Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Subjective: Long Term: Independent:: Iloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing
Uploaded by
Abie Jean Balbontin100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views5 pagesAcute Pancreatitis - nursing care plan
Original Title
acute pancreatitis- ncp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAcute Pancreatitis - nursing care plan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views5 pagesSubjective: Long Term: Independent:: Iloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing
Uploaded by
Abie Jean BalbontinAcute Pancreatitis - nursing care plan
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
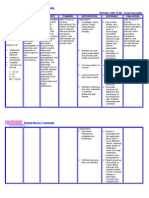
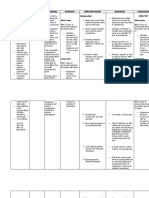
ILOILO DOCTORS’ COLLEGE
COLLEGE OF NURSING
West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo City
NURSING CARE PLAN
Defining Characteristics Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Identification Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Acute pain and Long Term: Independent: The goal is met after 5
Subjective: discomfort related to After 5 days of nursing Establish rapport. To gain patient trust and days of nursing
‘’ I am having a sudden inflammatory process intervention, patient will cooperation with the intervention the patient
onset of abdominal pain’’ of the pancreas no longer manifest patient and family. will verbalized relieved of
as verbalized by the patient. possible evidence by abdominal pain; Monitor and record VS. To have a baseline data for pain and comfort;
persisted pain that demonstrate use of planning and intervention. demonstrate used of
radiates at the back; relaxation techniques; Assess level of pain, noting To identify level of pain. methods that provide
tender in the follow prescribed specific location and intensity. relief.
epigastruim with pharmacological Promote position of comfort To promote
Objective: rebound tenderness measures. nonpharmacological pain
regimen.
Persisted pain that and a pain scale of management.
radiates at her back 9/10. Encourage adequate rest
Vomiting periods. To prevent fatigue.
Distress Short Term:
Anxious After 8 hours of nursing
Maintain fluid and electrolyte To assess fluid and
Rationale: intervention, the patient
Cyanotic balance. electrolyte status ( e.g.
Acute pain is caused will report pain relieved/
Pain scale ( 9/10) skin turgor, mucous
by edematous controlled; decrease
V/S taken as follows: pain using a scale of
membranes, intake and
distention of the output ). .
BP= 130/80 3/10.
pancreatic capsule,
HR= 115 bpm
local peritonitis
RR= 23/ min Maintain bed rest during acute Decreases metabolic rate
resulting from
Temp = 38.6 Celsius attack. Provide quiet, restful and GI stimulation and
enzyme release into
( fever) environment. secretions, thereby
the peritoneum,
Physical Exam reducing pancreatic
ductal spasm,or
( Abdomen)= Tender in activity.
pancreatic auto
the epigastruim with
digestion stimulated
rebound tenderness, Provide alternative comfort To promotes relaxation
by increased enzyme
reduced bowel sound measures (back rub), encourage and enables patient to
secretion when
Lab Results eating.
relaxation techniques. refocus attention; may
Wbc – 13.0 x/ ul ( inc.) enhance coping.
Note: Nursing
Platelets – 235/ul( dec.) Diagnosis Should be
Albumin 1.5 g/dl (dec.) base from (NANDA)
Protein -3.15 g/dl (dec.) Nursing Diagnosis
LDH – 486.7 u/l (inc.) Promote position of comfort on Reduces abdominal
Glucose – 123 mg/dl one side with knees flexed, pressure and tension,
(inc.) sitting up and leaning forward. providing some measure of
Neutrophils- 25% (dec.) ( semi- fowler’s position). comfort and pain relief.
Lymphocytes – 45 %
(inc.)
ALT – 48 IU/L (inc.)
AST- 93 IU/L ( inc.)
Serum lipase – 369
IU/L (inc.) Dependent: Tramadol is an effective
Serum creatinine – 5.1 Administer prescribed agent in the management
mg/dL ( inc.) medications, which may include of pain in acute
CT Scan - showed fat analgesics like Tramadol 100 pancreatitis. Tramadol is
stranding in the mg Q6H as PRN. used to relieve moderate to
pancreatic head moderately severe pain.
consisted of pancreatitis
and reactive thickening Patient should be kept
in the duodenum. Withhold food and fluid as NPO status until pain and
Ultrasound – gross indicated. nausea subside to limit or
ascites with echogenic reduce release of
fluid, increased pancreatic enzymes and
echotexture of liver, resultant pain.
obscured pancreas,
Grade 1 renal
parenchymal disease.
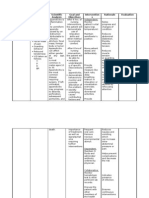
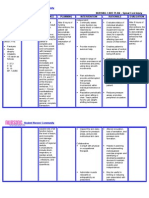
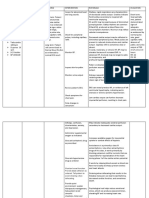
ILOILO DOCTORS’ COLLEGE
COLLEGE OF NURSING
West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo City
NURSING CARE PLAN
Defining Characteristics Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Identification Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Long Term: Independent: The goal is met after
Subjective: Imbalanced nutrition After 5days of nursing Establish rapport. To gain patient trust and nursing intervention
‘’I am having an less than body intervention, the patient cooperation with the patient and the patient have
abdominal pain and I have requirement maybe will demonstrate behaviors, family. displayed
no appetite’’ as verbalized related to loss of lifestyle change to regain Assess level of pain, noting To identify level of pain. normalization of
by the patient. digestive enzymes and maintain an specific location and intensity. laboratory values and
and insulin (related to appropriate weight. have demonstrated
pancreatic outflow Weight the pt. daily and A record of the pt. weight will behaviors, lifestyle
obstruction or document readings. help assess the progress of changes to regain and
necrosis/ auto treatment. maintain an
Objective: digestion) possible Maintain fluid and electrolyte appropriate weight.
Persisted pain that evidence by balance. To assess fluid and electrolyte
radiates at her back vomiting. status ( e.g. skin turgor, mucous
Vomiting Assess abdomen, noting membranes, intake and output ).
Distress Rationale: presence and character of Gastric distention and intestinal
Anxious Nutritional imbalance Short Term: bowel sounds, abdominal atony are frequently present,
Cyanotic occurs when there is After 8 hour of nursing distention and reports of resulting in reduced and absent
Pain scale ( 9/10) an abnormal level in intervention, the patient nausea. bowel sounds.
certain nutrients will display normalization
V/S taken as Review laboratory values that
caused by shortage or of laboratory values. indicate well- being or Laboratory test play a significant
follows:
excess in supply. deterioration. part in determining the patient
BP= 130/80
HR= 115 bpm nutritional status. An abnormal
RR= 23/ min Provide frequent oral care. value in a single diagnostic
Note: Nursing study may have may possible
Temp = 38.6 Celsius
Diagnosis Should be causes.
( fever)
base from (NANDA)
Wt. 80kilos To decrease vomiting stimulus
Nursing Diagnosis
Physical Exam Maintain NPO status and and inflammation and irritation
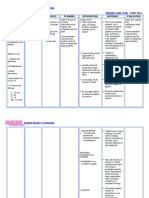
( Abdomen)= Tender gastric suctioning in acute of dry mucous membranes
in the epigastruim with phase. associated with dehydration.
rebound tenderness, Resume oral intake with clear To prevents stimulation and
reduced bowel sound liquids and advance diet release of pancreatic enzymes
Lab Results slowly to provide high-protein, (secretin).
Wbc – 13.0 x/ ul high-carbohydrate diet, when
( inc.) indicated. Oral feedings given too early in
Platelets – the course of illness may
235/ul( dec.) exacerbate symptoms. Loss of
Albumin 1.5 g/dl Dependent: pancreatic function and reduced
(dec.) Administer prescribed insulin production may require
Protein -3.15 g/dl medications such as antiemetics initiation of a diabetic diet.
