Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Development in Paper Machine Clothing To Meet Growing Needs
Uploaded by
Lev BOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Development in Paper Machine Clothing To Meet Growing Needs
Uploaded by
Lev BCopyright:
Available Formats
Development in paper machine clothing to meet growing needs.
Panda K. K , Routray D. G, Panda M. K
ABSTRACT
With the rising cost of paper production, the market is demanding more in terms of paper quality due to opening of
Indian economy, it is time to optimize M/c condition, parameters and processes. JKPM always believes in
continuous improvement and upgrade M/cs continuously by adopting new technologies in paper making. This
article presents basics in M/c clothing, an overview of latest clothing technologies and how JKPM adopted these
technologies from time to time to optimize cost of production and to improve paper quality. The changes made with
respect to furnish, wet end chemistry and recent development in m/c clothing are explained.
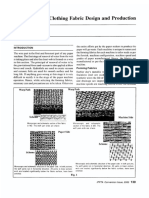
Introduction numerous innovative steps in this fabric
Technological developments, quality direction by upgrading its plant and D Optimum Retention
requirements, changes in furnish, wet machineries, processes and operational D Good Formation
end chemistry and moreover the costs parameter including m/c clothing. D Minimum Sheet two sidedness
of operation have led to rapid D Abrasion resistance
developments in paper machine Basics of Paper m/c clothing D Mechanical stability
clothings. JKPM being leader in taking Paper making consists of spreading a D optimum Off couch dryness
innovative steps updated its system to suspension of pulp evenly across a
the growing needs. paper machine forming fabric followed Function of the press fabric
by its dewatering in a manner that D Removal of water from the sheet in
M/c clothing plays a vital role in the yields a product with desirable
paper manufacturing process in terms the press nip
properties. As the solid content of the D Support the sheet in the press nip to
of cost of production and quality. M/c web increases additional water removal
clothing usually represents around 2% prevent crushing
becomes gradually more difficult, time D Pro vide uniform pressu re
of over all cost per ton of paper (see consuming, and expensive in terms of
figure). It is imperative that clothing distribution over the paper in the nip
both capital and operating cost. The D Impart a desirable surface finish to
design and application be focused on cost of dewatering the sheet in the wire
the largest cost driver. New technology the sheet.
section is 16%, in press section 7% in D Equalize pressure distribution over
introduced either in the process or in dryer section 77%. For this reason,
paper machine design forced the m/c void and land area of the roll to
operation of m/c clothing plays a vital eliminate or reduce shadow
clothing supplier to redesign physical role.
characteristic of the m/c clothing. This marking
aspect has become more significant D Act as a power transmission belt,
Basically m/c clothing is of two types driving all felt rolls in press section
with the globalization of Indian i.e wet end clothing and dry end
economy. To cope up with the changing clothing. Wet end clothing generally
environment JKPM continuously take Key indicators of good press
refer to wire and press section clothing fabric
Paper Manufacturing Cost i.e forming fabric and press fabric. Dry D Adequate strength
6%
2%
end clothing refer to dryer section i.e D Adequate void volume for low
10%
30%
Fiber dryer felts and dryer screen hydraulic pressure at the nip
Labour
Energy D Fine and smooth felt surface to
15% Other Function of the forming fabric minimize rewetting and press
Delivery
Chemical
D Convey the sheet from head box to fabric impression
15% 22%
Clothing the press section D Low compressibility felt to
D Forms a quality sheet maintain adequate void volume.
Machine Clothing Cost
D Functions as a filter media D Smooth surface to provide uniform
D Transmit power to the machine compression
D Adequate permeability for low
27.31%
32.15% Forming Fabric
Key indicators of good forming
Press fabric
Dryer Fabric
40.52%
JK Paper Ltd., Unit: JK Paper Mills,
Jaykaypur-765 017 (Orissa)
IPPTA J. Vol.21, No. 4, Oct.-Dec., 2009 121
hydraulic pressure dryer section. Fabric durability, easily prone to stretching,
dimension stability and structural creasing and fraying causing
Development of modern press stability are important factors
clothing influencing this function.
Dryer Clothing: Key parameters for dryer
D Dryer clothing can be classified as screen
D Wollen dryer felt D Simple and quick seaming
D Conventional dryer felt D No seam mark
D Needled batt-on- base and batt-on D Optimum dimensional stability
mesh D Uniform permeability
D Open mesh dryer felt D Low contamination tendency
D Dri screen dryer felt D Good drying performance.
Function of dryer fabric Ov er vi ew o f J. K. M/ c
Knuckle free
Conventional Batt –on- mesh
Felts Batt – on- base Combination felt
Non woven base
D Support and guide the sheet through configuration
dryer section At JKPM we have five machines Chronology of Forming Fabric change at JKPM
D Improved drying- The tension of including one MG machine. We
clothing improve the contact manufacture Photo copy paper, Writing
between the cylinder and the sheet and Printing paper, Bond, Coating base 2006:Triple Layer
causing increased heat transfer. and Poster paper. The following table
Free passage of vapor becomes an shows the configuration of the m/c with 1985: Double Layer
important function so as to achieve respect to web transfer, press section
faster and economical drying. For and dryer section which is the relevant 1980: Synthetic
this, modern screens with high parameter for m/c clothing selection
permeability are preferred over 1970: Metalic
conventional dryer felts. Developments In Forming
D Control of shrinkage- The tension Fabric At JKPM
of the clothing controls some of the D Metallic wire replaced with
shrinkage in the sheet. Synthetic forming fabric on all the
D It works as a driving element by machines
supporting the web through the Metallic wire had a very low life
due to its inflexibility. It is
M/c no Type of machine Web transfer type Press section Dryer section Press circuit
from wire to press
1 M Fourdriner open Open type 4 nos Pre dryer 30nos
with 3rd press as cylinder ,horizontal
reverse and 4th size press, post
press off set press dryer 7 nos dryer
st cylinder and two
1 press with
cooling cylinder
suction press
2 MG (Yankee open Open type plain MG cylinder 105 Flooding shower
cylinder) press provided
3 MF fourdriner Closed transfer with Dual press 1st Pre dryer 16 no. of Wire trimming
Shower provided
suction pick up. suction press center cylinder, horizontal 100
size press, post H.P.O shower
granite roll and top
Position, Distance and
roll rubber covered dryer 7no including
Angle adjustment
rd
roll . 3 press cooling cylinder
95
straight through Ceramic top
press top roll
granite roll and
bottom swimming 90
roll installed in the
Year 1997
4 MF fourdriner Closed transfer KMW unipress type Pre dryer 12nos of
combination of 606
st
1 press cylinder ,inclined Increas
e inwire life
suction pick up and suction press center size press ,post
press granite roll and top dryer 6nos dryer
roll rubber cover roll cylinder including
1alloy and cooling
cylinder Flood
ing
5 MF fourdriner Closed transfer KMW unipress type Pre dryer 19nos of Couch
shower
combination of 606 1 press cylinder ,inclined
st
suction pick up and suction press center size press ,post
press granite roll and top dryer 10nos dryer
roll rubber cover roll cylinder including
rd
.3 press straight 1alloy and cooling
through press with cylinder
FDR
Trimming
top roll granite roll
and bottom rubber
shower
cover blind drill roll.
IPPTA J. Vol.21, No. 4, Oct.-Dec., 2009 122
to eliminate this problem mechanical and (on line) chemical SLDF change to dryer screen
cleaning/conditioning systems to D In PM 1 & PM 5, 1st group
overcome problems relating to converted to unirun taking the
ASAdeposition. advantage of flat filament of dryer
Impact of furnish change on Developments In Press Fabric screen with increase in contact area.
