Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Study On Impact of GST On Indian Economy: Chirag Rana
Uploaded by
Pratyasha SarkarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Study On Impact of GST On Indian Economy: Chirag Rana
Uploaded by
Pratyasha SarkarCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR)
ISSN: 2319-7064
ResearchGate Impact Factor (2018): 0.28 | SJIF (2018): 7.426
A Study on Impact of GST on Indian Economy
Chirag Rana
Professor, M.Com, LLB.
Adhoc. Professor, Shah N. H. Commerce College Valsad, India
Abstract: Goods and Service Tax is an indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services. GST Law has replaced many indirect tax
laws that previously existed in India’s is one indirect tax for the entire country. There are 3 taxes applicable under GST: CGST, SGST &
IGST. GST will mainly remove the Cascading effect on the sale of goods and services. Removal of cascading effect will directly impact the
cost of goods. This paper gives an understanding about GST in India & its impact on the Indian Economy. The Evolution of GST in India is
also discussed in this research paper. The research objectives focus around the evolution of GST, how it works & how different sectors are
affected by GST.
Keywords: GST, Goods and services tax, Dual GST, Indian economy and value added tax
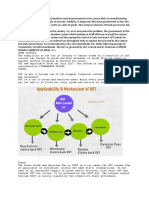
1. Introduction 12th Finance Commission. In the 2014 LokSabha election, the
BJP government was elected into power, with the
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a vast concept that consequential dissolution of the 15th LokSabha, the GST Bill
simplifies the giant tax structure by supporting and enhancing – approved by the standing committee for reintroduction –
the economic growth of a country. GST is a comprehensive lapsed. After the enactment of various GST law (Constitution
tax levy on manufacturing, sale and consumption of goods and 122 Amendment) Bill, 2014) was launched all over India with
services at a national level. The Goods and Services Tax Bill effect from 01 July 2017 the Jammu and Kashmir state
or GST Bill, also referred to as The Constitution (One legislature passed its GST act on 7 July 2017. The current
Hundred and Twenty-Second Amendment) Bill, 2014, initiates Structure of GST is a Central GST, State GST and Integrated
a Value added Tax to be implemented on a national level in GST in India.
India. GST will be an indirect tax at all the stages of
production to bring about uniformity in the system. On 3. Meaning
bringing GST into practice, there would be amalgamation of
Central and State taxes into a single tax payment. It would also What is GST?
enhance the position of India in both, domestic as well as „G‟ – Goods
international market. At the consumer level, GST would „S‟ – Services
reduce the overall tax burden, which is currently estimated at „T‟ – Tax
25-30%. Under this system, the consumer pays the final tax “Goods and Service Tax (GST) is a comprehensive tax levy on
but an efficient input tax credit system ensures that there is no manufacture, sale and consumption of goods and service at a
cascading of taxes- tax on tax paid on inputs that go into national level under which no distinction is made between
manufacture of goods. In order to avoid the payment of goods and services for levying of tax. It will mostly substitute
multiple taxes such as excise duty and service tax at Central all indirect taxes levied on goods and services by the Central
level and VAT at the State level, GST would unify these taxes and State governments in India.
and create a uniform market throughout the country.
Integration of various taxes into a GST system will bring Types of GST
about an effective cross utilization of credits. The current
system taxes production, whereas the GST will aim to tax What is CGST?
consumption. CGST full form is Central Goods and Services Tax.:-
CGST refers to the Central GST tax that is levied by the
2. History of GST in India Central Government of India on any transaction of goods and
services tax taking place within a state. It is one of the two
The first reform process of India's indirect tax regime was taxes charged on every intrastate (within one state)
started in 1986 by congress government, with the introduction transaction, the other one being SGST (or UTGST for Union
of the Modified Value Added Tax (MODVAT). A single Territories). CGST replaces all the existing Central taxes
common "Goods and Services Tax (GST)" was proposed and including Service Tax, Central Excise Duty, CST, Customs
given a go-ahead in 1999 during a meeting between the BJP Duty, SAD, etc. The rate of CGST is usually equal to the
Government and his economic advisory panel, which included SGST rate.
three former RBI governors. After BJP government is set up a
committee headed by the Finance Minister of West Bengal,
AsimDasgupta to design a GST model. In 2005, the Kelkar
committee recommended rolling out GST as suggested by the
Volume 8 Issue 4, April 2019
www.ijsr.net
Licensed Under Creative Commons Attribution CC BY
Paper ID: ART20197500 10.21275/ART20197500 1909
International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR)
ISSN: 2319-7064
ResearchGate Impact Factor (2018): 0.28 | SJIF (2018): 7.426
What is SGST? It will curb circulation of black money. This can happen
SGST full form is State Goods and Services Tax:- only if the “kacha bill” system, normally followed by
SGST (State GST) is one of the two taxes levied on every traders and shopkeepers is put to check.
intrastate (within one state) transaction of goods and services. GST will create corruption free environment in the country.
The other one is CGST. SGST is levied by the state where the GST will provide credit for the taxes paid by producers in
goods are being sold/purchased. It will replace all the existing the goods or services chain. This is expected to encourage
state taxes including VAT, State Sales Tax, Entertainment producers to buy raw material from different registered
Tax, Luxury Tax, Entry Tax, State Cesses and Surcharges on dealers and is hoped to bring in more vendors and suppliers
any kind of transaction involving goods and services. The under the purview of taxation.
State Government is the sole claimer of the revenue earned
under SGST. Negative impact of GST in India
The number of GST returns that each firm has to file are
What is IGST? quiet high which requires ample staff for maintaining the
IGST full form is Integrated Goods and Services Tax:- documents.
Integrated GST (IGST) is applicable on interstate (between For effective implementation of GST, tax administration
two states) transactions of goods and services, as well as on staff – both at central and state levels – would require to be
imports. This tax will be collected by the Central government trained properly in terms of concept, legislation and
and will further be distributed among the respective states. procedure.
IGST is charged when a product or service is moved from one Being a new tax, it will take some time for the people to
state to another. IGST is in place to ensure that a state has to understand it completely.
deal only with the Union government and not with every state
It is a consumption based tax, so in case of services the
separately to settle the interstate tax amounts.
place where service is provided needs to be determined.
Proper invoicing and accounting needs to be done to ensure
What is UTGST (or UGST)?
better compliance.
UTGST full form is Union Territory Goods and Services
Tax:-
The Union Territory Goods and Services Tax, commonly 5. Literature Review
referred to as UTGST, is the GST applicable on the goods and
services supply that takes place in any of the five Union World Bank (2018)and et all other research study on “GST in
Territories of India, including Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India” concluded that the Indian GST system is among the
Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Chandigarh, Lakshadweep and most complicated ones in the world, with its high tax rates and
Daman and Diu. This UTGST will be charged in addition to a larger number of tax rates and negative impact on its
the Central GST (CGST) explained above. For any transaction economy.
of goods/services within a Union Territory: CGST +
UTGST.The reason why a separate GST was implemented for Rathod M (2017) in his paper “An Overview of Goods and
the Union Territories is that the common State GST (SGST) Service Tax (GST) In India” concludes that GST will be a step
cannot be applied in a Union Territory without legislature. towards a developed India benefiting too many parties and
Delhi and Puducherry UTs already have their own legislatures, entire nation.
so SGST is applicable to them.
Nitin Kumar (2014) mentioned in his research paper that
implementation of GST will try to remove all the
4. Taxation System in India before GST shortcomings of present tax structure in India in his research
paper “Goods and Service Tax in India-A Way Forward”
Central Government levied taxes on the following:
1) Income Tax: Tax collected on the income of an individual
Monika Sehrawat and UpasanaDhanda (2015) in “GST in
2) Customs duties: Duties collected on the exports and
India: A key tax reform” concluded that introduction of GST
imports of goods
will undoubtedly boost the Indian economy but focus should
3) Service tax: Taxes gathered on various services
be given on rational design of GST model and timely
4) Central excise: Taxes on manufacturing of dutiable Goods
implementation.
