Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Page 2 Examples: FULL WORKED SOLUTIONS Are Available To Subscribers of
Uploaded by
АЙЗАТ ЖАРИМБЕТОВАOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Page 2 Examples: FULL WORKED SOLUTIONS Are Available To Subscribers of
Uploaded by
АЙЗАТ ЖАРИМБЕТОВАCopyright:
Available Formats
FULL
WORKED SOLUTIONS are available to subscribers of www.chemsheets.co.uk.
PAGE 2 EXAMPLES
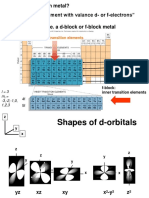
2 6 1 10
Fe [Ar] 4s 3d Cu [Ar] 4s 3d
3+ 5 + 10
Fe [Ar] 3d Cu [Ar] 3d
2 1 2+ 9
Sc [Ar] 4s 3d Cu [Ar] 3d
3+ 2 10
Sc [Ar] Zn [Ar] 4s 3d
2 3 2+ 10
V [Ar] 4s 3d Zn [Ar] 3d
2+ 3 1 5
V [Ar] 3d Cr [Ar] 4s 3d
metal atom Common ions Transition metal?
2 1 3+
Sc Sc [Ar] 4s 3d Sc [Ar] Yes
1 10 + 10 2+ 9
Cu Cu [Ar] 4s 3d Cu [Ar] 3d Cu [Ar] 3d Yes
2 10 2+ 10
Zn Zn [Ar] 4s 3d Zn [Ar] 3d No
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 1
TASK 1 – Drawing complexes
2+
[Ni(NH2CH 2CH 2NH2)3]
2+
+2
–
Ligand(s) CN NH3 H2NCH2CH2NH2
+
[Co(NH2CH2CH2NH2)2Cl2] [Pt(NH 3)Cl3]
Cl
– – 2–
Ligand(s) H2NCH2CH2NH2,Cl NH3,Cl C 2O 4
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 2
TASK 2 – Drawing pairs of complexes that are isomers
trans cis
trans cis
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 3
TASK 3 – Substitution reactions
1 a) Ligand(s) replaced by other ligand(s)
b) 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7
c) 5
–
d) Cl too big so cannot fit 6 around metal
e) 3, 4, 5, 6
2 a) 4–
2+ 4– 2–
b) [Pb(H2O)6] + EDTA → [Pb(EDTA)] + 6H2O
c) ΔH negligible as similar number and type of bonds broken / formed
ΔS positive as go from 2 to 7 particles
ΔG (very) negative and therefore reaction feasible
d) ΔG (very) positive and therefore reaction not feasible.
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 4
TASK 4 – Coloured complexes
1 a) d orbitals have different energy, visible light absorbed, for electrons to be excited from lower to
higher d orbitals, colour seen consists of those colours not absorbed
b) oxidation state, ligand, co-ordination number, shape; they affect the size of the energy gap
between the d orbitals and so the wavelength of visible light absorbed
2 a) ΔE = hν = hc
λ.
