Professional Documents
Culture Documents
اكمل و تمارين اعدادي هندسة ترم اول
Uploaded by
Ahmed aliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
اكمل و تمارين اعدادي هندسة ترم اول
Uploaded by
Ahmed aliCopyright:
Available Formats
Properties of matter prep.
Engineering 2022 - 1st term
Complete ) ( هذا السؤال يصلح ان يكون اختياري او صواب و خطأ
1) The measure various physical quantities three
fundamental units are commonly used in physics length ,
math and time
2) There are three systems of units MKS , CGS and FPS
3) In “ MKS “ system the units of length is meter , the unit
of mass is kilogram and the unit of time is second
4) In “ CGS “ system the unit of length is centimeter , the
unit of mass is gram and the unit of time is second
5) International system of units “ SI “ is a coherent system
consisting of six units they are meter , kilogram ,
second , ampere , degree Kelvin and candela
6) The main limitations of dimensional analysis are :
I. Doesn’t give us any information about the
dimensionless constant
II. It’s not applicable to trigonometrically and
exponential functions
III. It can’t used when a physical quantity depends
on more than three quantities
7) The main uses of dimensional equations are :
I. Test the correctness of equations
II. Derive the equations
III. Convert one system of units into another one
IV. Recapitulate important formulae
8) The ratio of stress to the strain is called elastic modulus
and it’s constant
PROF / AHMED ALI Tel.: 01115656361 SMART ACADEMY- 2022
Properties of matter prep. Engineering 2022 - 1st term
9) There are three elastic modules are young’s modulus ,
shear modulus and bulk modulus
10) The hook’s law is valid within the elastic limit and for
small strains
11) The shear stress is defined as the ratio of tangential
deforming face ( F ) to the area ( A ) of the face being
shared ( F / A )
12) The change in the length due to deforming face is
described by young’s modulus
13) The young’s modulus is defined as the ratio of tensile
F /A
stress to tensile strain ( Y = L / L )
14) The equation of Poisson’s ratio is
lateral strain d / d
=
longitudinal strain L / L
15) The ratio of lateral strain to the longitudinal strain is
called as Poisson's ratio
16) The physical meaning of Poisson's ratio is change in
length causes change in diameter
17) The isothermal bulk modulus is equal to
dP
B isothermal = P = but the adiabatic bulk modulus is
dV /V
dP
equal to B isothermal = p =
dV /V
PROF / AHMED ALI Tel.: 01115656361 SMART ACADEMY- 2022
Properties of matter prep. Engineering 2022 - 1st term
18) The isothermal process mean’s the process of change
in pressure or volume when the temperature is
constant , but the adiabatic process happened when the
system is isolated
19) When the fluid particles moves along the path , above a
certain velocity the flow becomes irregular and motion
is random and that’s called turbulent flow
20) The equation of continuity is A1 V1 = A2 V2
21) The relation between pressure , speed and elevation is
called as Bernoulli’s equation
22) The fluid witch using in Bernoulli’s equation is an
incompressible and non-viscous
23) Sprayer is an application of Bernoulli’s equation
24) The “ SI “ unit of Viscosity is N . S / m2 and “ CGS “
unit is Dyne . S / Cm2
25) The property of fluid of resisting the shearing
motion is called as Viscosity
26) The coefficient of viscosity ( ) mean’s the ratio
between shear stress and the change in shear strain
F. h A. V
and it’s equal ( )
27) Surface tension is the property of a liquid by which
the free surface of a liquid behaves like a stretched
membranes
28) The relation between the surface energy and the surface
tension is equal to T F 2L
PROF / AHMED ALI Tel.: 01115656361 SMART ACADEMY- 2022
Properties of matter prep. Engineering 2022 - 1st term
29) The angle of contact in the case of water is acute ( less
than 90 ) but the angle of contact in the case of mercury
is obtuse ( more than 90 )
30) Surface energy equal the sum of the mechanical work
done and the heat absorbed from the atmosphere
(S=T+H)
31) The surface tension in isothermal conditions equal
( T = S – H ) but in adiabatic conditions equal (S = T)
32) The mutual attraction between the molecules of the
same substance is called as cohesion force
33) The adhesion force is the mutual attraction between
the molecules of different substances
34) The excess of pressure inside a soap bubble is equal to
P 2T and it’s “ SI “ unit is Newton’s / m2
r
35) The angle between the free surface of a liquid and
the surface of a tube is called as angle of contact
36) When the rigid object is in motion , it has two motions
translational and rotational
37) The angle momentum of the particle is defined as the
cross product of its position vector ( r ) and linear
momentum ( p ) so ( L = r × p )
38) The relation between angular momentum and angular
velocity is L I . m r 2 .
