Professional Documents
Culture Documents
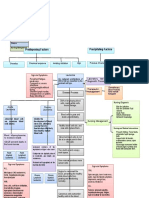
1-Definition Types: Aplastic Anemia
1-Definition Types: Aplastic Anemia
Uploaded by
Mohamed AhmedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1-Definition Types: Aplastic Anemia
1-Definition Types: Aplastic Anemia
Uploaded by
Mohamed AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
Non-severe: Low cell counts, may be asymptomatic , watchful waiting,
condition may not change
Can be moderate or severe
Severe AA: Neutrophil Aplastic Anemia is a rare
counts < 500, condition where the bone
Reticulocyte count < Between 600-900 people are
1-Definition marrow cannot produce an
20.000, platelet count diagnosed annually in the U.S.
< 20,000
Types adequate number of red blood
cells.
Can happen at any age
Very Severe AA:
Platelet count < 200;
all other blood counts
comparable to severe A bone marrow transplant, aka stem cell transplant,
AA often cures bone marrow failure.
Antibiotic therapy for recurring infections
Complete blood count (CBC) 2-Treatment
reveals pancytopenia: low
WBC, RBC, and platelet counts Blood Transfusions.
Liquid and solid bone marrow Immunosuppresive therapy
samples are tested to confirm a Bone Marrow Test
diagnosis
Infectious Disease
This test determines if
bone marrow is producingnew
Aplastic anemia
RBCs
Diagnostic Tests Treatments for other
Reticulocyte count shows autoimmune disorders
numbers of young like Rheumatoid Arthritis
red blood cells
Low levels Autoimmune Mechanisms
are typically and Lupus.
seen in AA
3-Causes
Contributes to most AA cases
Erythropoietin, iron,
vitamin B12, and folate
levels rule out other Drugs
causes of anemia
Chemotherapy and Radiation
Recurring infections due to neutropenia
Toxins
Frequent bleeding and mennorhagia due to
thrombocytopenia
Cells are replaced with fat
Tired, difficulty concentrating
Clinical Presentation
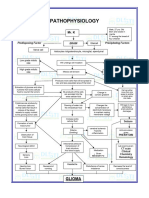
Pathophysiology
Bone marrow HPCs are the source
Loss of hematopoietic stem cells of mature cells in peripheral blood
Pale Skin and tissues
Shortness of Breath
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of ALL (Diagram)Document3 pagesPathophysiology of ALL (Diagram)Joann100% (77)
- Clinical Pathology MCQs and Ansewrs PDFDocument29 pagesClinical Pathology MCQs and Ansewrs PDFAmeer MattaNo ratings yet
- Trans OS216 Hema 15Document6 pagesTrans OS216 Hema 15api-3799593No ratings yet
- (Trans) Chapter 16: Anemias - Red Blood Cell Morphology and Approach To DiagnosisDocument4 pages(Trans) Chapter 16: Anemias - Red Blood Cell Morphology and Approach To Diagnosisgotvelvet world dominationNo ratings yet
- Determinants of HealthDocument33 pagesDeterminants of HealthNicole MedinaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Haematology-Lecture SlidesDocument55 pagesClinical Haematology-Lecture SlidesShiv Sookun100% (1)
- Blood FilmDocument2 pagesBlood FilmGerardLum100% (1)
- Anaesthesia For BurnsDocument51 pagesAnaesthesia For BurnsAnulatkNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Daviss Drug Guide For Nurses 16th Edition VallerandDocument27 pagesTest Bank For Daviss Drug Guide For Nurses 16th Edition VallerandCary Green100% (35)
- MCQ Q and A-OrthopaedicsDocument27 pagesMCQ Q and A-OrthopaedicsAnoop ErattakallilNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis: VASCULITIS Is A Primary Inflammatory Disease Process of The VasculatureDocument43 pagesVasculitis: VASCULITIS Is A Primary Inflammatory Disease Process of The VasculaturelihayatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To HematologyDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To HematologyMonica DomingoNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandVasculitis, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology AML DiagramDocument4 pagesPathophysiology AML DiagramKlerra Hope60% (5)
- Translation, Cultural Adaptation, and Validation of A Lipedema Symptoms QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesTranslation, Cultural Adaptation, and Validation of A Lipedema Symptoms QuestionnaireAlexandre Campos Moraes AmatoNo ratings yet
- Blood Test ResultsDocument1 pageBlood Test ResultsnindyaNo ratings yet
- Semana 4 PrepositionsDocument16 pagesSemana 4 PrepositionsEstudio Jurídico Abogadas AsociadasNo ratings yet
- Aplastic and Hypoplastic Anemias: Education GapsDocument13 pagesAplastic and Hypoplastic Anemias: Education GapsSari ChaerunisahNo ratings yet