b) absorbs orange light, what is left gives blue colour
c) 2.21 x 10-19J, 133 kJ mol-1
d) 4.19 x 10-19J, 252 kJ mol-1
e) Different ligand, therefore different energy gap between higher and lower d orbitals, therefore
different wavelength of visible light absorbed
3 a) ligand = particle that forms a co-ordinate bond to a metal ion,
bidentate = ligand that forms two co-ordinate bonds to metal ion
b) to intensity the colour as colour is very faint
c) [Fe(H2O)6]2+ + 3 bipy → [Fe(bipy)3]2+ + 6H2O
d) octahedral
e) 6
f)
g)
0.8
0.7
0.6
Absorbance
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
Concentration (mol dm-3)
h) 0.15 mol dm-3
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 5
TASK 5 – Variable oxidation states
2+
1 a) [Zn(NH3)4(H2O)2]
b) ligands
2 a) yellow → blue → green → violet
b) reducing agent
c) Zn → Zn2+ + 2 e–
d) easier to reduce transition metal in acid
e) some zinc reacts with acid to form hydrogen: Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
f) to prevent reaction with oxygen
g) VO2+ + 2H+ + e– → VO2+ + H2O
VO2+ + 2H+ + e– → V3+ + H2O
V3+ + e– → V2+
h) 2VO2+ + 4H+ + Zn → 2VO2+ + 2H2O + Zn
2VO2+ + 4H+ + Zn → 2V3+ + 2H2O + Zn
2V3+ + Zn → 2V2+ + Zn2+
+
3 a) [Ag(NH3)2]
b) [Ag(NH3)2]+ + e– → Ag + 2NH3
c) HCHO + H2O → HCOOH + 2H+ + 2e–
d) HCHO + H2O + 2[Ag(NH3)2]+ → HCOOH + 2Ag + 2NH4+ + 2NH3
4 4[Fe(H2O)4(OH)2] + O2 → 4[Fe(H2O)3(OH)3] + 2H2O
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 6
PAGE 17 EXAMPLES
e.g.1 mol KMnO4 = 0.0200 x 25.45/1000 = 0.000509
2+ 3
mol Fe in 25 cm = 5 x 0.000509 = 0.002545
2+ 3
mol Fe in 250 cm = 0.02545
mass Fe = 0.02545 x 55.8 = 1.42 g
% Fe = 100 x 1.42/1.51 = 94.0% (3sf)
e.g.2 mol KMnO4 = 0.00300 x 27.75/1000 = 0.00008325
2- 3
mol C2O4 in 25 cm = 2.5 x 0.00008325= 0.0002081
2- 3
mol C2O4 in 250 cm = 0.002081
mass H2C2O4 = 0.002081 x 90.0 = 0.187 g
% H2C2O4 = 100 x 0.187/2.34 = 8.00% (3sf)
TASK 6 – Redox titrations
1 mol KMnO4 = 0.0200 x 24.3/1000 = 0.000486
2+
mol Fe = 5 x 0.000486 = 0.00243
2+ -3
[Fe ] = 0.00243 / (20.0/1000) = 0.122 mol dm (3sf)
2 mol KMnO4 = 0.0200 x 25.00/1000 = 0.000500
2+
mol Fe = 5 x 0.000500 = 0.00250
mass Fe = 0.0250 x 55.8 = 0.1395 g
% Fe = 100 x 0.1395/3.00 = 4.65% (3sf)
3 mol KMnO4 = 0.0100 x 43.85/1000 = 0.0004385
2+ 3
mol Fe in 25 cm = 5 x 0.0004385 = 0.002193
2+ 3
mol Fe in 500 cm = 0.002193 x 20 = 0.04385
Mr = 12.18 = 277.8
0.04385
Mr xH2O = 277.8 – 151.9 = 125.9
x = 125.9/18.0 = 7 (nearest integer), Mr = 126 (3sf)
4 a) reaction is between two negative ions so is slow
2+
b) Mn produced in reaction acts as catalyst to increase rate
c) mol KMnO4 = 0.0200 x 27.50/1000 = 0.000550
2- 3
mol C2O4 in 25 cm = 2.5 x 0.000550= 0.001375
2- 3