PROF / AHMED ALI Tel.: 01115656361 SMART ACADEMY- 2022
Properties of matter prep. Engineering 2022 - 1st term
39) The relation between rotational kinetic energy and the
1
moment of inertia is equal E t . k I . 2
2
40) The moment of inertia of solid cylinder is equal
1
I M R2 but the moment of inertia of hoop is equal
2
I M R2
41) A physical or compound pendulum is a rigid body
suspended from a fixed axis , which is not passing
through the center of mass
42) The change of circuit parameter, characteristic, or
behaves due to instrument operation without
maintains is called as loading effect
43) The range is defined as that region enclosed by the
limits within which a particular quantity is measured
44) The smallest change in input that the instruments can
response to it is called as resolution
45) The deviation of the measured value from the true
value is called as error
46) Errors may come from different sources and are usually
classified under two main heading its systematic errors
and random errors
The kinetic energy of an object as the energy associated
with its motion through space.
PROF / AHMED ALI Tel.: 01115656361 SMART ACADEMY- 2022
Properties of matter prep. Engineering 2022 - 1st term
Some problems
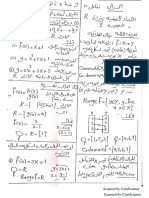
1) In Jaeger's experiment, a capillary tube of internal diameter
5x10-4 m dips 3x10-2m inside water contained in a beaker. The
difference in level of water manometer when the bubble is released
is 0.09 m. Calculate the Surface tension of water.
The Answer
2𝑇
= (𝐻𝜌2 𝑔 − ℎ1 𝜌1 𝑔)
𝑟
𝑟𝑔
T= (𝐻𝜌2 − ℎ1 𝜌1 )
2
Here r = 2.5×10-4 m
g = 9.8 m/s2
H = 0.09 m
h1 = 3×10-2 m = 0.03 m
ρ1 = ρ2 = 103 kg/m3
2.5×10−4 ×9.8
∴ T= (0.09 × 10−3 − 0.03 × 103 )
2
T = 73.5×103 N/m.
2) A mercury drop of radius 1 cm is sprayed into one million drops of
the same size. Calculate the energy expended. Surface tension of
mercury = 73x10-3 N/m.
The Answer
T = 35×10-3 N/m
R = 1 cm= 10-2 m
Radius of each small drop = r
PROF / AHMED ALI Tel.: 01115656361 SMART ACADEMY- 2022
Properties of matter prep. Engineering 2022 - 1st term
4 4
∴ πR3 = 106 × πr3
3 3
R = 100 r
𝑅 10−2
r= = = 10−4 𝑚
100 100
Increase in area = (106×4πr2) − 4πR2
= [10×4π(10-4)2] − 4π(10-4)2] − 4π(10-2)2
= 4π [10-2− 10-4]
= 4π ×99×10-4 m2
Energy expended = (surface tension) (increase in area)
= 35×10-3×4π×99×10-4 J
= 4.355×10-3 J
3) Calculate the amount of energy needed to break a drop of water of
diameter 2x10-3 m into 109 droplets of equal size. Surface tension
of water = 72x10-3 N/m.
