Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 6097998093028950266
5 6097998093028950266
Uploaded by
pankaj agarwal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesOriginal Title
5_6097998093028950266
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pages5 6097998093028950266
5 6097998093028950266
Uploaded by
pankaj agarwalCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
‘Scanned with CamScanner
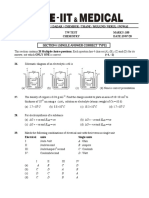
5.1. Define average rate and instantaneous rate. How
is instantaneous rate evaluated?
5.2. Define rate law and rate constant, Explain rate
law with two examples.
53. Explain the term order of a reaction with
examples. 5
5.4. What is pseudo-first order reaction? Give one
example.
55 Define integrated rate law. Derive the
expression for integrated rate law for first order
reaction, A ——> products.
5.6 Define half life of a reaction. Derive the
relationship between half life and rate constant
for a first order reaction. q
5.7 Describe one method to determine rate law and
order of a reaction.
5.8 Give the units of rate of reaction and rate
constants of first and zero order reactions.
5.9. The gas-phase reaction between NO and Br, is
represented by the equation.
2NO (g) + Br; (g) —> 2NOBr (g)
(a) Write the expressions for the rate
consumption of reactants and formation
products.
(b) Write the expression for the rat
reaction in terms of rates of const
reactants and formation of pr
5.10
equation.
2N,0; (g) ——>4NO;
(a) How is the rate of fo
Scanned with CamScanner
5.13 The reaction
H,0,(aq)+31-(aq)+2H* (aq) —>
2H,0()41; (aq)
is first order in HO and I, zero order in Hs
Write the rate law. ¢
5.14. The reaction A+ B ——> products is first order
in each of the reactants. (a) Write the rate lay,
(b) How does the reaction rate change if the
concentration of B is decreased by a factor 3
(c) What is the change in the rate if the
concentration of each reactant is
(d) What is the change in the rate i
tration of A is doubled and that of B is he
What is an elementary reaction? Wi
molecularity of an elementary
5.16 Distinguish between mol
reaction.
What do you mean by
5.15
Scanned with CamScanner
524 Write the rate law for the following reactions:
A reaction that is zero order in A and second
order in B.
(b) A reaction that is second order in NO ade
first order in Br,.
Define the term activation energy.
Arrhenius equation explain why
reaction (a) increases with i
temperature (b) increases with di
activation energy.
Scanned with CamScanner
ler the reaction 2A + B ——» 2C. Suppose
a particular moment during the reaction,
disappearance of A is 0.076 M/s, (a)
s the rate of formation of C? (b) What is
rate of consumption of B? (c) What is the
ie of the reaction?
{(a) 0.076 M/s (b) 0.038 M/s (c) 0.038 M/s]
Consider the reaction
31(aq) + S,0§ (aq) > Ty (aq) + 280} (aq)
afsox]_
Ata particular time t, are F 2.2x10? M/s.
at ]
What are the values of (a)-
[s,0F ] as]
(3)
dt
((a) 3.310 M/s
(c) 1.1102 M/s]
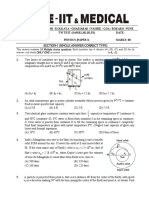
Consider the reaction 2A + 2B ——>2C + D.
From the following data, calculate the order and
rate constant of the reaction.
(b)- ==
at the same time?
(b) 11x10? M/s
5.4
we]
[A]/M [B],/M
0.488 0.160
0.244 0.160
0.244 0.320
Scanned with CamScanner
Write the rate law of the reaction.
[AJM [B/M
0.3 0.05
0.6 0.05
0.6 0.20
What is the rate constant andy
pean
stro iniger tac a *
C,H,Br, + 3 —_, CoH, B
= k(C,H,Bry][ I+]. The rat
found to be 1.x a9
5.6 Consider the reaction A, + B ——> products. If
the concentration of A, and B are halved, the
rate of the reaction decreases by a factor of 8-
If the concentration of A is increased by a factor
of 2.5, the rate increases by the factor of 2.5-
What is the order of the reaction? Write the rate
law.
[Third order, rate = Kl.
5.7 Consider the reaction C + D products. The
of the reaction increases by a factor of 4
concentration of C is doubled. The rate’
reaction is tripled when concentration Of
tripled. What is the order of the reé ct
the rate law. ’
[Third order, rate =
5.8 The reaction F,(g) + 2ClO{g) r
is first order in each of the reactan
of the reaction is 4.88 x 10*
0.015M and [CIO,] = 0.025 M.
rate constant of the reaction.
5,9 The reaction 2H, (g) +
+N, (g) is first order
NO. The rate co
5.10
Scanned with CamScanner
|
|
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Part - I: Subjective QuestionsDocument11 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questionspankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Health and Productivity: Vivek GhangasDocument8 pagesHealth and Productivity: Vivek Ghangaspankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Buffer Solution & Buffer CapacityDocument12 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Buffer Solution & Buffer Capacitypankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Answer Correct Type) : IIT - JEE: 2022 Xii - TW Test DATE: 19/07/20 TIME: 1 Hr. Physics MARKS: 100Document8 pagesSection-I (Single Answer Correct Type) : IIT - JEE: 2022 Xii - TW Test DATE: 19/07/20 TIME: 1 Hr. Physics MARKS: 100pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Class Xii (FC) (19-21) Class Xii - Baner Batches (19-21) Class Xii - Ps (19-21) Class Xii-Rga (19-21)Document1 pageClass Xii (FC) (19-21) Class Xii - Baner Batches (19-21) Class Xii - Ps (19-21) Class Xii-Rga (19-21)pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Answer Correct Type)Document5 pagesSection-I (Single Answer Correct Type)pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Answer Correct Type)Document5 pagesSection-I (Single Answer Correct Type)pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Sublimation Sublimation Dry Naphthalene: SurfaceDocument12 pagesSublimation Sublimation Dry Naphthalene: Surfacepankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Sublimation Sublimation Dry Naphthalene: SurfaceDocument12 pagesSublimation Sublimation Dry Naphthalene: Surfacepankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Rank List Online TWT (Eng) (Only For Pune) 2019-21 Batch DATE: 05-07-2020Document4 pagesRank List Online TWT (Eng) (Only For Pune) 2019-21 Batch DATE: 05-07-2020pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- 5 6082186772224147730Document3 pages5 6082186772224147730pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Rotational DynamicsDocument4 pagesRotational Dynamicspankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Result & Ranklist Online Major Test 5 - Advance 2019-21 BATCH DATE: 13-09-2020Document5 pagesResult & Ranklist Online Major Test 5 - Advance 2019-21 BATCH DATE: 13-09-2020pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Ps (19-21) Class Xii-Rga (19-21) Class Xii - Baner Batches (19-21) Class Xii (FC) (19-21)Document1 pageClass Xii - Ps (19-21) Class Xii-Rga (19-21) Class Xii - Baner Batches (19-21) Class Xii (FC) (19-21)pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Answer Correct Type)Document6 pagesSection-I (Single Answer Correct Type)pankaj agarwalNo ratings yet