State Governments levied the following taxes:
5) Value Added Tax (VAT): Sales of goods involve the
particular tax. The sales of the goods in intrastate 6. Research Methodology
arecovered by the VAT Law of that state, whereas those
among the inter-state is levied by the Central Sales Tax This study is descriptive in nature because here we have
Act. explained the probable impact of GST on different sectors. For
this secondary data has been collected through different
Positive Impact of GST in India articles, research papers and reports published about GST. So
GST will add to the government revenues by extending the this study highlights opportunities and challenges going to
tax base. All indirect taxes will come under one roof. occur to different sectors due to GST.
Volume 8 Issue 4, April 2019
www.ijsr.net
Licensed Under Creative Commons Attribution CC BY
Paper ID: ART20197500 10.21275/ART20197500 1910
International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR)
ISSN: 2319-7064
ResearchGate Impact Factor (2018): 0.28 | SJIF (2018): 7.426
6.1 Objectives of the Study general reduction as compared to the previous 10%-30% range
and the additional service tax of 15%.
To study the positive and negative impact of GST on Indian
Economy. Effect on inflation
To study about Goods and Service Tax and its impact on the Given the sampling of effects mentioned earlier, it can be said
economy. that GST is mostly viewed as an inflationary measure.
However, the Indian government believes otherwise. Hasmukh
6.2 Data Collection Adhia, Revenue Secretary, says that consumer price inflation
with GST implemented will go down by 2% by the end of
This paper is a descriptive paper based on secondary data 2017. Naturally, not many are convinced by this claim. The
collected from different books, news-paper articles and fact that the tax rate on services has been raised to 18% from
research journals. around 15% is already expected to raise inflation above levels
experienced before the institution of GST.
6.3 Effect of GST on Different Sector of Economy
Effect on Textile Industries
Effect on economic activity The GST on job work for textiles and textile products has been
It‟s difficult and too early to evaluate whether or not GST has reduced to 5% from 18%. Other impact of GST on textile
positively affected economic activity. The Indian government, industry is input tax credit, which is not allowed if a registered
however, believes that they are on the right track with GST. At taxpayer procures the inputs from composition scheme
least one Indian business executive shares this optimistic view taxpayers or the unorganized sector. It is available for the tax
of GST. In a report by The Indian Express, ICICI Bank CEO paid on capital goods.
Chanda Kocher was quoted to have said that GST is a
transformational structural reform which has multiple benefits. Effect on startups
These benefits include the establishment of a national market, The GST regime is believed to be good for the Indian startup
improved ease of doing business in India, better productivity sector as it carries with it tax credit on purchases, a simple
and efficiency, and improved compliance among taxpayers. compliance model, increased limits for registration, and the
GST‟s impact on the Indian economy can go either way: good ability to promote the free flow of goods and services. It takes
or not so good. Fortunately, there aren‟t that many analysts away the complication and confusion of the previous VAT
who express damningly averse views on the matter. With laws, especially for those in the ecommerce industry. GST
honest and efficient administration, GST may be a good move may stir inflation but there‟s the optimistic view that the
for the world‟s third largest economy. undesirable effects will not last long, and will eventually be
offset by the positive impact of an improving economy.
Impact of GST on Automobile Sector Earlier
The Automobile industry was paying a tax rate of a range Impact of GST on Telecom Sector
between 30-45%. But after implementation of GST, the rate is Goods and Services Tax or GST has been implemented, the
fixed at 18% which will positive impact this sector & which GST on telecommunication services are taxed at 18%, which
will be profitable to both the Manufacturers/ dealers and the is higher than rates charged earlier. It will affect the budget of
ultimate consumers. The standard and the social status of the common man.
