Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Corrected NCP Case 3 Intrapartum NCP
Uploaded by
Reyzel Pahunao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Corrected Ncp Case 3 Intrapartum Ncp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
105 views2 pagesCorrected NCP Case 3 Intrapartum NCP
Uploaded by
Reyzel PahunaoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
VII.
NURSING CARE PLAN
Name of Patient: A.R. Impression/Diagnosis: Pregnancy
Age & Sex: 22 y/o, F Ward/Bed: N/A
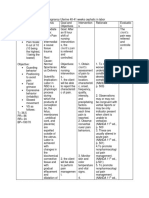
DEFINING NURSING DIAGNOSIS OUTCOME NURSING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
CHARACTERISTICS IDENTIFICATION/OBJECTIVE
LONG TERM: INDEPENDENT:
SUBJECTIVE: Pain and discomfort r/t Goals are met as
uterine contraction Within a week of nursing Offer the patient appropriate Massage is one of the most evidenced by reduced
“Naga sakit akon tiyan intervention, the patient will comfort measures like massage helpful non-pharmacological level of abdominal pain
upod sang cramp nga ga RATIONALE: recognize and utilize the methods during labor pain relief technique. The and lesser cramping
extend sa lower back ko”, to control pain and discomfort presence of stimulation like extended to her lower
as verbalized by the Pain and discomfort such as brought by the active phase of massage causes the opposite back.
patient. Abdominal pain with labor. of pain impulses to be stronger
cramping extended to lower and faster via tiny nerve fiber.
back is felt during the 1st SHORT TERM:
stage of labor and delivery To determine the intensity of
due by low uterine segments After 4 hours of nursing Assess the intensity of the pain pain and to provide effective
in combination with intervention, the patient will be using scale (0 to 10; 0 for no nursing interventions.
OBJECTIVE: isometric contraction of the able to: pain and 10 for worst pain).
uterus. Pain usually is felt in Allows for the development of
- Temperature=37.1°C the abdomen or back during Identify some non- Assess current knowledge of an individualized teaching plan
- Pulse Rate=88 bpm contractions (labor pains) pharmacological methods obstetric pain control measures for the client.
- Respiratory that reduce discomfort/pain
Rate=20cpm REFERENCE: Promotes relaxation and may
- Blood (Nanda Diagnoses, 2022) Verbalize understanding of enhance patient’s coping
Pressure=130/80 the use of obstetric pain Provide diversional activities. abilities by refocusing
mmHg control measures. attention.
- cervix is dilated at
3cm, • Demonstrate use of relaxation Coach use of appropriate May block pain impulses
- 50% effaced skills and diversional within the cerebral cortex
breathing/relaxation techniques
- fetal head at (-3) activities, as indicated. through conditioned responses
and abdominal effleurage
station and cutaneous stimulation and
- membranes are intact gives client a means of coping
- fetal heart tones
with and controlling the level
heard by stethoscope
on the left lower of discomfort.
abdominal quadrant DEPENDENT
at 140 beats per
minute DEPENDENT
Nubain is a preoperative
- bladder is distended analgesic, supplement for
Administer Nubain as
- Facial grimace surgical anesthesia, obstetric
prescribed by the physician.
- Agitated facial analgesic during labor.
expression
References: Doenges, M. E.,
Moorhouse, M. F., & Murr, A. C.
(2019). Nurses pocket guide:
diagnoses, prioritized interventions,
and rationales. Philadelphia: F.A.
Davis Company.