(dec.) drugs ( Metoclopramide 10mg
LDH – 486.7 u/l (inc.) IV Q8hr.)
Glucose – 123 mg/dl
(inc.) Provide insulin as appropriate. To decrease nausea and
Neutrophils- 25% vomiting.Decreased symptoms
(dec.) of gastric stasis.
Lymphocytes – 45 %
(inc.)
ALT – 48 IU/L (inc.) To corrects persistent
AST- 93 IU/L ( inc.) hyperglycemia caused by injury
Serum lipase – 369 to cells and increased release of
IU/L (inc.) Refer dietician for nutritional glucocorticoids. Insulin therapy
Serum creatinine – 5.1 support. is usually short-term unless
mg/dL ( inc.) permanent damage to pancreas
CT Scan - showed fat occurs.
stranding in the Dietitians can help in the
pancreatic head assessment of the patient’s
consisted of nutritional status and nutritional
pancreatitis and needs.
reactive thickening in
the duodenum.
Ultrasound – gross
ascites with echogenic
fluid, increased echo
texture of liver,
obscured pancreas,
Grade 1 renal
parenchymal disease.
You might also like
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPDiane Abanilla57% (7)
- Assessing and Managing Gastric PainDocument2 pagesAssessing and Managing Gastric PainMichael Joaquin0% (2)
- Risk for Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesRisk for Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalancerod navales100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Peptic UlcerAntonio G. Cordillon100% (1)
- Acute PancreatitisDocument2 pagesAcute PancreatitisAkocmeme Sanchez100% (1)
- NCP For Patient With GastritisDocument1 pageNCP For Patient With GastritisBer Anne33% (3)
- NCP PancreatitisDocument2 pagesNCP PancreatitisJeanelle GenerosoNo ratings yet
- NCP AppendicitisDocument2 pagesNCP Appendicitismnms0708100% (2)
- NCP Acute PancreatitisDocument4 pagesNCP Acute PancreatitisJamil Lorca94% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan: Chronic PancreatitisDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan: Chronic PancreatitisAnne B. Buenvenida100% (2)
- Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument3 pagesLiver Cirrhosis NCPSharmaine MadlaNo ratings yet
- NCP pAlPITATIONSDocument3 pagesNCP pAlPITATIONSHazel PalomaresNo ratings yet
- Managing Urinary Tract Obstruction Nursing InterventionsDocument8 pagesManaging Urinary Tract Obstruction Nursing Interventionsjyaba0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Colon Cancer PatientDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Colon Cancer PatientCyril Joy N. FernandoNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument2 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan Manaois100% (1)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJhel NabosNo ratings yet
- NCP Pain DiverticulitisDocument1 pageNCP Pain DiverticulitisAdhaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On Breast Cancer: Encourage Adequate Rest PeriodsDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan On Breast Cancer: Encourage Adequate Rest PeriodsZen Haven100% (4)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: "Ang Sakit NG Tiyan Short-Term: Independent: IndependentDocument1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: "Ang Sakit NG Tiyan Short-Term: Independent: IndependentKate Pedrajas100% (1)
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Document3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN-Lung-Cancerxxx 1Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: IndependentAdhaNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument2 pagesNCP For CTTKay D. BeredoNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis ADocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis APravesh Verma100% (1)
- Prostate Cancer NCPDocument1 pageProstate Cancer NCPKathleen Dimacali0% (1)
- Nursing Care for FatigueDocument2 pagesNursing Care for FatigueVecky TolentinoNo ratings yet
- NCP DiverticulitisDocument6 pagesNCP DiverticulitisLovely Cacapit100% (1)
- Improving Comfort with Endotracheal TubeDocument1 pageImproving Comfort with Endotracheal TubeSelwynVillamorPatenteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Angina PectorisDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan (NCP) For A Patient With Angina PectorisKian Herrera100% (1)
