Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Best Practice Guide - SCL Exclusion Zone Management
Uploaded by
mosbridgeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Best Practice Guide - SCL Exclusion Zone Management
Uploaded by
mosbridgeCopyright:
Available Formats
BEST PRACTICE GUIDE
SCL EXCLUSION ZONE
MANAGEMENT
MOVING LONDON FORWARD
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 1 of 14
A best practice guide produced in collaboration between
Joint Venture
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 1 of 14
Index
Part A – General
Purpose and Scope Page 4
Definitions, Roles & Responsibilities Page 5
Part B – Exclusion Zones and Restricted Areas
Requirements Page 8
Control & Release Page 9
Part C – Additional Information
Communication and Further Measures Page 13
Glossary of Terms Page 14
External Standards Page 14
Phonetic Alphabet Page 14
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 2 of 14
Part A – General
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 3 of 14
Section A
General
Purpose Scope
Falling ground or immature (green) The information provided in this
concrete within sprayed concrete lined document is applicable to all SCL
tunnels is a major risk to personnel works on the Crossrail project and has
working in a tunnel, and the main been prepared to establish principles
mitigation measure to prevent injury in relation to protecting personnel
is the use of exclusion zones for high from falling ground or immature
risk areas. concrete close to the working face.
This document relates to all areas
The purpose of this document is to of a tunnel where initial and primary
provide guidance on the consistent linings are being sprayed, including the
application of control measures to breakout for junctions and construction
be used on Crossrail sites in the of connecting tunnels. The principles
management of exclusion and listed within this guidance document
restriction zones around active working concerning exclusion zones also apply
areas in tunnels employing the Sprayed to the construction of sprayed concrete
Concrete Lining (SCL) methodology. This secondary linings and may be followed
guidance document has been prepared with suitable adjustments to consider
following discussions within CRL, the larger areas impacted and access
with the SCL contractors and with the routes available.
designers working on the project.
The information provided here relates
The guidance provided within this only to the management of, and testing
document should not be transferred to for safety related to potential falls
other projects without full consideration close to working areas. Other testing
of the specific risks associated with requirements for control of the quality
the ground, methods of working, plant, of the works are described within the
materials used and the competence and Works Information and must continue
experience of personnel being taken to be undertaken at the frequencies
into consideration. defined.
All tunnel working activities shall be
carried out in accordance with BS 6164:
2011 ‘Code of Practice for Health and
Safety in Tunnelling in the Construction
Industry’, and this document discusses
supplementary guidance information
which should be followed to assist in
complying with the requirement to
restrict access for personnel
(BS 6164 Table 1) in zones subject to
SCL falls.
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 4 of 38
Definitions Roles and Responsibilities
For the purposes of this document the The following defined roles should be
following definitions shall apply and identified and confirmed at each shift
should be used across the project in all briefing. The decision on who is best
documentation relating to this subject: placed to take on these roles shall
reside with the Principal Contractor
Exclusion Zone – an area defined on site responsible for the safety of personnel
where no personnel will be allowed to within the particular work area.
enter under any circumstances.
At no time should a person undertaking
Restricted Area – an area defined on a task that could distract them from the
site where there is authorised access role in question be in a position named
for defined personnel only, including below.
supervision and engineering teams.
Restricted areas may be split into The use of competent deputies and
separate areas with the higher number delegation of authority should be
(e.g. Restricted Area 2) being closest to established to cover times when the
the Exclusion Zone or working face. main named responsible person is away
from the work area, or will be distracted
Normal access zone – an area defined by undertaking his own defined tasks to
on site where authorised access through complete the works.
normal tunnel entry procedures is
allowed.