- A Practical Approach To Anaemia (MB Agarwal, 2017)Document5 pagesA Practical Approach To Anaemia (MB Agarwal, 2017)desytrilistyoatiNo ratings yet
- Barecuatro - Module 2 - Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesBarecuatro - Module 2 - Nursing Care PlanANGELICA CLAIRE BARECUATRONo ratings yet
- Drug Study MIDocument11 pagesDrug Study MIHannah ChiuNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Module 2 Lesson 1.1Document3 pagesNCM 106 Module 2 Lesson 1.1Joselyn M. LachicaNo ratings yet
- Blood: Leukocytes: OutlineDocument3 pagesBlood: Leukocytes: Outlinevinnie0905No ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYangeliccat_sweet157992No ratings yet
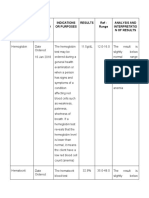
- Diagnostic AND Laboratory Procedures Date Ordered Date Results IN Indications or Purposes Results Ref - Range Analysis and Interpretatio N of ResultsDocument6 pagesDiagnostic AND Laboratory Procedures Date Ordered Date Results IN Indications or Purposes Results Ref - Range Analysis and Interpretatio N of ResultsRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- What Is Aplastic Anemia Final BrochureDocument2 pagesWhat Is Aplastic Anemia Final BrochureSareno PJhēaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrospinal FluidDocument12 pagesCerebrospinal FluidMuath M. AbusamrehNo ratings yet
- Hematology Week 8Document3 pagesHematology Week 8Rose Neil LapuzNo ratings yet
- Case 2Document3 pagesCase 2Joselyn M. LachicaNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument2 pagesHematologyMuhammad Hamza AlviNo ratings yet
- Cerebrospinal Fluid: Prepared By: Muath M. Abu-Samreh Supervisor: Dr. Samir KhalilDocument12 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid: Prepared By: Muath M. Abu-Samreh Supervisor: Dr. Samir KhalilMohammad Abu-SamrehNo ratings yet
- LeukemiaDocument1 pageLeukemiaFabshkieee 3No ratings yet
- Components of The Complete Blood Count (CBC) : © 2005 American Association For Clinical Chemistry 1Document2 pagesComponents of The Complete Blood Count (CBC) : © 2005 American Association For Clinical Chemistry 1anisa rachmitaNo ratings yet
- Haemogram RangesDocument3 pagesHaemogram RangesMayra SanchezNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exam Normal Value Details and IndicationsDocument5 pagesLaboratory Exam Normal Value Details and Indicationsmaeca101No ratings yet
- Diagnostics NephrolithiasisDocument7 pagesDiagnostics NephrolithiasisAnika GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology I 05 VasculitisDocument21 pagesRheumatology I 05 VasculitisWen Jie LauNo ratings yet
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Document3 pagesAcute Myeloid Leukemia (Drug Study)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- White Blood Cells and Its Disorders: Key PointsDocument24 pagesWhite Blood Cells and Its Disorders: Key PointsskNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ResultsDocument6 pagesLaboratory ResultsJimuel Brian ManelaNo ratings yet
- CP RBC DisorderDocument15 pagesCP RBC DisorderDETECTIVE CONANNo ratings yet
- 2.15 Interpretasi Darah 3 Sudah Di Stabilo PDFDocument1 page2.15 Interpretasi Darah 3 Sudah Di Stabilo PDFalodiaNo ratings yet
- Anemia SDocument8 pagesAnemia SCarlo SantosNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Anemia Algorithm HandoutDocument2 pagesDiagnosing Anemia Algorithm HandoutValentino Farroñay TafurNo ratings yet
- Cecilia Case Study 1 4Document2 pagesCecilia Case Study 1 4Tugs KNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Cerebrovascular Accident Hemorrhagic Right Lobe)Document4 pagesPathophysiology (Cerebrovascular Accident Hemorrhagic Right Lobe)jhonkivenNo ratings yet
- 20.guidelines AnaemiaDocument5 pages20.guidelines AnaemiaRed DevilNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan DarahDocument11 pagesPemeriksaan DarahJems BoruNo ratings yet
- Rotation5 SIC LarceñaDocument10 pagesRotation5 SIC LarceñanoemilauNo ratings yet
- Date & Time Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goals/Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesDate & Time Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goals/Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationBU MINo ratings yet
- Hematology 101: Interpreting Lab Results - Patterns and PitfallsDocument55 pagesHematology 101: Interpreting Lab Results - Patterns and PitfallsAmorrita Puspita Ratu100% (1)
