Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic: Crisis Management in Hospitality Industry: Skill Test
Uploaded by
Himanshu MalikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic: Crisis Management in Hospitality Industry: Skill Test
Uploaded by
Himanshu MalikCopyright:
Available Formats
1
SKILL TEST
Topic: Crisis Management in Hospitality Industry
Table of Contents
Sr. No. Topic Page No.
1 Learning Objectives 2
2 Introduction. 3
3 What is Crisis? 3
4 Types of Crises. 4
5 Objectives of Crisis Management. 4
6 Managing Crisis in Hospitality Industry. 5
7 Conclusion 6
8 References 7
Dr. Himanshu Malik Crisis Management in Hospitality Industry SVSU/2020/Estt/T/008_022_5005
2
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
By the end of this lecture on “Crisis Management in Hospitality Industry” the learner will be
able to
• Define Crisis.
• List different types of crises.
• State objectives of Crisis Management.
• Discuss the stages of crisis management in hospitality Industry.
Dr. Himanshu Malik Crisis Management in Hospitality Industry SVSU/2020/Estt/T/008_022_5005
3
INTODUCTION
The hospitality industry, its immaturity and dramatic expansion are noticeable, though
hospitality has a long history but the modern mass tourism practices started only after second
world war. The industry has a complex structure and it provides experiential products which
are a collective work of various stakeholders (Suppliers, Manufacturers, Employees, Investors,
Transport, Travel agencies Travel guides, Government and Non-Government Bodies)
associated with the industry which leads the potential problem of fragmented control.
This relation of mutual dependency amongst various components also translates that the crisis
for one may spread to the other. For instance, in case of a transport related crisis it will have
huge impact on tourists travelling to different destination, food supplies for hotels and
restaurants, employees travelling to work and earning of stakeholders.
This vulnerability of hospitality industry towards crisis of various nature makes it vital for
hospitality managers to understand and practice crisis management. This pre module guided
reading is intended for learners who are here to learn about crisis, types of crises, objectives of
crisis management and stages of crisis management.
WHAT IS CRISIS?
The Cambridge Advance Learners Dictionary defines Crisis as “A Situation That has reached
an extremely difficult or dangerous point; a time of great disagreement, Uncertainty or
suffering.”
On the other hand, the concise Oxford dictionary defines crisis as “A time of intense Difficulty
Or danger”
And the online oxford learners dictionary “A Crisis is a time of great danger, difficulty or doubt
when problems must be solved or important decisions must be made”
Henederson (2007) one of the leading authors on tourism crisis in his book “Managing Tourism
Crisis” states that Crisis does not have a universally acceptable definition however Crisis has
been described differently by various authors. These descriptions have three elements in
common namely
1. A triggering event causing significant change or having the potential to cause
significant change.
2. The perceived inability to cope with this change, and
3. A threat to the existence of the foundation of the organization.
For example, the present scenario of Covid19 is an event of crisis that is causing significant
changes in the hospitality operations, initially organizations were unable to cope with these
changes and many hospitality organizations have this threat to existence of their foundation.
Crises in hospitality industry also share these elements however certain crisis situation can be
predicted like those tourist destinations which are suffering from rising sea levels due to global
warming. There is remarkable range and variety of crises which are discussed in types of crises.
Dr. Himanshu Malik Crisis Management in Hospitality Industry SVSU/2020/Estt/T/008_022_5005
4
TYPES OF CRISES
Each crisis is unique, broadly Crisis can be categorized into following six categories.
1. Economic
2. Political
3. Socio-cultural
4. Environmental
5. Technological
6. Commercial
Economic Crisis is an event or situation of crisis that is related to financial threats which can
be external threats like recession, currency fluctuation, taxation or internal threats like rising
cost, falling revenues and unprofitability.
Political Crises consists of events that are caused by political environment and can cause
external threats to an organization in the form of Government policies, international relations,
Instability and Terrorism.
Socio-cultural Criss deals with the events of that are social or cultural in nature and this crisis
category causes external threats like Unrest and Crime and internal threats like Staffing and
Cultural conflicts.
Environmental Crisis is a situation that may rise because for environment related issues and
these can cause external threats related to Natural phenomena, Natural disaster, Pollution and
Health Scares and internal threats like overdevelopment and Environmental degradation.
Technological Crises includes situations of crisis concerned with technology and can cause
external threats of Computer system failure, Mechanical failure, Design fault and Fire and
internal threats like Transport accidents.