machine clothing at JKPM At JKPM D Accumulation of fluff in 1st bottom
Prior to commissioning of Fiber line, D Inner fabric removed from all the dryer cylinder problem solved and
furnish composition was m/c m/c runnability and quality
predominantly bamboo (around 80%). After the development of st
imp rov e d. PM -1 1 g r o u p
After New fiber line was commissioned combifelt we removed inner converted into unirun in the year
in 1998, the furnish was changed to fabrics in all the m/cs. By this 2007
predominately mixed tropical hard we not only saved energy but
wood(85%).This furnish composed also the downtime has been Conclusion
mostly of short fiber and consequently reduced to a great extent Adoption of new technology and right
more fines, which retained less in the b ec ause of re duce d felt quality of machine clothing always
wire. Double layer forming fabric was mounting time. However fiber gives a positive impact on productivity
useful in this case. bleeding problem faced with and quality of the product
t h i s c ha ng e w h ic h w a s
Changes inWet end chemistry eliminated by changing air
JKPM always believes in quality permeability of the felt in
improvement and hence trials of consultation with the supplier Chronology of Press Fabric change at JKPM
various chemicals are taken at wet end
on a continuous basis. In the early 90s D Reduction of P.U Felt permeability. 2004: Laminated
our sizing system was acidic/neutral. In PM-3 web transfer from wire
After that AKD with calcium carbonate to press is through suction pick 2001: Bat-on-mesh
was taken for a short period. We up arrangement . Pick up felt
switched over to ASA sizing on all the carries the web from wire to 1st
1998: Bat-on-base
machines since 2006. press nip.In this type of
arrangement we are facing sheet
D While taking trial of AKD with fluttering at the edges and some 1996: Combi Felt
calcium carbonate the life of the time sheet drop problem. Air
wire was drastically reduced to permeability of the P.U felt Upto 1980: Comventional
50% on all the m/c. In PM 1 wire reduced from 80 cfm to 40-50
damage occurred frequently due to cfm in consultation with
the high abrasiveness of Calcium supplier.
Carbonate. We changed the filler to D Shrink sleeve removed from the
Talcum which is less abrasive than suction press roll in the year 1998.
calcium carbonate, at that time. D Change the felt top layer finer
With this change, we could improve filament to avoid felt mark problem
wire life. D Vickery top converted to ceramic
D All m/cs were converted to ASA top on PM-3 to improve felt life
sizing as a part of continuous D H.P.O shower installed in all the
improvement to improve our press felts
product. However due to this, we D On line felt cleaning chemical
had to face numerous problem started in 2nd and 3rd press felts.
r ela tin g to hydrolys is a nd
deposition of ASA, which is sticky
in nature resulting in heavy Dryer fabric
deposition at the press felts, felt D In PM-3 dryer felt replaced with
rolls and press rolls. This gave us dryer screen taking the advantage
runnability problems due to sheet of high permeability of dryer fabric.
breaks and quality defects like Drying efficiency increased.
bluish spots on paper. Felt life D In PM-3 P.V.Blower system
reduced drastically. installed taking the advantage of Press felt conditioning at JKPM
D Before ASA sizing our felt dryer screen .
