Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Notes Light
Science Notes Light
Uploaded by
dwayne dixon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesScience Notes Light
Science Notes Light
Uploaded by
dwayne dixonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
travels at a
speed of
299 792 kps
through @
vacuum,
The Sun isthe main source of natural light. Sources of ight canbe natural
or made by people (artifical
Sources of natural light Sources of artificial light
Figure 14.1 Sources of it
Luminous and Illuminated Objects
A luminous objects one that produc its own ight. <= Sz]
Ripe 142 Luminous abject
je 142 Luminous objec es
ecoscRe
Cur. ae)
Mluminated (non-luminous) objects reflect light that shines on them.
‘A spoon reflecting light
Figure 143 Nor-luminous objects
‘The Moon, the Farth and other planets reflect the light that shines from the
Sun. Shiny objects like mirrors and spoons also reflect light.
How Light Travels
Can the boy sce the object through the straw when it
is straight? Can he see it when the straw is bent?
‘Why not? Can light travel through the bent straw? Light ats
What statement can you make gbout how light travels in
travels? Write it on the lines below. all directions
from its
How Light Behaves With
Different Materials
ve
ou 8080 i
weer ey
g6e esol
of} Transparent, translucent and opaque
Figure 14.4 How light passes through various materials
We can see clearly through transparent materials. Objects appear blurred when
a
materials,
ee
Figure 14.5 How shadows ae formed.
‘Shadows are formed when opaque objects block the light that shines on
‘them. The light cannot go around the object and so a dark area in the shape
Of the object is formed on any surface behind it.
Figure 14.6 Shadows 2t various times of the day.
‘Shadows formed! because of the light from the Sun are shorter at midday
when the Sun is overhead,
‘When light shines on an object, some of the light i absorbed, some may pass through
‘and some bounces back. When light bounces back from the surface of objects this is
called reflection. Opaque objects absorb some of the light that shines on them and
reflect the rest.
;—_
‘Smooth surface Irregular surface
Sinbhtltt rye ——‘eeedlheye | Sights Ste ttre
\
ye 14.7 Light reflected fam smooth and iregular surfaces.
Clear View
1 Name THREE natural and THREE artificial sources of light.
an
PR eS
List FIVE luminous and FIVE illuminated objects in your environment.
PEE
a a
a
Complete the table below using one or more of these phrases:
is reflected, is absorbed, is scattered, passes through
Object * How Light Behaves
‘Clear windowpane
‘Wooden door
Frosted windowpane
Mirror
Black bag
Light isa form of energy.
Light energy travels in waves.
‘The speed of light through a vacuum is 299 792 kps
Light can be natural or artificial (made by people).
Luminous objects produce their own light.
‘iluminated (non-luminous) objects reflect light that shines on
them,
Reflection is the bouncing back of light rays
‘The Moon and the Earth reflect light from the Sun.
Light travels in straight lines in all directions from its source.
Materials that allow most light to pass through them are
transparent.
“Materials that scatter the light passing through them are
‘translucent,
‘Materials that allow no light to pass through them are opaque.
‘Shadows are formed when opaque objects block the light that
shines on them.
In sunlight, shadows are shortest at midday.
Mirrors are clear glass, coated on one side with
silver or a shiny metal which reflects light.
Mirrors are good reflectors of light
Mirrors show reflections or images of objects
Mirrors can be flat (plane) oF curved.
Curved mirrors can be concave or convex.
po Plane mirrors show images that
qu sbie gn ons
‘sie omez or 6
baton fosido ot 25
Sigh bns fis bstoata =16 \y
et 26 od of 600g6
a6 roi of brifed
o natn al oe at
emer eon
ate rat side up.
Y are the same size
‘25 the object reflected.
(7 are reflected lft and ight
appear to be a far
‘behind the ior as
‘he objets in front oft
Figure 148 Images reflected in a plane miro.
Mirrors can be used to change the direction of light. They change the direction
light when used in devices such as reflecting telescopes, kaleidoscopes,
riscopes, overhead projectors, and medical and dental instruments.
What do I see?
Find out how a kaleidoscope and a periscope work. Which one
enables us to see over walls, around corners and under objects?
-Refraotion..
Light travels faster in gases than in liquids, and faster in liquids than in.
solids,
When light travels from a gas to a liquid, it slows down.
When light travels from a liquid to a solid, it slows down.
‘When light goes from a solid to a liquid or from a liquid to a gas, it
speeds up.
[As a result of the change in speed as light rays move from one substance to
the other, they are bent. The bending of light rays is called refraction.
If you put a pencil or a stick in a jar of water and look
atit from the side it appears broken. This happens
because the light rays coming from the pencil are bent
1a they pass from the air to the water,
-benses..
Lenses are made of transparent materials, such as glass or plastic, that are curved so
that light rays passing through them are bent or refracted.
Figure 149 Lights efracted in wate
‘Types of lenses
‘The Convex Lens: Convex lenses are curved outward on one or both sides, so that the
thickest part isin the middle. Light rays bend towards the thickest part of the lens 0
that the light rays passing through come together at a point called the focal point. The
distance between the centre of the lens and the focal point is called the focal length.