Commercial Crises are related to external threats of Regulations and Government intervention
and internal threats of competition, Labor dispute, Management decisions and human error.
These types of crises are just broad general category an individual event of crisis may fall in
multiple categories for example fire can be technical crisis when cause due to mechanical error
or electrical short circuit same can be environmental in case caused by natural disaster like
earthquake or lightening and it can also socio-cultural when caused by a mob protesting for
cultural rights.
OBJECTIVES OF CRISIS MANAGEMENT
After understanding the attributes of crisis as in how it can cause a significant threat and change
that organization are not prepared for as a result the existence and foundation of an organization
can be threatened. This makes it critical to understand the objectives an organization should
incorporate for managing crisis situations. Following are the objectives of Crisis Management.
Dr. Himanshu Malik Crisis Management in Hospitality Industry SVSU/2020/Estt/T/008_022_5005
5
• To reduce the likelihood for occurrence of a crisis situation.
• To shorten the duration of a crisis situation.
• To limit the impact of crisis to various stakeholders of the organization.
MANAGING CRISIS IN HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY
During the various situation of a crisis the hospitality industry has faced threats to man and
material and even closure of organizations. In order to ensure the safeguarding of various stake
holders an effective crisis management practice is required. As for the term crisis, crisis
management also lacks a universally acceptable definition however the that covers all
dimension to fit for hospitality industry was given by Santana (2004) as an “ongoing integrated
and comprehensive effort that organizations effectively put into place in an attempt to first and
foremost understand and prevent crisis, and to effectively manage those that occur, taking into
account in each and every step of their planning and training activities, the interests of their
stakeholders.”
The stages of crisis management as described by Henderson (2007) are six stages to effectively
understand and prevent crisis and also to manage those crises which occur. These stages are:
1. Pre-event,
2. Prodromal,
3. Emergency
4. Intermediate
5. Recovery, and
6. Resolution
Let us see various steps an organization of hospitality industry should take
Pre-event
• Appointment of a crisis team manager who will be in charge of environmental scanning,
identifying and assessing the risk of potential disasters or threats
• Establishment of a crisis management team and allocation of specific responsibilities
and duties to relevant individuals
• Brainstorming on possible scenarios and preparation of contingency crisis management
plans
• Assessment of capability to cope with the impacts of crisis
• Development and documentation of crisis management strategies which are aligned to
overall mission and objectives
• Identification of relevant external agencies and ascertainment of desired and likely level
of cooperation in times of crisis
• Determination of procedures for the procurement and allocation of necessary resources
• Communication of the crisis management plans to all levels of employees, making sure
that individuals are certain of their roles in the event of a crisis
• Development of a corporate culture of crisis awareness and preparedness
Dr. Himanshu Malik Crisis Management in Hospitality Industry SVSU/2020/Estt/T/008_022_5005
6
• Establishment of media communication strategies and management policies to be used
at all times
Prodromal
• Establishment of crisis management command center
• Activation of selected procedures
• Raising of level of preparedness across the organization
• Determination of primary objectives in the management of the crisis so as to focus the
direction of all actions to be taken
• Review and revision of marketing
Emergency
• Assurance of the safety and well-being of guests and staff Protection of property
• Commencement of evacuation procedures if necessary
• Activation of emergency services
• Introduction of health screening of staff and guests
• Intensification of existing routines of cleaning and disinfecting
• Contacting of partners and implementation of systems of cooperation
• Adherence to official directives
• Maintenance of open communication channels to reassure guests and employees
• Employment of media communications strategy
• Monitoring of marketing activity
• Application for official aid if provided
Intermediate
• Assistance to guests and employees in meeting their medium-term needs
• Assessment of the impacts of the crisis and extent of damage
• Cleaning up the residual impacts of the crisis
• Beginning of the restoration of normal business operations
• Modification of marketing
Recovery
• Full restoration of normal business operations
• Improvement of facilities and customer service
• Conducting of extensive advertising and promotional campaigns
• Entering into cooperative and collaborative initiatives
Resolution
• Closure of crisis management command center and debriefing of all parties involved in
managing the crisis
• Collation of feedback from all parties
• Review and enhancement of crisis management strategy, gathering knowledge from
lessons learned and applying it
Dr. Himanshu Malik Crisis Management in Hospitality Industry SVSU/2020/Estt/T/008_022_5005
7
CONCLUSION
The management of crisis and its stage may vary from industry to industry and organization to
organization. It majorly depends on the nature of crisis and its association with the
industry/organization. Another approach of managing crisis by distinct authors say that crisis
has only three stages which are pre-crisis, crisis, and post crisis or before crisis, during crisis
and after crisis. The interpretation or approach may vary by various authors and decision
makers however the main purpose behind the crisis management is to prevent crisis at first, be
ready when it occurs, response quickly and effectively during crisis and finally implement
recovery plans to get back to normal.