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 5 of 14
Exclusion Zone Supervisor Exclusion Zone Engineer
Responsibilities include: In most circumstances this will be
the Shift Engineer or his identified
• Monitoring and maintenance of the deputy for this role, but can be
systems in the work place required anyone competent at carrying out the
to define and communicate the appropriate testing. Responsibilities
limits of the exclusion zone include:
• Agreeing with the Exclusion Zone
• Performing any specified tests
Engineer (see below) that an
related to the release of an
Exclusion Zone can be temporarily
Exclusion Zone
or permanently released to a
Restricted Area • Monitoring any defined time
periods related to the first testing
Exclusion Zone Supervisor (deputy) for the release of an Exclusion Zone
Responsible for undertaking the • Agreeing with the Exclusion Zone
Exclusion Zone Supervisor’s role when Supervisor (or nominated deputy
nominated by that person, with suitable when acting as the Supervisor)
people identified at the briefing at the that an Exclusion zone can be
start of each shift. temporarily or permanently
released to a Restricted Area
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 6 of 14
Section B – Exclusion Zones and Restricted Access
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 7 of 14
Section B
Exclusion Zones and Restricted Areas
Requirements for a defined Requirements for a defined
Exclusion Zone Restricted Area
The following are the minimum The following are the minimum
requirements that should be in place requirements for a Restricted Area
for an Exclusion Zone and should be and shall be considered on a risk based
communicated to all personnel entering approach taking due cognisance of the
the tunnel and considered on a risk prevailing conditions and methods.
based approach taking due cognisance This area should always be as safe as
of the prevailing conditions and reasonably practical with safe systems
methods: of work established for all activities
undertaken in this area.
• Defined minimum strength of the
last concrete sprayed before an • A visible barrier defining the
Exclusion Zone may be changed to boundary between the Restricted
a Restricted Area. This should be Area and the Normal access zone
demonstrated by calculation by the • A minimum length of the total
contractor’s designer, accepted by Restricted Area
the Crossrail Project Manager, and
shall not be less than 0.25MPa • A list of personnel entitled to be
within each Restricted Area
• Defined time before the strength
testing is first carried out by an • A maximum number of personnel
approved method normally expected to be within
each restricted area during spraying
• Defined minimum distance from operations
the working face or a defined
position at the face. For the • A maximum number of personnel
Crossrail project this shall not be normally expected to be within each
less than 2m restricted area during excavation
operations
• A physical barrier defining the
boundary between the Exclusion • Arrangements to be put in place
Zone and the Restricted Area at all to allow other personnel to enter a
times except during excavation restricted area for a special reason.
In some cases this will involve
stopping work or restricting plant
movement
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 8 of 14
Control of Exclusion Zones • After a defined time for the
first test, monitor the strength
The Exclusion Zone will be under the development of the test panel
control of the named Exclusion Control using a properly calibrated
Supervisor or his nominated deputy, penetrometer following the
and under no circumstances should this manufacturer’s and relevant BS
person be in a position where they could guidelines with a sufficient number
be distracted from this function. of tests to remove variability
At all times the following must be in concerns in the results
place when an Exclusion Zone is in
operation: • When the panel test results have
achieved the specified minimum
• A physical barrier between the strength level, confirm agreement
Exclusion Zone and the Restricted between the Exclusion Zone
Area at all times except during Supervisor and Exclusion Zone
tunnel excavation Engineer that these requirements
have been met and it is acceptable
• A clear board or sign explaining to undertake penetrometer tests
the Exclusion Zone limits under on the profile of the last sprayed
particular work activities (see concrete
example in Appendix)
• Undertake strength development
Release of Exclusion and Restricted test, using a penetrometer, of the
Zones last sprayed profile to confirm that
this has achieved the minimum
The following process should be strength specified. This test should
followed during working activities be undertaken by standing as
before an Exclusion Zone can be close to the side wall as possible.
released to a Restricted Area: The central area of the tunnel
should remain an Exclusion Zone
• At the end of spraying activities where geometry (size) permits.
