Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map MI 2
Uploaded by
nicole barcenaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Map MI 2
Uploaded by
nicole barcenaCopyright:
Available Formats
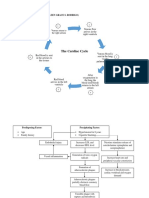
Risk Factors MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION Potential Complications
<40 years old or male
Signs and Symptoms Arrhythmias: depolarization due to lack of
Diabetes mellitus Intense and heavy chest pain oxygen
Dyslipidemia Pain unrelieved by nitroglycerine or resting Cardiogenic Shock: Tissue granulation due to
Hypertension Radiating pain to the left arm, jaw, neck macrophages causing tissue to become unstable
Family history of MIs Shortness of breath Pericarditis: Accumulation of the neutrophils at
Tobacco Smoking Nausea and vomiting the site.
Obesity Pale, cool, clammy skin and sweating Heart Failure
Sedentary lifestyle (diaphoresis) Papillary Muscle Rupture
High Fat Diet Increase HR and BP due to SNS stimulation. Pulmonary Edema
Women: May not feel heaviness on the chest Sudden Cardiac Death
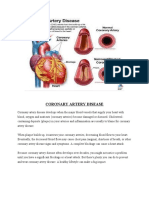
Disease Process: MI is cardiac muscle tissue death due to the lack of blood flow because of the complete occlusion in the coronary artery. The most
common cause of MI is atherosclerosis, which occurs when plaque, which is the accumulation of lipids over time, forms in the coronary artery. When plaque
accumulates in the coronary arteries, the flow of blood and oxygen to the myocardium is reduced. If the occlusion continues for an extended period of time, it
will cause chest pain and ischemia in the cardiac muscle, which will cause them to die (necrosis) if not treated within 20-40 minutes. Because of the ischemia,
muscle contractility decreases and cardiac output decreases, which stimulates the SNS and causes an increase in HR and BP.
Medical Intervention, Labs and Diagnostics Nursing Nursing Interventions
⬆️
Myoglobin ( 1-3 hr post injury): Heme protein that helps transport oxygen. Found
Diagnosis
in cardiac and skeletal muscle. Early marker but is not very specific in indicating MI. Administration of Oxygen: flow rate of
⬆️
Troponin ( 2-4 hrs post injury): Protein found in Myocardial Cells. Tropins I and T 2-4 L/min by nasal cannula. Given to
are specific for cardiac muscle making it recognized as a reliable and critical Decreased increase the circulation oxygen level.
markers for myocardial injury. Cardiac Output Monitor the Vital signs, ECG, LOC,
⬆️
CK-MB ( 4-6 hrs post injury): A cardiac-specific isoenzyme that increases when r/t blockage in heart and lung sounds: This is to be
there has been damage to the cardiac cells. the coronary able to notify the physician
EKG artery immediately if there are changes in
T-wave inversion: Because of ischemia Ineffective these datas to manage the
ST-segment elevation or depression: Sign of injury Tissue Perfusion complications
Abnormal Q wave: Absence of depolarization current r/t reduced blood Bed rest, head elevated for no >45
Morphine: To reduce pain and anxiety flow degrees: To reduce oxygen demand and
Aspirin: To slow clotting Acute Pain r/t ⬇️
chest discomfort. Also Preload,
Nitroglycerin: To dilate artery, increasing blood flow myocardial reducing heart workload.
Emergent PCI: Procedure to open the occluded artery and promote reperfusion ischemia Deep breathing exercises and position
⬇️ ⬇️
Beta Blockers: workload of the heart, slows heart rate, blood pressure. change: To maintain effective
Calcium Channel Blockers: Stops the transport of calcium into the cardiac muscle ventilation throughout the Lungs.
which dilates the coronary arteries.