REFERENCES
Dictionaries, O. L. S. (2017). Oxford Learners Dictionaries. Retrieved December, 2021.
Fowler, H. W., & Fowler, F. G. (1931). The concise Oxford dictionary of current English.
Henderson, J. C. (2007). Managing tourism crises. Routledge.
Walter, E. (2008). Cambridge advanced learner's dictionary. Cambridge university press.
*********
Dr. Himanshu Malik Crisis Management in Hospitality Industry SVSU/2020/Estt/T/008_022_5005
You might also like
- Taming the Risk Hurricane: Preparing for Major Business DisruptionFrom EverandTaming the Risk Hurricane: Preparing for Major Business DisruptionNo ratings yet
- Crisis Manag Project PDFDocument12 pagesCrisis Manag Project PDFutsmNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Study On Crisis ManagementDocument53 pagesA Detailed Study On Crisis ManagementZay YanNo ratings yet
- Crisis ManagementDocument13 pagesCrisis Managementalberto michelini100% (2)
- Dianne Mikko Z. Dela Cruz Joseph Reynald C. Dela Cruz, CCSSM Renissa F. Sacdalan Carl Luigi B. FabroDocument16 pagesDianne Mikko Z. Dela Cruz Joseph Reynald C. Dela Cruz, CCSSM Renissa F. Sacdalan Carl Luigi B. Fabrofelize padlla100% (1)
- HR Role in Crisis ManagementDocument47 pagesHR Role in Crisis ManagementRajiv SharmaNo ratings yet
- Crisis ManagementDocument9 pagesCrisis ManagementNaya LouNo ratings yet
- Skill Test: Topic: Crisis Management in Hospitality IndustryDocument31 pagesSkill Test: Topic: Crisis Management in Hospitality IndustryHimanshu MalikNo ratings yet
- Mba Crisis Management NotesDocument14 pagesMba Crisis Management NotesChauhan Neelam100% (1)
- DM Unit 3 NotesDocument11 pagesDM Unit 3 NotesPriya VNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Crisis ManagementDocument19 pagesA Framework For Crisis ManagementJasmin Mae MusniNo ratings yet
- Crisis ManagementDocument19 pagesCrisis Managementsssr3103No ratings yet
- Dilemma Management: Joined up thinking for our fragmented timesFrom EverandDilemma Management: Joined up thinking for our fragmented timesNo ratings yet
- Crisis ManagementDocument13 pagesCrisis ManagementRichard Peters100% (1)
- 5 - English PartDocument23 pages5 - English Partmahmoud el orabyNo ratings yet
- Crisis Leadership and Why It MattersDocument5 pagesCrisis Leadership and Why It Matterss dNo ratings yet
- Grundy 2013Document7 pagesGrundy 2013Blue moon MediaNo ratings yet
- Rebuilding Tourism For The Future Crisis Management of Upscale Hotels in Cabanatuan CityDocument46 pagesRebuilding Tourism For The Future Crisis Management of Upscale Hotels in Cabanatuan CityMARIVIC CAUSAPINNo ratings yet
- Lerbinger - The Crisis ManagerDocument41 pagesLerbinger - The Crisis ManagerTania Nicoleta100% (3)
- Crisis ManagementDocument17 pagesCrisis ManagementMasitala PhiriNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument15 pagesRisk ManagementABEGAIL MADLAONo ratings yet
- Crisis Management - Zamorylo S.Document7 pagesCrisis Management - Zamorylo S.Софія ЗаморилоNo ratings yet
- Engleski Jezik Case Study SeminarskiDocument13 pagesEngleski Jezik Case Study SeminarskirackovicbNo ratings yet
- Crisis ManagementDocument10 pagesCrisis ManagementDamon Smruti Ranjan100% (1)
- Crisis Management: Strategies for Mitigating and Recovering from DisastersFrom EverandCrisis Management: Strategies for Mitigating and Recovering from DisastersNo ratings yet
- S1 - Intro To RiskDocument25 pagesS1 - Intro To RiskHicham ManamparanNo ratings yet
- IC-86 Risk ManagementDocument240 pagesIC-86 Risk ManagementRishi RajNo ratings yet
- Crisis ManagementDocument3 pagesCrisis ManagementAnand ChaubeyNo ratings yet
- Manajemen PerubahanDocument30 pagesManajemen PerubahanSaputra steiNo ratings yet
- Crisis ManagementDocument31 pagesCrisis Managementjosephalcala79No ratings yet
