Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arboleda - Lab Report 1 Reference
Uploaded by
MJ Arboleda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
ARBOLEDA_LAB REPORT 1 REFERENCE (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesArboleda - Lab Report 1 Reference
Uploaded by
MJ ArboledaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
LAB REPORT 1
1. Title: Determination of Specific Gravity of Soil
2. Table of Contents
3. Introduction
4. Objectives
5. Terms and Definitions
6. Apparatus
7. Procedure
8. Observations
9. Result
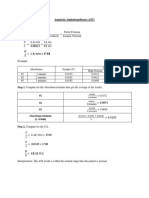
a. Specific Gravity of Given Soil
(650) - (450)_________
(650-450) – (850 -1000)
= 0.5714
The sample specimen utilized in this experiment had a specific gravity
of 0.5714. The theoretical specific gravity of the most common minerals
found in soils ranges from 2.6 to 2.9. The specific gravity of sandy soil
is reported to be 2.65, whereas clayey and silty soils have specific
gravities ranging from 2.6 to 2.9. Soils containing organic matter and
porous particles may have specific gravity values of less than 2.0,
whereas heavy compounds may have values of more than 3.0. The full
elimination of air from the sample is the principal cause of inaccuracy in
the experiment. Also, the loss of water during the hydration of the
oven-dried sample may cause inaccuracies. The presence of biological
material may lower the specific gravity as well.
10. Conclusion
The experiment's objectives were met since we were able to measure the
specific gravity of the soil sample. The experiment yielded a value of 0.5714.
The specific gravity may be used to calculate the degree of saturation. The
specific gravity of soils may be used to calculate the degree of saturation,
void ratio, and unit weight of damp soils. In soil engineering, the unit weight is
essential for the computation of pressure settlement and stability concerns. In
sedimentation analysis, specific gravity is also used to compute the particle
rise of soil.
11. Questions
a. If entrapped air is not removed completely, how will it affect the value
of specific gravity of solids?
- If there is a partial air in soil solids. Water cannot enter the soil because
it is occupied by imprisoned air. As a result, entrapped air reduces the value
of the sum of the solid's weight (pycnometer+solid+water), resulting in a drop
in the value of specific gravity.
b. Mention the practical application of specific gravity of soil solids.
- Specific gravity is a quantity with no dimensions. When we study
two liquids, their densities may be in different units. Density may be
measured in a variety of ways. So, in order to develop a simple way
to compare two liquids, the notion of specific gravity was
introduced. If we know the specific gravity of two liquids, we may
compare their densities.
12. Appendices
a. Calculations
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Cynthia A. Young - Soul Power - Culture, Radicalism and The Making of A U.S. Third World Le PDFDocument314 pagesCynthia A. Young - Soul Power - Culture, Radicalism and The Making of A U.S. Third World Le PDFmi101No ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Pore Pressure - SLB 2004 PDFDocument84 pagesPore Pressure - SLB 2004 PDFMaria MNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS 4 Quarter 1 Week 5: CompetencyDocument10 pagesMATHEMATICS 4 Quarter 1 Week 5: CompetencyJhenzNo ratings yet
- PROPERTIES of SOIL. Sample ProblemsDocument43 pagesPROPERTIES of SOIL. Sample ProblemsMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Deep ExcavationDocument59 pagesDeep ExcavationIsbelNo ratings yet
- 560-000-Pi-T-001 - 1 - Simbologia PDFDocument1 page560-000-Pi-T-001 - 1 - Simbologia PDFismylive100% (1)
- Chemistry: Quarter 1 - Module 5: "Recognize Common Isotopes and Their Uses."Document13 pagesChemistry: Quarter 1 - Module 5: "Recognize Common Isotopes and Their Uses."Norman100% (2)
- Fix Api: Developers GuideDocument36 pagesFix Api: Developers GuideAlex CurtoisNo ratings yet