You might also like
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationBUNDA, GLYZE A.No ratings yet
- 3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCDocument5 pages3011-1 - NCP & Drug Study - AMCAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Effects of Labor and Delivery ProcessDocument3 pagesAcute Pain Related To Effects of Labor and Delivery ProcessrlinaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Labor Pain ManagementDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Labor Pain ManagementFc CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- NURSING DIAGNOSIS (2) On Pregnant Woman Knowledge DeficitDocument2 pagesNURSING DIAGNOSIS (2) On Pregnant Woman Knowledge Deficitanon_168410816No ratings yet
- NCP 2 LRDR For PrintDocument2 pagesNCP 2 LRDR For PrintGeorge PandaNo ratings yet
- Rectal and Vaginal Suppository Insertion GuideDocument2 pagesRectal and Vaginal Suppository Insertion GuideMariah Jane TaladuaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Goals and Interventions for Post-Cesarean PainDocument2 pagesNursing Goals and Interventions for Post-Cesarean Painczeremar chanNo ratings yet
- NCP EpisiotomyDocument1 pageNCP EpisiotomyKaye CeprianoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Knowledge GainDocument4 pagesNutrition Knowledge GainTrisha CayabyabNo ratings yet
- DR NCP InfectionDocument2 pagesDR NCP Infectionkarl montanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Magda with EpisiotomyDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Magda with EpisiotomyRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- NCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Hydatidiform Mole PDFKimNo ratings yet
- Managing Premature Cervical DilatationDocument10 pagesManaging Premature Cervical DilatationRaiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment Planning EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment Planning EvaluationLuna GrayNo ratings yet
- NCP Severe Labor PainDocument3 pagesNCP Severe Labor PainPaolo EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Identification Planning Nursing Intervention Evaluation IndependentDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Identification Planning Nursing Intervention Evaluation IndependentQueenie Silva100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Interrupted Breastfeeding: Student Nurses' CommunityDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Interrupted Breastfeeding: Student Nurses' CommunitySaira SucgangNo ratings yet
- GonorrheaDocument2 pagesGonorrheaLeizel ApolonioNo ratings yet
- Subjective:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesSubjective:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationAyra PunzalanNo ratings yet
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityMiar QuestNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain WDocument1 pageNCP Acute Pain Wmiles sbNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan ChapterDocument1 pageFamily Nursing Care Plan ChapterJhe PangsNo ratings yet
- Acyclovir (Acycloguanosi Ne) : Systemic Administration History: AllergyDocument3 pagesAcyclovir (Acycloguanosi Ne) : Systemic Administration History: AllergyAnnahNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain OB Ward PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Acute Pain OB Ward PDFambiit25No ratings yet
- Date/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDate/ Time/ Shift Cues Need Nursing Diagnosis With Rationale Objectives of Care Nursing Interventions With Rationale EvaluationPauleen Trisha SamparaniNo ratings yet
- NCP For Pain OBDocument1 pageNCP For Pain OBMarvz QuegNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan for Improving HygieneDocument5 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan for Improving HygieneCLARENCE REMUDARONo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityJayson OlileNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Fatigue (Antepartum)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan - Fatigue (Antepartum)kaimimiyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan DiarrheaAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Nursing OutcomeDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goals Nursing OutcomemerryNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanJASMINE JOY BADUANo ratings yet
