Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laser Peripheral Iridotomy Guide
Uploaded by
Fapuw ParawansaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laser Peripheral Iridotomy Guide
Uploaded by
Fapuw ParawansaCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/236892500
Laser Peripheral Iridotomy
Article · January 2005
CITATIONS READS
0 9,802
5 authors, including:
Shalini Mohan Ramanjit Sihota
All India Institute of Medical Sciences All India Institute of Medical Sciences
97 PUBLICATIONS 323 CITATIONS 268 PUBLICATIONS 4,321 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Ologen Project View project
Immunological Basis of Symptomatology in Ocular Diseases View project
All content following this page was uploaded by Shalini Mohan on 31 May 2014.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
CURRENT PRACTICE
Laser Peripheral Iridotomy
Shalini Mohan, MS, Vinay Gupta, MD, Ramanjit Sihota ,MD, FRCS (Ed), FRCOphth
Introduction
Indications –
Laser peripheral iridotomy attempts to open a narrow
angle without eye being opened up & that too under topical 1. Angle closure glaucoma – acute, subacute/
anaesthesia, which permits equalization of pressure in intermittent with symptoms of angle closure,
anterior and posterior chambers of eye. Meyer
chronic with peripheral anterior
Schwickerath in 1956 created first iridotomy using broad-
synechiae(Figure 1 ).
spectrum, incoherent light source, xenon arch lamp.
Frequent corneal & lens opacities lead to rejection of the 2. Occludable angles with provocative tests positive
method. 3. Occludable angle with signs of previous attack /
critically narrow angle.
4. Fellow eye (As contralateal eye has 80 % chances
of getting acute attack)
5. Iris bombe
6. Phacomorphic glaucoma with pupillary block
element.
7. Luxated /subluxated lens (with intact vitreous
face).
8. Aphakic / pseudophakic pupillary block.
9. Nanophthalmos.
10. Incomplete surgical iridectomy.
11. Mixed Mechanism glaucoma (if filtering surgery
not required)
12. Aqueous misdirection syndrome
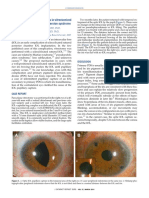
Figure 1 - Chronic ACG 13. Phakic IOLs
14. Plataeu iris syndrome
15. Pigmentary glaucoma
16. To deepen a narrow angle before laser
trabeculoplasty.
Figure 2 - Abraham Iridotomy Lens
Glaucoma Services
Dr. Rajendra Prasad Centre for Ophthalmic Sciences,
All India Institute of Medical Sciences,
Figure 3 - Nd YAG laser PI
New Delhi-110029
January, 2005 250 DOS Times - Vol.10, No. 7
Contact Lens – A contact lens with antireflective coating
Contraindications is used. Most commonly used is Abraham iridotomy lens
1. Patient unable to co-operate/ sit on slit lamp. (figure 2), which is a modified Goldmann type of fundus
2. Opaque / cloudy cornea. lens with a +66D planoconvex button bonded into a
decentered 8mm hole. Beside this Wise iridotomy lens
3. Widely dilated pupil.
(+103D) can also be used, only in, experienced hands as
4. Flat anterior chamber with iridocorneal touch. higher magnification causes difficulty in focusing and
5. Ongoing inflammation. decreases depth of focus (1). The advantages of contact lens
6. Rubeosis Iridis. are –
7. Angle closure not due to pupillary block (e.g. ICE • Acts as speculum – keeps the lids apart
membranes/ neovascular membranes). • Controls eye movements & blinking
Figure 4 - Angle closure Figure 4 - Angle closure opening after YAG PI
• Minimizes corneal epithelial burns & retinal burns by
Technique – acting as a heat sink. It causes relative divergence of
Instrumentation light at the cornea & retina, which reduces the power
Lasers – Various lasers used are pulsed Nd:YAG density to 1/4th.
(1064nm), Argon (514nm continuous/ Pulsed), krypton, • Focuses & increases the power density on the iris
Nd:YLF (1053nm), Diode (805nm), Dye laser (Rhodomine surface by a factor of 4.