conditioning system was only Production incresased by 7%
mechanical. Now we have both D In PM 3, PM 4 and PM-5 1st group
Presently we are using the following type of forming fabrics High pr.osc.shower
Air permeability in
M/c no. Weave Count/cm CFM FSI DI
1 16 Shed 2.5L 50/3*17 430 120 32
3 8 Shed double layer 63/2*23 422 110 21
4 8 Shed 2.5L 62/3*18 430 140 36 Uhle box
5 8 Shed 2.5L 60/3*18 440 138 37 Chemical
shower
IPPTA J. Vol.21, No. 4, Oct.-Dec., 2009 123
Presently following quality of press felt used in JKPM
PM # position Type of press felt Air permeability in GSM of felt
CFM
st
1 press Laminated felt 50 1500
nd
2 press Two layer bat-on-mesh 40 1600
3rd press Single layer bat-on-mesh 35 950
3 P.u.felt Two layer bat-on-mesh 65 to 70 1500
nd
2 press Laminated felt 50 to 55 1500
3rd press laminated 45 to 50 1700
4 P.u.felt Laminated 60 1600
nd
2 press Laminated 50 1600
l5 P.u.felt Laminated 60 1600
2nd press Laminated 50 1600
rd
3 press Laminated 45 to 50 1700
Presently following quality of Dryer screen used in JKPM
paper position Type of Dryer Air permeability in GSM of felt
machine no Screen CFM
st
1 1 Dryer group Flat Monofilament 120 to200 1150 to1300
nd
2 Dryer group Dryer Felt 15 to 20 2100 to 2200
3rd Dryer group Dryer Felt 15 to 20 2100 to2200
4th Dryer group Dryer Felt 15 to 20 2100 to 2200
5th Dryer group Dryer Felt 15 to 20 2100 to 2200
6th Dryer group Dryer Felt 15 to 20 2100 to 2200
st
3 1 Dryer group Monofilament 120 to200 1150 to1300
2nd Dryer group Monofilament 200 to 300 1150 to1300
3rd Dryer group Monofilament 300 to 400 1150 to1300
4th Dryer group Monofilament 300 to 500 1150 to1300
4 1st Dryer group Monofilament 120 to200 1150 to1300
2nd Dryer group Monofilament 200 to 300 1150 to1300
3rd Dryer group Monofilament 300 to 400 1150 to1300
4th Dryer group Monofilament 300 to 500 1150 to1300
5 1st Dryer group Flat Monofilament 120 to200 1150 to1300
nd
2 Dryer group Monofilament 200 to 300 1150 to1300
3rd Dryer group Monofilament 200 to 300 1150 to1300
4th Dryer group Monofilament 200 to 300 1150 to1300
5th Dryer group Monofilament 200 to 300 1150 to1300
th
6 Dryer group Monofilament 300 to 400 1150 to1300
400 to 500
Impact on Productivity
Wire Life and Production Trend Press Fabric & Production Trend Dryer Fabric & Produciton Trend
100 200 100 300 600 1000
80 80 250 500
150 800
200 400
60 60 600
100 150 300
40 40
100 400
50 200
20 20 50 100 200
0 0 0 0
Metallic Synthetic SL Synthetic DL 0 0
Conventional felt
Bat-on-mesh Laminated felt Dryer felt Dryer Fabric
Type of Wire Type of Press Fabrics Dryer Felt / Screen
Fabric Life Production Fabric Life Production Fabric Life Production
Impact on Quality ( Elimination/drastic reduction of certain defect modes)
Wire Impression Felt Impression
High High
Medium Medium
Low Low
Negligible
Very Low
No Felt Mark
Metallic Synthetic SL Synthetic DL Conventional felt Bat-on-mesh Laminated felt
IPPTA J. Vol.21, No. 4, Oct.-Dec., 2009 124
You might also like
- 2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 01Document4 pages2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 01Lev BNo ratings yet
- 2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 05Document4 pages2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 05Lev BNo ratings yet
- 2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Articel 03Document5 pages2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Articel 03Luis RosesNo ratings yet
- Designing of Forming Fabric Considering Paper Making AspectsDocument6 pagesDesigning of Forming Fabric Considering Paper Making AspectsLev BNo ratings yet
- 2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 06...Document4 pages2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 06...Lev BNo ratings yet
- Development Paper IndustryDocument20 pagesDevelopment Paper IndustryLarsNo ratings yet