mol C2O4 in 250 cm = 0.01375
Mr = 2.01 = 146.2
0.01375
Mr nH2O = 146.2 – 128.1 = 18.0
n = 18.0/18.0 = 1 (nearest integer), Mr = 146 (3sf)
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 7
5 mol KMnO4 = 0.00133 x 32.50/1000 = 0.00004323
2+ 3
mol Fe in 25 cm = 5 x 0.00004323 = 0.0002161
2+ 3
mol Fe in 250 cm = 0.0002161 x 10 = 0.002161
mass Fe = 0.002161 x 55.8 = 0.121 g
% Fe = 100 x 0.121/0.940 = 12.8% (3sf)
-
6 a) FeC2O4nH2O : MnO4 = 1 : 0.6
b) mol KMnO4 = 0.0200 x 28.50/1000 = 0.000570
3
mol FeC2O4nH2O in 25 cm = 5/3 x 0.000570 = 0.000950
3
mol FeC2O4nH2O in 250 cm = = 0.00950
Mr = 1.71 = 180.0
0.00950
Mr xH2O = 180.0 – 143.8 = 36.2
x = 36.2/18.0 = 2 (nearest integer), Mr = 180 (3sf)
7 mol KMnO4 = 0.0150 x 22.65/1000 = 0.0003398
2+ 3
mol Fe in 25 cm = 5 x 0.0003398 = 0.001699
2+ 3
mol Fe in 250 cm = 0.001699 x 10 = 0.01699
Mr = 8.492 = 499.9
0.01699
Mr xH2O = 499.9 – 284.0 = 215.9
x = 215.9/18.0 = 12 (nearest integer), Mr = 500 (3sf)
2+
8 Fe only mol KMnO4 = 0.0200 x 15.0/1000 = 0.0003000
2+ 3
mol Fe in 25 cm = 5 x 0.0003000 = 0.001500
2+ 3+
Fe + Fe mol KMnO4 = 0.0200 x 19.0/1000 = 0.0003800
2+ 3+ 3
mol Fe + Fe in 25 cm = 5 x 0.0003800 = 0.001900
3+ 3+
Fe mol Fe = 0.001900 – 0.001500 = 0.000400
2+ -3
[Fe ] 0.001500 / (25.0/1000) = 0.0600 mol dm (3sf)
3+ -3
[Fe ] 0.000400 / (25.0/1000) = 0.0160 mol dm (3sf)
9 mol KMnO4 = 0.0100 x 26.50/1000 = 0.000265
2+ 3
mol Fe in 20 cm = 5 x 0.000265 = 0.001325
2+ 3
mol Fe in 500 cm = 0.001325 x 25 = 0.03313
mass Fe = 0.03313 x 55.8 = 1.85 g
% Fe = 100 x 1.85/13.2 = 14.0% (3sf)
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 8
10 Acid-base titration to find moles of H2C2O4.2H2O only
mol NaOH = 0.100 x 17.35/1000 = 0.001735
3
mol H2C2O4.2H2O in 25 cm = ½ x 0.001735 = 0.0008675
3
mol H2C2O4.2H2O in 250 cm = 0.008675
Redox titration to find total moles of H2C2O4.2H2O and K2C2O4.xH2O
mol KMnO4 = 0.0200 x 24.85/1000 = 0.000497
2- 3
mol C2O4 in 25 cm = 2.5 x 0.000497 = 0.001243
2- 3
mol C2O4 in 250 cm = 0.01243
2-
mol of C2O4 from K2C2O4.xH2O = 00.01243 – 0.008675 = 0.00375
3
Mass of H2C2O4.2H2O in 250 cm = 0.008675 x 126.0 = 1.093 g
3
Mass of K2C2O4.xH2O in 250 cm = 1.78 – 1.093 = 0.687 g
Mr = 0.687 = 183.2
0.00375
Mr xH2O = 183.2 – 166.2 = 17.0
x = 17.0/18.0 = 1 (nearest integer), Mr = 183 (3sf)
11 a) mol KMnO4 = 0.0200 x 16.9/1000 = 0.000338
2+ 3
mol Fe in 25 cm = 5 x 0.000338 = 0.00169
2+ 3
mol Fe in 250 cm = 0.00169 x 10 = 0.0169
4-
b) mol EDTA = 0.100 x 17.6/1000 = 0.00176
3+ 3
mol Fe in 25 cm = 0.00176
3+ 3
mol Fe in 250 cm = 0.0176
3+
c) mol original Fe + Fe = 0.0176
mol original Fe = 0.0169
3+
mol original Fe = 0.0176 – 0.0169 = 0.0007
% rusted iron = 100 x 0.0007 = 4.0% (sf is very arguable!)