6G, 590nm), Diode laser pumped frequency doubled • Provides the magnification of the target site with less
Nd:YAG laser (532nm). Q-switched ruby was tried in past. loss of depth of field that occurs with increase
Nd:YAG is the laser of choice by most of the magnification of slit lamp.
ophthalmologists, all over the world followed by combined Slit Lamp – with high magnification (e.g.´40).
Argon & Nd – YAG laser. Photodisruption is independent
of iris colour and iridotomy rarely closes after Nd:YAG
laser rather than photocoagulation used by Argon / Diode
laser. Semiconductor Diode laser is more suitable for dark
brown irides as stromal penetration is better than Argon
laser.
Figure 5 - UBM Image Pre PI UBM image Post PI Figure 6 - Post Nd YAG PI bleeding
January, 2005 251 DOS Times - Vol.10, No. 7
Selection of Treatment Sites - Iridotomies should be Nd:YAG laser – The performance of iridotomy with
performed in superior quadrant, covered beneath the Nd:YAG laser (Figure 3) is quicker, more efficient & straight
upper eyelid to prevent a second pupil effect. The best site forward. Most Nd:YAG lasers come with He – Ne / diode
is superonasal quadrant to prevent direct injury to macula laser aiming beams. The two aiming spots are brought to
i.e. 10 o’clock in right eye & 1 o’clock in left. Initially focus and then they are defocused slightly posteriorly in
iridotomies were performed 1/3rd distance away from the iris stroma. Laser is fired at a focusing angle (cone angle)
limbus but now it has been realized that peripheral of 18 degrees after appropriate selection of the site.
placement is better, as it hides the iridotomy under Combined Argon/ Diode & Nd:YAG laser - the Argon
peripheral corneal haze, reduces the likelihood of sealing or Diode laser is used with very short pulses to chip out a
of iridotomy by posterior synechiae and lens opacities, if small opening, so that iris thickness becomes 1/4th & vessels
develop, are peripheral in location. 12 o’clock position is to over there coagulate. Then Nd:YAG laser completes the
be avoided because gas bubbles prelude adequate procedure. The shock waves of Nd:YAG causes injury to
visualization if argon laser is used & site can be left for cornea & lens and hemorrhage whereas closure of
future iridectomy during filtering surgery. Eyes with iridotomy is seen commonly after Argon. The combined
Silicon oil should have inferiorly placed iridotomy to avoid mechanism results in lower complication along with higher
blockage by the oil, which rises to the top. The best target rate of patency (9). It is especially useful in thick, brown
site is a crypt or a thinned area of iris as the penetration is irides, subjects with prominent iris vessels (rubeosis,
easier. In blue eyes, broad, dark & gray area is chosen for uveitis) & patients on anticoagulant therapy.
better absorption by pigments, if argon laser is used. Frequency doubled Nd – YAG laser – It is used in place
of Argon laser with similar results. As solid-state diode
Pre Laser Medication – laser pumps it, so it has the advantage of both the lasers.
• Informed consent taken after explaining the procedure Scanning electron microscopy showed less disruption of
the surface of the lesion as compared to Argon (5).
to the patient.
Nd:YLF laser – This picosecond (ps) laser is found to
• 2% topical Pilocarpine instilled, every 15 mins. for 3
have better results than nanosecond (ns) Nd:YAG laser in
applications, to maximally thin & stretch peripheral
studies (3). It has been seen that during laser treatment, the
iris.
trabecula of the iris stroma were not just torn apart as in a
• 1% Apraclonidine or 0.2% Brimonidine instilled ½ hour ns laser iridotomy, but completely removed within the
before to prevent postoperative IOP spikes. diameter of the applied spiral pattern and dispersed as
• Topical Anaesthesia is given with Proparacaine fine tissue debris into the anterior chamber.
hydrochloride (0.5%). Peribulbar needed only if patient Lasers Parameters
is uncooperative.