The Answer
R = 10-3m
4 3 4𝜋 3
𝜋𝑅 = 109 × 𝑟
3 3
R = 103 r
𝑅 10−3
r= = =10-6m
103 103
Increase in surface area
A = 109×4πr2 − 4πR2
A = 4π[109×(10-6)2−(10-3)2]
A = 4π × 999×10-6m2
PROF / AHMED ALI Tel.: 01115656361 SMART ACADEMY- 2022
Properties of matter prep. Engineering 2022 - 1st term
T = 72 × 10-3 N/m
Energy required = T × A
= 72× 10-3×4π×999×10-6 J
= 1.9040 ×10-4 J
4) Consider an oxygen molecule (O2) rotating in the ( XY ) plane
about the (z) axis. The rotation axis passes through the center of
the molecule, perpendicular to its length. The mass of each oxygen
atom is ( 2.66 x 10-26 kg ) , and at room temperature the average
separation between the two atoms is ( d = 1.21 x 10-10 m ) (The
atoms are modeled as particles.)
(A) Calculate the moment of inertia of the molecule about the (z) axis.
(B) If the angular speed of the molecule about the (z) axis is 4.60 x 1012
rad/s , what is its rotational kinetic energy?
Solution:
We apply the result we just calculated for the moment of inertia in the
equation for KR:
PROF / AHMED ALI Tel.: 01115656361 SMART ACADEMY- 2022
Properties of matter prep. Engineering 2022 - 1st term
5) Calculate the excess of pressure inside a soap bubble of radius
3x10-3m. Surface tension of a soap solution is =20x10-3 N/m.
Calculate also the surface energy of the soap bubble.
) و التوتر3×10-3m ( احسب الضغط القياسي داخل فقاعة من الصابون نصف قطرها
ثم أحسب الطاقة السطحية للفقاعة. ) 20×10-3N/m ( السطحي للصابون
The Answer
4𝑇
P=
𝑟
Here T = 20×10-3N/m , R = 3×10-3m
4×20×10−3
∴ P=
3×10−3
P = 26.66N/m2
surface energy = ( surface tension ) × ( total surface area )
= T × 2 × 4πr2
=
20 × 10-3 × 2 × 4π × ( 3 × 10-3 )2
= 4.525 × 10-6 J
مع التمنيات بالتوفيق
أحمد علي. د01115656361
ماجستير الرياضيات و االحصاء كلية البحوث و الدراسات االحصائية
دبلوم النانو فيزياء جامعة القاهرة
PROF / AHMED ALI Tel.: 01115656361 SMART ACADEMY- 2022
You might also like
- The Origin of Mass - IliopoulosDocument151 pagesThe Origin of Mass - IliopoulosWilliam Fernando Quintero QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Wave Forces On Vertical CylinderDocument22 pagesWave Forces On Vertical CylinderInayatul LailiyahNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Mathematics Paper 1 Term 1 Form Three 121/1Document13 pagesForm 3 Mathematics Paper 1 Term 1 Form Three 121/1Lindsay Halimani100% (2)
- Wave Forces on Small Diameter Structural MembersDocument25 pagesWave Forces on Small Diameter Structural Members금동민No ratings yet
- 01 Physics 9 Chap 1Document47 pages01 Physics 9 Chap 1Ashraf Javed50% (2)
- Viscosity Lab ReportDocument13 pagesViscosity Lab ReportBASEKI JANI100% (4)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics 12 May Chapter 2 Units and MeasurementsDocument18 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics 12 May Chapter 2 Units and Measurementsnithya M.No ratings yet
- Physics AssignmentDocument22 pagesPhysics AssignmentVeerareddy Vippala100% (1)
- 6 Chemical Bonding 2Document17 pages6 Chemical Bonding 2Akn NanthanNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Oce421 Lect19Document20 pagesOce421 Lect19Nyi NyiNo ratings yet
- Buet M.SC Wre Admission 2021 Question SolutionDocument9 pagesBuet M.SC Wre Admission 2021 Question SolutionAmit Kumar Mondol100% (1)
- XI Physics: Chapter - 2 Assignment - Units and MeasurementsDocument6 pagesXI Physics: Chapter - 2 Assignment - Units and MeasurementsVinitNo ratings yet
- Solution: Choose The Correct Answer From The Following Multiple Choices QuestionsDocument3 pagesSolution: Choose The Correct Answer From The Following Multiple Choices QuestionsabdullahNo ratings yet