for the particular advance, spray Use of specially formed protective
test panels for strength control canopies should be employed
testing using percentage dosage of where deemed necessary to ensure
accelerator used in the advance the safety of personnel working in
this area
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 9 of 14
• When the Exclusion zone Where tunnel geometry has allowed a
Supervisor and Exclusion Zone central area Exclusion Zone under the
Engineer agree that all minimum crown to remain, release of the full face
requirements have been met, the area shall only be permitted when:
Exclusion Zone Supervisor may
release the zone to a Restricted • All the above criteria for the
Area for defined operations within release of an Exclusion Zone have
this area. All works within this area been met
should be undertaken within 2m • Additional criteria set by the
of the side wall with the central contractor and accepted by the CRL
section of the tunnel (ie under PM for strength gain or time delay
the crown between approximately have been met
10 o’clock and 2 o’clock) should
remaining an Exclusion Zone A Restricted Area may be released to a
where tunnel geometry allows. Normal Access Zone when:
Use of specially formed protective
canopies should be employed • The exclusion zone has advanced
where deemed necessary to ensure or been removed so that the
the safety of personnel working in minimum length of the Restricted
this area Area(s) is not breached
• The Exclusion Zone Supervisor
or his deputy has agreed that
a change in status is acceptable
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 10 of 14
C510 – Whitechapel and Liverpool Street Station Tunnels
Exclusion Zones for Tunnelling Operations
Mucking Cycle:
Restriction Zone C: Restriction Zone B: Exclusion Zone A:
Access for personnel Access for Lead Miner, Engineer No access to any
involved in the & essential personnel. Entry only personnel.
works. * when excavator has stopped. *
Walkway ends 10m from excavator
Restriction Zone C * Restriction Zone B *
Escorted visitors may only No access on blind side of
enter restriction zone C only excavator.
if deemed suitable by their No entry passed dumper
escort. being loaded.
Spraying Cycle:
Restriction Zone D: Restriction Zone C: Restriction Zone B: Restriction Zone A:
Access for personnel Access for essential Access for Nozzleman, No access to any
involved in the works. personnel only, Inspectors engineer & personnel who personnel. *
No access along blind & maintenance. Permission have only been authorised by
side of mixer truck. * must be recieved from the the nozzleman.
pump man.
2m from trailing
Walkway ends Chains edge at Axis
Restriction Zone D * Restriction Zone C * Is applicable when any part of the spray is above axis level. When spraying only below axis level
Escorted visitors Restriction Zone B extends to the face and there is no Exclusion Zone A.
may only enter
restriction zone D
only if deemed Restriction Zone A * Under no circumstances must this area be entered until checks on a panel have been carried
suitable and safe by out and entry agreed as per the General SCL Methodology WMS.
their escort.
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 11 of 14
Section C – Additional Information
Best Practice Guide – Construction Railway Train Movements Page 12 of 14
Section C
Additional Information
Communication At any time that an area changes from
an Exclusion Zone to a Restricted
The following methods should be Area, or from a Restricted Area to an
used to communicate the necessity Exclusion Zone, the Exclusion Zone
and operation of Exclusion Zones Supervisor must ensure that all barriers
and Restricted Areas to all personnel are appropriately set-up and that
within the tunnel whether working in personnel undertaking tasks close to
the tunnel for any reason, or a visitor. the exclusion zone are notified and
All communication should be through aware.
properly inducted and competent
personnel: Further Measures
• All inductions CCTV monitoring systems at the face
should be used at all SCL locations
• Toolbox talks
unless agreed by the CRL PM and
• Shift briefings to operatives and Contractor PD that they are not
staff working in the tunnel appropriate in that location.