You might also like
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument19 pagesCongestive Heart FailureIlavenil PanduranganNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Guide for NursesDocument54 pagesHeart Failure Guide for NursesKacelyn QuibanNo ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDocument38 pagesCongestive Cardiac FailureSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument55 pagesIschemic Heart Disease: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentAndrassy Twinkle AlineaNo ratings yet
- Nstemi: How To Risk Stratify?Document32 pagesNstemi: How To Risk Stratify?dhannibernadetNo ratings yet
- Concept Map On DkaDocument7 pagesConcept Map On Dkaapi-546355187No ratings yet
- Modified CaseDocument22 pagesModified CaseAli HawamdeNo ratings yet
- Coronary Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris Myocardial InfarctionDocument44 pagesCoronary Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris Myocardial Infarctionalejandrino_leoaugustoNo ratings yet
- 403 Full PDFDocument10 pages403 Full PDFKuroto YoshikiNo ratings yet
- Cad ....Document94 pagesCad ....AnanthibalaNo ratings yet
- CardiologyDocument62 pagesCardiologysee yinNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection FractionDocument19 pagesHeart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fractioncosmin balanNo ratings yet
- Burn Injury PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBurn Injury PathophysiologyMonique Ann DanoyNo ratings yet
- Concise overview of chronic kidney disease (CKDDocument35 pagesConcise overview of chronic kidney disease (CKDgailNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Therapeutic Classification Pharmacologic ClassificationDocument3 pagesGeneric Name Therapeutic Classification Pharmacologic ClassificationAnselle CasilNo ratings yet
- DVT Guide: Symptoms, Risks and TreatmentDocument9 pagesDVT Guide: Symptoms, Risks and TreatmentGladys YaresNo ratings yet
- NSTEMI GuideDocument33 pagesNSTEMI GuidefauziahNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy My LectureDocument33 pagesCardiomyopathy My LectureAbraha HailuNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocument62 pagesCerebrovascular AccidentJaydee DalayNo ratings yet
- ConceptMap AMLDocument1 pageConceptMap AMLnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- History Taking and Physical Examination of Cardiovascular System-The EssentialsDocument72 pagesHistory Taking and Physical Examination of Cardiovascular System-The EssentialsReena Joanella TimbreNo ratings yet
- MR Elamin ShockDocument70 pagesMR Elamin ShockMohammed Abd AlgadirNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument14 pagesCongestive Heart FailureBella Trix PagdangananNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Patient With Pericardial EffusionDocument2 pagesNursing Management of Patient With Pericardial EffusionAgung Alber0% (3)
- Case Study: Congestive Heart FailureDocument7 pagesCase Study: Congestive Heart FailureXI-E / 21 / MARY TRIANANo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy: By: P.Dhilip KumarDocument29 pagesCardiomyopathy: By: P.Dhilip Kumarpreet kaur100% (1)
- Congestive Heart Failure OverviewDocument12 pagesCongestive Heart Failure OverviewkazelleNo ratings yet
- Hemiplegia Rehabilitation TechniquesDocument11 pagesHemiplegia Rehabilitation TechniquesFares EL DeenNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument10 pagesCardiac Tamponade: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentRahmi Fatma SariNo ratings yet
- Manage Stroke with Tests, Treatments & PreventionDocument27 pagesManage Stroke with Tests, Treatments & PreventionHanif SumonNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument25 pagesCongestive Heart FailuredevianiamalinaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing subarachnoid hemorrhage with CT and lumbar punctureDocument8 pagesDiagnosing subarachnoid hemorrhage with CT and lumbar punctureMohammadAwitNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Prepared By: DR Gloria Lyimo Facilitated By: DR MbeleDocument43 pagesGastrointestinal Bleeding: Prepared By: DR Gloria Lyimo Facilitated By: DR MbeleSamar AhmadNo ratings yet
- CHF Types, Signs, Symptoms, Diagnosis and ManagementDocument28 pagesCHF Types, Signs, Symptoms, Diagnosis and ManagementRamille ✯ de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument14 pagesChronic Renal FailureyazzzNo ratings yet
- Ischemic StrokeDocument49 pagesIschemic StrokeMirna Ayu Permata SariNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular DiseaseDocument37 pagesHemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular Diseasejbvaldez100% (1)
- CABGDocument9 pagesCABGBilal Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Danger Signs of PregnancyDocument3 pagesDanger Signs of PregnancyNesly Khyrozz LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Sultan Chaudhry Benny Dua Eric WongDocument7 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Sultan Chaudhry Benny Dua Eric Wongjamil aldasriNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure PathophysiologyDocument7 pagesCongestive Heart Failure PathophysiologyAileen Grace RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Pleural effusion diagnosis and causesDocument259 pagesPleural effusion diagnosis and causesAjay G BellamNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument15 pagesMyocardial InfarctionameerNo ratings yet
- Head Injury 1Document33 pagesHead Injury 1drvishal bhattNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapapi-252910411No ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument86 pagesCongestive Heart FailureNabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument124 pagesCongenital Heart DiseasemulkanmustafaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Congestive Heart FailureErin MarieNo ratings yet