- Targeting Quality at High SpeedDocument3 pagesTargeting Quality at High SpeedSelly YunitaNo ratings yet
- IJEART021004Document5 pagesIJEART021004erpublicationNo ratings yet
- IPPTA CI 2003 139 143 Paper Machine ClothingDocument5 pagesIPPTA CI 2003 139 143 Paper Machine ClothingnotengofffNo ratings yet
- 2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 04Document4 pages2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 04Lev BNo ratings yet
- Dryer Machine: Presented by-Ar-Rafi HridayDocument23 pagesDryer Machine: Presented by-Ar-Rafi HridayAr Rafi HridayNo ratings yet
- Right Selection of Clothing Design Key Factor For Machine PerformanceDocument6 pagesRight Selection of Clothing Design Key Factor For Machine PerformanceLev BNo ratings yet
- Effective Forming Fabric Concepts - For Economical Paper and Board Production PDFDocument4 pagesEffective Forming Fabric Concepts - For Economical Paper and Board Production PDFBiantoroKunartoNo ratings yet
- CottonPicks PrintingTechniques DigitalDocument4 pagesCottonPicks PrintingTechniques DigitalelisaNo ratings yet
- V27n2a06 PDFDocument14 pagesV27n2a06 PDFRosy Vargas CaroNo ratings yet
- 2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 11Document6 pages2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 11Lev BNo ratings yet
- Maintech Fabric Leaflet 200313Document2 pagesMaintech Fabric Leaflet 200313Rostom CharaallahNo ratings yet
- Turbair Vacuum Systems EngDocument4 pagesTurbair Vacuum Systems Engphool singhNo ratings yet
- VOITH MultiformvDocument3 pagesVOITH MultiformvKristina ivanovicNo ratings yet
- Cadcam and 3d PrintingDocument1 pageCadcam and 3d Printingapoorva jayaswalNo ratings yet
- IFASDocument57 pagesIFASImran KhanNo ratings yet
- ReplicationofScreen PrintingFabricviaInk JettextileDocument11 pagesReplicationofScreen PrintingFabricviaInk JettextileLieu DangNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air PDFDocument1 pageCompressed Air PDFDyeing DyeingNo ratings yet
- Kim 2018Document6 pagesKim 2018Bookaholic 11No ratings yet
- 2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 10Document12 pages2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 10Lev BNo ratings yet
- ENG - Weaving Applications - LuwaDocument7 pagesENG - Weaving Applications - LuwaAkshay KadiaNo ratings yet
- Expertip Tips Measuring Monitoring Wear Rate Forming FabricDocument5 pagesExpertip Tips Measuring Monitoring Wear Rate Forming FabricnotengofffNo ratings yet
- Srinivasan 2020Document8 pagesSrinivasan 2020Jasper JazNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Concrete in Hot TemperaturesDocument13 pagesMechanical Properties of 3D Printed Concrete in Hot TemperaturesIttoop R AncherilNo ratings yet
- Effects of Layer Thickness and Binder Saturation LevelDocument10 pagesEffects of Layer Thickness and Binder Saturation LevelDaniel SolesNo ratings yet
- Dressing For Success: Today's Paper Machine ClothingDocument4 pagesDressing For Success: Today's Paper Machine Clothingst7167No ratings yet
- 2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 02Document8 pages2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 02Lev BNo ratings yet
- Cartesian FDM Additive Manufacturing Smart Machine (Journal)Document6 pagesCartesian FDM Additive Manufacturing Smart Machine (Journal)DigvijayNo ratings yet
- Effect of FDM Process Parameters On Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Carbon fibre-PLA CompositeDocument7 pagesEffect of FDM Process Parameters On Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Carbon fibre-PLA CompositeMina AdelNo ratings yet
- Ink WashandWarpageDefectPredictionfromthein MoldDecorationProcessSimulation PDFDocument8 pagesInk WashandWarpageDefectPredictionfromthein MoldDecorationProcessSimulation PDFrishi memaneNo ratings yet
