 pagesModule 2Lucksnie LoveNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finl Statement AnalysisDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Finl Statement AnalysisMD Kawser Hamid RonyNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Management of Pepsi CoDocument93 pagesWorking Capital Management of Pepsi CoNawin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I 1.1 Introduction To The StudyDocument91 pagesChapter - I 1.1 Introduction To The StudyNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Business Finance Planning and Working CapitalDocument9 pagesGrade 12 Business Finance Planning and Working CapitalJade MonteverosNo ratings yet
- Bookkeeping LessonDocument81 pagesBookkeeping LessonKriziel ReyesNo ratings yet
- DM102 WK1 13Document68 pagesDM102 WK1 13Licht ZoraNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6Document26 pagesWorksheet 6Akshat JainNo ratings yet
- Readings - Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument35 pagesReadings - Introduction To Financial ManagementAnish AdhikariNo ratings yet
- K.S.Rangasamy College of Arts and (Autonomous)Document56 pagesK.S.Rangasamy College of Arts and (Autonomous)RidikSakthiNo ratings yet
- B215 AC01 - Numbers and Words - 6th Presentation - 17apr2009Document23 pagesB215 AC01 - Numbers and Words - 6th Presentation - 17apr2009tohqinzhiNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document8 pagesWeek 2Shanley Vanna EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Vijaya Bank performanceDocument60 pagesVijaya Bank performancesingrahul52No ratings yet
- Financial Accounting, 7e by Pfeiffer, Hanlon, Magee 2023, Solution Manual Chapter 1Document25 pagesFinancial Accounting, 7e by Pfeiffer, Hanlon, Magee 2023, Solution Manual Chapter 1Test bank WorldNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance of Bharathi FabricatorsDocument50 pagesFinancial Performance of Bharathi FabricatorsRanjith PNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Financial AnalysisDocument13 pagesChapter 9 - Financial AnalysisNicole Feliz InfanteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 3 SummaryDarlianne Klyne BayerNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Financial StatementsDocument15 pages1.1 Financial StatementsSandeep DhupalNo ratings yet
- 1financial ManagementDocument10 pages1financial ManagementwilliamNo ratings yet
- FM 8 Module 1 Financial Planning and ForecastingDocument16 pagesFM 8 Module 1 Financial Planning and ForecastingJasper Mortos VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Financial Statements (Cabrera & Cabrera, 2017)Document10 pagesLesson 1. Financial Statements (Cabrera & Cabrera, 2017)Axel MendozaNo ratings yet
- "Financial Statment Analysis": Dessrtion Report OnDocument51 pages"Financial Statment Analysis": Dessrtion Report Onpunny27100% (1)
- Modules For Online Learning Management System: Computer Communication Development InstituteDocument26 pagesModules For Online Learning Management System: Computer Communication Development InstituteAngeline AsejoNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Introduction To FSA 2023Document3 pagesLec 3 Introduction To FSA 2023Khadeeza ShammeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 An Overview of Financial AnalysisDocument14 pagesChapter-2 An Overview of Financial AnalysisfahadNo ratings yet
- W3 Module 5 Conceptual Framework Andtheoretical Structure of Financial Accounting and Reporting Part 3Document6 pagesW3 Module 5 Conceptual Framework Andtheoretical Structure of Financial Accounting and Reporting Part 3leare ruazaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Financial Management FunctionsDocument29 pagesUnderstanding Financial Management Functionsa NaniNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis1Document100 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis1chaluvadiinNo ratings yet
- Financial Performance of Kerala Gramin Bank Special Reference To Southern AreaDocument81 pagesFinancial Performance of Kerala Gramin Bank Special Reference To Southern AreaPriyanka Ramath100% (1)
- Business Finance Lesson 3Document34 pagesBusiness Finance Lesson 3Iekzkad RealvillaNo ratings yet
- Michelle Hanlon - Robert Magee - Glenn Pfeiffer - Thomas Dyckman - Financial Accounting Solutions Manual (2019)Document525 pagesMichelle Hanlon - Robert Magee - Glenn Pfeiffer - Thomas Dyckman - Financial Accounting Solutions Manual (2019)JackieNo ratings yet
- A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF SELECT AUTOMOBILE INDUSTRIES IN INDIA" (Four Wheelers)Document100 pagesA COMPARATIVE STUDY ON FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF SELECT AUTOMOBILE INDUSTRIES IN INDIA" (Four Wheelers)Prashanth PB82% (17)
- Financial Management Notes PDFDocument68 pagesFinancial Management Notes PDFtirumala ReddyNo ratings yet
- Conceptual FrameworkDocument5 pagesConceptual FrameworkElla CunananNo ratings yet
- Edited Acc and Fin FinalDocument16 pagesEdited Acc and Fin FinalTutornjckNo ratings yet
- Project 3Document115 pagesProject 3Sophia BernardNo ratings yet
- Finance For Non Financial Managers 7th Edition Bergeron Solutions ManualDocument9 pagesFinance For Non Financial Managers 7th Edition Bergeron Solutions ManualAzaliaSanchezNo ratings yet
- FM 1Document7 pagesFM 1Rohini rs nairNo ratings yet