- Cancer Pain ManagementDocument8 pagesCancer Pain ManagementMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For AppendicitisDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For AppendicitisMarife Lipana Reyes80% (5)
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Pancreatitis NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Acute Pancreatitis NCPderic89% (18)
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Guide to Managing ConstipationDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Guide to Managing ConstipationGio Baduria100% (1)
- Relief of Acute Gastric PainDocument4 pagesRelief of Acute Gastric PainJhaypee Soriano100% (3)
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPsphinx809100% (2)
- NCP. FistulectomyDocument2 pagesNCP. Fistulectomymitchelley80% (10)
- NCP Epidural HemDocument32 pagesNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- NCP - LeprosyDocument3 pagesNCP - LeprosyKevin DareNo ratings yet
- NCP 1Document5 pagesNCP 1Denisse Shazz Mae MaretNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing Pattern Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanJasonlee BaluyotNo ratings yet
- NCP AppendicitisDocument2 pagesNCP Appendicitisdon-timothy-abenojar-795686% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan ADocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan ACrystal WyattNo ratings yet
- Orbital Trauma NCP and Drug StudyDocument5 pagesOrbital Trauma NCP and Drug StudyDersly LaneNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument2 pagesNCP Impaired Urinary EliminationTrixy Marie EcotNo ratings yet
- CS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPDocument2 pagesCS5 (AGE) Acute Gastroenteritis NCPAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Afib NCPDocument3 pagesAfib NCPGen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease Care PlanDocument2 pagesCoronary Artery Disease Care PlanDanelle Harrison, RN100% (2)
- NCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaChenime Añana0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For CholecystitisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For CholecystitisEemyaj Jaymee88% (8)
- Care PlanDocument3 pagesCare Planbambam1aNo ratings yet
- Corrected NCP Case 3 Intrapartum NCPDocument2 pagesCorrected NCP Case 3 Intrapartum NCPReyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Pain & Pressure Ulcer ManagementDocument25 pagesNursing Care Plans for Pain & Pressure Ulcer ManagementZhyraine CaluzaNo ratings yet
- NCP AppendicitisDocument4 pagesNCP AppendicitisAisha LakibulNo ratings yet
- 3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCDocument5 pages3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan-Epigastric PainDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan-Epigastric PainK-anne Cherubic100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Peptic UlcerJefferson Baluyot PalmaNo ratings yet
- PREOP3Document1 pagePREOP3Void LessNo ratings yet
- Labor Pain NCPDocument4 pagesLabor Pain NCPBea Dela Cena60% (5)
- Subjective: Sto: Diagnostic:: Assessme NT Explanatio Nofthe Problem Planning Interven Tion Rationale Evaluati ONDocument3 pagesSubjective: Sto: Diagnostic:: Assessme NT Explanatio Nofthe Problem Planning Interven Tion Rationale Evaluati ONRona PieNo ratings yet
- MY Portfolio: (Kitchen Tools & Equipments)Document10 pagesMY Portfolio: (Kitchen Tools & Equipments)Abie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement - 4DDocument1 pageAcknowledgement - 4DAbie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- MY Portfolio: (Kitchen Tools & Equipments)Document10 pagesMY Portfolio: (Kitchen Tools & Equipments)Abie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute Ischemic Heart DiseaseAbie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Life-Threatening Conditions, Acutely Ill/ Multi - Organs Problems, High Acuity and Emergency SituationsDocument21 pagesCare of Clients With Life-Threatening Conditions, Acutely Ill/ Multi - Organs Problems, High Acuity and Emergency SituationsAbie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- Chinese