- Solution: Choose The Correct Answer From The Following Multiple Choices QuestionsDocument3 pagesSolution: Choose The Correct Answer From The Following Multiple Choices QuestionsabdullahNo ratings yet
- Student Solutions to Thermodynamics QuestionsDocument3 pagesStudent Solutions to Thermodynamics QuestionsabdullahNo ratings yet
- Solution: Choose The Correct Answer From The Following Multiple Choices QuestionsDocument3 pagesSolution: Choose The Correct Answer From The Following Multiple Choices QuestionsabdullahNo ratings yet
- Basic Fluid Concepts and Properties (μ, ρ, γDocument41 pagesBasic Fluid Concepts and Properties (μ, ρ, γMiraJo-LingNo ratings yet
- Department of Applied Physics Question Bank-I Semester PH6151-Engineering Physics - I UNIT-II - Properties of Matter and Thermal PhysicsDocument4 pagesDepartment of Applied Physics Question Bank-I Semester PH6151-Engineering Physics - I UNIT-II - Properties of Matter and Thermal PhysicsJohn Ernie SelmarNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics PDFDocument3 pages11 Physics PDFSanjay_Sharma_8073No ratings yet
- Class-11th Physics ASSIGNMENT UNIT-1 ForcesDocument3 pagesClass-11th Physics ASSIGNMENT UNIT-1 ForcesRimple SwamiNo ratings yet
- Code Q3 OLABH Qs Ans Solution NEET 2022Document71 pagesCode Q3 OLABH Qs Ans Solution NEET 2022Anantha PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Extra WEAR SolutionsDocument7 pagesExtra WEAR SolutionsGiannis MamalakisNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: University of LeedsDocument16 pagesFluid Mechanics: University of LeedsHasitha MadusankaNo ratings yet
- Thermofluids Dimensional Analysis and Similarity ExamplesDocument5 pagesThermofluids Dimensional Analysis and Similarity ExamplesRobyn GautamNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics Solutions - Chapter 26Document76 pagesFundamentals of Physics Solutions - Chapter 26maddmagg100% (1)
- JME 3700 Final Exam: May 4, 2020 NameDocument5 pagesJME 3700 Final Exam: May 4, 2020 NameMichael WendlNo ratings yet
- Round 1 Section 1 Nov 2019Document8 pagesRound 1 Section 1 Nov 2019Mehnaz kNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Example ProblemsDocument4 pagesModule 3 Example ProblemsMark Kevin EnriquezNo ratings yet
- DPP 1Document3 pagesDPP 1Mihika Tamrakar VIII DNo ratings yet
- Solutions Code 0 JEEAdvanced2013 VMC SolvedDocument28 pagesSolutions Code 0 JEEAdvanced2013 VMC SolvedShashank ShekharNo ratings yet
- Ta Zc233 Ec-3r Second Sem 2017-18Document2 pagesTa Zc233 Ec-3r Second Sem 2017-18Abhishek SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Units and DimensionsDocument2 pagesUnits and DimensionsDheeraj Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Exam 2022 Session 2 - 27 Jul Shift 1Document25 pagesJEE Main Exam 2022 Session 2 - 27 Jul Shift 1Jeshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Python Exercise: (X+ Y) (x+3 Y)Document2 pagesPython Exercise: (X+ Y) (x+3 Y)Lorna AhlaamiNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument28 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelJazzNo ratings yet
- Solution of Fundamentals of Physics 9th Edition SoDocument1,643 pagesSolution of Fundamentals of Physics 9th Edition SoIbrahim MalikNo ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 2: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocument19 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 2: Back of Chapter QuestionsTHE VCNo ratings yet
- 24.09.22 - SR - STAR CO-SC (MODEL-A) - Jee - Main - GTM-2 - QPDocument20 pages24.09.22 - SR - STAR CO-SC (MODEL-A) - Jee - Main - GTM-2 - QPSanthosh GoparajuNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Measurement and UncertainitesDocument8 pagesTopic 1 Measurement and UncertainitesmimiNo ratings yet