0.0176
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 9
Page 24 - Reaction of metal aqua ions with NaOH(aq)
aqua ion reaction observation equation
– green solution → [Fe(H2O)6]
2+ -
+ 2OH → [Fe(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2H2O
add some OH
green precipitate
2+
Fe(H2O)6
–
add XS OH no visible reaction _
– blue solution → [Cu(H2O)6]
2+ -
+ 2OH → [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2H2O
add some OH
blue precipitate
2+
Cu(H2O)6
–
add XS OH no visible reaction _
– orange solution → [Fe(H2O)6]
3+ -
+ 3OH → [Fe(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3H2O
add some OH
brown precipitate
3+
Fe(H2O)6
–
add XS OH no visible reaction _
– colourless solution 3+ -
add some OH [Al(H2O)6] + 3OH → [Al(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3H2O
→ white precipitate
3+
Al(H2O)6
– - -
add XS OH no visible reaction [Al(H2O)3(OH)3] + OH → [Al(H2O)2(OH)4] + H2O
Page 25 - Reaction of metal aqua ions with NH3(aq)
aqua ion reaction observation equation
2+ +
green solution → [Fe(H2O)6] + 2NH3 → [Fe(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2NH4
add some NH3
green precipitate
2+
Fe(H2O)6
_
add XS NH3 no visible reaction
blue solution → [Cu(H2O)6]
2+
+ 2NH3 → [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2NH4
+
add some NH3
blue precipitate
2+
Cu(H2O)6
[Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] + 4NH3 →
add XS NH3 no visible reaction 2+ -
[Cu(H2O)2(NH3)4] + 2H2O + 2OH
orange solution → [Fe(H2O)6]
3+
+ 3NH3 → [Fe(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3NH4
+
add some NH3
brown precipitate
3+
Fe(H2O)6
add XS NH3 no visible reaction _
colourless solution 3+ +
add some NH3 [Al(H2O)6] + 3NH3 → [Al(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3NH4
→ white precipitate
3+
Al(H2O)6
add XS NH3 no visible reaction _
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 10
Page 25 - Reaction of metal aqua ions with Na2CO3(aq)
aqua ion reaction observation equation
2+ 2- green solution → 2+ 2-
Fe(H2O)6 add some CO3 [Fe(H2O)6] + CO3 → FeCO3 + 6H2O
green precipitate
2+ 2-
blue solution → 2+ 2-
Cu(H2O)6 add some CO3 blue-green [Cu(H2O)6] + CO3 → CuCO3 + 6H2O
precipitate
3+ 2-
3+ 2-
orange solution → 2[Fe(H2O)6] + 3CO3 →
Fe(H2O)6 add some CO3 brown precipitate &
2[Fe(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3H2O + 3CO2
gentle bubbles
3+ 2-
colourless solution 2[Al(H2O)6] + 3CO3 →
3+ 2-
Al(H2O)6 add some CO3 → white precipitate
2[Al(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3H2O + 3CO2
& gentle bubbles
Page 26 – Acid-base character of metal hydroxide precipitates
add excess acid add excess alkali
metal hydroxide
observation equation observation Equation
+
green ppt → [Fe(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2H → no visible
[Fe(H2O)4(OH)2] _
green solution [Fe(H2O)6]
2+ reaction
+
blue ppt → [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2H → no visible
[Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] _
blue solution [Cu(H2O)6]
2+ reaction
+
brown ppt → [Fe(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3H → no visible
[Fe(H2O)3(OH)3] _
violet solution [Fe(H2O)6]
3+ reaction
+ -
white ppt → [Al(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3H → white ppt → [Al(H2O)3(OH)3] + OH →
colourless 3+
[Al(H2O)3(OH)3] colourless -
solution [Al(H2O)6] solution [Al(H2O)2(OH)4]
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 11