- Risk For InjuryDocument1 pageRisk For Injuryandycamille7No ratings yet
- Managing Labor Pain NaturallyDocument2 pagesManaging Labor Pain Naturallyjay kusainNo ratings yet
- Post-CS Nursing Care Plan GoalsDocument7 pagesPost-CS Nursing Care Plan GoalsshinloNo ratings yet
- NCP1 - EpisiotomyDocument2 pagesNCP1 - EpisiotomyCarmel Joy DifuntorumNo ratings yet
- NCP PostpartumDocument6 pagesNCP PostpartumLovely Anne ArqueroNo ratings yet
- NCP Case 1Document6 pagesNCP Case 1boomer SeargeNo ratings yet
- Labor Nursing Care Plan 1Document4 pagesLabor Nursing Care Plan 1Anna Mae DollenteNo ratings yet
- NCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyDocument7 pagesNCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyD CNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Pain ManagementDocument2 pagesPostpartum Pain ManagementDarien AquinoNo ratings yet
- NCP Disturbed Body ImageDocument2 pagesNCP Disturbed Body ImageDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Bigleap - Immediate Care of The Newborn (Updated)Document5 pagesActivity 2 - Bigleap - Immediate Care of The Newborn (Updated)Cameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Abc NCPDocument3 pagesAbc NCPKL AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Child - ImmunizationsDocument1 pageChild - ImmunizationsJOHN100% (1)
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPAriaNo ratings yet
- Promoting Proper BreastfeedingDocument12 pagesPromoting Proper BreastfeedingAmal MUTIANo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Labor Pain and AnxietyDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plans for Labor Pain and AnxietyJP2001No ratings yet
- EsophagomyotomyDocument3 pagesEsophagomyotomySamVelascoNo ratings yet
- HEALTH-TEACHING (Safety)Document3 pagesHEALTH-TEACHING (Safety)Asterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- NCP (Acute Pain)Document2 pagesNCP (Acute Pain)jennilois100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN (Disturbed Body Image)Document1 pageNURSING CARE PLAN (Disturbed Body Image)Kay D. BeredoNo ratings yet
- Spina Bifida NCPDocument3 pagesSpina Bifida NCPShahzad GulfamNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study For Ob WardDocument7 pagesNCP and Drug Study For Ob WardAce Fabrigas100% (1)
- Mga NCP For Preterm Birth Case 2Document9 pagesMga NCP For Preterm Birth Case 2John Rendel LopezNo ratings yet
- NCP MakingDocument1 pageNCP MakingRose Camille Delos Santos DatuinNo ratings yet
- NCP LaborDocument2 pagesNCP LaborAjea Marie JaymeNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario No. 3 Intrapartum Labor Stage 1Document2 pagesCase Scenario No. 3 Intrapartum Labor Stage 1Reyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- Labor Pain NCPDocument4 pagesLabor Pain NCPBea Dela Cena60% (5)
- Iloilo Doctors' College Nursing Case Presentation on Normal Labor and Delivery ProcessDocument66 pagesIloilo Doctors' College Nursing Case Presentation on Normal Labor and Delivery ProcessReyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- NCP: Labor Stage 1 Active PhaseDocument10 pagesNCP: Labor Stage 1 Active PhaseJavie100% (3)
- Case Scenario No. 3 Guide QuestionsDocument6 pagesCase Scenario No. 3 Guide QuestionsReyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- Case 2 Guide Questions ChangedDocument9 pagesCase 2 Guide Questions ChangedReyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- G4 Case Presentation 2Document48 pagesG4 Case Presentation 2Reyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- BSN2B G4 Case-2Document16 pagesBSN2B G4 Case-2Reyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Symptoms GuideDocument56 pagesPregnancy Symptoms GuideReyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- MC2 (Biochemistry Lec) Quiz 5 (LIPIDS) Name: Reyzel Mae PahunaoDocument3 pagesMC2 (Biochemistry Lec) Quiz 5 (LIPIDS) Name: Reyzel Mae PahunaoReyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyReyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document1 pageQuiz 1Reyzel PahunaoNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts QuizDocument3 pagesCell Parts QuizReyzel Pahunao100% (1)
- Goals and principles of community health nursingDocument4 pagesGoals and principles of community health nursingNoemiNo ratings yet