- TROUBLE SHOOTING GUIDE Blanket SurfaceDocument6 pagesTROUBLE SHOOTING GUIDE Blanket SurfaceLai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Doyle Sheet-Fed Cleaning Systems For Corrugated Printing: Efficient Filter CycloneDocument2 pagesDoyle Sheet-Fed Cleaning Systems For Corrugated Printing: Efficient Filter CycloneRedOne KhasmiNo ratings yet
- Paper Breil2016Document20 pagesPaper Breil2016吳昇晃No ratings yet
- Polymers: Preparation of Hydrophobic Surface On PLA and ABS by Fused Deposition ModelingDocument14 pagesPolymers: Preparation of Hydrophobic Surface On PLA and ABS by Fused Deposition ModelingUsman SikandarNo ratings yet
- 3D-Printing: Diploma in Electronic & Telecommunication 2021-2023Document32 pages3D-Printing: Diploma in Electronic & Telecommunication 2021-2023Śhībäm Śąhů100% (1)
- Fabric Processing Formation PDFDocument2 pagesFabric Processing Formation PDFBiangkerokNo ratings yet
- 3dp - Infill PatternDocument5 pages3dp - Infill PatternrakeshcuteNo ratings yet
- Differences Paper and Paperboard enDocument4 pagesDifferences Paper and Paperboard enAbyNo ratings yet
- OKI Pro9541WT Brochure 0220 EN-EN Lores tcm70-254421Document4 pagesOKI Pro9541WT Brochure 0220 EN-EN Lores tcm70-254421backhole001No ratings yet
- Fosroc Renderoc Sxtra: Constructive SolutionsDocument2 pagesFosroc Renderoc Sxtra: Constructive SolutionsVincent JavateNo ratings yet
- Twogether Article 33 en 20 Premium TissueDocument4 pagesTwogether Article 33 en 20 Premium TissueDany ZuñeNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214785322020971 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S2214785322020971 MainTayyab AliNo ratings yet
- Next-Gen Next-Gen: Materials and ProcessesDocument36 pagesNext-Gen Next-Gen: Materials and ProcesseskikorrasNo ratings yet
- Article Daikin PDFDocument1 pageArticle Daikin PDFSoni IlizNo ratings yet
- Highcon Beam: Digital Cutting and Creasing For Mainstream ProductionDocument4 pagesHighcon Beam: Digital Cutting and Creasing For Mainstream ProductionshruthiNo ratings yet
- New Developments in Paper and Board DryingDocument10 pagesNew Developments in Paper and Board Dryingadel boukadoumNo ratings yet
- IPPTA 104-49-59 Innovative Steam ShowerDocument11 pagesIPPTA 104-49-59 Innovative Steam ShowerAmri ZalNo ratings yet
- Solids Drying: Basics and ApplicationsDocument4 pagesSolids Drying: Basics and ApplicationsrahulNo ratings yet
- Magazine LResDocument8 pagesMagazine LResahmedNo ratings yet
- IRJMETS - Ni Njoman Manik Susantini-Rama Wahyu RDocument10 pagesIRJMETS - Ni Njoman Manik Susantini-Rama Wahyu RNi Njoman Manik SusantiniNo ratings yet
- Designand Fabricationof Pneumatic Paper Cup Making MachineDocument7 pagesDesignand Fabricationof Pneumatic Paper Cup Making Machinekaveriatakari786No ratings yet
- 16 - Chapter 8 PDFDocument60 pages16 - Chapter 8 PDFJavier Martinez CañalNo ratings yet
- New Developments in Paper and Board DryingDocument10 pagesNew Developments in Paper and Board DryingSahil DesaiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Processing Parameters On Properties of LDocument7 pagesEffect of Processing Parameters On Properties of LNAJJEMBA WINNIFREDNo ratings yet
- 2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 10Document12 pages2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 10Lev BNo ratings yet
- Right Selection of Clothing Design Key Factor For Machine PerformanceDocument6 pagesRight Selection of Clothing Design Key Factor For Machine PerformanceLev BNo ratings yet
- 2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 11Document6 pages2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 11Lev BNo ratings yet
- Matching The Change in Raw Material: Fiber & Fabric Development For The Board & Packaging SectorDocument6 pagesMatching The Change in Raw Material: Fiber & Fabric Development For The Board & Packaging SectorLev BNo ratings yet