Page 26 – Substitution with similar sized ligands e.g. NH3(aq)
aqua ion reaction observation equation
2+ green solution → 2+ +
Fe(H2O)6 add excess NH3 [Fe(H2O)6] + 2NH3 → [Fe(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2NH4
green precipitate
2+
blue solution → 2+ 2+
Cu(H2O)6 add excess NH3 blue precipitate → [Cu(H2O)6] + 4NH3 → [Cu(H2O)2(NH3)4] + 4H2O
deep blue solution
3+ orange solution → 3+ +
Fe(H2O)6 add excess NH3 [Fe(H2O)6] + 3NH3 → [Fe(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3NH4
brown precipitate
3+ colourless solution 3+ +
Al(H2O)6 add excess NH3 → white precipitate [Al(H2O)6] + 3NH3 → [Al(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3NH4
Page 27 – Substitution with bigger ligands e.g. Cl-(aq)
aqua ion reaction observation equation
2+ – green solution → 2+ – 2–
Fe(H2O)6 add excess Cl [Fe(H2O)6] + 4Cl → [FeCl4] + 6H2O
yellow solution
2+ – blue solution → 2+ – 2–
Cu(H2O)6 add excess Cl [Cu(H2O)6] + 4Cl → [CuCl4] + 6H2O
yellow solution
3+ – orange solution → 3+ – –
Fe(H2O)6 add excess Cl [Fe(H2O)6] + 4Cl → [FeCl4] + 6H2O
yellow solution
3+ – colourless solution → 3+ – –
Al(H2O)6 add excess Cl [Al(H2O)6] + 4Cl → [AlCl4] + 6H2O
colourless solution
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 12
TASK 9 – REACTIONS OF INORGANIC COMPLEXES
2+ -
1 blue solution → blue precipitate [Cu(H2O)6] + 2OH → [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2H2O
no further reaction with excess
3+ +
2 colourless solution → white precipitate [Al(H2O)6] + 3NH3 → [Al(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3NH4
no further reaction with excess
2+ 2-
3 green solution → green precipitate [Fe(H2O)6] + CO3 → FeCO3 + 6H2O
no further reaction with excess
3+ 2-
4 orange solution → brown ppt & bubbles 2[Fe(H2O)6] + 3CO3 → 2[Fe(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3H2O +
3CO2
no further reaction with excess
3+ – –
5 orange(or violet) solution → yellow solution [Fe(H2O)6] + 4Cl → [FeCl4] + 6H2O
no further reaction with excess
3+ -
6 colourless solution → white precipitate [Al(H2O)6] + 3OH → [Al(H2O)3(OH)3] + 3H2O
- –
white precipitate → colourless solution [Al(H2O)3(OH)3] + OH → [Al(H2O)2(OH)4] + H2O
2+ +
7 blue solution → blue precipitate [Cu(H2O)6] + 2NH3 → [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2NH4
2+
blue precipitate → deep blue solution [Cu(H2O)4(OH)2] + 4NH3 → [Cu(H2O)2(NH3)4] + 2H2O +
-
2OH
2+ – 2–
8 pink solution → blue solution [Co(H2O)6] + 4Cl → [CoCl4] + 6H2O
no further reaction with excess
2+ -
9 green solution → green precipitate [Fe(H2O)6] + 2OH → [Fe(H2O)4(OH)2] + 2H2O
no further reaction with excess
2+ – 2–
10 colourless solution → white precipitate [Zn(H2O)6] + 4Cl → [ZnCl4] + 6H2O
no further reaction with excess
2+ 2-
11 colourless solution → white precipitate [Zn(H2O)6] + CO3 → ZnCO3 + 6H2O
no further reaction with excess
© www.CHEMSHEETS.co.uk 30-October-2017 Chemsheets A2 1027 Page 13
You might also like
- Powerful and Durable JCB JS200 Tracked ExcavatorDocument6 pagesPowerful and Durable JCB JS200 Tracked ExcavatorMB Viorel100% (1)
- STAR GLASS - D66f5e - PDFDocument126 pagesSTAR GLASS - D66f5e - PDFJessie O.BechaydaNo ratings yet
- Challenges Faced by Irregular StudentsDocument13 pagesChallenges Faced by Irregular StudentsTicag Teo80% (5)
- NMR Booklet AnswersDocument13 pagesNMR Booklet AnswersSumaira AliNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atomic Structure EXAMPRODocument36 pages1.1 Atomic Structure EXAMPROamandasparkle100% (1)