consumers get uplifted. There is a huge boom in the
Automobile Industry as a result of implementation of Goods 7. Conclusion
and Services Tax. It is now done that the industry will get
benefits out of GST with minimum hassle-free procedures and Efficiency & equity in the economy can be brought by proper
rate fixation across the nation. taxation system in the country. While comparing challenges
with its positive and negative, it is clearly visible that its
Effect on consumer goods and service positive impact are more compared to challenges. A good tax
When it comes to consumer goods and services, the main system should focus on income distribution as well as generate
concerns are food and the services sector. For these, the GST revenues to government. To Implementing GST is to maintain
brings good and not so good news. The good news is that food simplicity and transparency in taxation system. GST will give
products are charged 0%. The not so good news is that Indian economy a strong and smart tax system for economic
services in general are seeing an increase of 18% from 15%. development. But for gaining those benefits country will need
On the other hand, the implementation of GST increases the to build strong mechanism. The objective GST is to replace
tax on footwear and garments priced at INR 500 from the VAT; GST will be solving all the complexities present in the
previous 14.41% to 18% but those priced lower than INR 500 current indirect tax system. It will be giving relief to various
are taxed lower at 5%. For ready-made garments, the rates are parties like consumers, producers and Government.
lowered to 12% from 18.16%. Mobile services rates are
slightly increased, though, because of the new 18% rate, from
15% before. When it comes to direct-to-home and cable
services, the new fixed rate of 18% can be considered a
Volume 8 Issue 4, April 2019
www.ijsr.net
Licensed Under Creative Commons Attribution CC BY
Paper ID: ART20197500 10.21275/ART20197500 1911
International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR)
ISSN: 2319-7064
ResearchGate Impact Factor (2018): 0.28 | SJIF (2018): 7.426
References
Journals
[1] World Bank, (2018) “GST: India” published by WB,
Washington, USA.
[2] Rathod, M. (2017). An Overview of Goods and Service
Tax (GST) In India. Journal of Commerce and
Management.
[3] Palil, M.R. &Ibrahim, M.A.(2011). The Impacts of Goods
and Services Tax (GST) on Middle Income Earners in
Malaysia. World Review of Business Research, 1(3), 192-
206.
[4] KPMG. (2011). Economic Analysis of the Impacts of
Using GST to Reform Taxes. CPA Australia,
(September), 54
[5] Chadha, R. (2009). Moving to Goods and Services Tax in
India: Impact on India‟s Growth and International Trade.
National Council of Applied Economic Research.
Website
[6] Www.tradingeconomics.com. retrieved Mar12, 2018.
[7] www.economicstimes.com.retrieved Mar08, 2018.
[8] www.saginfotech.com
[9] www.economictimes.indiatimes.com
[10] www.gstindia.com
[11] www.cleartax.in
[12] www.taxmantra.com
Volume 8 Issue 4, April 2019
www.ijsr.net
Licensed Under Creative Commons Attribution CC BY
Paper ID: ART20197500 10.21275/ART20197500 1912
You might also like
- The GST and Economic GrowthDocument4 pagesThe GST and Economic GrowthEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- GST Project Raghav, Shubham, KanavDocument5 pagesGST Project Raghav, Shubham, KanavRAGHAV JAGGANo ratings yet
- GST: Impact On Indian Economy: PallavikapilaDocument3 pagesGST: Impact On Indian Economy: PallavikapilaVishal kumarNo ratings yet