Figure 14.10
Aconex
Tens
ght rays
bend inwards
ti
thier ens, the shorter the focal length.
sex lenses can produce upside-down images.
Convex lenses can be used as magnifiers
‘The lens in the eye is a convex lens.
vex lenses are used to correct farsightedness.
Com
Ire Concave Lens: Concave lenses are curved inwards, They are thicker at the
ids and thinner in the middle. Light rays bend towards the thicker ends so
that light rays passing through are spread outward.
+ Concave lenses produce upright images that are
smaller than the objects whose images are produced.
‘used to correct nearsightedness
. Light rays
spread out
Figure 14.11, A concave lens
© Concave lenses are
Convex and concave lenses are used in many instruments such as these:
kT @&
microscope telescope camera binoculars
| Se=O
projector eyeglasses
Figure 14.12 Some instruments in which lens
{Use your dictionary, an encyclopedia or the Internet find out haw these
{instruments are used and which lenses the)
WEDS PORE
heSpecteum.
A prism is a triangular-shaped object made
6f glass or another transparent material.
‘When light passes through a prism it is
refracted. This causes the light rays (white
ligh®) to be separated into the six colours (the
spectrum) that make up a ray of light. The
colours are red, orange, yellow, green, blue
and violet. The colour indigo is no longer Figure 14.13 A prism
included in the spectrum. Scientists say indigo is a shade of blue or violet and
so should not be regarded as a spectral colour. The colours of the spectrum
can be seen in a rainbow and a soap bubble.
|
‘The primary
colours of
pigment
(substances
used for
colouring) are
magenta, cyan
Figure 14.14 F and yellow,
‘The primary colours of light are red, | The secondary
blue and green. When combined | Colours of
they produce white light. The pigment are
secondary colours of ight are orange, green
yellow, cyan and magenta and purple, Figure 14.15
‘The colour of an object is the colour that is reflected by the object. All other
colours are absorbed.
Objects appear white when all the colours of light are reflected,
Objects appear black when all the colours of light are absorbed.
ee ered
Activity
Light Riddles
Answer these riddles:
3) Tam made of transparent material
Tam thick in the middle and thin at my edges.
Light rays bend and meet at a point when they passthrough me.
Tam found in the human eye. What am I2
am made of transparent material.
Tam thin in the middle and thick at the edges.
Light rays spread outwards when they pass through me
Tean be found in a flashlight. What am [-_______——
Mirrors are good reflectors of light
‘Mirrors can be flat, concave or convex
Tn concave mirrors images may appear upsicie down.
Codcave mirrors are used in flashlights, headlights and telescopes.
In convex mirrors images appear upright
Convex mirrors show a wider area than concave mirrors and are used in
stores and as rear-view mirrors.
Refraction is the bendling of light rays.
Light rays bend when they slow down or go faster.
Lenses are transparent materials that bend light rays.
‘Convex lenses cause light rays to bend invrards and meet at a point called
the focal point.
‘Convex lenses can be used as magnifiers
‘A convex lens is found in the human eye and in cameras.
Concave lenses cause light rays to spread outwards.
‘A prism is used to separate white light into the colours of the spectrum.
‘The colours of the spectrum are red, orange, yellow, green, blue and violet.
‘The colour of an object is the colour reflected by the object.
‘Objects appear white when all the colours of light are reflected.
‘Objects appear black when all the colours are absorbed.
*
x
*
*
x
*
*
x
x
*
x
*
x
®
x
*
®
ee
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- O Level Geo 2004 June ADocument12 pagesO Level Geo 2004 June Adwayne dixonNo ratings yet
- Ability Test - Practice Paper 3Document6 pagesAbility Test - Practice Paper 3dwayne dixon100% (1)
- GSAT Mathematics Revision ToolkitDocument35 pagesGSAT Mathematics Revision Toolkitdwayne dixonNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 - Ability Test 7 Mock Exam: Write Your Name and School BelowDocument11 pagesGrade 6 - Ability Test 7 Mock Exam: Write Your Name and School Belowdwayne dixonNo ratings yet
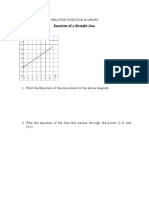
- Equation of A Straight LineDocument5 pagesEquation of A Straight Linedwayne dixonNo ratings yet
- Plants Test: Grass Grasshopper Bird DogDocument10 pagesPlants Test: Grass Grasshopper Bird Dogdwayne dixonNo ratings yet
- Machines Test: Use The Diagram To Answer 19 and 20Document14 pagesMachines Test: Use The Diagram To Answer 19 and 20dwayne dixonNo ratings yet
- Soil Test: Use The Diagram of The Soil Profile To Answer Item 114 - 115Document11 pagesSoil Test: Use The Diagram of The Soil Profile To Answer Item 114 - 115dwayne dixonNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal SystemDocument6 pagesPlant and Animal Systemdwayne dixonNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument15 pagesRocks and Mineralsdwayne dixonNo ratings yet