0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5K views7 pagesFinancial Management Formula Sheet: Chapter 1: Nature, Significance and Scope of Financial Management
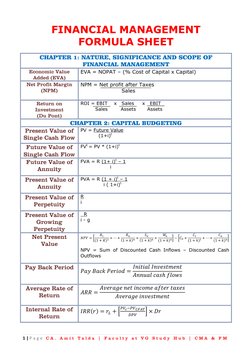
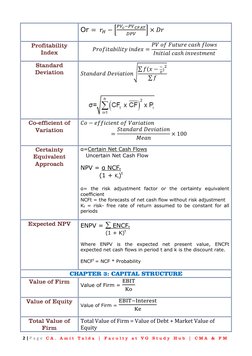
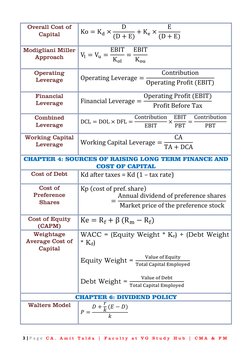
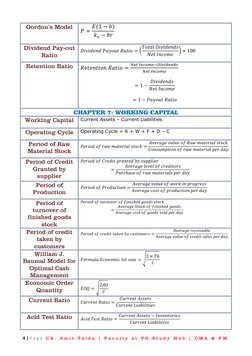
This document contains formulas and concepts related to financial management. It covers topics like capital budgeting, capital structure, cost of capital, dividend policy, working capital management, security analysis, and portfolio management. Key formulas include net present value, internal rate of return, weighted average cost of capital, dividend payout ratio, current ratio, beta, capital asset pricing model, and Sharpe portfolio. Chapters also discuss concepts like operating leverage, financial leverage, capital market line, single and multi index models.
Uploaded by
Aakash TiwariCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5K views7 pagesFinancial Management Formula Sheet: Chapter 1: Nature, Significance and Scope of Financial Management
This document contains formulas and concepts related to financial management. It covers topics like capital budgeting, capital structure, cost of capital, dividend policy, working capital management, security analysis, and portfolio management. Key formulas include net present value, internal rate of return, weighted average cost of capital, dividend payout ratio, current ratio, beta, capital asset pricing model, and Sharpe portfolio. Chapters also discuss concepts like operating leverage, financial leverage, capital market line, single and multi index models.
Uploaded by
Aakash TiwariCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Chapter 2: Capital Budgeting
- Chapter 1: Nature, Significance and Scope of Financial Management
- Chapter 3: Capital Structure
- Chapter 4: Sources of Raising Long Term Finance and Cost of Capital
- Chapter 7: Working Capital
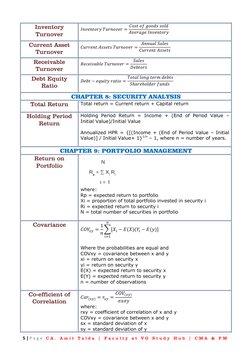
- Chapter 8: Security Analysis
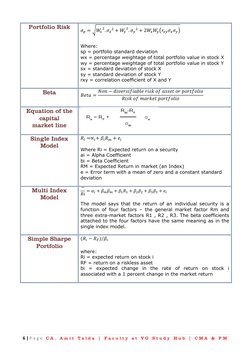
- Chapter 9: Portfolio Management
- Important Material & Initiatives