Culture Health Beliefs and Practices: Iloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo CityDocument8 pagesChinese Culture Health Beliefs and Practices: Iloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo CityAbie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- Iloilo Doctors' College Nursing Care Plan for Anaphylactic ShockDocument7 pagesIloilo Doctors' College Nursing Care Plan for Anaphylactic ShockAbie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular AssessmentDocument182 pagesCardiovascular AssessmentAbie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- Case Study in ChinaDocument5 pagesCase Study in ChinaAbie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- 1 Aka 57Document4 pages1 Aka 57Richard FadhilahNo ratings yet
- UConn Criminal Information SummaryDocument2 pagesUConn Criminal Information SummaryEllyn SantiagoNo ratings yet
- SCL 90R Scales AnalysisDocument9 pagesSCL 90R Scales AnalysisCarolina Almonacid60% (10)
- MCQ'S: Deflation Inflation Recession None of The AboveDocument18 pagesMCQ'S: Deflation Inflation Recession None of The Abovesushainkapoor photoNo ratings yet
- SIOP Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesSIOP Lesson PlanSmithRichardL1988100% (3)
- Call for Papers: Reevaluating Postsocialism as a Global ResourceDocument2 pagesCall for Papers: Reevaluating Postsocialism as a Global ResourcegioanelaNo ratings yet
- SF PLT Managing Picklists Admin PDFDocument38 pagesSF PLT Managing Picklists Admin PDFHiNo ratings yet
- Training Curriculum On Drug Addiction Counseling - Chapter 5Document139 pagesTraining Curriculum On Drug Addiction Counseling - Chapter 5Pinj Blue100% (1)
- Gomez FL Bar Complaint v. PerezDocument6 pagesGomez FL Bar Complaint v. PerezJudgeHSNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Cultural Intelligence On Global BusinessDocument5 pagesThe Impact of Cultural Intelligence On Global BusinessAna Mihaela IstrateNo ratings yet
- Soil MechanicsDocument117 pagesSoil MechanicsChiranjaya HulangamuwaNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Boolean Algebra SimplificationDocument72 pagesDigital Electronics Boolean Algebra Simplificationtekalegn barekuNo ratings yet
- Guide Number 5 My City: You Will Learn To: Describe A Place Tell Where You in The CityDocument7 pagesGuide Number 5 My City: You Will Learn To: Describe A Place Tell Where You in The CityLUIS CUELLARNo ratings yet
- Neelam Shahzadi CVDocument3 pagesNeelam Shahzadi CVAnonymous Jx7Q4sNmtNo ratings yet
- Power and PoliticsDocument11 pagesPower and Politicsrahil yasin89% (9)
- 2017 Wassce Gka - Paper 2 SolutionDocument5 pages2017 Wassce Gka - Paper 2 SolutionKwabena AgyepongNo ratings yet
- The Irrefutable Laws of Leadership SummaryDocument6 pagesThe Irrefutable Laws of Leadership Summarycoachersland100% (3)
- TASK 9adhDocument5 pagesTASK 9adhAyan FaridiNo ratings yet
- Oxford Quantum Theory Lecture NotesDocument92 pagesOxford Quantum Theory Lecture Notest ElderNo ratings yet
- BSBMGT608C Manage Innovation Case Study AC GilbertDocument13 pagesBSBMGT608C Manage Innovation Case Study AC Gilbertbacharnaja9% (11)
- Basic Accounting Lecture 05202018Document188 pagesBasic Accounting Lecture 05202018Rheea de los SantosNo ratings yet
- The Future of The Past: The Contemporary Significance of The Nouvelle ThéologieDocument15 pagesThe Future of The Past: The Contemporary Significance of The Nouvelle ThéologiefesousacostaNo ratings yet
- Advocate - Conflict of InterestDocument7 pagesAdvocate - Conflict of InterestZaminNo ratings yet
- Assignment AnuDocument11 pagesAssignment AnuanushadaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Jur ErbrinkDocument245 pagesThesis Jur Erbrinkgmb09140No ratings yet
- Spare Order 28.03Document27 pagesSpare Order 28.03Ankit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Jurnal-Ayu Santika NovinDocument10 pagesJurnal-Ayu Santika NovinSitti Hajar ONo ratings yet
- 01 FontanesiDocument7 pages01 FontanesizegorszyNo ratings yet
- Colourcon HRMDocument8 pagesColourcon HRMMohamed SaheelNo ratings yet
- BS NursingDocument5 pagesBS NursingDenise Louise PoNo ratings yet