• Site visitor briefings to all other The following additional measures
visitors should be considered and adopted
where appropriate:
• Record site specific requirements
on RESS where appropriate and • The use of thermal imaging
would not affect clarity of RESS technology to support the strength
testing and time restrictions and
Visible and protected (e.g. laminated) to search for local cold spots in
display boards depicting the Zones inaccessible areas that can not be
and Areas clearly and graphically (see examined by penetrometer testing
Appendix for example). These boards
should be at least A1 size and located • Traffic light systems or boards
close to the boundary between the to reinforce the physical barriers
Exclusion Zone and the Restricted Area, used, particularly at the boundary
and at the entry to the Restricted Area. between the Normal Access Zone
and the Restricted Area
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 13 of 14
38
Glossary of terms used in this Guide
CCTV Closed Circuit Television
CRL Crossrail Limited
PD Project Director
PM Project Manager
SCL Sprayed Concrete Lining
External standards that support the use of this Guide
BS 6164:2011 Code of practice for health and safety in tunnelling in the
construction industry
Phonetic alphabet
A Alpha J Juliet S Sierra
B Bravo K Kilo T Tango
C Charlie L Lima U Uniform
D Delta M Mike V Victor
E Echo N November W Whisky
F Foxtrot O Oscar X X-ray
G Golf P Papa Y Yankee
H Hotel Q Quebec Z Zulu
I India R Romeo
Numerals should be spelled out, not given as whole numbers:
121 is ‘one-two-one’, NOT ‘one hundred and twenty one’
Best Practice Guide – Construction
SCL ExclusionRailway
Zone Management
Train Movements Page 14 of 14
MOVING LONDON FORWARD
Best Practice Guide – SCL Exclusion Zone Management Page 15 of 14
You might also like
- High Order Large Eddy Simulation for Shock-Boundary Layer Interaction Control by a Micro-ramp Vortex GeneratorFrom EverandHigh Order Large Eddy Simulation for Shock-Boundary Layer Interaction Control by a Micro-ramp Vortex GeneratorNo ratings yet
- SCL Exclusion Zone Management GuideDocument16 pagesSCL Exclusion Zone Management GuidemgkashiNo ratings yet
- Construction Supervision Qc + Hse Management in Practice: Quality Control, Ohs, and Environmental Performance Reference GuideFrom EverandConstruction Supervision Qc + Hse Management in Practice: Quality Control, Ohs, and Environmental Performance Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- PS Confined Space 19072023Document3 pagesPS Confined Space 19072023Gustavo DucaNo ratings yet
- Excavation and Trenching: Standard Operating ProceduresDocument6 pagesExcavation and Trenching: Standard Operating ProceduresNTAMBO KABEKENo ratings yet
- Cat A 2 SOP 33 FR TankDocument14 pagesCat A 2 SOP 33 FR TankajitNo ratings yet
- Confined Space ProcedureDocument9 pagesConfined Space Procedurelucky414No ratings yet
- MS-10178 Atmosferas PeligrosasDocument14 pagesMS-10178 Atmosferas PeligrosasAndrés Acosta LaraNo ratings yet
- Guidance Note For Drop Zone Management Within The VESI - February 2016Document7 pagesGuidance Note For Drop Zone Management Within The VESI - February 2016Tigor GurningNo ratings yet
- Confined Space: Standard Operating ProceduresDocument5 pagesConfined Space: Standard Operating ProceduresNTAMBO KABEKE100% (2)
- Site ControlDocument24 pagesSite ControlEkum EdunghuNo ratings yet
- Confined-Space Entry ProgramDocument16 pagesConfined-Space Entry Programamjadkhan6573833No ratings yet
- Method Statement Bottom Up Roof Slab Concreting: Page 1 of 10Document10 pagesMethod Statement Bottom Up Roof Slab Concreting: Page 1 of 10J. Kumar Infraprojects LtdNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Systems PIP PLSC0011 Trenching and Excavation For PipelinesDocument26 pagesPipeline Systems PIP PLSC0011 Trenching and Excavation For PipelinesAbimelech SalasNo ratings yet