- CH 11 Lab Human InheritanceDocument13 pagesCH 11 Lab Human InheritanceBao HoangNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio of GliomaDocument1 pagePathophysio of GliomaEf RoqueNo ratings yet
- Human Body - A Visual Encyclopedia (PDFDrive) - 69-71Document3 pagesHuman Body - A Visual Encyclopedia (PDFDrive) - 69-71Neeha NMNo ratings yet
- 1.BC 5800 PrincipleDocument37 pages1.BC 5800 PrinciplekiryNo ratings yet
- Anaemia 2023 SepakoDocument3 pagesAnaemia 2023 SepakoLeslie MbisanaNo ratings yet
- Hematology 1 L1 Introduction To Hematology 1 LectureDocument2 pagesHematology 1 L1 Introduction To Hematology 1 LectureChelze Faith DizonNo ratings yet
- Chronic HepatitisDocument2 pagesChronic HepatitisMohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Meningococalmeningitis: Presented by Class 6 B Community Medicine DepartmentDocument41 pagesMeningococalmeningitis: Presented by Class 6 B Community Medicine DepartmentMohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: GastritisDocument2 pagesSigns and Symptoms: GastritisMohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: GastritisDocument2 pagesSigns and Symptoms: GastritisMohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Omacor: Municipal Planning and Development OfficeDocument9 pagesOmacor: Municipal Planning and Development OfficeArthur MericoNo ratings yet
- Lapsus Ortho Word - Id.enDocument17 pagesLapsus Ortho Word - Id.eninhaNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet in RW 6Document2 pagesAnswer Sheet in RW 6edrianclydeNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 10 (Health) Las Q3week 1 and 2Document5 pagesMapeh 10 (Health) Las Q3week 1 and 2Dianne DimailigNo ratings yet
- Hachinski Ischaemia ScoreDocument1 pageHachinski Ischaemia ScoreAbdur RasyidNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal History: Basic InfoDocument10 pagesMusculoskeletal History: Basic InfoTom MallinsonNo ratings yet
- The Medical & Surgical Practice of NaProTechnology (2004, Hilgers)Document1,290 pagesThe Medical & Surgical Practice of NaProTechnology (2004, Hilgers)Anonymous tpwOhymCbiNo ratings yet
- Proposal FormDocument9 pagesProposal FormAmbuj ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument32 pagesUntitledclares danilaNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Applied Medicine BY: Dr. Kinza IftikharDocument17 pagesHeart Failure: Applied Medicine BY: Dr. Kinza IftikharsabaamjadNo ratings yet
- Journal of The American Medical Association: CCOVID-19 in Pregnant WomenDocument6 pagesJournal of The American Medical Association: CCOVID-19 in Pregnant WomenAnonymous Pb39klJNo ratings yet
- What Is A Physical Disability?: Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)Document14 pagesWhat Is A Physical Disability?: Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)XIARESSE DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument113 pagesMetalsمصطفى أحمدNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol: (Chod / Pod Method)Document2 pagesCholesterol: (Chod / Pod Method)psychejaneNo ratings yet
- List ProcedureDocument122 pagesList ProcedureChristina Dian RinestiNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Pada Kasus PediatrikDocument41 pagesPneumonia Pada Kasus PediatrikasriNo ratings yet
- Gizi Mutakhir Probiotik Dan Prebiotik: Dr. Rauza Sukma Rita, PH.DDocument32 pagesGizi Mutakhir Probiotik Dan Prebiotik: Dr. Rauza Sukma Rita, PH.DShania TrijuitaNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Class V Worksheet Lesson 11Document2 pagesSocial Studies Class V Worksheet Lesson 11Rashi BakshNo ratings yet
- S1 Guideline Lipedema: AWMF Register No. 037/012 Class: S1Document27 pagesS1 Guideline Lipedema: AWMF Register No. 037/012 Class: S1ThuaretNo ratings yet
- SWT Nedelka Cartagena enDocument2 pagesSWT Nedelka Cartagena enChristian Lazo FerreyraNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis - Emergency Treatment - UpToDateDocument49 pagesAnaphylaxis - Emergency Treatment - UpToDatealinaNo ratings yet
- Final Thesis. CWs - En.de - De.fr - Fr.enDocument81 pagesFinal Thesis. CWs - En.de - De.fr - Fr.enBeera InstituteNo ratings yet
- RACGP How To Complete A Death CertificateDocument4 pagesRACGP How To Complete A Death CertificateFlavin AmbroseNo ratings yet
- Pre Test TNT VerDocument6 pagesPre Test TNT VerHanditoSarwwotatwadhikoNo ratings yet