- 2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 04Document4 pages2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 04Lev BNo ratings yet
- 2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 02Document8 pages2009 Issue 4 IPPTA Article 02Lev BNo ratings yet
- 1-Polo - MSDSDocument5 pages1-Polo - MSDSSaad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Paper PollutionDocument4 pagesPaper PollutionmeowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 IndustriesDocument16 pagesChapter 5 IndustriesHussain100% (1)
- Advantage Semi ExtensibleDocument2 pagesAdvantage Semi ExtensibleDaniel GoffNo ratings yet
- Selecting Laboratory Tests To Predict Effectiveness of Retention and Drainage Aid ProgrammesDocument14 pagesSelecting Laboratory Tests To Predict Effectiveness of Retention and Drainage Aid Programmesshalu29No ratings yet
- Cambridge Primary ProgressionTests - Past Papers PDFDocument3 pagesCambridge Primary ProgressionTests - Past Papers PDFPinky Dey8% (13)
- Service Manual C211/C212/C216/C224: PN: RCFM2105Document769 pagesService Manual C211/C212/C216/C224: PN: RCFM2105cidapecas pecasNo ratings yet
- Divinity Original Sin 2 ScrollsDocument6 pagesDivinity Original Sin 2 Scrollsbeans54No ratings yet
- 9D Research GroupDocument9 pages9D Research Groupapi-291828723No ratings yet
- Examination of Charred DocumentsDocument21 pagesExamination of Charred DocumentsmithraNo ratings yet
- mp500 SMDocument82 pagesmp500 SMМайор ДеяновNo ratings yet
- D 780 - 95 R99 Rdc4mc05nvi5oqDocument2 pagesD 780 - 95 R99 Rdc4mc05nvi5oqHernan MartNo ratings yet
- Compuload CL4070 Printer PDFDocument2 pagesCompuload CL4070 Printer PDFsongs SomervilleNo ratings yet
- Booklet Nivel B 3° 4° 5°Document185 pagesBooklet Nivel B 3° 4° 5°Carolina MedranoNo ratings yet
- Bizhub C360 C280 C220 Spec and Install GuideDocument23 pagesBizhub C360 C280 C220 Spec and Install GuideEdward Azadex ThomasNo ratings yet
- Digital Media SyllabusDocument7 pagesDigital Media SyllabusDájanique LeonardNo ratings yet
- Judith H. Hofenk de Graaff, Wilma G.Th. Roelofs, Henk Van KeulenDocument6 pagesJudith H. Hofenk de Graaff, Wilma G.Th. Roelofs, Henk Van Keulendie lutionNo ratings yet
- DuPont Tyvek Users GuideDocument39 pagesDuPont Tyvek Users Guideprashantpatil99kNo ratings yet
- Canon imagePRESS C910 C810 C710 Specification SheetDocument3 pagesCanon imagePRESS C910 C810 C710 Specification Sheetbill postersNo ratings yet
- Artikel 3 (Weber's Theory of Location of Industries)Document10 pagesArtikel 3 (Weber's Theory of Location of Industries)Muhammad Fakruhayat Ab Rashid0% (1)
- Mid Term Top Sheets Midyear 2019Document79 pagesMid Term Top Sheets Midyear 2019Waqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Constructing A Cardboard Building - Design GuideDocument16 pagesConstructing A Cardboard Building - Design GuidePaul GrimesNo ratings yet
- TestDocument87 pagesTestmnmnmnmNo ratings yet
- Yamaha R1 Paper Assembly-CompleteDocument15 pagesYamaha R1 Paper Assembly-CompletexuanvNo ratings yet
- BS 4415 1 1992 Determination of PDFDocument12 pagesBS 4415 1 1992 Determination of PDFali ahmadNo ratings yet
- Booklet With List - 4th Year 2023Document51 pagesBooklet With List - 4th Year 2023Ariadna Fiori TaboadaNo ratings yet
- Brochure Fisher Pulp Paper Solutions en 127238 PDFDocument32 pagesBrochure Fisher Pulp Paper Solutions en 127238 PDFDwinaRahmayaniNo ratings yet
- Inglés 3 CuadernilloDocument140 pagesInglés 3 CuadernillogabysoteloNo ratings yet
- PROF. NO.28 Project Profile On Handmade Paper Manufacturing UnitDocument6 pagesPROF. NO.28 Project Profile On Handmade Paper Manufacturing UnitNitesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Paper PulpDocument28 pagesPaper PulpFACEtubeNo ratings yet