- Removal of Equipment (SAMPLE)Document9 pagesRemoval of Equipment (SAMPLE)Hasann MaawiaNo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces (Galvanizing Guidelines, 1999 Feb)Document7 pagesConfined Spaces (Galvanizing Guidelines, 1999 Feb)Prabath Nilan GunasekaraNo ratings yet
- OHS PROC 113 BarricadesDocument9 pagesOHS PROC 113 BarricadesPhillip L100% (1)
- Unclassified: Operating Limits and Conditions P-50099Document17 pagesUnclassified: Operating Limits and Conditions P-50099Patrick AyanNo ratings yet
- Excavation and Trenching PlanDocument21 pagesExcavation and Trenching PlanRaha SherifNo ratings yet
- Road Safety AwarenessDocument11 pagesRoad Safety AwarenessSajidNo ratings yet
- Method Statement Base Slab Concreting: Page 1 of 8Document8 pagesMethod Statement Base Slab Concreting: Page 1 of 8J. Kumar Infraprojects LtdNo ratings yet
- Excavation and Trenching Implementation PlanDocument29 pagesExcavation and Trenching Implementation Planracing.phreakNo ratings yet
- Drilling Riser, Wellhead & Conductor Structural Integrity Management in New & Remote Offshore RegionsDocument20 pagesDrilling Riser, Wellhead & Conductor Structural Integrity Management in New & Remote Offshore RegionsImelda PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Selection de Paginas 100 - 150Document51 pagesSelection de Paginas 100 - 150Giosett Alejandro VillegasNo ratings yet
- Job Procedure For Rock Blasting: Site Grading and Enabling Works For 5 Stream Alumina RefineryDocument9 pagesJob Procedure For Rock Blasting: Site Grading and Enabling Works For 5 Stream Alumina RefineryRishi RajNo ratings yet
- Appendix 9 - Eni Safety StandardDocument241 pagesAppendix 9 - Eni Safety StandardMurtadda MohammedNo ratings yet
- Barricading and Signage ProcedureDocument10 pagesBarricading and Signage ProcedureAristotel C. Cabais, RN50% (2)
- SSPC-QP 8 Qualification ProcedureDocument6 pagesSSPC-QP 8 Qualification ProcedureRinush SinagaNo ratings yet
- NFP0011A - Ground Disturbance ProcedureDocument40 pagesNFP0011A - Ground Disturbance ProcedureWajdi MansourNo ratings yet
- SBPL-Confined Space Rescue PlanDocument14 pagesSBPL-Confined Space Rescue Plannoushad e tNo ratings yet
- SSPC QP 2Document9 pagesSSPC QP 2vijay rajputNo ratings yet
- Confined-Space-Entry ProcedureDocument18 pagesConfined-Space-Entry ProcedureMayur100% (1)
- Operate Articulated Dump Trucks SafelyDocument6 pagesOperate Articulated Dump Trucks SafelyVarlee KamaraNo ratings yet
- Guidance On Practice For Inter-Facility Connectivity SelectionDocument7 pagesGuidance On Practice For Inter-Facility Connectivity Selectionpushloop1243No ratings yet
- Safe Work Method Statement For Demolition Work: Safework NSWDocument16 pagesSafe Work Method Statement For Demolition Work: Safework NSWDaniel TOMBENo ratings yet
- Method Statement - Excavation, Bracing & Backfilling WorksDocument10 pagesMethod Statement - Excavation, Bracing & Backfilling WorksKamal Deo ShahNo ratings yet
- Safety Department guidance on ionising radiationsDocument7 pagesSafety Department guidance on ionising radiationsLenaj EbronNo ratings yet
- Permit Work System Rev.03Document75 pagesPermit Work System Rev.03tusharDJ100% (1)
- Policy and Procedure Utility Shutdown: ORF Manual OGD-1107-DTR-1205 Division of Technical Resources Dhhs/Nih/Od/OrfDocument8 pagesPolicy and Procedure Utility Shutdown: ORF Manual OGD-1107-DTR-1205 Division of Technical Resources Dhhs/Nih/Od/OrfGreeshma CertvalueNo ratings yet
- Lifting Operations 2.034Document10 pagesLifting Operations 2.034svdnolen0% (1)