- Christopher Westra - Laws of Attraction PDFDocument3 pagesChristopher Westra - Laws of Attraction PDFZachary LeeNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets A2 1027 (Transition Metals)Document32 pagesChemsheets A2 1027 (Transition Metals)bejoc90699No ratings yet
- A2 Chemistry Revision Workshop NotesDocument31 pagesA2 Chemistry Revision Workshop NotesVesna NikolicNo ratings yet
- (Jean Oliver and Alison Middleditch (Auth.) ) Funct (B-Ok - CC)Document332 pages(Jean Oliver and Alison Middleditch (Auth.) ) Funct (B-Ok - CC)Lorena BurdujocNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2020Document34 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2020Anonymous hrjVVK100% (1)
- SAQ Ans 6Document3 pagesSAQ Ans 6harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets A2 038 Transition Metals Introduction Ans Xj75Document3 pagesChemsheets A2 038 Transition Metals Introduction Ans Xj75Ana White0% (1)
- Chemsheets-A2-Transition-Metals WorkbookDocument32 pagesChemsheets-A2-Transition-Metals WorkbookmlbgurpreetttNo ratings yet
- 5.3.2 Transition Metals PDFDocument11 pages5.3.2 Transition Metals PDFkrishnaviNo ratings yet
- 12-d and F-Block Elements - 115302Document7 pages12-d and F-Block Elements - 115302baharaygul30No ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document30 pagesLecture 9JetNoKunNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/31Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/31Tshegofatso SaliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Cet 2021 - Version Code - B2 Solutions: Ans (C)Document15 pagesChemistry - Cet 2021 - Version Code - B2 Solutions: Ans (C)Swati NaikNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/33Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/33Tshegofatso SaliNo ratings yet
- Isomer Dan Spektrokimia Ok 2017Document90 pagesIsomer Dan Spektrokimia Ok 2017joyoNo ratings yet
- First Row Transition MetalsDocument4 pagesFirst Row Transition MetalsDanielle BelconNo ratings yet
- Magnetochemie SeminarzumPraktikum 2012Document25 pagesMagnetochemie SeminarzumPraktikum 2012SANKAR VNo ratings yet
- Transition Metals PDFDocument30 pagesTransition Metals PDFMaheshNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal ComplexesDocument27 pagesTransition Metal Complexeskaushik bhartiyaNo ratings yet
- The D-Block Elements. General Properties: Mr. Kale Vinod NDocument23 pagesThe D-Block Elements. General Properties: Mr. Kale Vinod NLavinia DonaldNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Revision Guide Transition Metals AqaDocument11 pages2.5 Revision Guide Transition Metals Aqashafiqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Hints and Solutions:: (Chemistry)Document8 pagesHints and Solutions:: (Chemistry)Sourabh RajNo ratings yet
- Chelate Effect: Coordination ChemistryDocument13 pagesChelate Effect: Coordination ChemistryNikitha AkulaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Transition Metals: Complex FormationDocument11 pages2.5 Transition Metals: Complex FormationSONIEH SYLVIUSNo ratings yet
- 172 PGTRB Chemistry Study Material Reagents List PDFDocument5 pages172 PGTRB Chemistry Study Material Reagents List PDFMjothibowthanNo ratings yet
- Wa0005Document26 pagesWa0005Dixon ECNo ratings yet