- How to Handle Goods and Service Tax (GST)From EverandHow to Handle Goods and Service Tax (GST)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- An Analysis of GST Collection of India SDocument6 pagesAn Analysis of GST Collection of India SAditi ChandraNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Method of Collecting Data Primary DataDocument8 pages2.1 Method of Collecting Data Primary Datadeepak sipaniNo ratings yet
- Earlier The Constitution Empowered The Central Government To Levy Excise Duty On Manufacturing and Service Taxes On The Supply of ServicesDocument3 pagesEarlier The Constitution Empowered The Central Government To Levy Excise Duty On Manufacturing and Service Taxes On The Supply of ServicesIshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Guide To CGST, SGST and IGST: Inter-State Vs Intra-StateDocument6 pagesGuide To CGST, SGST and IGST: Inter-State Vs Intra-StateSuman IndiaNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On GSTDocument15 pagesA Project Report On GSTAnjali RatudiNo ratings yet
- Complete GST NotesDocument102 pagesComplete GST Noteslawsaba6No ratings yet
- CTP AssignmentDocument10 pagesCTP AssignmentANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- GST in 40Document7 pagesGST in 40KeertiNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax REASERCH - EditedDocument6 pagesGoods and Services Tax REASERCH - EditedRohit Tripathi ModicareNo ratings yet
- GST's Impact on Indian EconomyDocument10 pagesGST's Impact on Indian EconomyKetan YadavNo ratings yet
- impactofgstonindianeconomypaperDocument10 pagesimpactofgstonindianeconomypaperharshitverma1762No ratings yet
- Ijems V4i5p107Document4 pagesIjems V4i5p107Annpourna ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Ayushi PatraDocument12 pagesAyushi PatraAdithya anilNo ratings yet
- Indirect TaxDocument24 pagesIndirect Taxpradeep100% (1)
- GST and Its Impact 3 PDFDocument3 pagesGST and Its Impact 3 PDFanushka kashyapNo ratings yet
- GST AssgmntDocument16 pagesGST AssgmntMuhammed Samil MusthafaNo ratings yet
- UTKARSH YADAV (Sec - B) (Research Paper)Document8 pagesUTKARSH YADAV (Sec - B) (Research Paper)UTKARSH YADAVNo ratings yet
- Project 3Document17 pagesProject 3Hemant MandalNo ratings yet
- GST Economics ProjectDocument11 pagesGST Economics ProjectAbeer ChawlaNo ratings yet
- 'SWOT' Analysis On Goods and Services Tax (GST) in IndiaDocument4 pages'SWOT' Analysis On Goods and Services Tax (GST) in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- GST Unit 1Document23 pagesGST Unit 1hpotter46103No ratings yet
- GST IntroductionDocument103 pagesGST IntroductionAnonymous MhCdtwxQINo ratings yet
- Impact of Goods and Services Tax (GST) On Indian EconomyDocument5 pagesImpact of Goods and Services Tax (GST) On Indian EconomyMCOM 2050 MAMGAIN RAHUL PRASADNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Goods and Services Tax (GST)Document7 pagesIntroduction To Goods and Services Tax (GST)Anjali PawarNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST on Automotive IndustryDocument101 pagesImpact of GST on Automotive IndustryVikrant60% (5)
- IMPACT OF GST ON INDIAN ECONOMYDocument10 pagesIMPACT OF GST ON INDIAN ECONOMYbijay2022No ratings yet
- A Study On Impact of GST On The Prices in Odisha: Samira PatraDocument14 pagesA Study On Impact of GST On The Prices in Odisha: Samira PatraBiplab SwainNo ratings yet
- Ijm - 08!04!002 GST ArticleDocument8 pagesIjm - 08!04!002 GST ArticleAnand JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST On Indian Economy PaperDocument10 pagesImpact of GST On Indian Economy PaperDevil DemonNo ratings yet
- Introduction to GST in India - CGST, SGST, IGST and UTGST TypesDocument2 pagesIntroduction to GST in India - CGST, SGST, IGST and UTGST Types777priyankaNo ratings yet