- RD ManualDocument6 pagesRD Manualapple m.No ratings yet
- Maternity and Womens Health Care 10th Edition by Lowdermilk Test BankDocument10 pagesMaternity and Womens Health Care 10th Edition by Lowdermilk Test Bankthiamity35n0No ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health - Lesson 1Document2 pagesMaternal and Child Health - Lesson 1BabyJane GRomeroNo ratings yet
- Pengetahuan Ibu Tentang Mobilisasi Dini Pasca Persalinan Normal Pervaginam Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Labuhan Rasoki Kecamatan Padangsidimpuan Tenggara Tahun 2018Document6 pagesPengetahuan Ibu Tentang Mobilisasi Dini Pasca Persalinan Normal Pervaginam Di Wilayah Kerja Puskesmas Labuhan Rasoki Kecamatan Padangsidimpuan Tenggara Tahun 2018Geuman ChajgoNo ratings yet
- Community Resource ListDocument6 pagesCommunity Resource Listapi-240620529No ratings yet
- NOELLE® S554.100: Childbirth and Neonatal Resuscitation Patient SimulatorDocument4 pagesNOELLE® S554.100: Childbirth and Neonatal Resuscitation Patient SimulatorAna Diana DucaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Loss: Stillbirth and MiscarriageDocument4 pagesPregnancy Loss: Stillbirth and MiscarriageMely GallardoNo ratings yet
- Set A: Community Health Nursing and Care of Mother and ChildDocument11 pagesSet A: Community Health Nursing and Care of Mother and ChildAldrin NavarroNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Congress of The Philippines Metro Manila Fifteenth Congress Third Regular SessionDocument48 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Congress of The Philippines Metro Manila Fifteenth Congress Third Regular SessionkllyNo ratings yet
- Cultural Sensitivit Y: A Guidebook For Physicians & Healthcare ProfessionalsDocument30 pagesCultural Sensitivit Y: A Guidebook For Physicians & Healthcare ProfessionalsneuronurseNo ratings yet
- Pedrito Dela Torre vs Divine Spirit General Hospital DoctorsDocument6 pagesPedrito Dela Torre vs Divine Spirit General Hospital DoctorsJenicaNo ratings yet
- Einc Skills ChecklistDocument3 pagesEinc Skills ChecklistKENT AUSTRIANo ratings yet
- Top diagnoses at Nopdopan District Hospital in 2021Document2 pagesTop diagnoses at Nopdopan District Hospital in 2021Frank AllanNo ratings yet
- Government College Nursing Anemia Nutritional DeficiencyDocument7 pagesGovernment College Nursing Anemia Nutritional Deficiencypriyanka100% (2)
- Tugas 1Document20 pagesTugas 1lastia meilinaNo ratings yet
- CHN ReviwerDocument1 pageCHN ReviwerHeccie Duque-LarraquelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument16 pagesNursing Care PlansSantos Kyla Patricia T.No ratings yet
- Threatened Preterm LabourDocument12 pagesThreatened Preterm LabourQp Nizam100% (5)
- Postpartum Period and ComplicationsDocument63 pagesPostpartum Period and ComplicationsSharmaineAnnePoliciosNo ratings yet
- A Breech Baby at The End of Pregnancy PDFDocument4 pagesA Breech Baby at The End of Pregnancy PDFPrassaad ArujunanNo ratings yet
- Home Birth GuidelinesDocument32 pagesHome Birth Guidelinesana mariaNo ratings yet
- CPG PerinatalDocument7 pagesCPG PerinatalReuter Lloyd MarianoNo ratings yet
- Care Plan for Intranatal CareDocument11 pagesCare Plan for Intranatal CareBhumi ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Birth AsphyxiaDocument26 pagesBirth Asphyxiawizborrlyzo006No ratings yet
- Jaipurgoldentariff PDFDocument139 pagesJaipurgoldentariff PDFyogesh israniNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Breastfeeding Guide The Thompson MethodDocument48 pagesUltimate Breastfeeding Guide The Thompson MethodlisibulavouNo ratings yet
- Contoh Abstract Yang Systematic Review a Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis Comparing the Use of Foley Catheters, Misoprostol, And Dinoprostone for Cervical Ripening in the Indu... - PubMed - NCBIDocument2 pagesContoh Abstract Yang Systematic Review a Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis Comparing the Use of Foley Catheters, Misoprostol, And Dinoprostone for Cervical Ripening in the Indu... - PubMed - NCBIWienda GeraldineNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of A Family During Labor and BirthDocument2 pagesNursing Care of A Family During Labor and BirthNanami MomozonoNo ratings yet