- Module 12 - Financial Statement AnalysisDocument33 pagesModule 12 - Financial Statement AnalysisGRACE ANN BERGONIONo ratings yet
- Aee Unit-3Document55 pagesAee Unit-3downloaderNo ratings yet
- Confidential NotesDocument35 pagesConfidential Noteskamaljit kaushikNo ratings yet
- Financial Stements Analysis-2Document30 pagesFinancial Stements Analysis-2Mega capitalmarketNo ratings yet
- Chapter VDocument1 pageChapter VBryanNo ratings yet
- Chapter I (ENG)Document3 pagesChapter I (ENG)BryanNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument1 pageIntroductionBryanNo ratings yet
- A Batang Walang Pananaw sa Buhay na Nabuhay UlitDocument1 pageA Batang Walang Pananaw sa Buhay na Nabuhay UlitBryanNo ratings yet
- Bio DataDocument1 pageBio DataBryanNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: FinalDocument7 pagesBusiness Finance: FinalBryanNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: FinalDocument8 pagesBusiness Finance: FinalBryanNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: FinalDocument7 pagesBusiness Finance: FinalBryanNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship: Understanding the 4MsDocument6 pagesEntrepreneurship: Understanding the 4MsBryanNo ratings yet
- Research AssignmentDocument1 pageResearch AssignmentBryanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2: FinalDocument8 pagesFundamentals of Accountancy, Business and Management 2: FinalBryanNo ratings yet
- Fabm2 Final M2Document8 pagesFabm2 Final M2BryanNo ratings yet
- Oatey2021 CommercialCat LCS1146B 022421 WEB LR 1Document204 pagesOatey2021 CommercialCat LCS1146B 022421 WEB LR 1Pablo CINo ratings yet
- MB1 - The Australian Economy PA 7092016Document8 pagesMB1 - The Australian Economy PA 7092016ninja980117No ratings yet
- Abdulbasit MohammedDocument170 pagesAbdulbasit MohammedGooftilaaAniJiraachuunkooYesusiinNo ratings yet
- MR Khurram Chakwal 6kw Hybrid - 024627Document6 pagesMR Khurram Chakwal 6kw Hybrid - 024627Shahid HussainNo ratings yet
- Osg VS Ayala LandDocument17 pagesOsg VS Ayala LandJan BeulahNo ratings yet
- Day 1 What Is Phased Array How Phased Array Works? Beam Forming Beam Focusing Beam Streeing Sectorial Scan and Linear ScanDocument64 pagesDay 1 What Is Phased Array How Phased Array Works? Beam Forming Beam Focusing Beam Streeing Sectorial Scan and Linear ScanvibinkumarsNo ratings yet
- Compound Sentences FANBOYS WorksheetDocument7 pagesCompound Sentences FANBOYS WorksheetVerenice SuarezNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Assignment SolutionsDocument2 pagesWeek 2 - Assignment SolutionsSanyamNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Plant For The New MillenniumDocument21 pagesHydrogen Plant For The New Millenniumapi-3799861100% (2)
- Mayne Pharma Annual Report 2012Document78 pagesMayne Pharma Annual Report 2012Deepa DevanathanNo ratings yet
- Robotic Surgery History and SystemsDocument28 pagesRobotic Surgery History and SystemsLidhi DileepNo ratings yet
- D20 Q12Document7 pagesD20 Q12Luca PitocchiNo ratings yet
- 452-Chapter 15 PDFDocument14 pages452-Chapter 15 PDFYoan Barriga BerriosNo ratings yet
- Solenoid Valves 2/2 210: Pilot Operated FL Oating Diaphragm 3/8 To 2Document4 pagesSolenoid Valves 2/2 210: Pilot Operated FL Oating Diaphragm 3/8 To 2AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Manual Micro DNC 2dDocument31 pagesManual Micro DNC 2dDiego GarciaNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior and Marketing Plan ComponentsDocument6 pagesFactors Influencing Consumer Behavior and Marketing Plan ComponentsK59 Ng� V? Minh Th?No ratings yet
- F404-15 Standard Consumer Safety Specification For High ChairsDocument19 pagesF404-15 Standard Consumer Safety Specification For High ChairsAhmed AlzubaidiNo ratings yet
- Routine Pile Load Test-Ga-13.04.2021Document1 pageRoutine Pile Load Test-Ga-13.04.2021Digambar JadhavNo ratings yet
- The Role of Business in Social and Economic Development Chapter 1Document18 pagesThe Role of Business in Social and Economic Development Chapter 1Emil EscasinasNo ratings yet
- HOUSEKEEPING SESSION PLANDocument2 pagesHOUSEKEEPING SESSION PLANScarlette Beauty Enriquez100% (1)
- Baja2018 Unisa Team3 Design ReportDocument23 pagesBaja2018 Unisa Team3 Design ReportDaniel MabengoNo ratings yet
- Osha CFR 1910Document16 pagesOsha CFR 1910CI Amilcar100% (3)
- Tender Status Report Delhi-Mumbai Expressway 10.01.19Document66 pagesTender Status Report Delhi-Mumbai Expressway 10.01.19chtrp100% (2)
- Industry Standard: What Are The Benefits For You?Document4 pagesIndustry Standard: What Are The Benefits For You?Zarnimyomyint MyintNo ratings yet
- Document - University Admission SystemDocument100 pagesDocument - University Admission SystemNaresh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Execution and Documentation Requirements For Life Cycle Cost AnalysesDocument20 pagesExecution and Documentation Requirements For Life Cycle Cost AnalysessmetNo ratings yet
- TM 9-1651 Data Transmission System m3, January 1942Document78 pagesTM 9-1651 Data Transmission System m3, January 1942Advocate100% (1)
- Contractor DatabaseDocument10 pagesContractor DatabaseVishal SaxenaNo ratings yet
- mPassBook 161022 150423 2918Document4 pagesmPassBook 161022 150423 2918Ashish kumarNo ratings yet
- Ict OhsDocument26 pagesIct Ohscloyd mark cabusogNo ratings yet