- Explosives in Demolition - Exclusive ZoneDocument2 pagesExplosives in Demolition - Exclusive ZoneVignesh KmNo ratings yet
- CIS16-2009 - Guidelines For Works at Confined Areas in Construction SiteDocument42 pagesCIS16-2009 - Guidelines For Works at Confined Areas in Construction SiteVincent 2020No ratings yet
- Plans and Preparation Manual - Roadside SafetyDocument22 pagesPlans and Preparation Manual - Roadside SafetyJuncel BayogoNo ratings yet
- Barricade StandardDocument5 pagesBarricade StandardPerwez21No ratings yet
- Confined Spaces Program EssentialsDocument20 pagesConfined Spaces Program EssentialsIoana UrsanNo ratings yet
- NR 33 - Confined - SpacesDocument20 pagesNR 33 - Confined - SpacesCPSSTNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Procedure: ScopeDocument9 pagesConfined Space Procedure: Scopeandi permanaNo ratings yet
- Guide to using generic Safe Work Method StatementsDocument11 pagesGuide to using generic Safe Work Method StatementsAnshuman GNo ratings yet
- SWMS Work in A Confined SpaceDocument5 pagesSWMS Work in A Confined SpaceTamo Kim ChowNo ratings yet
- D4276 7489 PDFDocument4 pagesD4276 7489 PDFJuan Esteban ArjonaNo ratings yet
- NGM-ADMIN-HS-PROC-009 - Confined Space ProcedureDocument14 pagesNGM-ADMIN-HS-PROC-009 - Confined Space ProcedureAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Ed Well ControlDocument18 pagesEd Well ControlAmeer BabylonianNo ratings yet
- PNR-000069 - 08 - PNR-00069 - Critical Activities Requirements-Rev08Document79 pagesPNR-000069 - 08 - PNR-00069 - Critical Activities Requirements-Rev08nathalia ferreiraNo ratings yet
- National Water Company's Excavation Safety GuideDocument17 pagesNational Water Company's Excavation Safety GuidemerinofalNo ratings yet
- Range Design JSP403 Vol2 Chap05 DLRSCDocument11 pagesRange Design JSP403 Vol2 Chap05 DLRSCBallisticsNo ratings yet
- Working Near Overhead Powerlines: Standard Operating ProceduresDocument4 pagesWorking Near Overhead Powerlines: Standard Operating ProceduresNTAMBO KABEKENo ratings yet
- Confined Space Policy: Potential Fatal Risks PolicyDocument3 pagesConfined Space Policy: Potential Fatal Risks PolicyOfer GardenNo ratings yet
- 2864Document36 pages2864rakanNo ratings yet
- Cse ProcedureDocument24 pagesCse ProcedureMuhammad Usman100% (1)
- Hazard AreaDocument2 pagesHazard Areamohamed abourayaNo ratings yet
- Fixed End MomentsDocument1 pageFixed End MomentsHarold DeanNo ratings yet
- Lime MortarsDocument22 pagesLime MortarsmosbridgeNo ratings yet
- Composite Beam Design To EC4Document148 pagesComposite Beam Design To EC4mosbridgeNo ratings yet
- Companion To EC5Document262 pagesCompanion To EC5mosbridgeNo ratings yet
- Linea de CedenciaDocument175 pagesLinea de CedenciaKatherine Prado100% (1)
- Elastic Critical Moment For Lateral Torsional BucklingDocument14 pagesElastic Critical Moment For Lateral Torsional BucklingAndrey SemjonovNo ratings yet
- Advice Note Bolt Not Protruding Beyond NutDocument1 pageAdvice Note Bolt Not Protruding Beyond NutmosbridgeNo ratings yet
- Designers' Guide To Eurocode 1 - Actions On BridgesDocument256 pagesDesigners' Guide To Eurocode 1 - Actions On Bridgesalbsteinpor100% (3)
- New Concrete StandardsDocument20 pagesNew Concrete StandardsAlan Toomey50% (2)
- Smart EE June 2022 - PackageDocument19 pagesSmart EE June 2022 - PackageMercy FeNo ratings yet
- Delhi (The Capital of India) : Ebook by Ssac InstituteDocument27 pagesDelhi (The Capital of India) : Ebook by Ssac InstituteAnanjay ChawlaNo ratings yet
- PediculosisDocument14 pagesPediculosisREYMARK HACOSTA100% (1)
- SMEs, Trade Finance and New TechnologyDocument34 pagesSMEs, Trade Finance and New TechnologyADBI EventsNo ratings yet
