Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Relative Poverty
Uploaded by
Nainika Reddy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesRelative Poverty
Uploaded by
Nainika ReddyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Relative Poverty:
It refers to poverty relation to different classes or regions.
It is a measure of inequality of income.
It is an indicator of the contract between the lives of the poor & the lives of those
around them.
Absolute Poverty:
It refers to the actual number of people who living below the poverty line.
It is a measure of income.
It is measured with the help of the concept of the poverty line.
The govt’s approach to, poverty reduction was of three dimensions:
Growth oriented approach: It was believed that if there is a growth of gross domestic
product & per capita income by allowing the rich to flourish, it would eventually
benefit the lower income groups through increased economic activity & reduced
unemployment. It was felt that rapid industrial development & transformation of
agriculture through green revolution would benefit the underdeveloped regions & the
more backward sections of the society.
Creation of income generation assets & poverty alleviation programmes: Creation of
income generating assets implies resources like land, social networks, which
encourage empowerment & community services, fixed public assets like wells,
clinics, schools, bridges, dams etc which generate employment. Policy makers
thought of making these income earning assets accessible to the poor so that they
could earn a regular income. This was done through the implementation of poverty
alleviation programmes.
The third approach is to provide minimum basic amenities to the people through
public expenditure on social consumption needs – provision of food grains at
subsidized rates, education health, water supply & sanitation. This will improve the
living standards of the people.
The scheme I will apply for assistance is Opportunities for Self-Employment.
This is because the scheme focuses on offering low interest rates on loans by
banks and other financial institutions for setting up small enterprises and start-
ups.
Some measures that can be taken are: -
Increasing economic growth rate through capital formation
Keeping a check on population growth/ growth rate – population control
Reducing income and wealth inequalities
Development of proper deliver mechanism and PDS
Reduction in corruption to ensure that maximum help reaches the poor
Development of infrastructure
Achieving a lower rate of inflation
Providing better health care facilities
Increasing employment opportunities
Providing social security to the poor
Gender equality and women empowerment
Better living conditions and access to essentials like drinking water, food etc.
Setting up more NGO’s to help the poor
Setting up rural credit system and ensure its proper functioning
Development of rural area – building roads, proper housing, etc.
Creation of income earning assets
Organising training camps for imparting vocational training and skills
You might also like
- Chapter 3 BMIS SCMSBDocument75 pagesChapter 3 BMIS SCMSBNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- StoryDocument2 pagesStoryNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- BMIS Chapter 4 SCMSBDocument35 pagesBMIS Chapter 4 SCMSBNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Determination of Income and EmploymentDocument43 pagesDetermination of Income and EmploymentNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Horticulture in India: A Presentation OnDocument9 pagesHorticulture in India: A Presentation OnNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
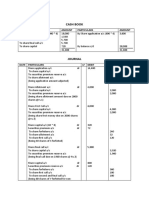
- Cash Book: Particulars Amount Particulars AmountDocument2 pagesCash Book: Particulars Amount Particulars AmountNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- DEEP WATER by WILLIAM DOUGLAS. (A PDF by Mrs. Arlene Andrews)Document2 pagesDEEP WATER by WILLIAM DOUGLAS. (A PDF by Mrs. Arlene Andrews)Nainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand TulikaDocument31 pagesAggregate Demand TulikaNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Gaining Ratio New Ratio - Old Ratio Difference Between Sacrificing Ratio and Gaining RatioDocument17 pagesGaining Ratio New Ratio - Old Ratio Difference Between Sacrificing Ratio and Gaining RatioNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Issue of Share CapitalDocument2 pagesIssue of Share CapitalNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- UNIT1 - Introduction To ManagementDocument18 pagesUNIT1 - Introduction To ManagementNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- UNIT5 - MotivationDocument21 pagesUNIT5 - MotivationNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Motivation: Session 1: Motivation and Its ImportanceDocument21 pagesUnit 5 - Motivation: Session 1: Motivation and Its ImportanceNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- UNIT8 - Information Technology and BusinessDocument14 pagesUNIT8 - Information Technology and BusinessNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- UNIT2 - Concept of ManagementDocument17 pagesUNIT2 - Concept of ManagementNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: Leadership: Session 1: Meaning, Definition and Importance of LeadershipDocument13 pagesUnit 6: Leadership: Session 1: Meaning, Definition and Importance of LeadershipNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- UNIT4 - CommunicationDocument13 pagesUNIT4 - CommunicationNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Chapter 7 - SCMDocument11 pagesChapter 7 - SCMhieuanhshinochiNo ratings yet
- Final Publish Paper ABDocument15 pagesFinal Publish Paper ABJayesh AdakmolNo ratings yet
- Internship report-IOCLDocument42 pagesInternship report-IOCLRoopam Saxena83% (6)
- BBA 2513 Business Ethics 5 SemesterDocument17 pagesBBA 2513 Business Ethics 5 Semesterjen sherpaNo ratings yet
- ENTREPR. Q1-M3, Ladrido JJDocument4 pagesENTREPR. Q1-M3, Ladrido JJAdiel SeraphimNo ratings yet
- OPIM313 Review QuestionsDocument5 pagesOPIM313 Review QuestionsCHERYL SIEW-KEI ODERMATTNo ratings yet
- Tax-1 SyllabusDocument16 pagesTax-1 SyllabusJennica Gyrl DelfinNo ratings yet
- How I Made $2293.26 Per Day From My LaptopDocument2 pagesHow I Made $2293.26 Per Day From My LaptopBest mindsetNo ratings yet
- 5 Common Myths About Internet MarketingDocument8 pages5 Common Myths About Internet MarketingFauziNo ratings yet
- Doka Formwork Catalogue 2011Document516 pagesDoka Formwork Catalogue 2011andrijapopovic82% (11)
- Service Marketing MixDocument2 pagesService Marketing MixAvadhesh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Compendium of PNB Products & ServicesDocument125 pagesCompendium of PNB Products & ServicesRomanshu PorwalNo ratings yet
- 3 The Global Economy1Document36 pages3 The Global Economy1Aldrien CatipayNo ratings yet
- SANS10090Document40 pagesSANS10090Jamie BrownNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Employees' Personal Values On Achieving Organizational Strategic GoalsDocument35 pagesThe Effect of Employees' Personal Values On Achieving Organizational Strategic GoalsSachin ChachanNo ratings yet
- Key Facts StatementDocument3 pagesKey Facts Statementshirine.mrouehNo ratings yet
- Proposed Credible Information System For National Sports Football TeamDocument7 pagesProposed Credible Information System For National Sports Football TeamIjbmm JournalNo ratings yet
- Destination Management SystemDocument14 pagesDestination Management Systemnamatovu100% (1)
- Research Proposal of Nilushi Minoli SenadeeraDocument4 pagesResearch Proposal of Nilushi Minoli Senadeeraranjann349No ratings yet
- Topics: Advertising: Importance of Advertising, Advertising To Editorial Ratio, Online Versus Newspaper AdvertisingDocument27 pagesTopics: Advertising: Importance of Advertising, Advertising To Editorial Ratio, Online Versus Newspaper Advertisingcamryn jonesNo ratings yet
- Slide Notes Unit 2 Organising KMBN101Document51 pagesSlide Notes Unit 2 Organising KMBN101SimranNo ratings yet
- Assignment Chapter6 StaffingDocument3 pagesAssignment Chapter6 Staffinglegend hereNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Supply Chain ManagementDocument7 pagesAspects of Supply Chain ManagementKamal SanguriNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Conference Brief (Govt Agency)Document6 pagesPreliminary Conference Brief (Govt Agency)Janine AranasNo ratings yet
- Holiday Inn Manila v. NLRCDocument2 pagesHoliday Inn Manila v. NLRCMekiNo ratings yet
- Needs Prioritisation MethodsDocument20 pagesNeeds Prioritisation MethodsWALTER simsokweNo ratings yet
- 会计英语 (中英对照)Document122 pages会计英语 (中英对照)lunwenNo ratings yet
- CIA Challenge Exam (Part 2)Document146 pagesCIA Challenge Exam (Part 2)JohnNo ratings yet
- Lectura 1Document34 pagesLectura 1Carlo CastilloNo ratings yet
- Canada Life To Share - Offer ReceivedDocument3 pagesCanada Life To Share - Offer ReceivedDominik PapaNo ratings yet