- Left-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Case PresentationDocument64 pagesLeft-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Case PresentationNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Hepatomegaly 1Document5 pagesHepatomegaly 1Bobby ParksNo ratings yet
- Chest CaseDocument19 pagesChest CaseNesma AdelNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome Nursing Care GuideDocument24 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome Nursing Care GuideAbdulrahman Ahmed100% (1)
- Atrial Fibrillation: Presented by ShehzadiDocument17 pagesAtrial Fibrillation: Presented by ShehzadisamNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument43 pagesHeart FailuresimonjosanNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular Disease - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesPeripheral Vascular Disease - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDr. Mohammed AbdulWahab AlKhateebNo ratings yet
- MIDocument22 pagesMIGagauz SiliviaNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury in Children: Azilah SulaimanDocument30 pagesAcute Kidney Injury in Children: Azilah SulaimanHandre Putra100% (1)
- Myocarditis, (Inflamed Heart Muscles) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMyocarditis, (Inflamed Heart Muscles) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- LV Systolic FunctionDocument36 pagesLV Systolic Functionsruthimeena6891No ratings yet
- EchocardiogramDocument14 pagesEchocardiogramMaria EdelNo ratings yet
- Syllabus On HypertensionDocument9 pagesSyllabus On HypertensionNiña Antoniette GutangNo ratings yet
- Prasugrel Vs Tikagrelor AppendixDocument34 pagesPrasugrel Vs Tikagrelor AppendixSlobodan ObradovicNo ratings yet
- Marfan SyndromeDocument4 pagesMarfan SyndromeAtheer AlenziNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory Systems QuizDocument4 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory Systems QuizGusthe Jebb AzarconNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument18 pagesCirculatory SystemRussiel DagohoyNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and Immunity: Student Learning OutcomesDocument8 pagesLymphatic System and Immunity: Student Learning Outcomeslily1liang-1No ratings yet
- Rat Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesRat Circulatory SystemAnkit NariyaNo ratings yet
- A&P 2nd Sem Final 4.2020Document6 pagesA&P 2nd Sem Final 4.2020kiysumiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Tables-Veins of The Head and NeckDocument8 pagesAnatomy Tables-Veins of The Head and NeckTracie YWNo ratings yet
- FIX Leg UlcerDocument59 pagesFIX Leg UlcerDekka Andra100% (2)
- Crisis HypertensionDocument9 pagesCrisis HypertensionmerahdanmerahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument67 pagesCardiovascular DiseasesokaciaNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 7Th Edition Sherwood Test Bank Cells To Systems 7Th Edition Sherwood Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument68 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 7Th Edition Sherwood Test Bank Cells To Systems 7Th Edition Sherwood Test Bank Full Chapter PDFcleopatrabanhft1vh7100% (9)
- Cerebral blood flow and metabolism modeling/TITLEDocument39 pagesCerebral blood flow and metabolism modeling/TITLEbs19b017 KartikNo ratings yet
- Clinical Hemodynamic Correlation in Mitral StenosisDocument82 pagesClinical Hemodynamic Correlation in Mitral StenosisHristo MateevNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Bio-Score Bab 1 (Form 5)Document45 pagesJawapan Bio-Score Bab 1 (Form 5)azamsensei94% (32)
- Dysrhythmia Interpretation Modules 1-6 June 2012Document126 pagesDysrhythmia Interpretation Modules 1-6 June 2012Jess Varose100% (3)
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery After Endovascular Embolization For Large Arteriovenous MalformationsDocument65 pagesStereotactic Radiosurgery After Endovascular Embolization For Large Arteriovenous MalformationsVladyslav BurykNo ratings yet
- Heart Rate, Life Expectancy and The Cardiovascular System: Therapeutic ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesHeart Rate, Life Expectancy and The Cardiovascular System: Therapeutic ConsiderationsTapan Kumar RoyNo ratings yet
- CMR - Guide - 2nd - Edition - 148x105mm - 03may2017 - Last VersionDocument124 pagesCMR - Guide - 2nd - Edition - 148x105mm - 03may2017 - Last VersionCristián Martínez BocazNo ratings yet
- Atrial Myxoma As A Cause of Stroke: Case Report and DiscussionDocument4 pagesAtrial Myxoma As A Cause of Stroke: Case Report and DiscussionNaveedNo ratings yet
- MCQ Anatomy-thorax-Abdo-PelvisDocument100 pagesMCQ Anatomy-thorax-Abdo-PelvisMatt McCannNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology of The BrainDocument107 pagesAnatomy Physiology of The BrainRadha RamineniNo ratings yet
- Achim 2022Document8 pagesAchim 2022BözskeNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology and EtiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiology and EtiologyAgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- ECase 08 - Tutorial 1 - 2021 Josh ThomasDocument15 pagesECase 08 - Tutorial 1 - 2021 Josh ThomasjoshNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Management of Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF) For HemodialysisDocument14 pagesPreoperative Management of Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF) For HemodialysisRafael CellestineNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Neurology and Neurotherapy Ijnn 2 030Document2 pagesInternational Journal of Neurology and Neurotherapy Ijnn 2 030Anis Rita PratiwiNo ratings yet