- Starters For Ten - Transition Skills AnswersDocument10 pagesStarters For Ten - Transition Skills AnswerskrisnuNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/32Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/32Tshegofatso SaliNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/32Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/32RamY El NahasNo ratings yet
- Chelate Effect 2007Document29 pagesChelate Effect 2007Ragini SinghNo ratings yet
- CH 19Document36 pagesCH 19SylviaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Transition Metals IntroductionDocument48 pagesLesson 1 Transition Metals Introductiontiahayes2801No ratings yet
- Reaction Rates and StoichiometryDocument5 pagesReaction Rates and StoichiometryDavid Genesis Climacosa PedeglorioNo ratings yet
- IsomeríasDocument11 pagesIsomeríasVictor Manuel Hernández EstebanNo ratings yet
- Exams 2018 - MetallurgyDocument3 pagesExams 2018 - Metallurgyfanpop botherNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument15 pagesRedoxInês AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms: January 2020Document225 pagesInorganic Reaction Mechanisms: January 2020AdistaNo ratings yet
- Solution 2Document12 pagesSolution 2Varad DNo ratings yet
- The D-And F - Block Elements: Very Short Answer Questions (VSA)Document9 pagesThe D-And F - Block Elements: Very Short Answer Questions (VSA)Bhavana VNo ratings yet
- Complexometric Titrations: 3 Year Students, General-ScienceDocument50 pagesComplexometric Titrations: 3 Year Students, General-ScienceHesham AlsoghierNo ratings yet
- Solution 1 SolidDocument11 pagesSolution 1 SolidVarad DNo ratings yet
- Experiment Spot Test-Qualitative Analysis For CationsDocument2 pagesExperiment Spot Test-Qualitative Analysis For CationsragnaroktwizyNo ratings yet
- 15 Transition Metals Edexcel PDFDocument13 pages15 Transition Metals Edexcel PDFGanna109No ratings yet
- Topic 9.4 2009 Transition Elements Prelim SolnDocument17 pagesTopic 9.4 2009 Transition Elements Prelim SolndeadbeanNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundsDocument12 pagesCoordination Compoundspinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- 17-Transition-Metals-Iedxcel ReviseDocument13 pages17-Transition-Metals-Iedxcel ReviseFathmath ShereleenNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledHarsh GargNo ratings yet
- Jee Main 10 April 2023 Shift 1 Resonance Chemistry Question Paper With SolutionsDocument8 pagesJee Main 10 April 2023 Shift 1 Resonance Chemistry Question Paper With SolutionsPankaj BabareNo ratings yet
- CourseDocument18 pagesCourseflamepixerxNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-25-02-11th (PQRS & J)Document11 pagesCHEMISTRY-25-02-11th (PQRS & J)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 - D BlockDocument47 pagesTopic 7 - D Blockizz isalahNo ratings yet
- Mod 5 Revision Guide 4 Transition MetalsDocument14 pagesMod 5 Revision Guide 4 Transition Metalsjohn mNo ratings yet
- Part III 2019 Updated QBDocument6 pagesPart III 2019 Updated QBteresa tsoiNo ratings yet
- The Transition Elements: Practice ExamplesDocument15 pagesThe Transition Elements: Practice Exampleskennethleo69No ratings yet
- Chapter 6: An Introduction To The Chemistry of D-Block ElementDocument16 pagesChapter 6: An Introduction To The Chemistry of D-Block ElementseechaiNo ratings yet
- D - Block Compounds: Inorganic ChemistryDocument11 pagesD - Block Compounds: Inorganic ChemistryApoorv RastogiNo ratings yet
- PLKVKTCSFC - F6 - 2019-2020 - Chem Ans - Kuok KellyDocument8 pagesPLKVKTCSFC - F6 - 2019-2020 - Chem Ans - Kuok KellyOof GucciNo ratings yet