- Gst-General Studies Project - Krishna Agarwal.11-DDocument17 pagesGst-General Studies Project - Krishna Agarwal.11-DKrishna AgarwalNo ratings yet
- GST prospects in IndiaDocument6 pagesGST prospects in IndiaShayan ZafarNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Basis of GSTDocument10 pagesConstitutional Basis of GSTNANDINI RAJ N RNo ratings yet
- Economy ProjectDocument12 pagesEconomy Projectdrishti goelNo ratings yet
- i Je Mr 2021110417Document7 pagesi Je Mr 2021110417BADDAM PARICHAYA REDDYNo ratings yet
- GST in India: An Analysis of its Concept, Implementation and ImpactDocument26 pagesGST in India: An Analysis of its Concept, Implementation and ImpactSukrit GandhiNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax The New EconomicDocument8 pagesGoods and Services Tax The New EconomicPratyasha SarkarNo ratings yet
- GST in IndiaDocument26 pagesGST in IndiaAKHIL H KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- GST Explained: Understanding India's Major Tax ReformDocument8 pagesGST Explained: Understanding India's Major Tax ReformApoorva Chandra100% (1)
- LAW OF TAXATIONDocument10 pagesLAW OF TAXATIONKavyanjali SinghNo ratings yet
- GST to Improve E-Commerce in IndiaDocument5 pagesGST to Improve E-Commerce in IndiaNAMRATA BHATIANo ratings yet
- Title:Gst: TH TH NDDocument5 pagesTitle:Gst: TH TH NDNAMRATA BHATIANo ratings yet
- Title:Gst: TH TH NDDocument5 pagesTitle:Gst: TH TH NDNAMRATA BHATIANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Goods and Services Tax (GST)Document6 pagesIntroduction To Goods and Services Tax (GST)Tax NatureNo ratings yet
- GST and India's Industrial Policies ExplainedDocument22 pagesGST and India's Industrial Policies ExplainedJyotiNo ratings yet
- A Review On GST Execution and Its Effect PDFDocument9 pagesA Review On GST Execution and Its Effect PDFAsma KhanNo ratings yet
- Ashish TaxDocument20 pagesAshish TaxAshish RajNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST On The Indian EconomyDocument16 pagesImpact of GST On The Indian EconomySandeep TomarNo ratings yet
- GST Definition, Objective, Framework, Action Plan & Scope: Historical Background of GSTDocument6 pagesGST Definition, Objective, Framework, Action Plan & Scope: Historical Background of GSTRamapriyaiyengarNo ratings yet
- NeerajMandhan - Vinayak - GST AND INDERECT TAXESDocument33 pagesNeerajMandhan - Vinayak - GST AND INDERECT TAXESkanikaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Indirect Tax Regime - 240324 - 105644Document53 pagesUnit 3 - Indirect Tax Regime - 240324 - 105644shree varanaNo ratings yet
- Article1Document5 pagesArticle1SatendraNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST on Small Businesses in DamanDocument33 pagesImpact of GST on Small Businesses in DamanSawan PatelNo ratings yet
- GST Fast Track Notes PDFDocument69 pagesGST Fast Track Notes PDFJayadeepNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Gst in India ( Content to Be Take From the 20 Articles).DocxDocument67 pagesAn Overview of Gst in India ( Content to Be Take From the 20 Articles).DocxBADDAM PARICHAYA REDDYNo ratings yet
- Key Features: HistoryDocument3 pagesKey Features: HistorypranitaNo ratings yet
- 2.isca Irjss 2018 012Document15 pages2.isca Irjss 2018 012lamaNo ratings yet
- Goods and Services Tax The New EconomicDocument8 pagesGoods and Services Tax The New EconomicPratyasha SarkarNo ratings yet
- Demonetization and Its Impact On Indian EconomyDocument19 pagesDemonetization and Its Impact On Indian EconomyPratyasha SarkarNo ratings yet
- Master of Commerce (Project)Document13 pagesMaster of Commerce (Project)anon_447269421No ratings yet
- The Role of Microfinance in Poverty Reduction: Evidence From South AsiaDocument10 pagesThe Role of Microfinance in Poverty Reduction: Evidence From South AsiaPratyasha SarkarNo ratings yet