- Board PhysicsDocument9 pagesBoard PhysicsDurgesh Yadav100% (1)
- Final ExamPhysics1 (1)Document3 pagesFinal ExamPhysics1 (1)thảo nguyễn thanhNo ratings yet
- Additional Tutorial 1Document3 pagesAdditional Tutorial 1lllNo ratings yet
- For Candidates Applying For Physics, and Physics and PhilosophyDocument8 pagesFor Candidates Applying For Physics, and Physics and PhilosophyAhmad HaikalNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics 2 MEC 3706 Exercise Sheet 2 and SolutionDocument18 pagesAerodynamics 2 MEC 3706 Exercise Sheet 2 and SolutionJarvis AsiNo ratings yet
- Surface Tension PDFDocument7 pagesSurface Tension PDFNsBhasinNo ratings yet
- Cebep Reviewer Set 1Document33 pagesCebep Reviewer Set 1Loysa Agtarap MataNo ratings yet
- Compile BLM Ada Punya Anggi Nina Rana DiviDocument10 pagesCompile BLM Ada Punya Anggi Nina Rana DiviSelma Regita MahardiniNo ratings yet
- Road DustDocument20 pagesRoad DustErikos StapountzisNo ratings yet
- 24.09.22 SR - Star Co-Sc (Model-A) Jee Main Gtm-2 QPDocument23 pages24.09.22 SR - Star Co-Sc (Model-A) Jee Main Gtm-2 QPbchandu3264No ratings yet
- PHY111 Unit and DimensionDocument14 pagesPHY111 Unit and DimensionOluwaferanmi OgunleyeNo ratings yet
- Atomic Energy Central School mid-term exam physics questionsDocument3 pagesAtomic Energy Central School mid-term exam physics questions39 Yogendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Solution- CopyDocument28 pagesPhysics Solution- CopysharadamastaNo ratings yet
- hw_3solution.pdfDocument6 pageshw_3solution.pdfanna.heeohNo ratings yet
- 9 Vlaski S Use of Broms Method PDFDocument8 pages9 Vlaski S Use of Broms Method PDFMonal RajNo ratings yet
- Engineering Academy: ESE Conventional Revision TEST - IDocument8 pagesEngineering Academy: ESE Conventional Revision TEST - Ividya chakitwarNo ratings yet
- CFD Ansys Ex 3Document13 pagesCFD Ansys Ex 3anil yadavNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document11 pagesAssignment 1Robert JacksonNo ratings yet
- Indian Association of Physics Teachers National Standard Examinations 2008 - 2009 Solutions / AnswersDocument7 pagesIndian Association of Physics Teachers National Standard Examinations 2008 - 2009 Solutions / AnswersKshitij SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Aug-Dec 2013: Professor Dr. Luis E. Lesser Carrillo Hydrogeologist/Environmental EngineenerDocument44 pagesFluid Mechanics Aug-Dec 2013: Professor Dr. Luis E. Lesser Carrillo Hydrogeologist/Environmental EngineenerarunyogaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Etching: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.4Document14 pagesChemical Etching: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.4Василь ІванинаNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For C-100 2020 (Atomic Structure) Question One: Choose The Correct AnswerDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank For C-100 2020 (Atomic Structure) Question One: Choose The Correct AnswerAhmed aliNo ratings yet
- Q1: Answer (T) For True Sentences or (F) For False Sentences: (One Mark For Each)Document5 pagesQ1: Answer (T) For True Sentences or (F) For False Sentences: (One Mark For Each)Ahmed aliNo ratings yet
- Vector and Kinematics Problems AnswersDocument14 pagesVector and Kinematics Problems AnswersAhmed aliNo ratings yet
- مذكرة التفاضلDocument41 pagesمذكرة التفاضلAhmed aliNo ratings yet