- Strat - Finals (22Document60 pagesStrat - Finals (22MJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- CE 22 - Final ExaminationDocument3 pagesCE 22 - Final ExaminationMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key PTDocument42 pagesAnswer Key PTMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Date: Aug. 19, 2017 From: Obesity, Fitness & Wellness Week Publisher: Newsrx LLC Document Type: Report Length: 452 WordsDocument2 pagesDate: Aug. 19, 2017 From: Obesity, Fitness & Wellness Week Publisher: Newsrx LLC Document Type: Report Length: 452 WordsMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- CCHM322 Lab Trans 1Document8 pagesCCHM322 Lab Trans 1MJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Eco PDF FreeDocument26 pagesEngineering Eco PDF FreeMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Dry Density of Soil in SituDocument29 pagesDetermination of The Dry Density of Soil in SituMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Cchem Lec Trans 1 1Document6 pagesCchem Lec Trans 1 1MJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Aminotransferases Computation GuideDocument6 pagesAminotransferases Computation GuideMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics - Problems 1Document2 pagesSoil Mechanics - Problems 1MJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Fixtures LinesDocument3 pagesPlumbing Fixtures LinesMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering and Computer Studies: Lyceum of The Philippines University-LagunaDocument18 pagesCollege of Engineering and Computer Studies: Lyceum of The Philippines University-LagunaMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 2: Septic TankDocument2 pagesEngineering Utilities 2: Septic TankMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Arboleda Oe3 ReplikaDocument1 pageArboleda Oe3 ReplikaMJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Joint Department Admin Order No. 2Document8 pagesJoint Department Admin Order No. 2business permits and licenses div.No ratings yet
- Legend of Legaia ArtsDocument5 pagesLegend of Legaia ArtsFlorian Marteein YambaliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4Rocel Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction, Market Share and ProfitabilityDocument15 pagesCustomer Satisfaction, Market Share and Profitabilityxaxif826550% (2)
- ApexSQL Propagate 2018 ReleasedDocument2 pagesApexSQL Propagate 2018 ReleasedPR.comNo ratings yet
- CSS 211Document173 pagesCSS 211Adikwu Anyebe OwoichoNo ratings yet
- ECE 4316: Digital Signal Processing: Dr. Hany M. ZamelDocument19 pagesECE 4316: Digital Signal Processing: Dr. Hany M. ZamellovelearnNo ratings yet
- IGS System-1Document11 pagesIGS System-1manojNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument153 pagesThesisMarius BrătanNo ratings yet
- Defining Submission PhasesDocument1 pageDefining Submission Phasesmohan krishnaNo ratings yet
- Arduino YunDocument1 pageArduino YunTerrance MasterNo ratings yet
- Types of SoilDocument9 pagesTypes of SoilNilima Aparajita SahuNo ratings yet
- 15 Canteens and RestroomsDocument5 pages15 Canteens and RestroomsОлександра СеменкоNo ratings yet
- Rajala Varaprasad Reddy: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesRajala Varaprasad Reddy: ObjectiveRAKESH REDDY THEEGHALANo ratings yet
- LimnaiosG Final ReportDocument11 pagesLimnaiosG Final ReportGiorgos LakemanNo ratings yet
- Midwich Cuckoos EssayDocument2 pagesMidwich Cuckoos EssayVasuda MukundanNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument2 pagesPythonVaibhaw ShiwarkarNo ratings yet
- Sherwood Engineering VHF/UHF Test ResultsDocument7 pagesSherwood Engineering VHF/UHF Test ResultsIU8JTANo ratings yet
- Brand CoolnessDocument21 pagesBrand CoolnessDaiene VilarNo ratings yet
- GlobalDocument9 pagesGlobaldaily foot ball highlightsNo ratings yet
- Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument20 pagesNature of Inquiry and ResearchJewelrhey Radcliffe MiddletonNo ratings yet
- 70-270: MCSE Guide To Microsoft Windows XP Professional Second Edition, EnhancedDocument46 pages70-270: MCSE Guide To Microsoft Windows XP Professional Second Edition, EnhancedManish BansalNo ratings yet
- VadafoneDocument12 pagesVadafoneSantosh MirjeNo ratings yet