- 55aaa 385 389.13977 PDFDocument6 pages55aaa 385 389.13977 PDFRadhika RajendranNo ratings yet
- Demonetization and Its Impact On Indian Economy: February 2017Document10 pagesDemonetization and Its Impact On Indian Economy: February 2017Not KnownNo ratings yet
- Citation 347516135Document1 pageCitation 347516135Pratyasha SarkarNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice 67Document1 pageTax Invoice 67shiva kumarNo ratings yet
- Complete GST Book PDFDocument351 pagesComplete GST Book PDFAGNIHOTRAM RAM NARAYANANo ratings yet
- Credit Memo - MH3M300182Document1 pageCredit Memo - MH3M300182AltafNo ratings yet
- Tax InvoiceDocument3 pagesTax InvoiceAyas AhamedNo ratings yet
- Train TicketiDocument1 pageTrain TicketiAjay PanmandNo ratings yet
- ModbusDocument1 pageModbusMANIKANDAN ARUNNo ratings yet
- 2.2016 Syllabus Paper-18 - Jan21 Indirect Tax Laws & Practice Study NotesDocument972 pages2.2016 Syllabus Paper-18 - Jan21 Indirect Tax Laws & Practice Study NotesRadhakrishnaraja RameshNo ratings yet
- Original Redignton Invoice India PDFDocument4 pagesOriginal Redignton Invoice India PDFishajain6920No ratings yet
- Electronic Reservation Slip (ERS) : 6325624061 12391/shramjeevi Exp Ac 3 Tier Sleeper (3A)Document3 pagesElectronic Reservation Slip (ERS) : 6325624061 12391/shramjeevi Exp Ac 3 Tier Sleeper (3A)MASTER SANDEEP SANDYNo ratings yet
- PRN91Document2 pagesPRN91AMSARAJA MNo ratings yet
- GST Taxmann Com2Document35 pagesGST Taxmann Com2Kamna AgrwalNo ratings yet
- OD119978131985722000Document1 pageOD119978131985722000pankaj hitlarNo ratings yet
- GST Invoice for Battery and Inverter SaleDocument1 pageGST Invoice for Battery and Inverter SaleAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Best E-Accounting Training in Pitampura DelhiDocument6 pagesBest E-Accounting Training in Pitampura DelhiPeter JohnNo ratings yet
- Gmail - Your IndiGo Itinerary - QIPW5Z PDFDocument6 pagesGmail - Your IndiGo Itinerary - QIPW5Z PDFpramukhNo ratings yet
- Kelkar CommitteeDocument6 pagesKelkar Committeedevika_verma240% (1)
- ForwardInvoice ORD321555329Document2 pagesForwardInvoice ORD321555329Aman KapoorNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument2 pagesPDFRidzwan SayyedNo ratings yet
- Request Letter - Client Letter HeadDocument4 pagesRequest Letter - Client Letter HeadPrateek GuptaNo ratings yet
- GST Invoice: Perfect SoftconDocument1 pageGST Invoice: Perfect SoftconpiyushjainpcNo ratings yet
- 2154 CustomerInvoiceDocument1 page2154 CustomerInvoiceKarthik Alugoori0% (1)
- Accounting Entries Under GSTDocument7 pagesAccounting Entries Under GSTPiousPatialaNo ratings yet
- Pendrive BillDocument1 pagePendrive BillNITIN VERMANo ratings yet
- Report ON Impact of GST On Logistics Industry in India Project Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment For The Award of Degree ofDocument31 pagesReport ON Impact of GST On Logistics Industry in India Project Report Submitted in Partial Fulfillment For The Award of Degree ofakshara pradeepNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsComp Invoice 2772073Document1 pageElectronicsComp Invoice 2772073Keegan ColacoNo ratings yet
- InvoiceDocument1 pageInvoicesyed aamiriNo ratings yet
- Po 38022751Document13 pagesPo 38022751Swapnil PatilNo ratings yet
- Rapido Auto - Railway STN To OfcDocument3 pagesRapido Auto - Railway STN To OfcShaik MastanvaliNo ratings yet
- Vendor Validation Policy v3 - 1601553886Document5 pagesVendor Validation Policy v3 - 1601553886MANOJ PANDANo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice Rules ExplainedDocument1 pageTax Invoice Rules ExplainedArun kumarNo ratings yet