- Parts PDFDocument10 pagesParts PDFashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- مذكرة اختياري بالاجابات للجزء النظريDocument8 pagesمذكرة اختياري بالاجابات للجزء النظريAhmed aliNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Circuits True or False No. 1Document2 pagesElectrical and Electronic Circuits True or False No. 1Ahmed aliNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant NotesDocument42 pagesNuclear Power Plant Notesbhaskar bhaleraoNo ratings yet
- Science Corner Production 3 @2021Document1 pageScience Corner Production 3 @2021Davies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Phys22 Fad Student Book AkDocument21 pagesPhys22 Fad Student Book AkSamah MohamedNo ratings yet
- Negative permeability and permittivity of metamaterialsDocument6 pagesNegative permeability and permittivity of metamaterialsNewton GomesNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics FormulaDocument2 pagesO Level Physics FormulaAukasha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nat Reviewer Physical ScienceDocument45 pagesNat Reviewer Physical SciencedenmarkkalboNo ratings yet
- Planck's Blackbody Radiation Law: Presentation in Different Domains and Determination of The Related Dimensional ConstantsDocument25 pagesPlanck's Blackbody Radiation Law: Presentation in Different Domains and Determination of The Related Dimensional ConstantssurendraNo ratings yet
- Two-Dimensional Motion Physics ProblemsDocument4 pagesTwo-Dimensional Motion Physics ProblemsMarcial Aguilar BarahonaNo ratings yet
- AtmotsferaDocument241 pagesAtmotsferaCarlos Andres Barrera BarreraNo ratings yet
- CBSE 2020 Grade 12 Physic Theory Series HMJ/1 SET-3 Code No. 55/1/3Document15 pagesCBSE 2020 Grade 12 Physic Theory Series HMJ/1 SET-3 Code No. 55/1/3Darkest LifeNo ratings yet
- Molecular Dynamics Simulation On Evaporation of Water and Aqueous Droplets in The Presence of Electric FieldDocument11 pagesMolecular Dynamics Simulation On Evaporation of Water and Aqueous Droplets in The Presence of Electric FieldSaeed AbdNo ratings yet
- WPH12 01 Que 20211012Document28 pagesWPH12 01 Que 20211012Abdo AlkelaniNo ratings yet
- CFD Simulation of Flow Through Packed Beds Using Finite Volume TechniqueDocument220 pagesCFD Simulation of Flow Through Packed Beds Using Finite Volume Techniquecholila_tamzysiNo ratings yet
- Tutorials On Electric FieldDocument2 pagesTutorials On Electric FieldNkeng100% (1)
- EP 222: Classical Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 2Document2 pagesEP 222: Classical Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 2Ashok GargNo ratings yet
- Aits 2122 CRT I JeemDocument20 pagesAits 2122 CRT I JeemAtharv Sanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Huang Et Al-2019-Journal of The American Ceramic SocietyDocument12 pagesHuang Et Al-2019-Journal of The American Ceramic Societyचन्द्रभाल सिंहNo ratings yet
- The Circle PDFDocument16 pagesThe Circle PDFEbookcrazeNo ratings yet
- GC2 Q3 Week-2B-1Document6 pagesGC2 Q3 Week-2B-1Gerrylie GallardoNo ratings yet
- Electric FieldDocument4 pagesElectric Fieldsebut saja anonimNo ratings yet
- Multiplication 1Document45 pagesMultiplication 1OnucaNo ratings yet
- Grade9 CBSE MotionDocument40 pagesGrade9 CBSE MotionSamarth KatariyaNo ratings yet
- Muktijuddher Potovumi (1947-1966) by NH Ahmed ShamimDocument12 pagesMuktijuddher Potovumi (1947-1966) by NH Ahmed ShamimNaziah Rahman Chowdhury Tania100% (1)
- Dipole Moments and Molecular StructureDocument4 pagesDipole Moments and Molecular Structurevenkitheboss100% (1)
- Equation of State: Eos - Linear - Polynomial Eos - GruneisenDocument1 pageEquation of State: Eos - Linear - Polynomial Eos - GruneisenDhairyasheel BhutkarNo ratings yet
- Vector DifferentiationDocument33 pagesVector DifferentiationShawkat Khanz TuhinNo ratings yet