- COORDINATION COMPOUNDS - Class Notes - JEE MindmapDocument22 pagesCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS - Class Notes - JEE Mindmapadsaditya24No ratings yet
- OKS Seminar04Document17 pagesOKS Seminar04KrenarNo ratings yet
- Institute Test PDF ReportDocument8 pagesInstitute Test PDF ReportIshan SharmaNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2018 Paper - 2 Question With Solution - ChemistryDocument17 pagesJEE Advanced 2018 Paper - 2 Question With Solution - ChemistrySanju PatelNo ratings yet
- PDA Technical Documents on Sterilization ProcessesDocument3 pagesPDA Technical Documents on Sterilization ProcessesManas MishraNo ratings yet
- R4850G2 Rectifier Data Sheet 05Document2 pagesR4850G2 Rectifier Data Sheet 05PP CharlyNo ratings yet
- AFPRP Final Group 25Document19 pagesAFPRP Final Group 25Pranay NitnawareNo ratings yet
- Berkowitz Et Al (2010) - Skills For Psychological Recovery - Field Operations GuideDocument154 pagesBerkowitz Et Al (2010) - Skills For Psychological Recovery - Field Operations GuideRita CamiloNo ratings yet
- Conditions For The Emergence of Life On The Early Earth: Summary and ReflectionsDocument15 pagesConditions For The Emergence of Life On The Early Earth: Summary and Reflectionsapi-3713202No ratings yet
- My Demo DemoDocument19 pagesMy Demo DemoAlex LopezNo ratings yet
- Islamic Center Design With Islamic ArchiDocument11 pagesIslamic Center Design With Islamic ArchiMuhammad Sufiyan SharafudeenNo ratings yet
- 02 Lightning Rods and AccessoriesDocument78 pages02 Lightning Rods and Accessoriesmoosuhaib100% (1)
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument12 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Anxiety, Depression and Self-Esteem in Children With Well-Controlled AsthmaDocument6 pagesAnxiety, Depression and Self-Esteem in Children With Well-Controlled AsthmaAbdallah H. KamelNo ratings yet
- Mutual FundDocument2 pagesMutual Fundkum_praNo ratings yet
- Edited Hydraulics Lecture - Part 2 - OrificesDocument36 pagesEdited Hydraulics Lecture - Part 2 - OrificesVincentNo ratings yet
- Foundations On Expansive Soils: 3.1. BackgroundDocument31 pagesFoundations On Expansive Soils: 3.1. BackgroundbiniNo ratings yet
- XII Class Assignment Programs 2023-24Document8 pagesXII Class Assignment Programs 2023-24Sudhir KumarNo ratings yet
- Carbon Disulfide: Hazard SummaryDocument5 pagesCarbon Disulfide: Hazard SummaryAlyssa ZerlinaNo ratings yet
- DissertationDocument15 pagesDissertationNicole BradyNo ratings yet
- MPX English Final Version VOLUME 3Document878 pagesMPX English Final Version VOLUME 3Adrian MacayaNo ratings yet
- Toyota Genuine ATF WSDocument14 pagesToyota Genuine ATF WSKirillNo ratings yet
- 17a03g - Mosfet - DualDocument5 pages17a03g - Mosfet - DualEletronica01 - BLUEVIXNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Mira FixDocument16 pagesJurnal Mira Fixarisanto micoNo ratings yet
- Albert Einstein - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument34 pagesAlbert Einstein - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaalhanunNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Permutations and CombinationsDocument14 pages6.4 Permutations and CombinationsAns SembiringNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ THI HSGDocument13 pagesĐỀ THI HSGahmad amdaNo ratings yet
- Art for Ages 1-3 Focuses on DevelopmentDocument3 pagesArt for Ages 1-3 Focuses on DevelopmentPresley AbrauNo ratings yet