- A Detailed Study On Crisis ManagementDocument66 pagesA Detailed Study On Crisis ManagementVikash GovindNo ratings yet
- Business Continuity Strategies: Protecting Against Unplanned DisastersFrom EverandBusiness Continuity Strategies: Protecting Against Unplanned DisastersNo ratings yet
- Crisis Management 2Document14 pagesCrisis Management 2Richmond CandidoNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document14 pagesGroup 5Juliana JuareNo ratings yet
- Global Crisis Management: The Transnational Model of Multinational OrganizationsDocument3 pagesGlobal Crisis Management: The Transnational Model of Multinational OrganizationsYash SinghNo ratings yet
- Crisis Management Is The Process by Which An Organization Deals With A Major Unpredictable Event That Threatens To Harm The OrganizationDocument4 pagesCrisis Management Is The Process by Which An Organization Deals With A Major Unpredictable Event That Threatens To Harm The OrganizationAssan Abdraimov100% (1)
- Crisis ManagementDocument14 pagesCrisis ManagementHatem BakrNo ratings yet
- Disaster Crisis Management - Digital NotessssDocument83 pagesDisaster Crisis Management - Digital NotessssBhanudai BhandariNo ratings yet
- UNDRR Resilience of SMEs ReportDocument68 pagesUNDRR Resilience of SMEs ReportCristian RamírezNo ratings yet
- Complete ProjectDocument99 pagesComplete ProjectDANJUMA ADAMUNo ratings yet
- Lea Chapter 1 2 Esma WieserDocument6 pagesLea Chapter 1 2 Esma WieserWieser EsmaNo ratings yet
- Session 4 - Crisis ManagementDocument36 pagesSession 4 - Crisis Managementmohammed naserNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Crisis ManagementDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Crisis ManagementAk FdNo ratings yet
- Skripta Za Engleski UKUDocument102 pagesSkripta Za Engleski UKUmina_maric5No ratings yet
- Crisis Management CH 1Document6 pagesCrisis Management CH 1Mohamed HamedNo ratings yet
- Crisis Management - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument18 pagesCrisis Management - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediacorvoirNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Successful Crisis ManagementDocument11 pagesStrategies For Successful Crisis ManagementAlberto QuintavoNo ratings yet
- (Main) Tourism Crises - Causes Consequences and Management The Management of Hospitality and Tourism Enterprises PDFDrive (161 178)Document18 pages(Main) Tourism Crises - Causes Consequences and Management The Management of Hospitality and Tourism Enterprises PDFDrive (161 178)Tấn phát NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The 2007-09 Financial Crisis: Learning The Risk Management Lessons January 2010Document50 pagesThe 2007-09 Financial Crisis: Learning The Risk Management Lessons January 2010Khushi ShahNo ratings yet
- PR On Organization CrisisDocument8 pagesPR On Organization CrisisRanjeet Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Toyota in Crisis: Denial and Mismanagement: Victor L. Heller and John R. DarlingDocument10 pagesToyota in Crisis: Denial and Mismanagement: Victor L. Heller and John R. DarlingYasir ChhipaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management 1Document21 pagesRisk Management 1Ajay Chauhan100% (1)
- Crisis Capital: Your Operations & Leadership During A Crisis? WDocument9 pagesCrisis Capital: Your Operations & Leadership During A Crisis? WcliffseowNo ratings yet
- Crisis Management in Hotel Business - Insights FroDocument20 pagesCrisis Management in Hotel Business - Insights FroVipul PatilNo ratings yet
- Mod 4 Disaster MGMTDocument13 pagesMod 4 Disaster MGMTCharnjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Ansa 027Document15 pagesAnsa 027Palm ReaderNo ratings yet
- Crisis ManagementDocument17 pagesCrisis Managementhardikpatel15109711No ratings yet