- TNTCL Cost Data 2021 22Document95 pagesTNTCL Cost Data 2021 22Akd DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Service Parts List: 54-26-0005 2551-20 M12™ FUEL™ SURGE™ 1/4" Hex Hydraulic Driver K42ADocument2 pagesService Parts List: 54-26-0005 2551-20 M12™ FUEL™ SURGE™ 1/4" Hex Hydraulic Driver K42AAmjad AlQasrawi100% (1)
- Themes in Romeo and JulietDocument7 pagesThemes in Romeo and JulietChiosa AdinaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineer with Experience in Heavy Mining Machinery MaintenanceDocument1 pageMechanical Engineer with Experience in Heavy Mining Machinery MaintenanceCertified Rabbits LoverNo ratings yet
- SS1c MIDTERMS LearningModuleDocument82 pagesSS1c MIDTERMS LearningModuleBryce VentenillaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2-Week 2-Module 4-Evidence of EvolutionDocument16 pagesGeneral Biology 2-Week 2-Module 4-Evidence of EvolutionFEMALE Dawal LaizaNo ratings yet
- Body Shaming Among School Going AdolesceDocument5 pagesBody Shaming Among School Going AdolesceClara Widya Mulya MNo ratings yet
- 96 Amazing Social Media Statistics and FactsDocument19 pages96 Amazing Social Media Statistics and FactsKatie O'BrienNo ratings yet
- INVENTORY MANAGEMENT TechniquesDocument24 pagesINVENTORY MANAGEMENT TechniquesWessal100% (1)
- European Business in China Position Paper 2017 2018 (English Version)Document408 pagesEuropean Business in China Position Paper 2017 2018 (English Version)Prasanth RajuNo ratings yet
- Steel Glossary RBC Capital GoodDocument10 pagesSteel Glossary RBC Capital Goodrajesh pal100% (1)
- 4 TheEulerianFunctions - 000 PDFDocument16 pages4 TheEulerianFunctions - 000 PDFShorouk Al- IssaNo ratings yet
- Answer Questions Only: Chemical Engineering DeptDocument2 pagesAnswer Questions Only: Chemical Engineering DepthusseinNo ratings yet
- Reversing a String in 8086 Micro Project ReportDocument4 pagesReversing a String in 8086 Micro Project ReportOm IngleNo ratings yet
- Bal - 2011 - The New HRM in The 21st Century - A Strategic ViewDocument15 pagesBal - 2011 - The New HRM in The 21st Century - A Strategic ViewJoaquínMartínezMiñoNo ratings yet
- Organic Facial Remedies Versus Inorganic Facial RemediesDocument13 pagesOrganic Facial Remedies Versus Inorganic Facial Remediesapi-271179911No ratings yet
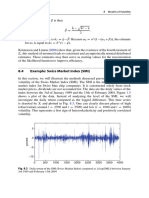
- 8.4 Example: Swiss Market Index (SMI) : 188 8 Models of VolatilityDocument3 pages8.4 Example: Swiss Market Index (SMI) : 188 8 Models of VolatilityNickesh ShahNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The FUPLA 2 Tools: Project DatabaseDocument2 pagesAn Overview of The FUPLA 2 Tools: Project DatabaseJulio Cesar Rojas SaavedraNo ratings yet
- The Interview: P F T IDocument14 pagesThe Interview: P F T IkkkkccccNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide To E-Commerce TechnologyDocument420 pagesComplete Guide To E-Commerce Technologypilatus100% (4)
- Winkens Et Al 2009Document8 pagesWinkens Et Al 2009Marta SanchezNo ratings yet
- District Wise List of Colleges Under The Juridiction of MRSPTU BathindaDocument13 pagesDistrict Wise List of Colleges Under The Juridiction of MRSPTU BathindaGurpreet SandhuNo ratings yet
- Starting A Business Candle Making 2009Document2 pagesStarting A Business Candle Making 2009Carlo Fabros Junio100% (4)
- Second Quarterly Examination Math 9Document2 pagesSecond Quarterly Examination Math 9Mark Kiven Martinez94% (16)
- Durand Et Al JHRC 1997 Experimental Design Optimization of The Analysis of Gasoline by Capillary Gas ChromatographyDocument6 pagesDurand Et Al JHRC 1997 Experimental Design Optimization of The Analysis of Gasoline by Capillary Gas ChromatographyCatalinaSalamancaNo ratings yet