Lasers Duration Power (mW) Spot No. of
Method - Whatever the method used, full penetration (secs) size (µ) shots
is indicated by mushroom clouds of pigments liberated
Argon 0.02-0.05 1000-1500 50 50-100
from pigment epithelium known as “Smoke Signals” (1), (6).
continuous
There is also visible gush of aqueous, deepening of anterior
(short pulse*)
chamber & decrease in iris bombe. Visualization of the
lens capsule ensures a full thickness opening. Argon 0.1-0.2 1000 50 1-30
Transillumination is not a reliable sign. continuous
(long pulse**)
Argon laser - There are various method for Argon laser.
Argon pulsed 0.2 20-25 50 2-250
1. Hump technique – a localized elevation is created with
Nd:YAG 0.1 500 100 -
a large diameter, low energy burns & then it is
frequency
penetrated with a small, intense burn.
doubled
2. Drumhead technique – large diameter, low energy
Nd:YAG - 4-6mJ - 1-10
burns are put around the intended treatment site &
then penetrated with small diameter, high energy Combined
burn. Argon 0.02-.05 1000 50 5-25
+ Nd:YAG - Fixed 4-6 mJ Fixed 1-10
3. Straight / Direct method – iris is penetrated directly. It
is the most commonly used method. Diode 0.05-0.1 750-1250 50-75 50-100
4. Chipping / superimposed technique – it is to deliver Pulsed dye 1 µ sec 200mJ 250 -
energy to one spot repeatedly until penetration takes (Rhodamine 6G)
place. * For dark brown iris. ** For blue, hazel, light brown iris
January, 2005 252 DOS Times - Vol.10, No. 7
Post Laser Regimen – phacoanaphylactic endophthalmitis are also reported
1. Topical Prednisolone acetate 1 % - 4 times for 3-5 days. by some researchers.
2. Stop Pilocarpine to prevent posterior synechiae Outcome – Patient is ambulatory immediately. Follow
up is done at 1 hour, 1 week, & 4 weeks. If iridotomy remains
3. Tab Acetazolamide 250 mg stat
patent 4-6 weeks the opening usually remains open.
4. Topical Apraclonidine 1% / Brimonidine 0.2%
A study of 500 patients by Sihota et.al. at Dr. R.P. Centre
5. The status of iridocorneal angle should be assessed showed that iridotomy alone or with topical medication
immediately by gonioscopy after the procedure & later was sufficient to control intraocular pressure in about half
on when topical medications discontinued (figure 4 & the acute eyes, 3/4th of subacute, but only 30% of chronic
5). subgroup (8).
Complications – Visually significant complications can
Suggested Readings
be seen in few individuals.
1. Belshar CD, Greff JL. Laser Therapy of Angle Closure
1. Post laser IOP spikes – It is caused by reduction of
Glaucoma. Principles and Practice of ophthalmology,
outflow facility. Various studies have reported rise of
Albert & Jakobiec: 2000; Ed II; Vol IV; ch 224: 2941 –
IOP in 1/3rd cases (7). It can be prevented by 1 drop of
2953.
Apraclonidine (1%) or Brimonidine (0.2%) ½ hour
before laser & immediately after (1) (6). 2. Gaasterland DE. Rodrique MM, Thomas G. Threshold
for lens damage during Q Switched Nd:YAG laser
2. Anterior uveitis – It is because of blood aqueous barrier
iridectomy. A study on rhesus monkey eyes.
breakdown. Therefore, topical Prednisolone 1% is given
Ophthalmology: 1988; 92:1616.
for first 3-5 days.
3. Gerd G, Johan R, Ursula SE, Kaster N, Elsayed EH, Horst
3. Pupillary distortion – More common with Argon (6).
L, Alfred V. Initial Clinical Experience With the
4. Corneal epithelial defects & corneal burns (epithelial/ Picosecond Nd:YLF laser for Intraocular Therapeutic
endothelial). Applications: Br J Ophthalmol 1998; 82: May: 504 –
5. Bleeding / Hyphaema – Bleeding is seen commonly 509.
(50%) (6) after Nd:YAG laser (figure 6 ). One study 4. H Su CT, Shen CS, Herry SL C. Midterm follow up of
reported significant bleeding only in 12.2% of cases (4). Nd:YAG laser iridotomy in Asian Eyes; Ophthalmic
Applying pressure with contact lens can stop it. Surgery, Lasers & Imaging: 2003 July/ Aug vol 34; No.4.
6. Cataract – Threshold for lens damage is 6 mJ with 1-2 5. Marcio MA, Rafael AS, Peter AN. Diode Laser Pumped,
pulses per bursts (2). Focal opacities develop, which Frequency Doubled Nd:YAG Laser Peripheral
are generally non – progressive (6). Anterior capsular Iridotomy: Ophthalmic surgery & Lasers 1997; 28: 305-
rupture & zonular disruption are also reported. 10.
7. Diplopia / Ghost image / Monocular blurring – If 6. Ritch R, Liebmann JM. Laser Iridotomy & peripheral
opening is not covered under upper lid. iridoplasty: The Glaucomas, Glaucoma Therapy: Vol
8. Closure of Iridotomy – Closure is defined as opening III 1996: 1549 – 1564.
becoming smaller by 50% or more (1). It generally occurs 7. Robin AL, Pollack IP, deFaller JM. Comparison Of
within first 6-8 weeks & occurs 40% more commonly Nd:YAG & Argon Laser Iridotomies. Ophthalmology.
after Argon laser. Therefore minimum diameter should 1984; 91:1011-16.
be 150 – 200µ. Patency must be confirmed by
8. Sihota R, Agarwal HC. Profile Of The Subtypes Of
visualization of anterior lens capsule or vitreous face.
Angle Closure Glaucomas In A Tertiary Hospital In
Provocative tests should be employed to confirm
North India: Indian J Ophthalmol 1998 March 46 (1)
functional patency.
25-9.
10. Retinal / Macular burns – These can be minimized by
9. Zhang X, Peng D. Combined Argon And Nd:YAG Laser
aiming beam towards peripheral nasal retina.
Peripheral Iridectomy: A New Approach In Clinical
11. Malignant glaucoma, sterile hypopyon, cystoid Practice. : Yan Ke Xue Bao. 1996 Sep; 12 (3): 158-62.
macular oedema, pupillary pseudomembrane &
January, 2005 253 DOS Times - Vol.10, No. 7
View publication stats
You might also like
- Occular DiseasesDocument32 pagesOccular Diseasesflash.43612No ratings yet
- Biology Lab Activity 1Document6 pagesBiology Lab Activity 1Adrian Anthony Villaluz GasatayaNo ratings yet
- IndianJOphthalmol66111539-5652093_154200Document15 pagesIndianJOphthalmol66111539-5652093_154200aarushi singhNo ratings yet
- The Open Globe MediumDocument120 pagesThe Open Globe MediumAna Raquel RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Multifocal Intraocular Lenses: Roberto BellucciDocument5 pagesMultifocal Intraocular Lenses: Roberto BellucciMaria ArNo ratings yet
- Eye ExaminationDocument34 pagesEye ExaminationSashwini DheviNo ratings yet
- Microscopy Hand NotesDocument10 pagesMicroscopy Hand NotesAmeeraNo ratings yet
- RANON, LYAN ANACLETO Q M12 AMDocument3 pagesRANON, LYAN ANACLETO Q M12 AMNady BalberoNo ratings yet
- OSPE Eye (Sabiha Madam)Document83 pagesOSPE Eye (Sabiha Madam)Ggah VgggagagsgNo ratings yet
- Fundoscopy Tutorial: Slide 1Document26 pagesFundoscopy Tutorial: Slide 1SaraNo ratings yet
- gt0912 F4 LarocheDocument3 pagesgt0912 F4 LarocheMichael CraneNo ratings yet
- OptometristDocument3 pagesOptometristAshleyNo ratings yet
- IridoplastiaDocument3 pagesIridoplastiaVicky ChacónNo ratings yet
- RANON, LYAN ANACLETO Q M13 PMDocument13 pagesRANON, LYAN ANACLETO Q M13 PMNady BalberoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Eka 1 PDFDocument4 pagesJurnal Eka 1 PDFfyddienNo ratings yet
- MS Eent (Nle)Document3 pagesMS Eent (Nle)Maginalyn CangasNo ratings yet
- Refraction DisorderDocument41 pagesRefraction DisorderWilson HalimNo ratings yet
- Refractive Lens ExchangeDocument4 pagesRefractive Lens ExchangeS Rahakbauw JangkupNo ratings yet
- Common Eye Diseases 2022Document33 pagesCommon Eye Diseases 2022Shia LevyNo ratings yet
- Slit Lamp and CLs Complications HandoutDocument24 pagesSlit Lamp and CLs Complications HandoutRaeesah MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Intra Ocular Lens Technology - A Review of Journey From Its InceptionDocument9 pagesIntra Ocular Lens Technology - A Review of Journey From Its InceptionDaisy Arora KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Eye FunctionsDocument16 pagesEye FunctionskranthichokkakulaNo ratings yet
- De Guzman, M.J., ACTIVITY PAPER #2 Microscopy Asynchronous ActivityDocument4 pagesDe Guzman, M.J., ACTIVITY PAPER #2 Microscopy Asynchronous ActivityMaui Vecinal de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- A Review of Drug-Induced Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma For Non-Ophthalmologists PDFDocument8 pagesA Review of Drug-Induced Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma For Non-Ophthalmologists PDFMeida Putri UtamiNo ratings yet
- Management of Pediatric CataractDocument26 pagesManagement of Pediatric CataractatikafmmNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Phase Hand Outs Special SensesDocument10 pagesComprehensive Phase Hand Outs Special SensesTravis PastranaNo ratings yet
- Pupil Capture of Intraocular Lens in Vitrectomized Eye With Primary Pigment Dispersion SyndromeDocument2 pagesPupil Capture of Intraocular Lens in Vitrectomized Eye With Primary Pigment Dispersion SyndromeHuang WanjingNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading KBRDocument27 pagesJournal Reading KBRGrahita PoernomoNo ratings yet
- Acrysof - IQ - Vivity - Clinical ExperienceDocument8 pagesAcrysof - IQ - Vivity - Clinical ExperienceJulian NickNo ratings yet
- Comparison of The Optical Behaviour of Five Different Multifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lenses in A Model EyeDocument12 pagesComparison of The Optical Behaviour of Five Different Multifocal Diffractive Intraocular Lenses in A Model Eye7zhm9d9dbpNo ratings yet
- 1MicroscopeDocument3 pages1MicroscopeMary Jane TiangsonNo ratings yet
- Nat FlaxDocument5 pagesNat FlaxTyasBanggaPribadieNo ratings yet
- Myopia or Nearsightedness: A Refractive Error of The EyeDocument9 pagesMyopia or Nearsightedness: A Refractive Error of The EyeClaire LimosNo ratings yet
- Optics and Refraction OverviewDocument5 pagesOptics and Refraction OverviewJessa Mae Nona DionisioNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Anatomy and Physiology GuideDocument13 pagesOphthalmology Anatomy and Physiology GuidesafrinaNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Contact LenseDocument63 pagesPaediatric Contact LenseGurria NaheedNo ratings yet
- Cataracts by Idris HarunaniDocument2 pagesCataracts by Idris Harunanix2tnnwjhtvNo ratings yet
- JR - KBR - Scleral Fixation of Single Pieces Foldable IOL Using Double Flanged Technique - Karina AdistiariniDocument23 pagesJR - KBR - Scleral Fixation of Single Pieces Foldable IOL Using Double Flanged Technique - Karina AdistiariniKarina Adistiarini BudijantoNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Femtosecond LaserDocument5 pagesOphthalmology Femtosecond LaserChandrika MaluftiNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Microscopy and Slide PreparationmaddiDocument5 pagesActivity 1 Microscopy and Slide PreparationmaddiIMMORTAL SOULNo ratings yet
- Correcting Presbyopia First Phakic Diffractive IOLDocument9 pagesCorrecting Presbyopia First Phakic Diffractive IOLFrancescFranquesaNo ratings yet
- 1 MicrosDocument7 pages1 MicrosJachelle KateNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment in Optic and Refraction by Prof Chua, Dr. Chieng, DR - Ngo and Dr. AlhadyDocument107 pagesSelf-Assessment in Optic and Refraction by Prof Chua, Dr. Chieng, DR - Ngo and Dr. AlhadyKelvin TeoNo ratings yet
- Ijss Jun Oa14Document4 pagesIjss Jun Oa14Yunanda RizkiNo ratings yet
- Ijss Jun Oa14Document4 pagesIjss Jun Oa14Yunanda RizkiNo ratings yet
- Refractive ErrorsDocument38 pagesRefractive ErrorszahraaNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma 2 Lecture PACG MBBS BY Prof Munim SuriDocument28 pagesGlaucoma 2 Lecture PACG MBBS BY Prof Munim SuriMunim SuriNo ratings yet
- Magnification in Endodontics: A ReviewDocument5 pagesMagnification in Endodontics: A ReviewAndrei BerdichewskyNo ratings yet
- Hyperopia & Aphakia 3Document60 pagesHyperopia & Aphakia 3Mamtha MMNo ratings yet
- 12 DecDocument43 pages12 DecJayesh ThakkarNo ratings yet
- GT0907 03Document2 pagesGT0907 03Michael CraneNo ratings yet
- EHS 304 Laser Alignment Training HandoutsDocument14 pagesEHS 304 Laser Alignment Training HandoutskriesnamuktipradanaNo ratings yet
- Pit RGP PalembangDocument6 pagesPit RGP PalembangSILVYNo ratings yet
- The Eye - Garcia Tatiana - Hilares LuisDocument21 pagesThe Eye - Garcia Tatiana - Hilares LuisLuis HilaresNo ratings yet
- Clinical Ophthalmology for UndergraduatesFrom EverandClinical Ophthalmology for UndergraduatesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Progress in Microscopy: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: Modern Trends in Physiological SciencesFrom EverandProgress in Microscopy: International Series of Monographs on Pure and Applied Biology: Modern Trends in Physiological SciencesNo ratings yet
- Le Mire 2004Document2 pagesLe Mire 2004Fapuw ParawansaNo ratings yet
- Tau Ben Slag 2018Document5 pagesTau Ben Slag 2018Fapuw ParawansaNo ratings yet
- Red Eye: A Guide For Non-Specialists: MedicineDocument14 pagesRed Eye: A Guide For Non-Specialists: MedicineFapuw Parawansa100% (1)
- Laser Peripheral Iridotomy Curriculum: Lecture and Simulation PracticalDocument7 pagesLaser Peripheral Iridotomy Curriculum: Lecture and Simulation PracticalFapuw ParawansaNo ratings yet
- PDF PPK Ik Mata Final Ok CompressDocument128 pagesPDF PPK Ik Mata Final Ok CompressFapuw ParawansaNo ratings yet
- Vitrectomy: Edited by Zongming SongDocument104 pagesVitrectomy: Edited by Zongming SongFapuw ParawansaNo ratings yet
- FCSO A57507 Iridotomy Updated 10102019 Effective 10032018Document7 pagesFCSO A57507 Iridotomy Updated 10102019 Effective 10032018Fapuw ParawansaNo ratings yet
- Oct and Retina Thea WebsiteDocument198 pagesOct and Retina Thea WebsiteSmaraNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Eye Disease: An Illustrated Guide To Diagnosis and ManagementDocument81 pagesDiabetic Eye Disease: An Illustrated Guide To Diagnosis and ManagementFapuw ParawansaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Clinical Guide To Ophthalmic Drugs 23rd EdDocument52 pages2019 Clinical Guide To Ophthalmic Drugs 23rd EdSmaraNo ratings yet
- NobelEsthetic Proc&Prod - 2010 - GBDocument116 pagesNobelEsthetic Proc&Prod - 2010 - GBNiaz AhammedNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Should Not Be Provided For Free Regardless of A PersonDocument1 pageHealthcare Should Not Be Provided For Free Regardless of A PersonLinh ChiNo ratings yet
- TriumphDebate SeptOct2021 OfficialBriefDocument134 pagesTriumphDebate SeptOct2021 OfficialBriefRebecca WardNo ratings yet
- Determining The Effectiveness of Neem and Papaya L-2Document8 pagesDetermining The Effectiveness of Neem and Papaya L-2Ariana hazelNo ratings yet
- 2010 PHC Regional Analytical Reports Ashanti RegionDocument230 pages2010 PHC Regional Analytical Reports Ashanti RegionMariam SharifNo ratings yet
- Dehlendorf2021 PCC DevelopmentDocument6 pagesDehlendorf2021 PCC Developmentinggar ratnakusumaNo ratings yet
- 1 Colostomy and IleostomyDocument4 pages1 Colostomy and IleostomyAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- COAHS Nurse's Notes on Patient CareDocument4 pagesCOAHS Nurse's Notes on Patient CareLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- WDR22 Booklet 1Document74 pagesWDR22 Booklet 1Khánh Hoàng NamNo ratings yet
- Mifepristone & MisoprostolDocument6 pagesMifepristone & MisoprostolnanimadallaNo ratings yet
- Road safety insights from analysis of factors causing accidentsDocument14 pagesRoad safety insights from analysis of factors causing accidentsAnil DangiNo ratings yet
- PED011 Final Req 15Document3 pagesPED011 Final Req 15macabalang.yd501No ratings yet
- U.S. Army Patent For Weaponized MycoplasmaDocument81 pagesU.S. Army Patent For Weaponized MycoplasmaAdam F.100% (1)
- I STATDocument24 pagesI STATPraveen RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Vote Ryan Aldred For Usdaw ECDocument2 pagesVote Ryan Aldred For Usdaw ECUSDAWactivistNo ratings yet
- Overcome Anxiety, Depression and Gain ControlDocument3 pagesOvercome Anxiety, Depression and Gain ControlPranavNo ratings yet
- Abortion Research PaperDocument6 pagesAbortion Research Paperapi-511989965No ratings yet
- Nutrition 3 QPDocument11 pagesNutrition 3 QPRizwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Au 31 Februari 2017Document149 pagesAu 31 Februari 2017Agnes CynthiaNo ratings yet
- AP14 - DTC Support Manual - 20160930Document817 pagesAP14 - DTC Support Manual - 20160930tallerr.360No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Stanhope: Public Health Nursing, 9th EditionDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Stanhope: Public Health Nursing, 9th EditionSALWA0% (2)
- PSYC 6213 Unit2Document6 pagesPSYC 6213 Unit2hibasaleemmNo ratings yet
- Maharani Gayatri Devi Girls' School COVID SOPDocument5 pagesMaharani Gayatri Devi Girls' School COVID SOPDARSHIKA SHEKHAWATNo ratings yet
- Wa0033Document10 pagesWa0033Obrian RobinsonNo ratings yet
- ORGS 1136 - Week 4 Notes ORGS 1136 - Week 4 NotesDocument3 pagesORGS 1136 - Week 4 Notes ORGS 1136 - Week 4 NotesTara FGNo ratings yet
- Life Saving Rules Poster in EnglishDocument11 pagesLife Saving Rules Poster in Englishkumalk3815No ratings yet
- The Role of The District Public Health Nurses: A Study From GujaratDocument33 pagesThe Role of The District Public Health Nurses: A Study From Gujaratመሰረት ሀብቴNo ratings yet
- Automation of Drug Dispensing: Feedback From A Hospital PharmacyDocument5 pagesAutomation of Drug Dispensing: Feedback From A Hospital PharmacyIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Standardization and Upgrading of Barmm HospitalsDocument41 pagesStandardization and Upgrading of Barmm HospitalsApipah Datudacula-MacabangkitNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Permit To Operate (PTO) Air Pollution Source InstallationsDocument3 pagesApplication Form For Permit To Operate (PTO) Air Pollution Source InstallationsMiguel Antonio Uy EscolarNo ratings yet