- Bank@Campus Account - ICICI Bank LTDDocument1 pageBank@Campus Account - ICICI Bank LTDKumar RanjanNo ratings yet
- Applications: FX-SC8XIOR34-0 Module Installation InstructionsDocument16 pagesApplications: FX-SC8XIOR34-0 Module Installation InstructionsUdo IheanachoNo ratings yet
- T301 Summary of Pump Control PanelsDocument10 pagesT301 Summary of Pump Control PanelsRanjani SNo ratings yet
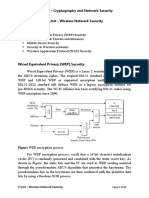
- V Unit - Wireless Network SecurityDocument22 pagesV Unit - Wireless Network SecurityBRINDHA C it2018No ratings yet
- Hubungan Pola Makan Dan Kebiasaan Olah Raga Dengan Kadar Gula Darah Penderita Diabetes Melitus Tipe Ii Di Rs Pku Muhammadiyah SurakartaDocument15 pagesHubungan Pola Makan Dan Kebiasaan Olah Raga Dengan Kadar Gula Darah Penderita Diabetes Melitus Tipe Ii Di Rs Pku Muhammadiyah SurakartaNova SanggelNo ratings yet
- Management of Primary Dysmenorrhoea by Dry Cupping: A ReviewDocument5 pagesManagement of Primary Dysmenorrhoea by Dry Cupping: A ReviewWilyanto YangNo ratings yet
- Needlestick InjuryDocument24 pagesNeedlestick InjuryAli AlisonNo ratings yet
- Standa Modules 2022Document39 pagesStanda Modules 2022vlado_314No ratings yet
- 6009Document5 pages6009Oktasari Dyah AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Sati Accomplishment ReportDocument4 pagesSati Accomplishment Reportmaricel a.esmeroNo ratings yet
- Ead 230005-00-0106Document14 pagesEad 230005-00-0106Ana Luísa EvaristoNo ratings yet
- A Brief Note On Plants of Medicinal Importance To LivestockDocument84 pagesA Brief Note On Plants of Medicinal Importance To LivestockSunil100% (1)
- Mill ScaleDocument6 pagesMill ScaleJhovanny RendónNo ratings yet
- Potato ProjectDocument10 pagesPotato Projectkillerfox70No ratings yet
- The Best Broccoli Cheese Soup (Better-Than-Panera Copycat) - Averie CooksDocument1 pageThe Best Broccoli Cheese Soup (Better-Than-Panera Copycat) - Averie CooksEmily WillisNo ratings yet
- Method of Statement For 54 MT Tower Rev 02Document10 pagesMethod of Statement For 54 MT Tower Rev 02zia uddinNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of Rock Slope Engineering Practice Based On Findings of Landslide StudiesDocument8 pagesEnhancement of Rock Slope Engineering Practice Based On Findings of Landslide StudiesHuy Le QuangNo ratings yet
- 1 CDocument4 pages1 CsudiroNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle Management & Skill DevelopmentDocument53 pagesLifestyle Management & Skill DevelopmentRana SinghNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Sturmer Final PaperDocument7 pagesBenjamin Sturmer Final Paperapi-549208885No ratings yet
- IT Projection ToolDocument7 pagesIT Projection ToolsaurabhmanitNo ratings yet
- One-Sample Tests of Hypothesis: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument15 pagesOne-Sample Tests of Hypothesis: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinImam AwaluddinNo ratings yet
- ELI 250c: Mortara'S Next Generation 12-Lead ElectrocardiographsDocument2 pagesELI 250c: Mortara'S Next Generation 12-Lead ElectrocardiographszainalfikraNo ratings yet
- Vampire Cortex Prime Conversion V.1Document38 pagesVampire Cortex Prime Conversion V.1Jeferson MoreiraNo ratings yet
- SingjuDocument3 pagesSingjuhbNo ratings yet
- Monster Hunter 3rd Guide ItemsDocument20 pagesMonster Hunter 3rd Guide ItemsJoe Wick100% (1)
- Meaning and Scope of Supply Under GSTDocument5 pagesMeaning and Scope of Supply Under GSTRohit BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Listening Practice Answer Key OUT AND ABOUT 1Document2 pagesListening Practice Answer Key OUT AND ABOUT 1Marta Sampedro GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Finance EeeeeDocument11 pagesFinance EeeeeJendeukkieNo ratings yet
- MemsDocument3 pagesMemssteve johnsNo ratings yet