- Technology Consulting: Amruta Kulkarni Anu Abraham Rajat JainDocument9 pagesTechnology Consulting: Amruta Kulkarni Anu Abraham Rajat JainRajat JainNo ratings yet
- A Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesFrom EverandA Poison Like No Other: How Microplastics Corrupted Our Planet and Our BodiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemFrom EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNo ratings yet
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Petroleum Process SafetyFrom EverandIntroduction to Petroleum Process SafetyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Incidents That Define Process SafetyFrom EverandIncidents That Define Process SafetyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsFrom EverandGuidelines for Auditing Process Safety Management SystemsNo ratings yet
- Nutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeFrom EverandNutritional and Therapeutic Interventions for Diabetes and Metabolic SyndromeNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 3D Printing of Concrete: State of the Art and Challenges of the Digital Construction RevolutionFrom Everand3D Printing of Concrete: State of the Art and Challenges of the Digital Construction RevolutionArnaud PerrotNo ratings yet
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationFrom EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsFrom EverandPractical Industrial Safety, Risk Assessment and Shutdown SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Rules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersFrom EverandRules of Thumb for Maintenance and Reliability EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Safety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryFrom EverandSafety Fundamentals and Best Practices in Construction IndustryNo ratings yet
- Radium Girls: Women and Industrial Health Reform, 1910-1935From EverandRadium Girls: Women and Industrial Health Reform, 1910-1935Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Guidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Implementing Process Safety ManagementNo ratings yet
- Autophagy in Health and DiseaseFrom EverandAutophagy in Health and DiseaseBeverly RothermelNo ratings yet
- Safety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straight forward Guide to Functional Safety, IEC 61508 (2010 EDITION) and Related Standards, Including Process IEC 61511 and Machinery IEC 62061 and ISO 13849From EverandSafety Critical Systems Handbook: A Straight forward Guide to Functional Safety, IEC 61508 (2010 EDITION) and Related Standards, Including Process IEC 61511 and Machinery IEC 62061 and ISO 13849Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Safety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaFrom EverandSafety and Intelligent Transport Systems Development in the People’s Republic of ChinaNo ratings yet
- One Health: Integrated Approach to 21st Century Challenges to HealthFrom EverandOne Health: Integrated Approach to 21st Century Challenges to HealthJoana C. PrataNo ratings yet
- The Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeFrom EverandThe Invisible Rainbow: A History of Electricity and LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Exercise, Sport, and Bioanalytical Chemistry: Principles and PracticeFrom EverandExercise, Sport, and Bioanalytical Chemistry: Principles and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection Engineering in Building DesignFrom EverandFire Protection Engineering in Building DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- The Construction Safety Guide: Injury and Illness Prevention through DesignFrom EverandThe Construction Safety Guide: Injury and Illness Prevention through DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)