Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ss
Uploaded by
balaji0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesSignals and systems
Original Title
ss
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSignals and systems
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesSs
Uploaded by
balajiSignals and systems
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
at | [islam
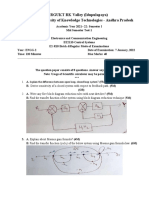
BE (Full Time) - END SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS APRIL / MAY 2019
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
3 SEMESTER
EC 8351 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND SYSTEM DESIGN
(Regulation 2012)
Time: 3 Hours Answer ALL Questions ‘Max. Marks 100
PART-A (10 x 2=20 Marks)
1, Convert BEAig to octal.
2. Express F=xy + x°z as a product of maxterms.
3. Draw the schematic of a 4 to 1 mux.
4. Draw the circuit of a full adder using two half-adders and an OR-gate.
5. Write all the states possible in a 4-bit Johnson counter.
6. What is lock out in counters?
7. Mention two problems in asynchronous sequential circuits.
8. Define static-0 hazard?
9. Define fan out.
10. Draw the circuit of a CMOS inverter.
PART-B (5 x 16 = 80 Marks)
11. Obtain simplified SOP using Quine McCluskey / tabulation method for
F(asb,c,d)=2( (0,3,5,6,7,10,12,13)
12a) Design a combinational circuit with three inputs, x , y and z and three
outputs, 4, B and C. Whén the binary input is 0, 1, 2, or 3, the binary output
is one greater than the input. When the binary input is 4, 5, 6, or 7, the binary
output is two less than the input. Realize the circuit using an appropriate
decoder,
OR
12b) Design a 3-bit binary to 2s complement ‘converter. Realize using an
appropriate decoder.
(PTO)
13a) Design a synchronous sequential counter with states 0,6,7,4,5.2,3,1,0,6...
repeat using JK FFs
OR
13b) Obtain the state table and state diagram for a circuit consisting of two T FFs,
an external input, x, and output, y, described by the equations Ty=Qa x, TB=X
and y=QaQa.
14a) Obtain a reduced pft for an asyne. seq. circuit with two inputs A and B and
one output Z where Z changes whenever AB=11. Assume that the two
inputs do not change simultaneously and initial Z=0
OR
14b) Explain essential hazard with an example.
15a) Explain the working of a TTL tristate gate
OR
15b) Explain the working of 2-input CMOS NAND and NOR gates.
seeeieee
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- BALAMDocument1 pageBALAMbalajiNo ratings yet
- Apb Interview QuestionsDocument1 pageApb Interview QuestionsbalajiNo ratings yet
- Router Lint ReportDocument16 pagesRouter Lint ReportbalajiNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations: Homogeneous DEDocument3 pagesDifferential Equations: Homogeneous DEbalajiNo ratings yet
- ET Class On 10-02-2021Document7 pagesET Class On 10-02-2021balajiNo ratings yet
- ET Lecture On 10-05-2021 & 11-05-2021Document26 pagesET Lecture On 10-05-2021 & 11-05-2021balajiNo ratings yet
- Ai Ynr: LPT yDocument5 pagesAi Ynr: LPT ybalajiNo ratings yet
- RGUKT RK Valley (Idupulapaya) Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies - Andhra PradeshDocument3 pagesRGUKT RK Valley (Idupulapaya) Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies - Andhra PradeshbalajiNo ratings yet
- Exact Differential EquationsDocument2 pagesExact Differential EquationsbalajiNo ratings yet
- Classification of 2 Order PDE: CalculusDocument2 pagesClassification of 2 Order PDE: CalculusbalajiNo ratings yet
- Common To Electronics and Communication Engineering and Biomedical Engineering III SemesterDocument3 pagesCommon To Electronics and Communication Engineering and Biomedical Engineering III SemesterbalajiNo ratings yet
- Experiment-I: Conditional Statements & LoopsDocument2 pagesExperiment-I: Conditional Statements & LoopsbalajiNo ratings yet
- Year & Sem: E1S1 Lab Code: EE1701 Lab Name: Electrical Technology Lab No. of Credits: 2 L T&Ps P 0 0 2Document1 pageYear & Sem: E1S1 Lab Code: EE1701 Lab Name: Electrical Technology Lab No. of Credits: 2 L T&Ps P 0 0 2balajiNo ratings yet
- EE1101Document2 pagesEE1101balajiNo ratings yet
- Advanced English LabDocument1 pageAdvanced English LabbalajiNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab Experiment-I: List of ExperimentsDocument1 pageElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab Experiment-I: List of ExperimentsbalajiNo ratings yet
- Electronics & Communications Engineering Syllabus: Page 1 of 67Document2 pagesElectronics & Communications Engineering Syllabus: Page 1 of 67balajiNo ratings yet
- Year & Sem: E1S1 Course Code: MA1101 Course Name: Engineering Mathematics-I No. of Credits: 4 L T&Ps P 2 2 0Document1 pageYear & Sem: E1S1 Course Code: MA1101 Course Name: Engineering Mathematics-I No. of Credits: 4 L T&Ps P 2 2 0balajiNo ratings yet
- Year & Sem: E1S1 Course Code: CS6101 Course Name: C No. of Credits: 4 L T&Ps P 2 2 0Document1 pageYear & Sem: E1S1 Course Code: CS6101 Course Name: C No. of Credits: 4 L T&Ps P 2 2 0balajiNo ratings yet
- Spectros PDFDocument28 pagesSpectros PDFbalajiNo ratings yet
- Quiz On IntegralsDocument7 pagesQuiz On IntegralsbalajiNo ratings yet