0% found this document useful (0 votes)
101 views4 pagesElevator Forces and Plane Velocity Analysis
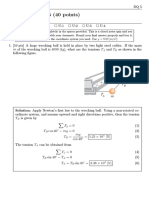
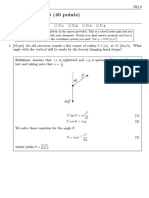
The document is a physics quiz with 4 questions. Question 1 asks the student to calculate the wind velocity vector given information about an airplane's airspeed and flight path. Question 2 provides masses and tensions and asks the student to draw a free body diagram and calculate an unknown mass. Question 3 asks the student to calculate scale readings in different situations involving suspended objects. Question 4 asks about reaction forces on an elevator passenger and whether they are accelerating.
Uploaded by
Jan Adrian Galang FranciscoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
101 views4 pagesElevator Forces and Plane Velocity Analysis
The document is a physics quiz with 4 questions. Question 1 asks the student to calculate the wind velocity vector given information about an airplane's airspeed and flight path. Question 2 provides masses and tensions and asks the student to draw a free body diagram and calculate an unknown mass. Question 3 asks the student to calculate scale readings in different situations involving suspended objects. Question 4 asks about reaction forces on an elevator passenger and whether they are accelerating.
Uploaded by
Jan Adrian Galang FranciscoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd